Reading method of material simplification brightness coefficient table for illumination design computing platform
A technology that simplifies brightness and design calculations. It is applied in the field of online lighting design and calculation platforms. It can solve problems such as not being able to adapt to new applications in time, not being able to provide data or code interfaces, and not having code-level openness, so as to increase CPU calculation cycles and Consumption of storage controls, high computing efficiency, and ease of network deployment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
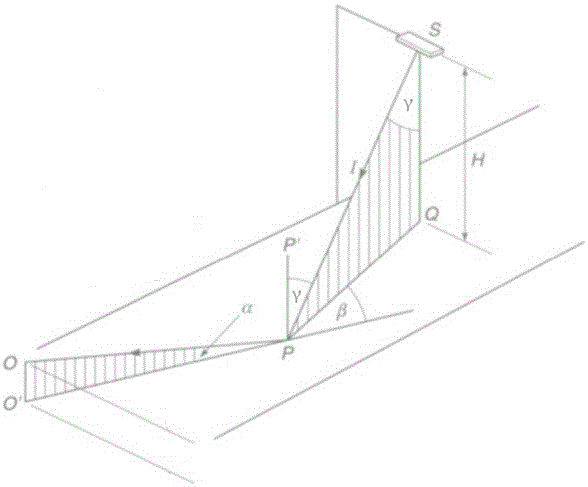
[0036] *The description of the simplified luminance coefficient of the RT format file is divided into three parts: header, boundary and data. Among them, the table header describes the creation date, designer, Q0 value, material type and several reserved items of the table. The demarcation part is the demarcation line between the table header and the data, which is used for boundary identification and compatibility with subsequent version upgrades. The data part is marked according to the horizontal and vertical coordinates β and γ, respectively representing the simplified luminance coefficient values of the corresponding points of β and γ.
[0037] Taking cement concrete pavement data as an example, the overall representation of the *RT format file is as follows image 3 shown.
[0038] The header part is described as follows:
[0039] The first line (R_Table:2015-09-08): "R_Table:" indicates that the attribute of this table is a simplified luminance coefficient table de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com