A low-temperature sintering process for manganese-zinc ferrite
A low-temperature sintering technology of manganese-zinc ferrite, which is applied in the field of manganese-zinc ferrite, can solve the problem of high energy consumption in the sintering process of manganese-zinc ferrite, and achieve the effect of reducing production costs and energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
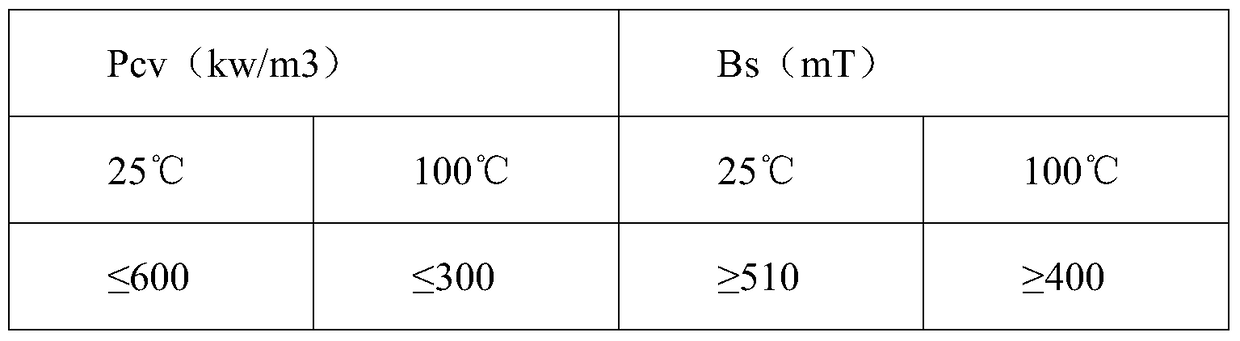
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] (1) One-time sanding: add water to the main material and carry out sand grinding until the particle size of the material is 1 μm, then dry it and wait for use. The main material is composed of the following molar percentage components: 52mol% Fe 2 o 3 , 9mol% ZnO, the balance is MnO;
[0021] (2) Pre-sintering: pre-sintering the dried main material in a nitrogen atmosphere at 600°C for 1 hour to obtain a pre-sintered material;
[0022] (3) Secondary sanding: add dopant to the calcined material and mix evenly, add water for sand milling until the particle size of the material is 0.7 μm, then dry to obtain sand abrasive, in which the dopant is CaCO 3 , Nb 2 o 5 , ZrO 2 and SnO 2 , based on the mass of pre-fired material, add 500ppm CaCO 3 , 200ppm Nb 2 o 5 , 100ppmZrO 2 and 400ppm SnO 2 ;
[0023] (4) Granulation: add 8% of the mass of the abrasive to the sand abrasive, and a PVA solution with a mass percentage concentration of 8%, stir evenly, and then spray a...
Embodiment 2
[0026] (1) One-time sanding: add water to the main material and sand it until the particle size of the material is 1.5 μm, then dry it and wait for use. The main material is composed of the following components in molar percentages: 53mol% Fe 2 o 3 , 10mol% ZnO, the balance is MnO;
[0027] (2) Pre-sintering: pre-sintering the dried main material in a nitrogen atmosphere at 950°C for 3 hours to obtain a pre-sintered material;
[0028] (3) Secondary sanding: add dopant to the calcined material and mix evenly, add water for sand milling until the particle size of the material is 1 μm, then dry to obtain sand abrasive, in which the dopant is CaCO 3 , Nb 2 o 5 , ZrO 2 and SnO 2 , based on the mass of pre-fired material, add 600ppm CaCO 3 , 300ppm Nb 2 o 5 , 200ppmZrO 2 and 500ppmSnO 2 ;
[0029] (4) Granulation: add 10% of the mass of the abrasive to the sand abrasive, and a PVA solution with a mass percentage concentration of 9%, stir evenly, and then spray and granula...
Embodiment 3
[0032] (1) One-time sanding: Add water to the main material and sand it until the particle size of the material is 1.2 μm, then dry it and wait for use. The main material is composed of the following components in molar percentages: 52.5mol% Fe2 o 3 , 9.5mol% ZnO, the balance is MnO;
[0033] (2) Pre-sintering: pre-sintering the dried main material in a nitrogen atmosphere at 850°C for 1.5 hours to obtain a pre-sintered material;
[0034] (3) Secondary sanding: add dopant to the calcined material and mix evenly, add water for sand milling until the particle size of the material is 0.8 μm, then dry to obtain sand abrasive, in which the dopant is CaCO 3 , Nb 2 o 5 , ZrO 2 and SnO 2 , based on the mass of pre-fired material, add 550ppm CaCO 3 , 250ppm Nb 2 o 5 , 150ppmZrO 2 and 450ppm SnO 2 ;
[0035] (4) Granulation: add 9% of the mass of the abrasive to the sand abrasive, and a PVA solution with a mass percentage concentration of 8.5%, stir evenly, and then spray and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com