A priority packet scheduling method and system utilizing data topological information
A topology information, packet scheduling technology, applied in the direction of program startup/switching, multi-program installation, etc., can solve problems such as confusion, neighbors cannot be statically determined, and it is difficult to statically analyze dependencies.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0100] The following is embodiment 1 of the present invention, as follows:
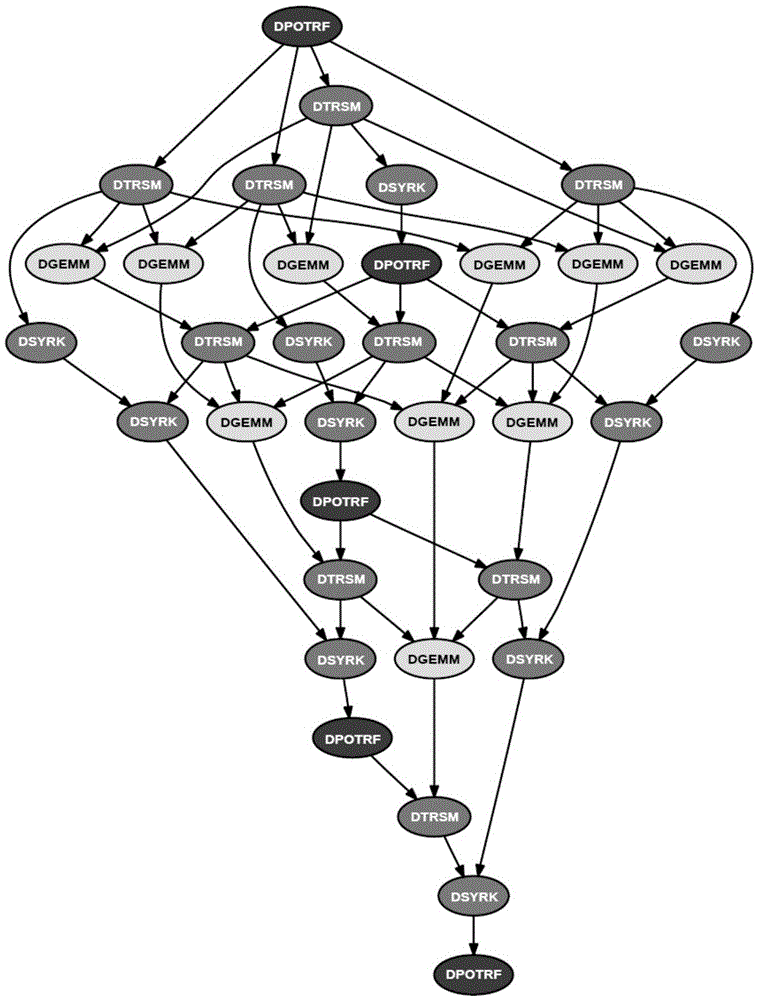
[0101] This is the stencil calculation of 3d7p using Jacobi iteration. The stencil calculation is carried out in a three-dimensional grid space, and the two space axes are divided into global tasks. The discrete space uses a fixed grid and the data is stored in a single array.
[0102]
[0103]
[0104]
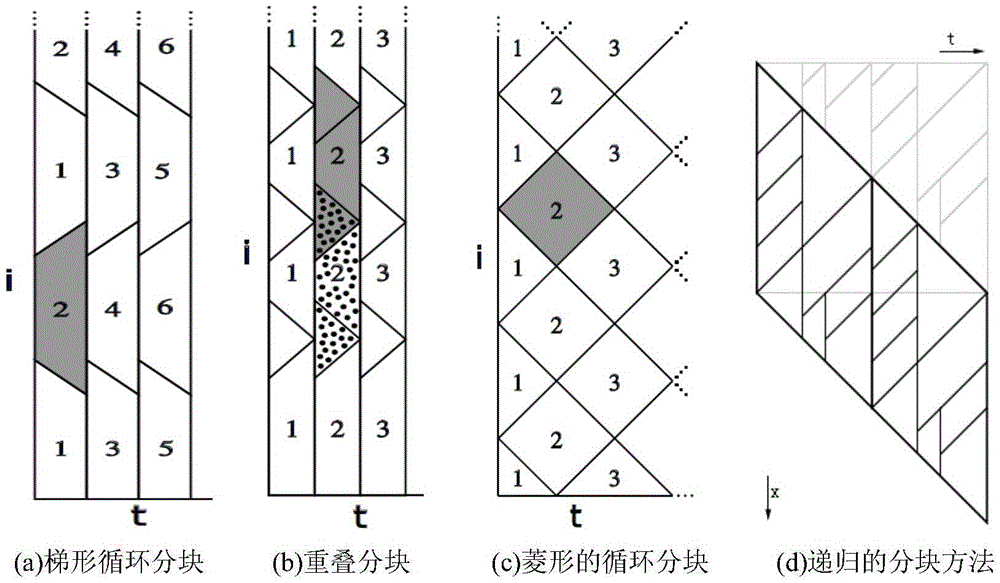
[0105] The size of the slice here is 12^3. Double-precision calculation is used. There are 2 grid variables involved in the calculation. The current machine's L3 cache is 20M. Because this calculation has neighbor dependence in 6 directions of the three spatial axes, then The grouped data footprint is 8*2*(wx+wt-1)*(wy+wt-1)*(wz+wt-1)*12*12*12 with , But the latter has higher intra-group reuse. So the grouping shape selected by the scheduling system is , That is, the window height of the time axis and the block width of the space axis are both 4, and the maximum data reuse in the group is 4.
[0106] ...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Embodiment 2 of the present invention is as follows:
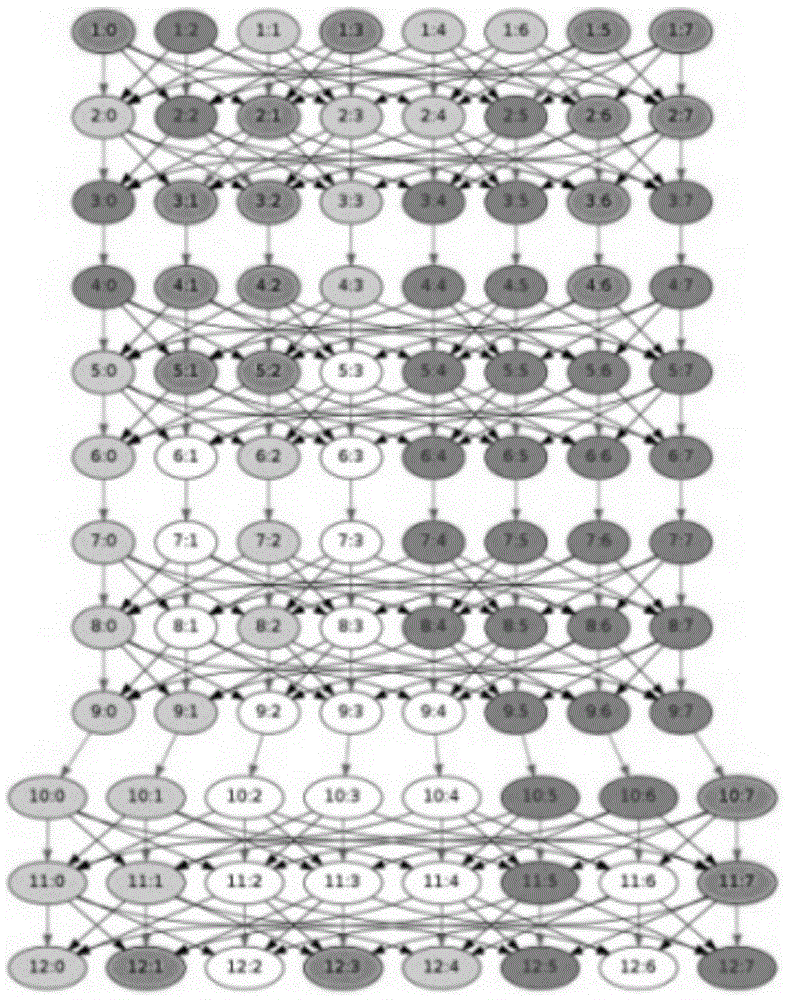
[0110] This embodiment is an application hotspot for solving the Poisson equation. The present invention adopts adaptive refinement of the grid. The grid fragmentation is dynamic and irregular, and the data is stored in a fragmented format instead of a single array.
[0111] In the priority grouping of the scheduling system, there is no obvious difference from Embodiment 1.
[0112] What is mainly shown here is how users describe: the division of grid space, the mapping of task graph to grid space, and the expression of irregular neighbor data dependence.
[0113]
[0114]
[0115] ● Shown below is a subroutine inside looseGSRB(), its main function is to realize the data exchange in the shaded area of adjacent data slices. However, in the adaptive grid method, the number and location of neighbors cannot be determined statically.
[0116] .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com