Method for determining optimal master block among distributed node clocks of network system
A distributed node and network system technology, applied in the direction of time division multiplexing system, electrical components, multiplexing communication, etc., can solve the problems of limited synchronization process, inconvenient use, difficult comparison, etc., to avoid external interference, The method is simple and reliable, and the effect of simplifying the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
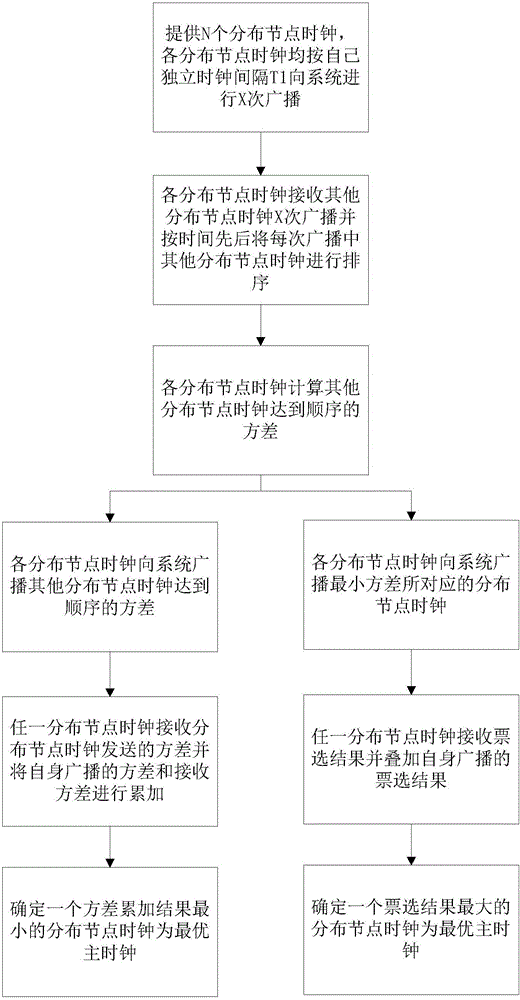
[0028] The method for determining the optimal master clock in the distributed node clocks of the network system of the present invention includes N distributed node clocks;
[0029] a. Each distributed node clock broadcasts to the system X times according to its own independent clock interval T1;
[0030] b. Each distribution node clock receives X broadcasts of other distribution node clocks and sorts the other distribution node clocks in each broadcast in chronological order;
[0031] c. Each distribution node clock calculates the variance of the arrival order of other distribution node clocks;
[0032] d. Confirm that a distribution node clock is the optimal master clock of the network system through the variance. The above-mentioned confirmation through the variance means that each distribution node clock broadcasts the variance of the arrival sequence of other distribution node clocks to the system, and any distribution node clock receives the distribution The variance se...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The method for determining the optimal master clock in the distributed node clocks of the network system of the present invention includes N distributed node clocks;
[0038] a. Each distributed node clock broadcasts to the system X times according to its own independent clock interval T1;
[0039] b. Each distribution node clock receives X broadcasts of other distribution node clocks and sorts the other distribution node clocks in each broadcast in chronological order;
[0040] c. Each distribution node clock calculates the variance of the arrival order of other distribution node clocks;
[0041] d. Confirm that a distribution node clock is the optimal master clock of the network system through the variance. The above-mentioned confirmation through the variance means that each distribution node clock broadcasts the distribution node clock corresponding to the minimum variance to the system, and any distribution node clock receives votes The results are superimposed on...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The method for determining the optimal master clock in the distributed node clocks of the network system of the present invention includes N distributed node clocks;
[0047] a. Each distributed node clock broadcasts to the system X times according to its own independent clock interval T1;
[0048] b. Each distribution node clock receives X broadcasts of other distribution node clocks and sorts the other distribution node clocks in each broadcast in chronological order;
[0049] c. Each distribution node clock calculates the variance of the arrival order of other distribution node clocks;
[0050] d. Confirm that a distributed node clock is the optimal master clock of the network system through the variance. The described variance confirmation means that each distributed node clock broadcasts to the system the variance of other distributed node clocks to the system and the distribution node corresponding to the minimum variance Clock, any distribution node clock receiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com