Machine vision material level gauge and its method for measuring material level
A technology of machine vision and material level gauge, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, machines/engines, and engine lubrication, etc. It can solve the problems of ignoring parameter changes, ignoring the imaging principle characteristics of video and image equipment, complex and changeable image sizes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
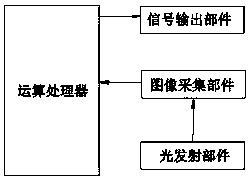
[0083] This embodiment provides a machine vision material level gauge, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a light emitting part, an image acquisition part, an operation processor and a signal output part. Both the light emission part and the image acquisition part are set in the measurement space where the material to be tested is located, and the operation processor is respectively connected to the image acquisition part and the signal output part. ;
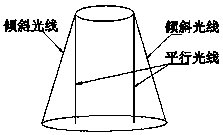
[0084] The light emitting part is used to project at least two beams of parallel light perpendicular to a certain cross-section of the material to be tested and at least one beam of oblique light at a preset angle with each parallel light to the surface of the material to be tested;
[0085] The image acquisition part is used to collect images of parallel light spots and oblique light spots formed after each parallel light and each oblique light irradiates the surface of the material to be tested, and sends the images to th...
Embodiment approach 2
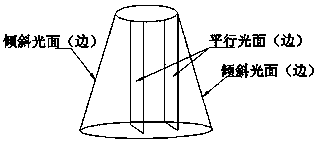
[0096] This embodiment is a specific example of Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the light emitting part and the image acquisition part are both arranged on the top of the container where the material to be tested is located, and the light emitting part is used to project two beams perpendicular to the surface of the material to be tested. When the parallel light of a certain cross-section of the material to be tested and a beam of oblique light with a preset angle with any beam of parallel light are irradiated on the surface of the material to be tested, the corresponding Two parallel light spots and one oblique light spot are located on the same straight line;
[0097] The arithmetic processor is used to calculate the image in the image between the two parallel light spots according to the actual distance between the two parallel lights, the actual distance between the light source of the oblique light and the parallel light at a preset angle, the preset angle, The pitch an...
Embodiment approach 3
[0101] This embodiment is a further improvement of Embodiment 2. The main improvement is that in Embodiment 2, two parallel light spots and one oblique light spot are located on the same straight line, but when the surface of the material has a slope that is not flat, they are located on the same straight line The three light spots on the top are likely to be located at different material level heights. In this case, when collecting the images of the three from top to bottom, it is easy to cause the acquisition of The focal lengths of the three light spots are different in the image, which leads to the fact that the distance between the three images in the collected image cannot completely correspond to the actual distance, which leads to inaccurate material level information obtained by the subsequent operation processor; therefore, in this embodiment , two parallel light spots and one oblique light spot located on the same straight line and at the same height of the material ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com