Compositions and methods for treating clostridium difficile-associated diseases
A clostridium difficile and composition technology, applied in the field of antibodies or antigenic fragments thereof, isolated polypeptides, and vectors containing the nucleic acid molecule, can solve the increased morbidity and mortality of Clostridium difficile-related diseases, prolonged Hospitalization time, additional medical expenses, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
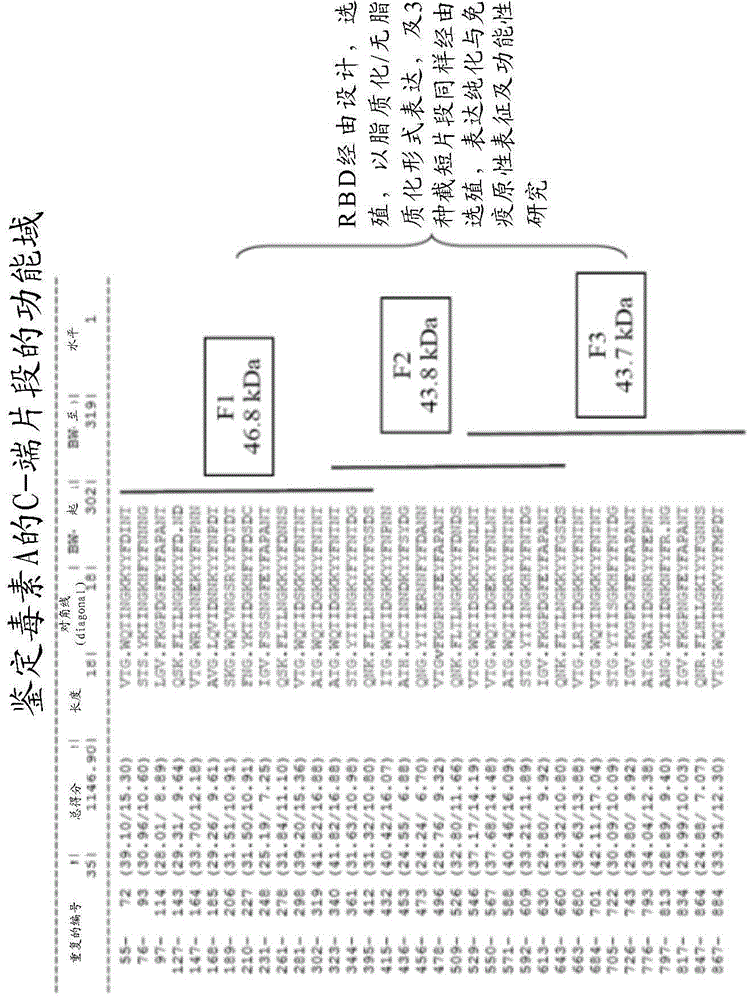
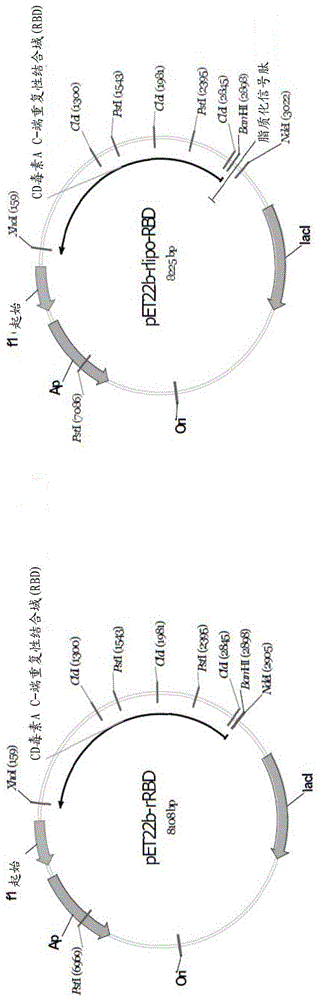
[0039] The present invention relates to a novel polypeptide comprising the receptor binding domain (RBD) of Clostridium difficile (Cd) toxin A (tcdA). Unexpectedly, such polypeptides, especially when expressed in lipidated form, are highly immunogenic and capable of inducing immunity against Cd challenge in animal models.
[0040] Polypeptides comprising one or more CdtcdA functional domains, and nucleic acids encoding the polypeptides are described below.
[0041] An exemplary polypeptide comprises a C-terminal portion of tcdA that includes the receptor binding domain (RBD) of tcdA, ie, tcdA-RBD or RBD. Listed below are the nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1) encoding tcdA-RBD and the amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 2) of tcdA-RBD. The putative receptor binding region within the RBD is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 as underlined.
[0042] tcdA-RBD nucleic acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1)
[0043] TTTAATAGCGAGAATGAACTGGATCGTGATCATCTGGGCTTCAAAATCATCGATAATAAAACCTATTATTATGATGAAGATAGCAAAC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com