Application of cd1c in the diagnosis of bacterial-negative pulmonary tuberculosis
A tuberculosis, bacteria-negative technology, applied in the application field of CD1c in the diagnosis of bacteria-negative pulmonary tuberculosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
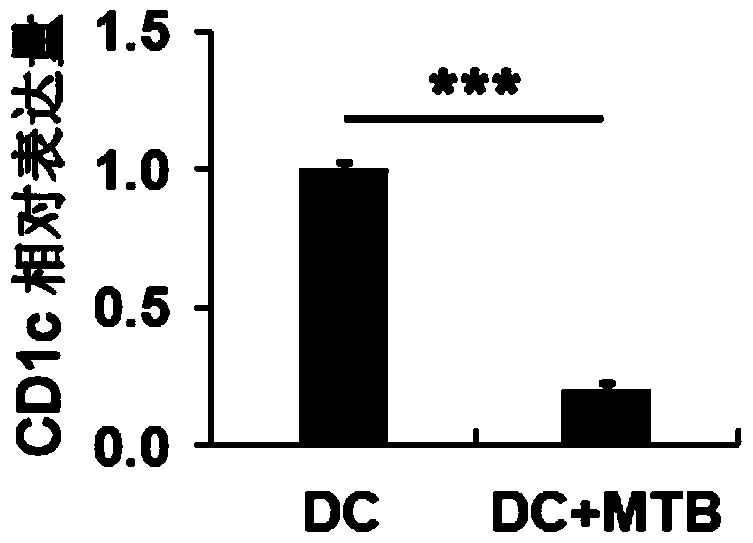
[0020] Example 1 Down-regulation of CD1c expression in DCs infected with MTB
[0021] Isolation of PBMC from healthy volunteers, immunomagnetic separation of CD14 + Monocytes were induced with GM-CSF and IL-4 to differentiate into DCs, and the resulting DCs were infected with MTB. After 72 hours, the expression level of CD1c in DC was detected by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR.
[0022] Test results such as figure 1 As shown, it can be seen that the expression level of CD1c in DC after MTB infection is significantly reduced, indicating that MTB infection inhibits the expression of CD1c.
Embodiment 2
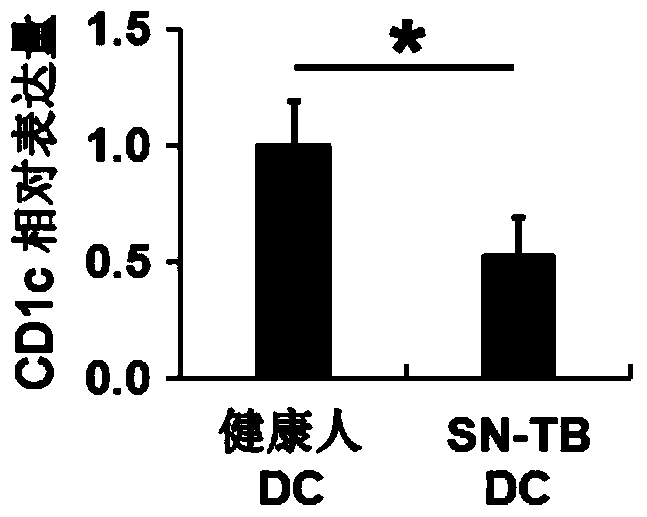
[0023] Example 2 Down-regulation of CD1c expression in DCs of bacterium-negative pulmonary tuberculosis patients
[0024] Isolation of PBMCs from bacterium-negative pulmonary tuberculosis patients and healthy volunteers, immunomagnetic separation of CD14 + For monocytes, GM-CSF and IL-4 were used to induce monocytes to differentiate into DCs. After 72 hours, real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR was used to detect the expression of CD1c.
[0025] Test results such as figure 2 As shown, it can be seen that the expression level of CD1c in the DCs of bacteria-negative pulmonary tuberculosis patients was significantly lower than that of healthy volunteers ( P <0.05).
Embodiment 3
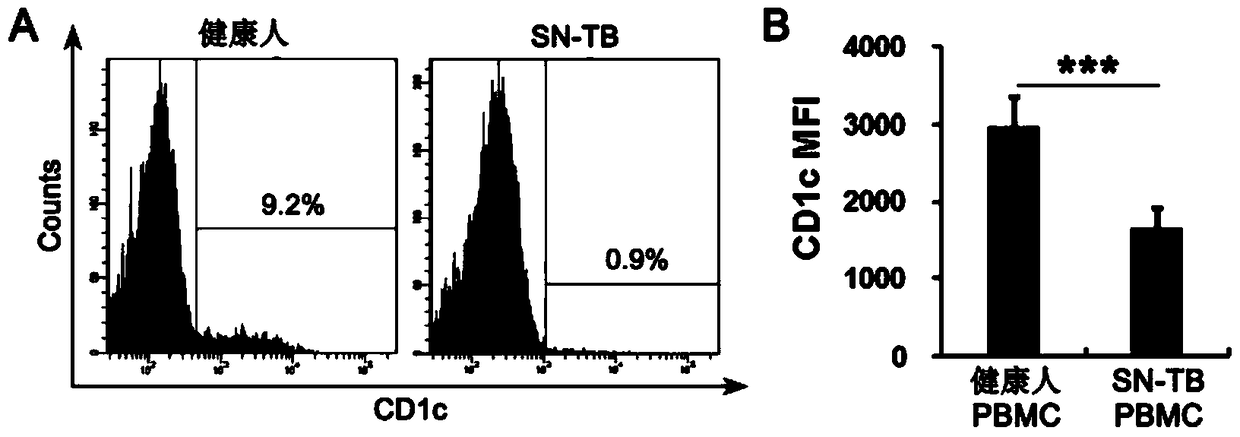
[0026] Example 3 Down-regulation of CD1c expression in PBMCs of patients with bacterium-negative pulmonary tuberculosis
[0027] PBMCs from 119 bacterium-negative pulmonary tuberculosis patients and healthy volunteers were isolated, and the expression of CD1c on the cell surface was detected by flow cytometry.
[0028] Test results such as image 3 As shown, it can be seen from it that the PBMCs expressing CD1c on the cell surface of bacterium-negative pulmonary tuberculosis patients were 0.9%, which was significantly lower than that of healthy volunteers (9.2%), as shown in image 3 Shown in A; the average fluorescence intensity test results also show that the fluorescence intensity of CD1c expression in PBMCs of bacterium-negative pulmonary tuberculosis patients is significantly lower than that of healthy volunteers ( P image 3 Shown in B; it shows that the expression level of CD1c in PBMC of patients with bacterial negative pulmonary tuberculosis is significantly lower th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com