A method and device for replacing outer rotor motor bearings
An external rotor motor and bearing technology, which is applied in the direction of electromechanical devices, manufacturing motor generators, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of high labor intensity for bearing installation and replacement, difficult replacement of motor bearings, easy damage of end covers and cables, etc., to achieve Save resources and labor intensity, prevent the cable from being crushed, and the effect of smooth steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
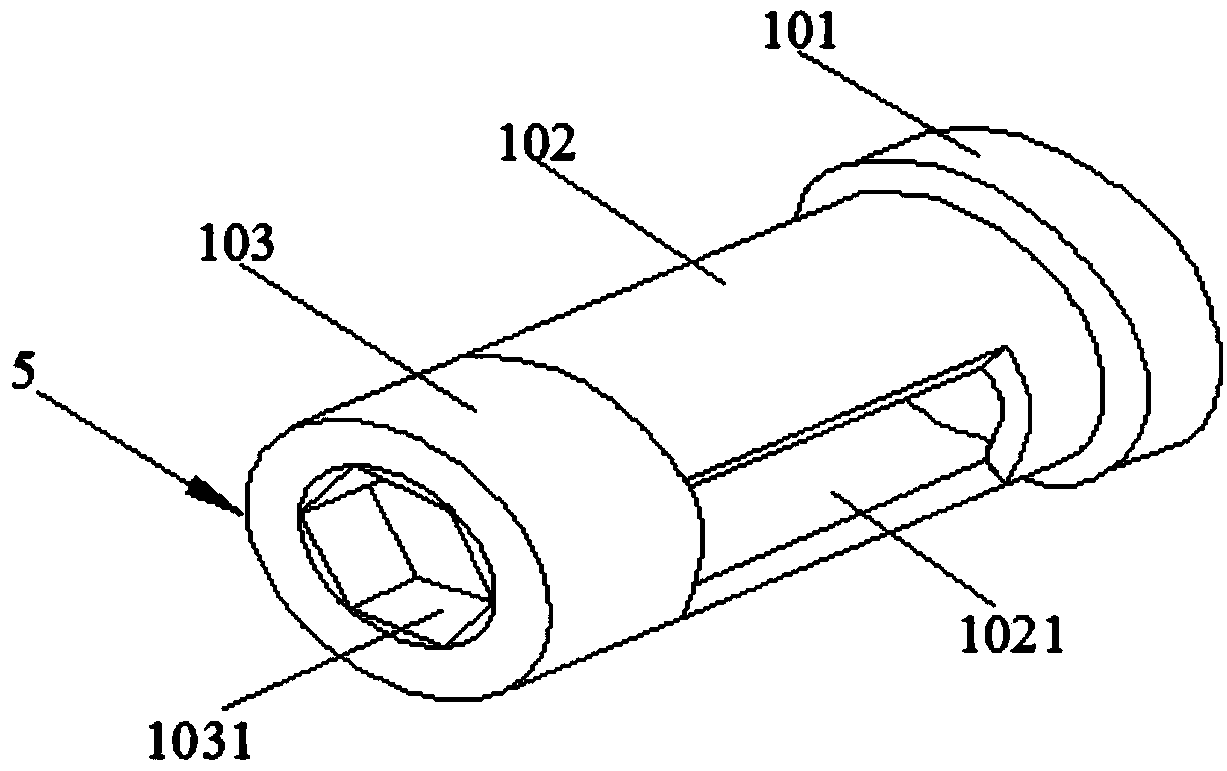
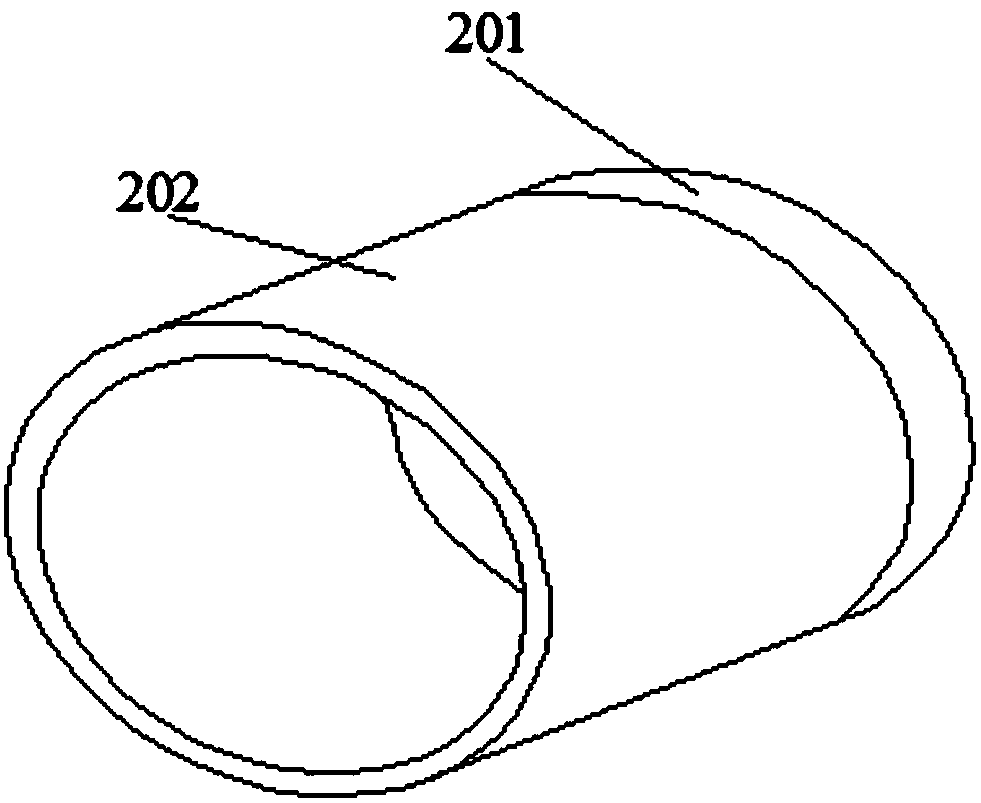
[0034] The outer rotor motor bearing of the present invention is a commercially available outer rotor motor bearing. The outer rotor motor bearing includes a first end cover, a second end cover, a stator, a rotor, an inner circlip and an outer circlip, and the two ends of the stator are connected to the first end respectively. The cover is connected with the second end cover, the first end cover is provided with a bearing chamber, the rotor is placed in the stator, the rotor includes cables and bearings, the cables are placed in the bearings, the rotor at the cable end penetrates into the stator, the cables pass through the bearing chamber, and the bearings There is an oil protection cover in the room, and the inner and outer retaining springs fix the oil protection cover.
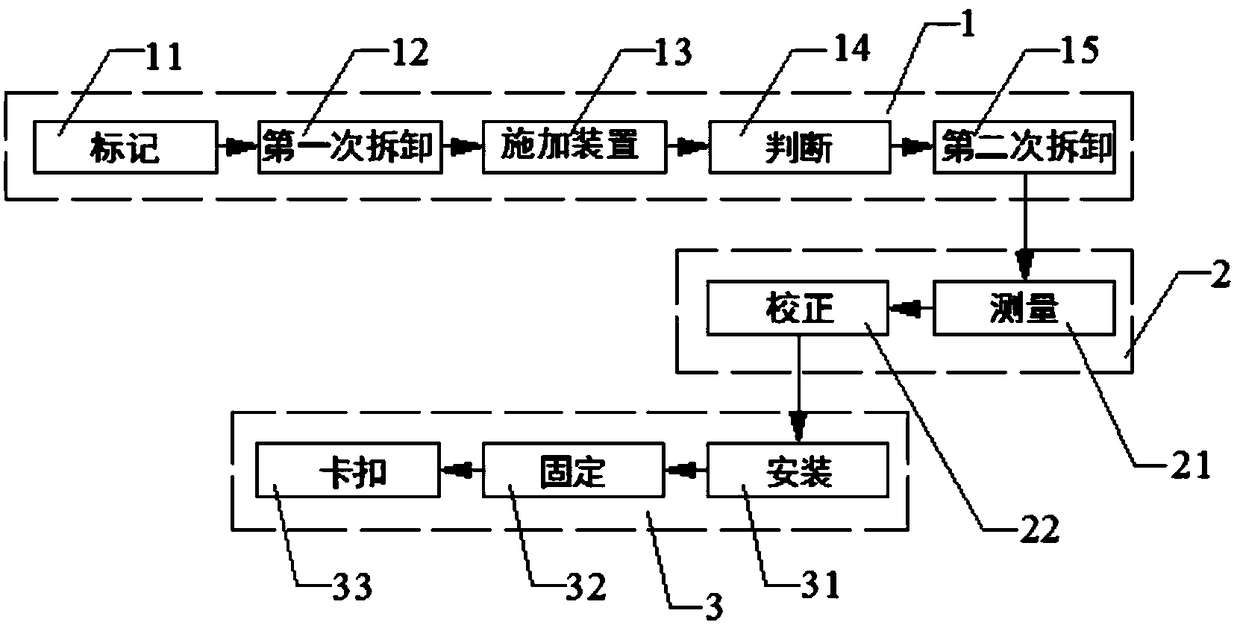
[0035] Such as Figures 1 to 4 As shown, a method for replacing bearings of an outer rotor motor includes disassembly, detection and assembly, wherein the disassembly steps include:
[0036] Marking: Mark...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the detection step includes:
[0054] Measurement: use the end cap depth gauge to measure the depth from the notch plane of the end cap to the plane of the bearing chamber; correction, when the bearing chamber is worn, perform turning correction or replacement on the lathe, otherwise, turning correction is not required.
Embodiment 3
[0056] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the assembling steps include: assembling the rotor, assembling the rotor into the first end cover; assembling the stator, assembling the stator outside the rotor; assembling the second end cover, aligning the second end cover The seam of the cover and the seam of the stator are pressed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com