A Method of Key Encryption Using Multidimensional Technology
A key encryption and key technology, applied in key distribution, can solve the problems of easy forgetting of passwords or keys, insufficient security performance of passwords or keys, loss of passwords or keys, etc. Large, easy-to-remember effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A kind of method that uses multi-dimensional technology to carry out key encryption of the present invention, comprises the following steps:
[0027] (1) Call the function MDS_InitEncryptionKeyManager() to initialize the data operation environment of the multi-dimensional key;
[0028] (2) Call the function MDS_ReadUserPassword() to read the key and geometric characteristics entered by the user; read the key and geometric characteristics entered by the user, including key bits and corresponding geometric structures;
[0029] (3) Call the function MDS_ReadExtSettings() to read the additional encryption level configuration of the key. If there is no additional encryption level configuration, NULL will be returned; the additional confidentiality level configuration of the key includes the configuration of the key rotation angle and micro determinants information;
[0030] (4) Call the function MDS_CreateMDSPassword() to create a multi-dimensional key according to the key ...
Embodiment 2
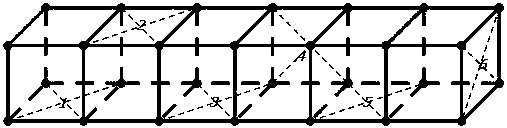
[0033] as attached figure 1 As shown, the same group of 6-digit keys can be projected onto different surfaces of the spatial geometry in the multi-dimensional space, and these spatial geometric correspondences can reduce the complexity of the original 6-digit key Upgrade to the security level of 26-bit key, which greatly increases the difficulty of cracking (the cracking time of 26-bit pure digital key is about 7920000000 years).
[0034] The formula for calculating the complexity increase: v = 2*k+(k-1)*(n-2), where v is the number of keys after the complexity increase, k is the number of non-contact surfaces of the spatial geometry, and n is the number of geometry .
[0035] The above process of increasing the number of digits of the key will not greatly increase the difficulty of memory for the user. The user only needs to assign different digits to the corresponding geometric surface on the basis of setting the traditional 6-digit key to complete the key upgrade process. ...
Embodiment 3
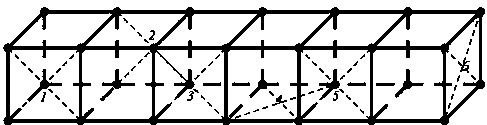
[0037] When the level of the key in Embodiment 2 still cannot meet the requirements, in addition to increasing the original length of the key, the security factor of the key can be further greatly improved by determining the level of the cluster determined by the surface identification of the key. Set the unlocking process of the key to 90° to the left for authentication, and the level of the surface identification determinant is determined by the number of bits of the binary data that constitutes the surface of the geometry, as shown in the attached figure 2 As shown, because the keys to be stored are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 respectively, the number of bits constituting the fixed point of the geometry can adopt the default value of 2, so the length of each number of bits on the surface of the geometry is 8, that is Arbitrary values in ASCII encoding can be stored.
[0038] When the ASCII digit length cannot meet the requirements of the security level, more digit information can b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com