A method for preparing electrode active materials of lead-acid batteries in pairs by electrochemical method
A technology for electrode active materials and lead-acid batteries, applied in battery electrodes, lead-acid batteries, battery recycling, etc., to achieve the effects of simplifying operating units, improving product quality, and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
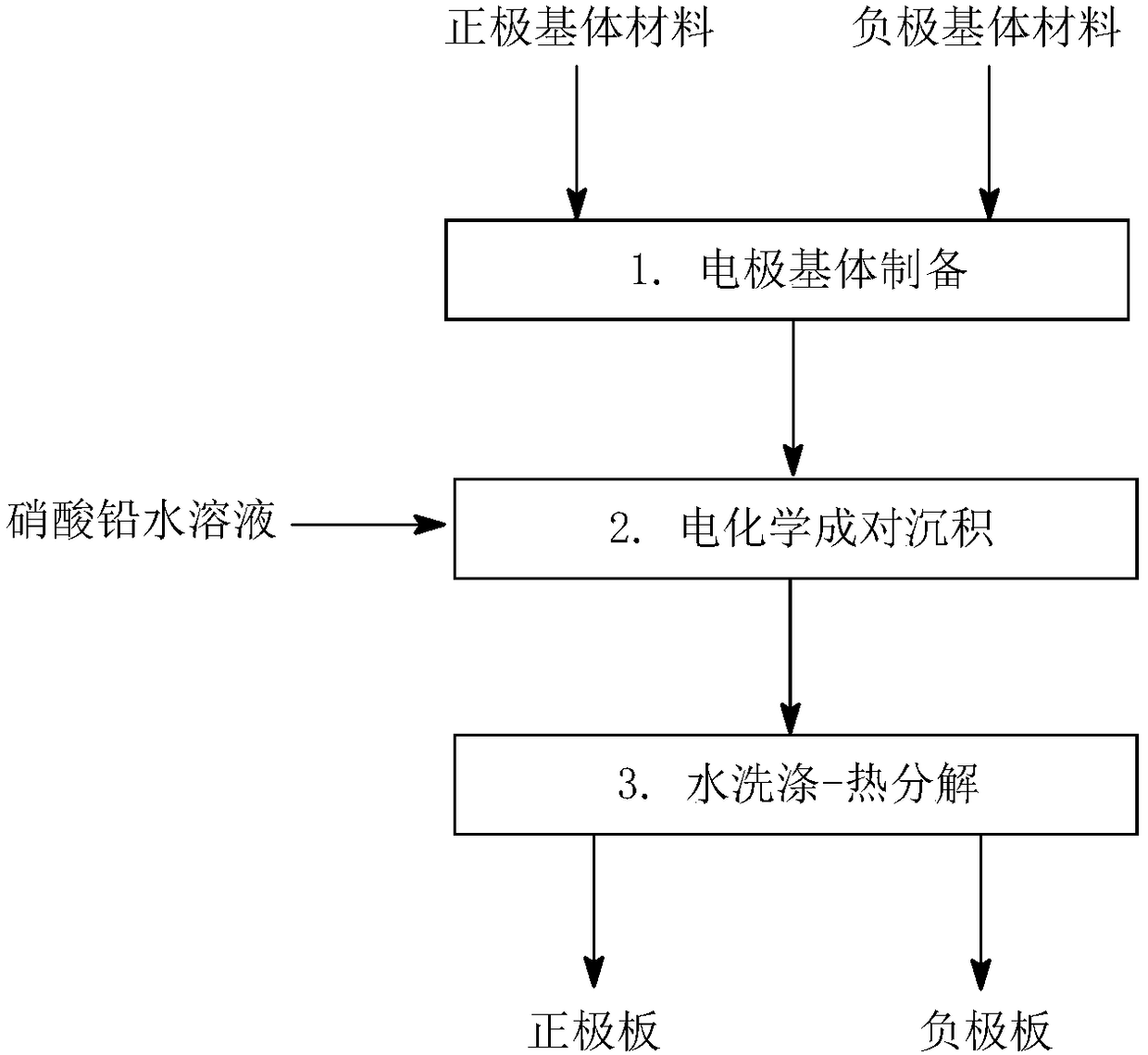
[0046] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for preparing the active material of the lead battery electrode in pairs by an electrochemical method, that is, the method in which the lead ion in the aqueous solution undergoes electrochemical oxidation and reduction reactions at the anode and the cathode to prepare the positive and negative active materials of the lead battery. In particular, a kind of lead nitrate obtained by leaching lead monoxide with nitric acid from the lead paste of waste lead storage battery is used as raw material, and the Pb in the aqueous solution is made 2+ Oxidation reaction occurs at the anode to obtain lead dioxide, which is used as the positive electrode active material of the lead storage battery; Pb 2+ A reduction reaction occurs at the cathode to obtain metallic lead, which is used as the negative electrode active material of the lead storage battery; the nitric acid in the electrolyte is regenerated, and is recycled as a leaching agent for dissol...
Embodiment 2
[0051] (1) Electrode substrate preparation: mechanically grind the netted titanium substrate, degrease the surface in aqueous hydroxide solution, etch in oxalic acid solution, and wash with water to obtain a surface-treated titanium substrate; use the obtained titanium metal as an electrode matrix, made of SnCl 4 , SbCl 3 , citric acid, and ethylene glycol to form a precursor, wherein the molar ratio of ethylene glycol to citric acid is 2.0:1. The molar ratio of Sn to ethylene glycol in the precursor is 1.0:6.0, and the total molar ratio of Sb to ethylene glycol is 1.0:24.0. The precursor solution is coated on the obtained electrode substrate by the coating method. In the thermal decomposition equipment, the obtained titanium substrate is dried at 100 ° C, and then roasted at 520 ° C. The coating-drying roasting operation is repeated 20 times. The obtained titanium substrate electrodes with metal oxides on the surface are respectively used as the anode and cathode for the ne...
Embodiment 3
[0055] (1) Electrode matrix preparation: positive and negative matrix electrodes were prepared respectively.
[0056] The plate-shaped metal titanium substrate is mechanically polished, the surface is degreased in an aqueous solution of hydroxide and carbonate, etched in an oxalic acid solution, and a surface-treated titanium substrate is obtained by washing with water; the obtained metal titanium substrate is used as an electrode substrate, by SnCl 4 , SbCl 3 , PbCl 2 , citric acid, and ethylene glycol to form a precursor, wherein the molar ratio of ethylene glycol to citric acid is 6.0:1, the molar ratio of Sn to ethylene glycol in the precursor is 1.0:24.0, and SbCl 3 and PbCl 2 The ratio to ethylene glycol is 1.0:24.0 respectively, and the precursor of the intermediate layer coating is coated on the obtained electrode substrate by the coating method; in the thermal decomposition equipment, the obtained titanium substrate electrode is dried at 50 °C, Baking treatment at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com