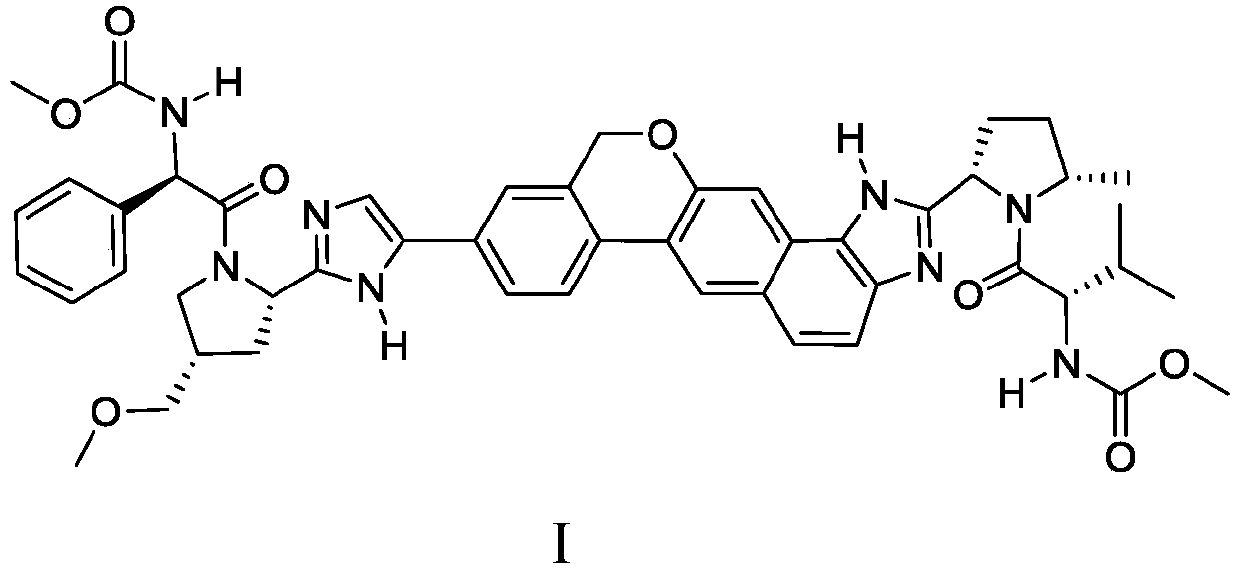
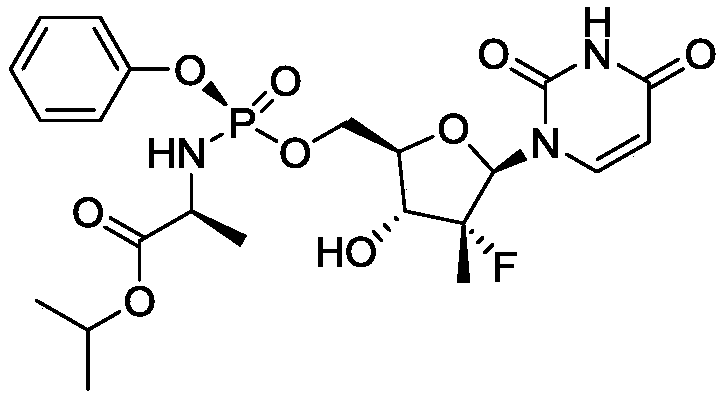
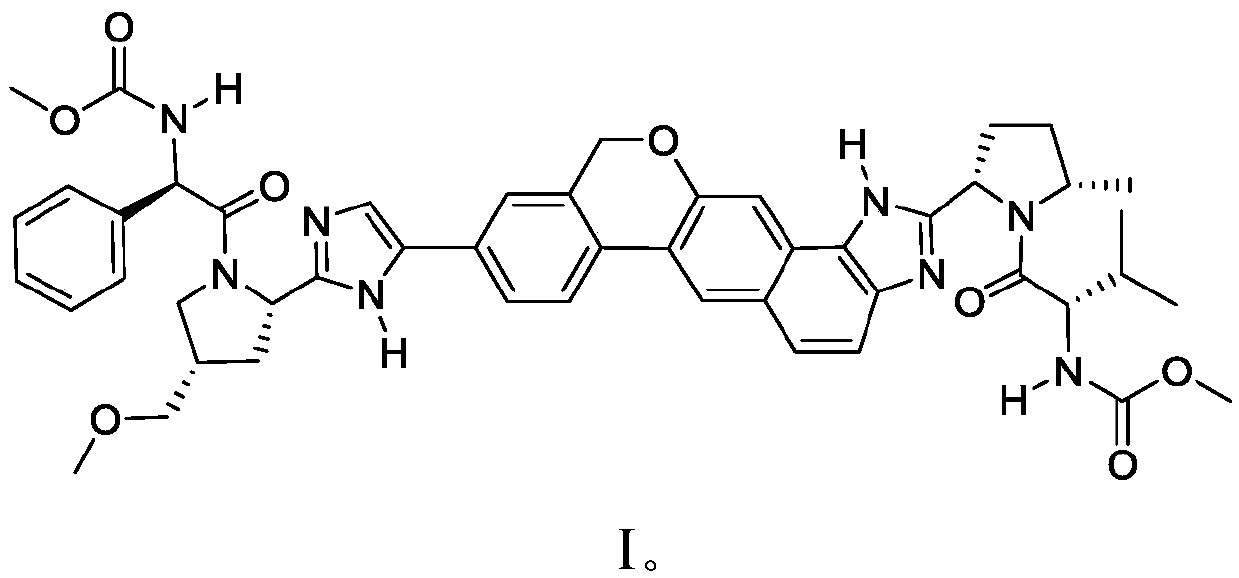
Combination formulation of two antiviral compounds
A compound and composition technology, applied in the field of compound preparations of two antiviral compounds, can solve the problems of unknown treatment benefit of sofosbuvir
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0216] Example 1: Tablet Preparation and Formulation
[0217] A. Dose Selection of Tablets
[0218] i. Sofosbuvir
[0219] The dose of sofosbuvir chosen for the tablet is 400 mg once daily. Support for the 400 mg sofosbuvir dose can be derived from early virological and human exposure data E max PK / PD modeling, which also supported selection of 400 mg sofosbuvir higher than other tested doses.
[0220] Mean sofosbuvir major metabolite AUC for 400 mg sofosbuvir dose tau Associated with approximately 77% of the maximum obtainable HCV RNA change from baseline (the value at the apex of the plateau of the exposure-response sigmoid curve) as determined by this model. In Recurve E max In the model, there is a relatively linear exposure-response relationship in the range of 20-80% of the maximum effect. Therefore, given that sofosbuvir exposure from the 200 mg tablet appears to be dose proportional to single doses up to 1200 mg, doses below 400 mg are expected to produce a sizab...
Embodiment 2
[0255] Example 2: Drug-Drug Interaction Between SOF and Compound 1
[0256] The PK drug-drug interaction between SOF and Compound I was assessed. Compound I plasma exposure (AUC tau 、C max and C tau ) was not affected by SOF co-administration and therefore no dose adjustment was required for Compound I. Sofosbuvir plasma exposure increased approximately 1.8-fold when co-administered with Compound I (C max ) and 2.4-fold (AUC). When SOF was co-administered with compound I (solid dispersion, compound I: copovidone 1:1), the C max and AUC increased by about 1.6-fold and 1.8-fold, respectively, when co-administered with Compound I was approximately 1.8-fold (C max ) and 2.4-fold (AUC). The Cmax of SOF metabolite II (the major circulating nucleoside metabolite of SOF) decreased by about 36%, but the AUC was not affected by co-administration of SOF and Compound I. See Table 6.
[0257] Table 6
[0258]
[0259]
[0260] Note: Data reported as GLSM. Contemporaneous g...
Embodiment 3
[0262] Example 3: Food Effects
[0263] Exposure of Compound I solid dispersion (Compound I:copovidone 1:1) administered as a single agent with a high-fat / high-calorie diet (HFM) was modestly reduced (14% of AUC) compared to fasted administration and a 25% reduction in Cmax) (Table 7). The relative increase in exposure of Compound I (solid dispersion) when administered as part of Sofosbuvir / Compound I (solid dispersion) FDC with HFM resulted in a modest increase in exposure compared to fasted administration (AUC ~20% improvement and ~5% improvement in Cmax, Table 8). This increase in exposure indicates an increase in the bioavailability of Compound I administered as part of a sofosbuvir / Compound IFDC relative to Compound I administered as a single agent tablet. Table 8 below shows the Compound I exposure and GMR of the fixed dose combination under different fed states.
[0264] Table 7
[0265]
[0266]
[0267] Table 8
[0268]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com