Germanate glass cladding/semiconductor fiber core composite material optical fiber
A technology of germanate glass and composite materials, which is applied in the direction of cladding optical fiber, optical waveguide light guide, glass manufacturing equipment, etc., can solve the problem of composite optical fiber without obtaining performance, and achieve excellent infrared transmission performance, excellent drawing performance, and anti-corrosion Effect of high laser damage threshold
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The preparation and method of the multi-component germanate glass cladding / germanium semiconductor core fiber are as follows:
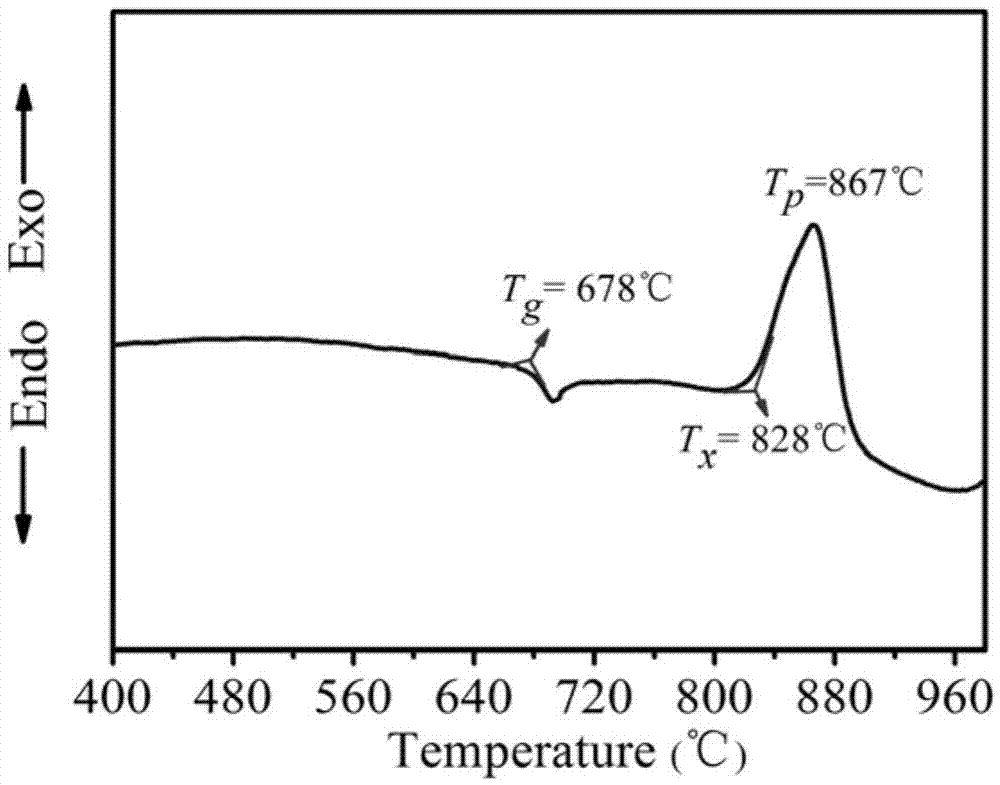
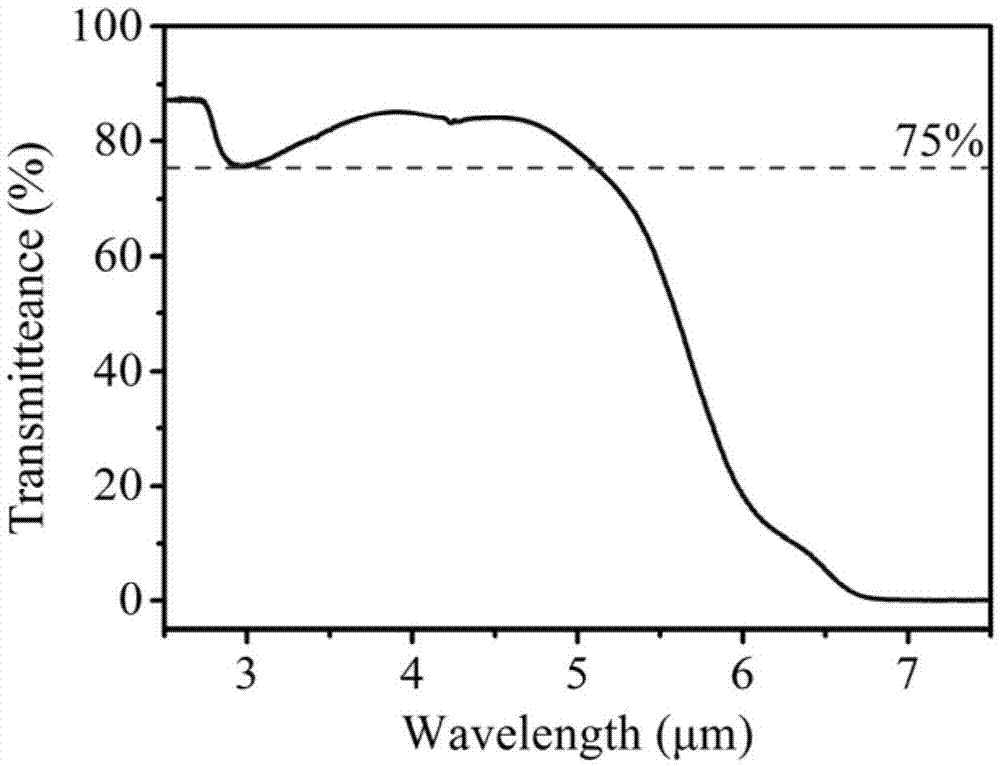
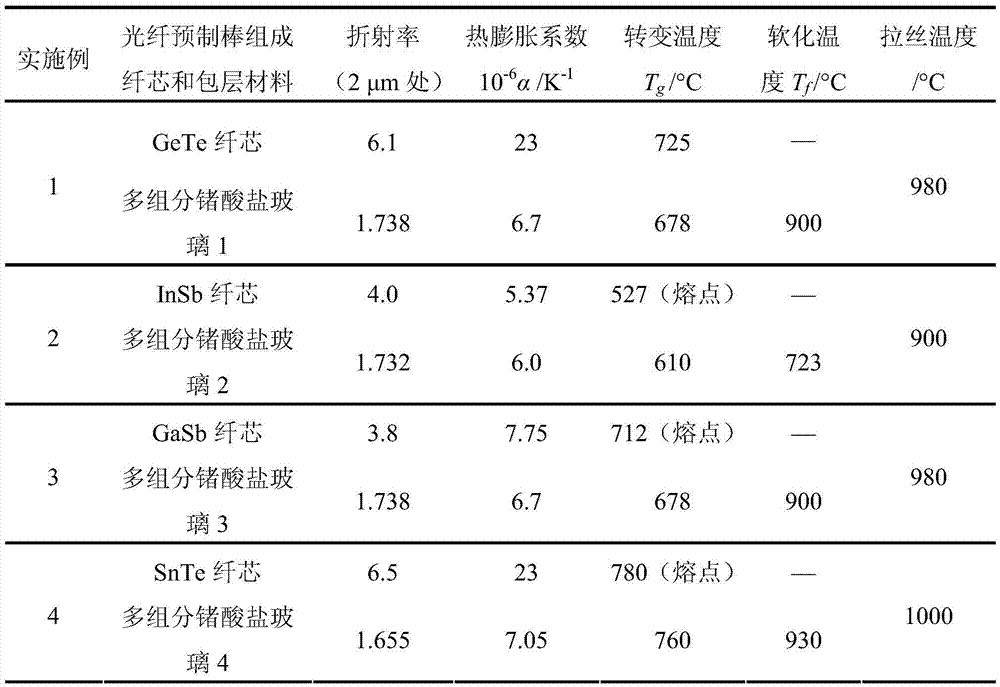
[0023] (1) The traditional fusion-annealing method is used to melt bulk multi-component germanate clad glass. In terms of mass percentage, the glass raw material formula is: BaO15%, Ga 2 o 3 15%, GeO 2 65%, La 2 o 3 5% (purity 99.99%). Weigh 800 g of raw materials according to the proportion, mix them evenly, add them into a platinum crucible, and dissolve them at 1400°C for 5 hours. During this period, the reaction atmosphere method is used to remove water, and at the same time, it is protected by oxygen. After molding, keep it warm at 600°C for 20 hours, and then cool to room temperature with the furnace. The multicomponent germanate glass transition temperature T g is 678°C (such as figure 1 DSC measurement), the infrared transmission performance is shown in figure 2 middle.
[0024] (2) Machining of cladding glass: After precisio...
Embodiment 2
[0029] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 lies in that the formulation of the multi-component germanate cladding glass and the semiconductor material are different. The multi-component germanate clad glass is calculated by mass percentage, and the glass raw material formula is: BaO20%, Ga 2 o 3 17%, GeO 2 60%, La 2 o 3 3% (purity 99.99%). Indium antimonide (InSb) semiconductor is used as the core material of the optical fiber. The melting point of InSb is 527°C, and it is the direct bandgap semiconductor with the narrowest bandgap among III-V semiconductors. The forbidden band width of InSb at room temperature is 0.18eV, and its transmission spectrum covers the entire mid-wave infrared band (7-30μm). In terms of energy band characteristics, the conduction band of InSb has strong non-parabolic properties, which makes it have a large nonlinear effect, especially three-wave mixing. In addition, InSb has high carrier mobility, high photon absorption effi...
Embodiment 3
[0031] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 lies in the core semiconductor material. The GaSb semiconductor is selected as the fiber core. The GaSb semiconductor has a melting point of 712°C and a bandgap width of 0.726eV (1709nm) at room temperature. It can use energy level transitions to emit light and achieve 1.7-1.8μm near-infrared emission. GaSb core fiber. In addition to having luminescent properties, undoped GaSb will exhibit p-type semiconductor characteristics and high hole mobility. GaSb core fibers or thinner micro-nano fibers can be used for metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) and other optoelectronic devices. Bulk GaSb is filled into cylindrical holes in multi-component germanate cladding glass, assembled into optical fiber preforms, and then drawn down at 980°C to make optical fibers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bandgap width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com