Semiconductor light emitting element
A technology for light-emitting elements and semiconductors, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as low luminous efficiency and achieve the effect of improving light extraction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0059] The structure of the first embodiment of the semiconductor light emitting element of the present invention will be described.
[0060] structure
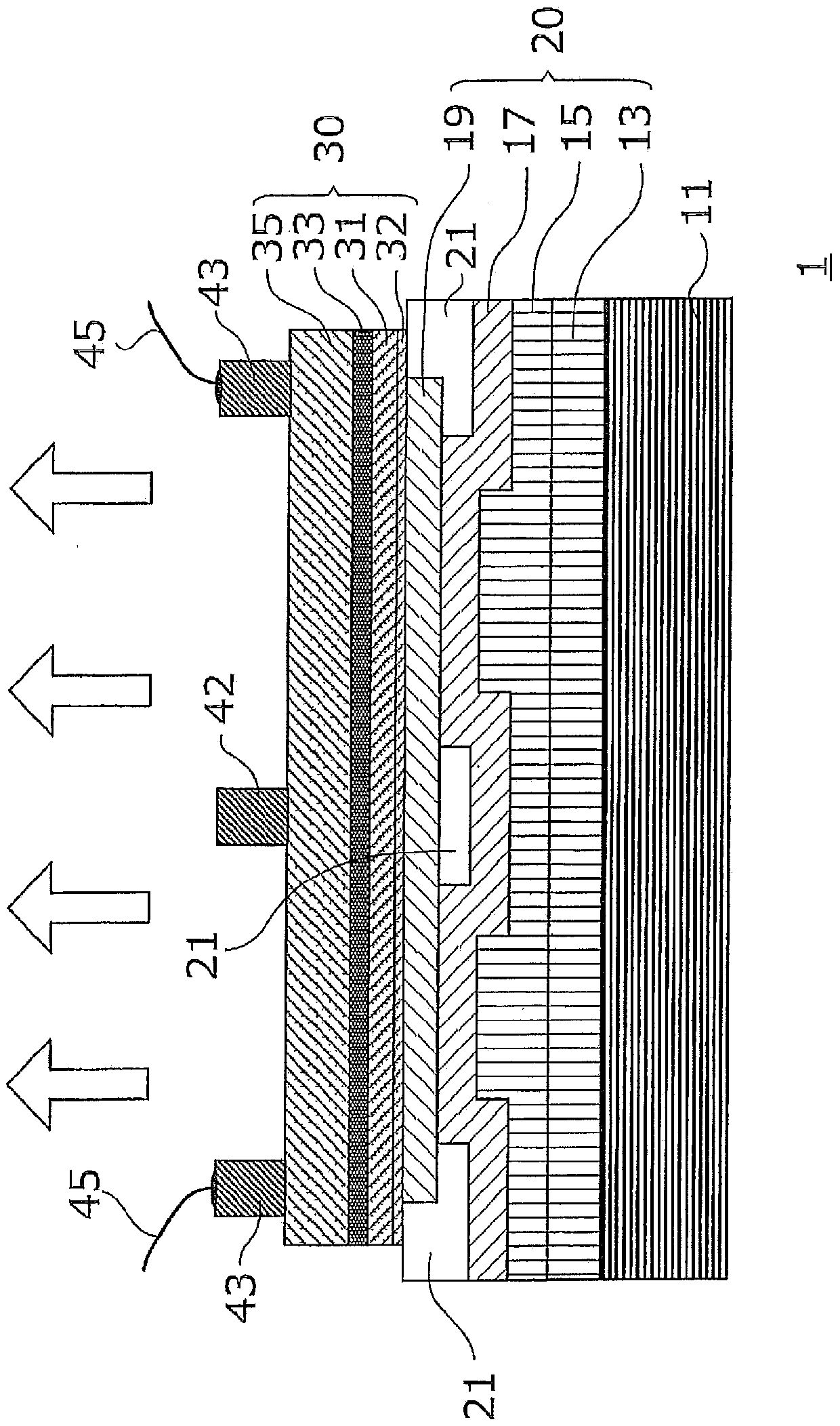
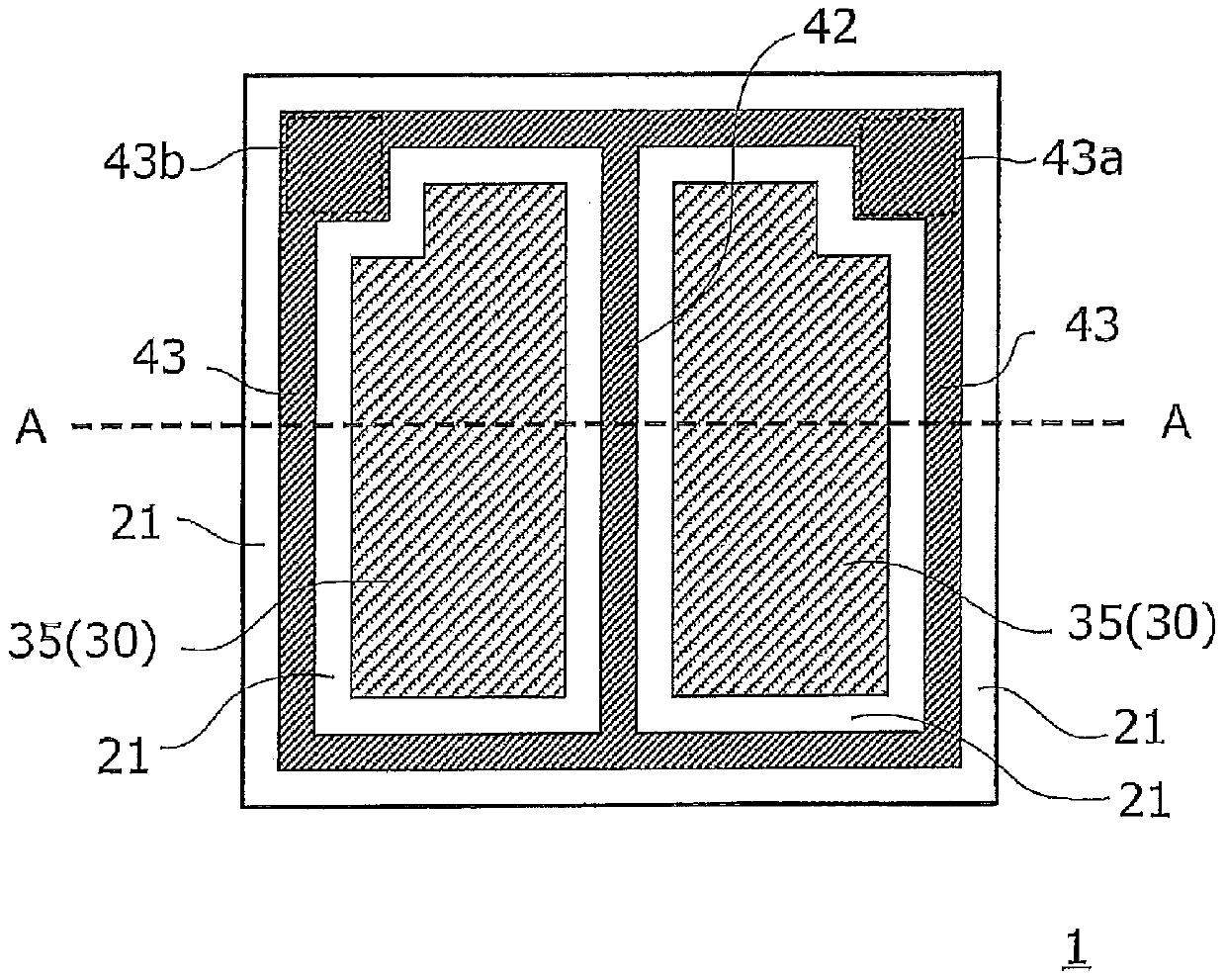
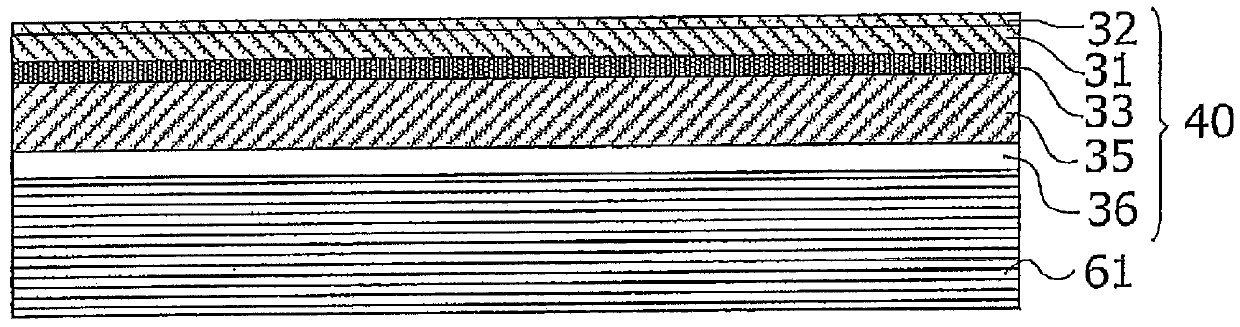
[0061] Figure 1A It is a cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of the semiconductor light emitting element of the first embodiment. The semiconductor light emitting element 1 is configured to include a support substrate 11, a conductive layer 20, an insulating layer 21, a semiconductor layer 30, and n-side electrodes (42, 43). The semiconductor layer 30 is formed by stacking a p-type semiconductor layer ( 32 , 31 ), a light emitting layer 33 , and an n-type semiconductor layer 35 sequentially from below. in addition, Figure 1B It is a schematic plan view when viewing the semiconductor light emitting element 1 from above, Figure 1A and Figure 1B Corresponds to the A-A line sectional view in.
[0062] (Support substrate 11)
[0063] The supporting substrate 11 is formed of, for example, a conductiv...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0135] The structure of the second embodiment of the semiconductor light emitting element of the present invention will be described. In addition, the same code|symbol is attached|subjected to the same structure as 1st Embodiment, and description is abbreviate|omitted.
[0136]
[0137] image 3 It is a cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of the semiconductor light emitting element of the second embodiment. Compared with the semiconductor light emitting element 1 of the first embodiment, the semiconductor light emitting element 1 a further includes an insulating layer 22 (corresponding to "the second insulating layer"). The insulating layer 22 is also made of SiO 2 , SiN, Zr 2 o 3 , AlN, Al 2 o 3 And so on.
[0138] More specifically, the insulating layer 22 is formed at a position directly under the formation position of the n-side electrodes ( 42 , 43 ) and sandwiched between the reflective electrode 19 and the p-type semiconductor layer 32 . F...
Embodiment
[0151] The semiconductor light emitting element 1 of the first embodiment manufactured by the method described above is referred to as Example 1, the semiconductor light emitting element 1a of the second embodiment is referred to as Example 2, and Figure 5 The semiconductor light-emitting element 50 shown is used as a comparative example, and the current-voltage characteristics and light-emitting characteristics are compared.
[0152] Figure 5It is a cross-sectional view schematically showing the structure of a semiconductor light emitting element formed as a comparative example. Compared with the semiconductor light emitting element 1 , the insulating layer 23 provided on the upper surface of the reflective electrode 19 is provided instead of the insulating layer 21 formed on the bottom surface of the reflective electrode 19 . The insulating layer 23 is formed for the purpose of spreading the current flowing in the light emitting layer 33 in the horizontal direction by bei...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com