Method for increasing superconducting critical current density of ex-situ magnesium diboride block through self reaction
A technology of critical current density and magnesium diboride, which is applied in the field of superconductivity, can solve problems such as poor connectivity and limited critical current density, and achieve the effects of simplifying the preparation process, convenient source, and improving connectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
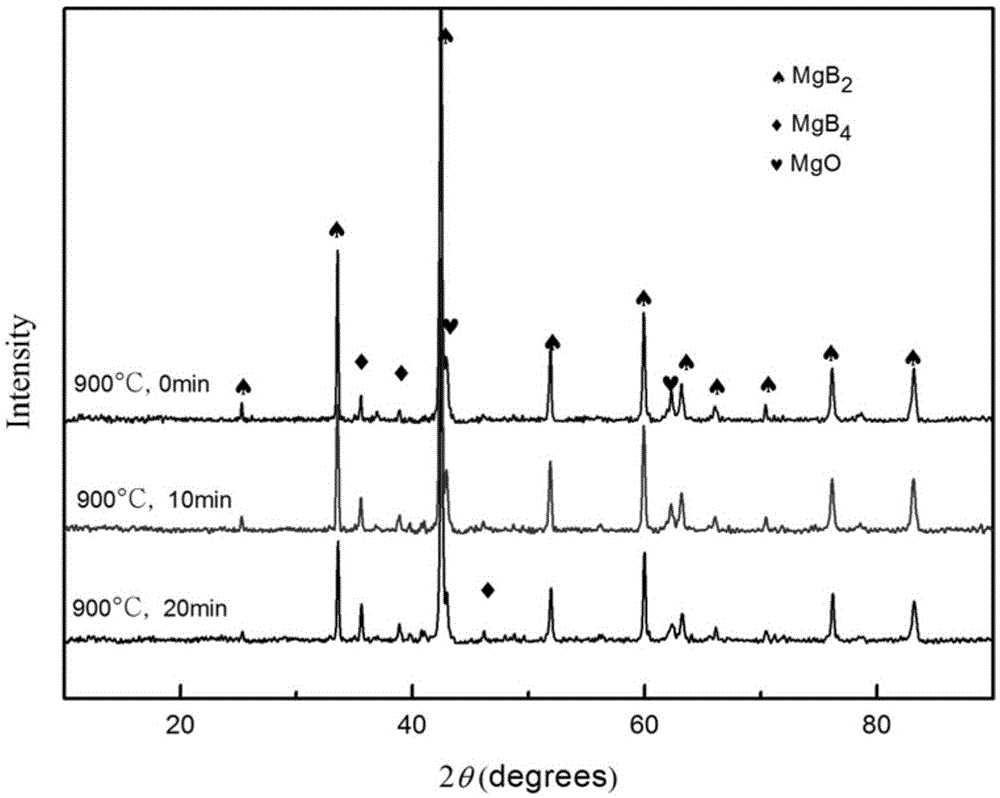
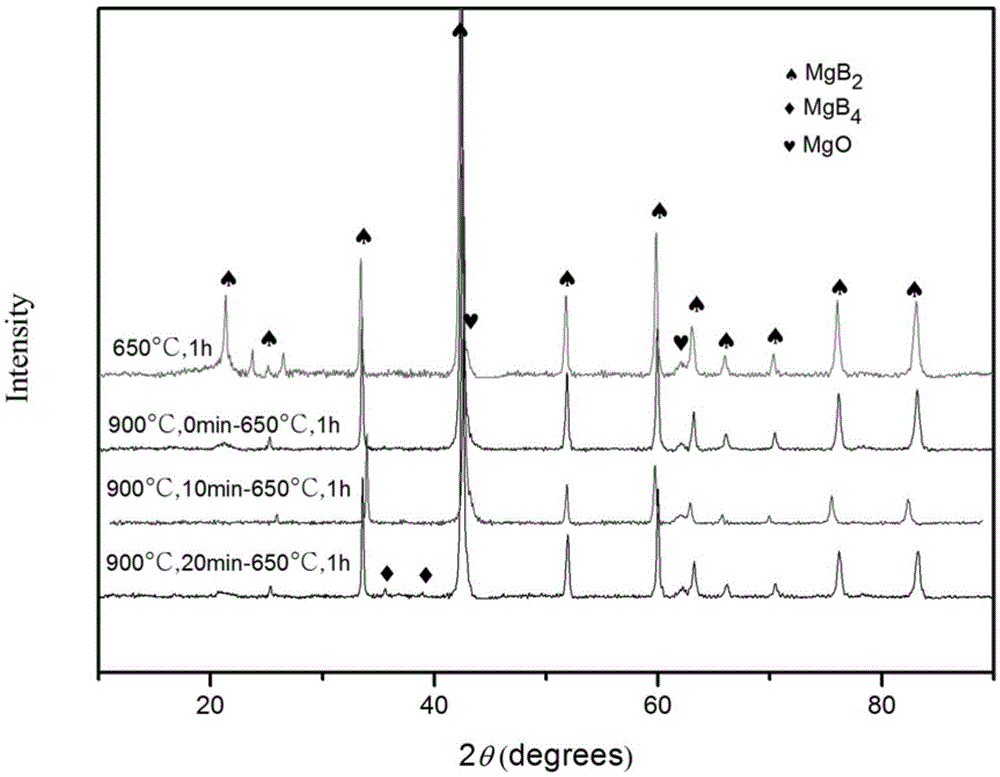
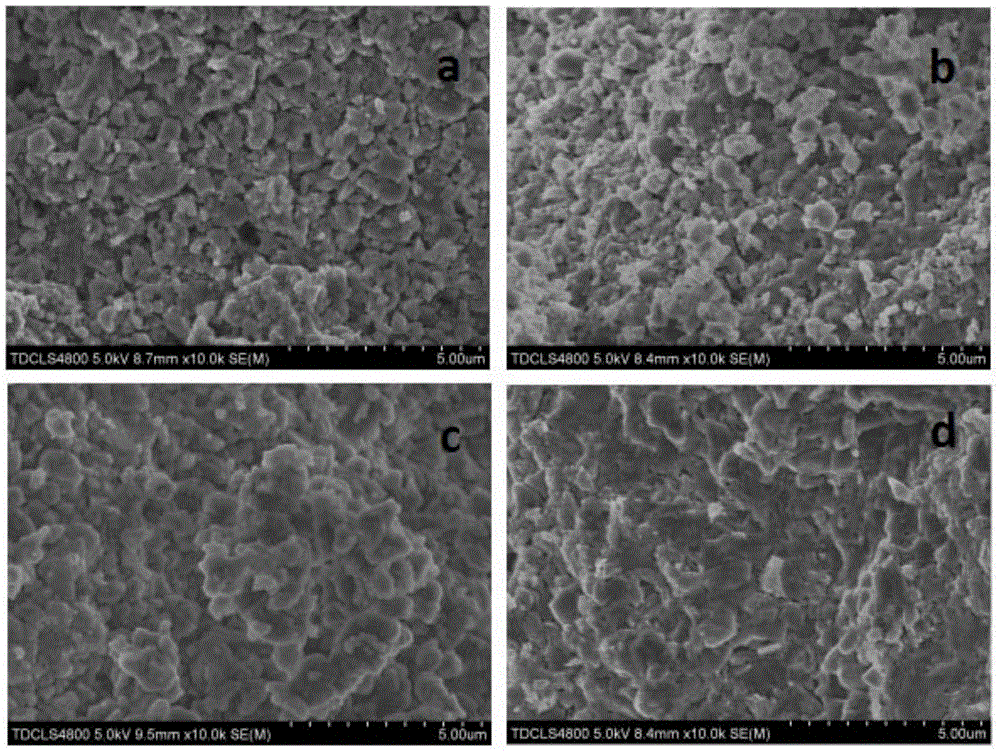
[0025] commercial MgB 2 Powder 20mg, in The mold was kept at a pressure of 3 MPa for 2 minutes, and finally the cylindrical block was put into a high-temperature differential scanning calorimeter for sintering in an argon protective atmosphere. The rate is reduced to 650°C, maintained at this temperature for 1 hour, and finally cooled to room temperature at a rate of 40°C / min. This sample is named b, and the conditions are 900°C, 0min-650°C, 1h. The phase composition of the prepared sample was determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), such as figure 2 The corresponding samples are shown in . From figure 2 It can be seen that the sample contains a small amount of MgB 4 . The microstructure was then observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), image 3 Figure b in middle is the corresponding SEM scanning picture. Finally, grind the sample to 4×2×1mm 3 The cuboid was tested for comprehensive physical properties, and the curve of the critical current density changing w...
Embodiment 2
[0027] commercial MgB 2 Powder 30mg, in The mold was kept at 5 MPa for 2 minutes, and finally the cylindrical block was put into a high-temperature differential scanning calorimeter for sintering in an argon protective atmosphere. The heating rate was 10°C / min. Decrease to 650°C at a rate of 40°C / min, keep at this temperature for 1 hour, and finally cool to room temperature at a rate of 40°C / min. The sample is named c, and the conditions are: 900°C, 10min—650°C, 1h. The phase composition of the prepared sample was determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), such as figure 2 The corresponding samples are shown in . From figure 2 It can be seen that the sample contains a small amount of MgB 4 . The microstructure was then observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), image 3 Figure c in the middle is the corresponding SEM scanning picture. Finally, grind the sample to 4×2×1mm 3 The cuboid was tested for comprehensive physical properties, and the curve of the critical c...
Embodiment 3
[0029] commercial MgB 2 Powder 60mg, in Keep the pressure in the mold at 10MPa for 2 minutes, and finally put the cylindrical block into the tubular sintering furnace for sintering in the argon protective atmosphere. The heating rate is 10°C / min. The rate is reduced to 650°C, kept at this temperature for 1 hour, and finally cooled to room temperature at a rate of 40°C / min. The sample is named d, and the conditions are: 900°C, 20min—650°C, 1h. The phase composition of the prepared sample was determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), such as figure 2 The corresponding samples are shown in . From figure 2 It can be seen that the sample contains a small amount of MgB 4 . The microstructure was then observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), image 3 Figure d in the middle is the corresponding SEM scanning picture. Finally, grind the sample to 4×2×1mm 3 The cuboid was tested for comprehensive physical properties, and the curve of the critical current density changing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com