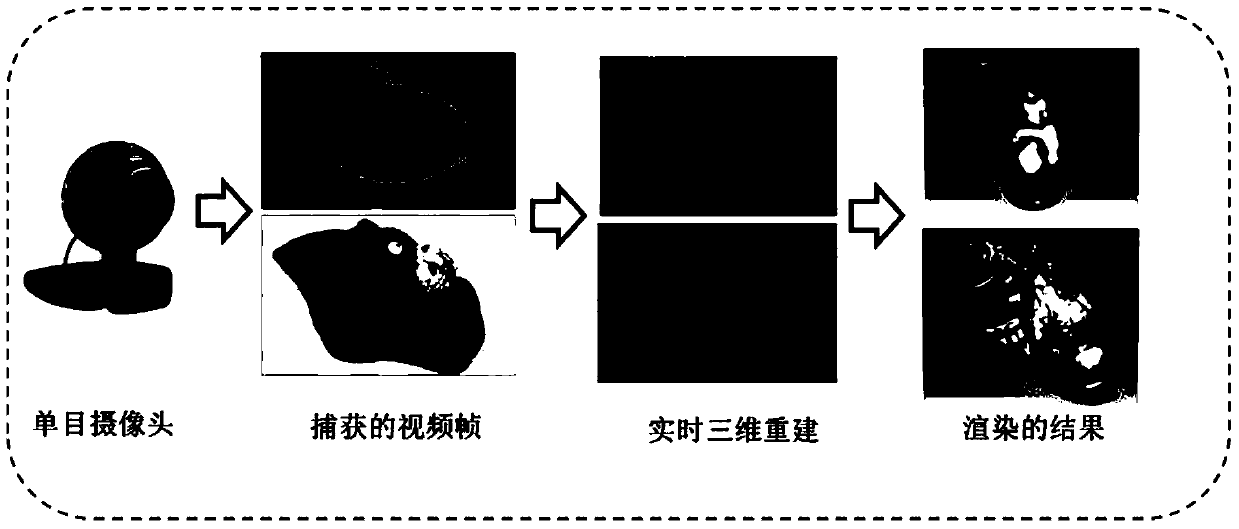
Robust real-time 3D reconstruction method based on consumer-grade camera
A real-time 3D, camera technology, applied in 3D modeling, image enhancement, image analysis, etc., can solve the problems of incompleteness, high computational cost, inaccurate model, etc., to achieve efficient noise, noise suppression, and real-time visualization of the reconstruction process. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
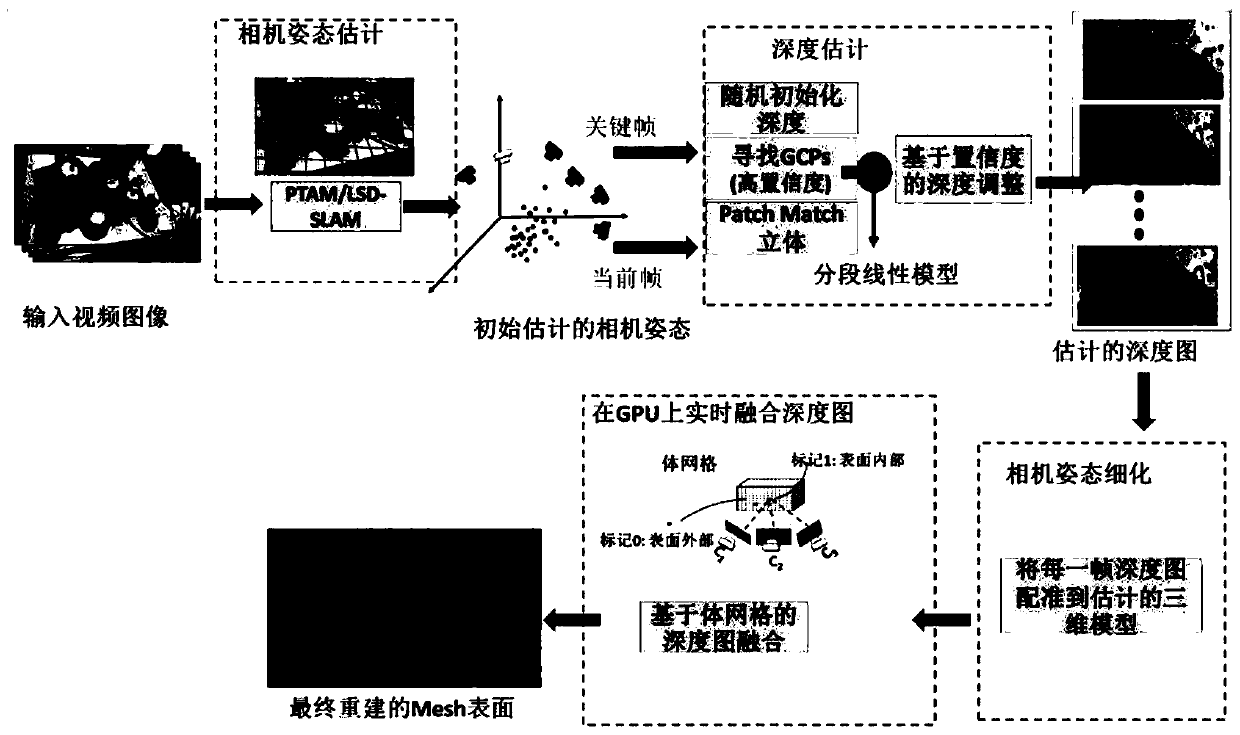
[0028] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1 to Figure 10 Describe this embodiment, the robust real-time 3D reconstruction method based on a consumer-grade camera in this embodiment is implemented in the following steps:
[0029] 1. During the movement of the camera, based on the current video frame of the camera as input, estimate the camera pose of each video frame in the scene coordinate system:
[0030] 2. Select the best key frame in the video frame for depth estimation;
[0031] 3. Use a fast and robust depth estimation algorithm to estimate the depth information of each video frame to obtain a depth map of each video frame:
[0032] 4. Transform the depth map of each video frame into a truncated symbol distance field, and incrementally fuse on voxels, and finally the initial triangular mesh surface, that is, a robust real-time 3D reconstruction method based on a consumer-grade camera is completed.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is that the step one is specifically:
[0034] (a) Build a set of keyframe collections
[0035] During the movement of the camera, keyframe k is selected from the video frame according to the temporal distance and spatial distance threshold, each keyframe corresponds to an estimated camera pose, and all keyframes form a keyframe set
[0036] (b) Constructing a 3D graph
[0037] Three-dimensional map Contains point cloud data in where p i is a 3D point in the point cloud data, for base of The number of elements in the keyframe when a new keyframe is added to the keyframe collection , it is combined with the keyframe Perform stereo matching in other key frames, and generate new point cloud data to join point cloud Every three-dimensional point p in i It records its three-dimensional coordinates, normal direction, and pixel featur...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0046] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation modes one or two is that the step two is specifically:
[0047] (1) Collection of key frames The key frames in are arranged in ascending order of the baseline size of the current frame, and the first M frames are selected to form a subset, and the key frame subset with the smallest angle with the current frame is selected. Assume that the camera center coordinates in the key frame collection are c 1 ,c 2 ,c 3 ... c n , the camera center coordinate of the current frame is c, the calculation method of the baseline between the current frame and the mth key frame is:
[0048]
[0049] (2) According to the size of the baseline, sort in ascending order, and select a subset of key frames according to the distance threshold T The T value is defined as twice the average distance between adjacent key frames, and the angle between the current frame and the key...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com