Novel methods and antibodies for treating coagulapathy
A technology for coagulation disorders and antibodies, applied in the fields of antibodies, gene therapy, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as lack of high blood clots
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0267] The following embodiments are provided to aid understanding of the present invention, however, the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
[0268] In one embodiment, the invention relates to inhibitors (such as but not limited to antibodies, Fab or other fragments, peptides or aptamers) that bind to protein S and inhibit the interaction of protein S with APCs.
[0269] In one embodiment, the invention relates to an antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof that binds to protein S and inhibits the interaction of protein S with APC.
[0270] In one embodiment, the invention relates to an antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof that binds to protein S and inhibits the interaction of protein S with APCs without interfering with known non-coagulation functions of protein S.
[0271] In one embodiment, the present invention relates to the use of an antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof that binds to protein S and inhibits the interaction...
Embodiment 1
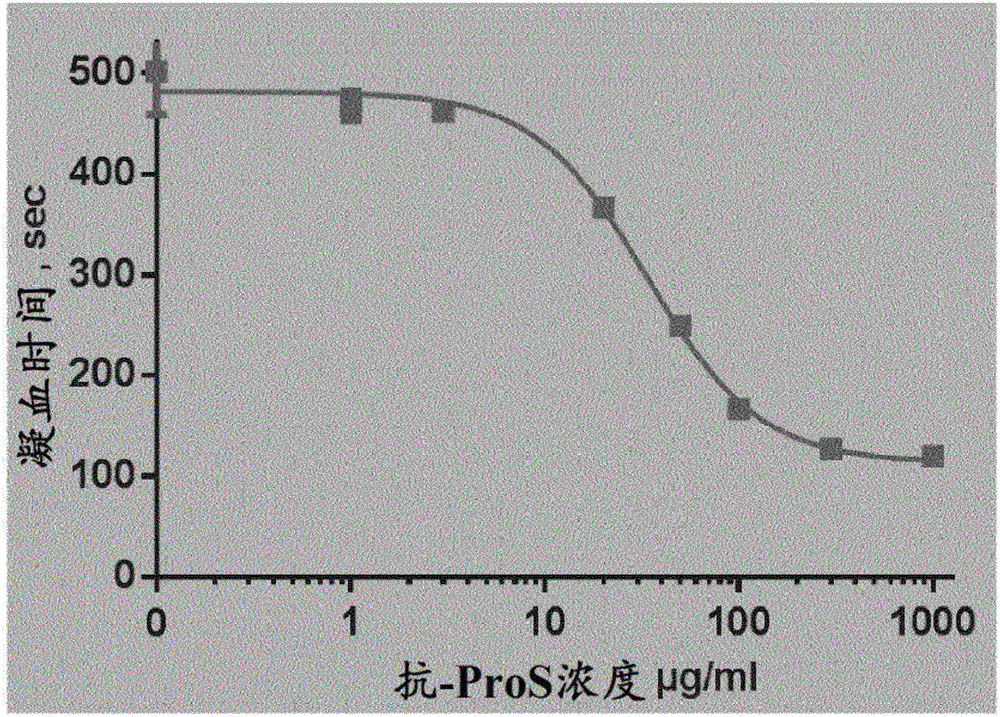
[0472] Example 1: Polyclonal Antibodies Against Protein S Improve APTT in Human Hemophiliac Plasma
[0473] In FVIII-deficient human plasma, polyclonal anti-Protein S antibody concentration-dependently shortened clotting time in the presence of APC ( figure 1 ). Congenitally FVIII-deficient human plasma (George King Biomedical Inc.) was treated with 0.3 μg / ml APC (Innovative Research) and indicated levels of polyclonal anti-protein S (DAKO #A0384) together with APTT reagent (APTT-SP, IL) before recalcification. Incubate at 37°C for 300 sec. The time to fibrin clot formation was measured using an ACL9000 (ILS). Average EC 50 It was 37.1 μg / ml (SD=2.4, n=3 experiments), corresponding to about 250 nM.
Embodiment 2
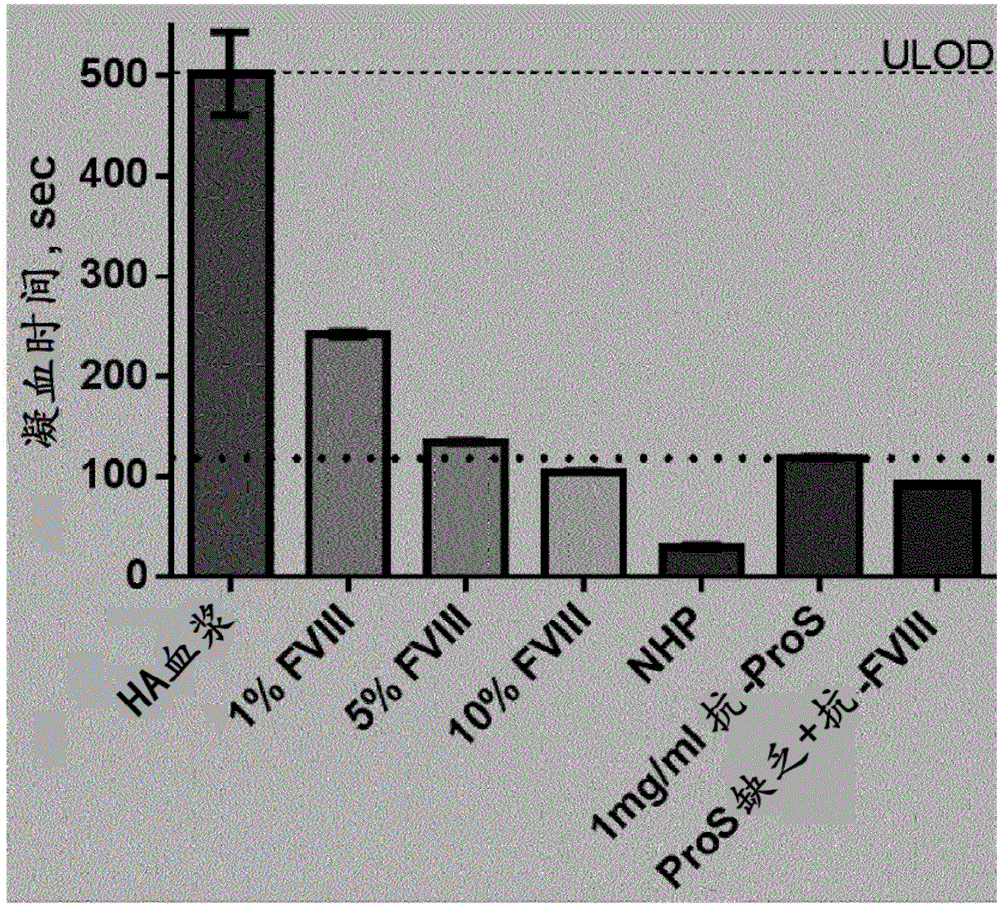
[0474] Example 2: Procoagulant effect of anti-Protein S antibody compared to FVIII in hemophilia A plasma
[0475] The maximum effect of anti-Protein S antibody in FVIII-deficient plasma was compared with the clotting times of normal human plasma and human plasma with 1%, 5% and 10% FVIII (internal), respectively ( figure 2 ). The data indicated that the complete response with anti-protein S was similar to the clotting time of plasma with 5-10% FVIII. The effect of complete neutralization of protein S was confirmed by establishing the clotting time of protein S-deficient plasma (HaemochromDiagnostica) with excess neutralizing FVIII antibody (internal), similar to protein S and FVIII doubly deficient plasma.
[0476]Plasma was mixed with APC (0.3 μg / ml) and antiprotein S (DAKO, #A0384) or FVIII in various combinations together with APTT reagent (APTT-SP, IL) and incubated at 37°C before recalcification 300sec. The time to fibrin clot formation was measured using an ACL9000 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com