Adaptive mixed data lossless compression method
A data lossless and compression method technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, code conversion, etc., can solve the problems of reducing compression performance and occupying bits, and achieve the effect of improving compression efficiency, high compression rate and strong flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
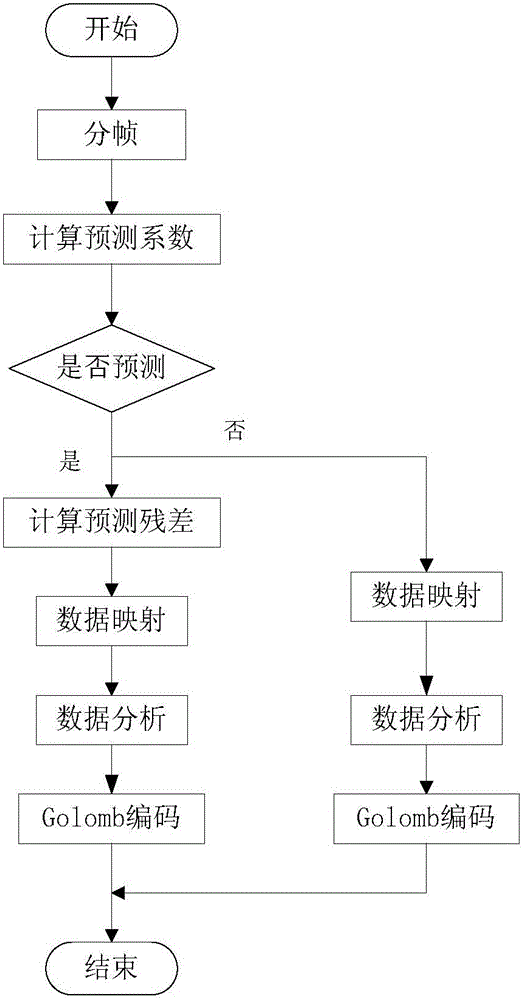
[0077] see figure 1 , the adaptive hybrid data lossless compression method described in a preferred embodiment of the present invention, comprising:
[0078] S1 divides the input data to be encoded into frames. Framing is a method that divides a series of input data streams to be encoded into frames, which is convenient for processing the data to be encoded, speeding up the processor, and providing editability by framing, which is most digital signal compression. An important and necessary feature of an algorithm.
[0079] S2 respectively calculates the prediction coefficients of each frame of data to be encoded.
[0080] S3 judges whether the data to be encoded of each frame needs to be linearly predicted according to the prediction coefficient.
[0081] If the data to be encoded in this frame needs to be linearly predicted, then
[0082] S3.11 Calculate the prediction residual.
[0083] S3.12 Map the data to be coded for each frame to be coded.
[0084] S3.13 Analyze t...
Embodiment 2
[0094] In the adaptive mixed data lossless compression method described in this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1, S2 uses the Levinson-Durbin Levinson-Durbin algorithm to calculate the linear prediction coefficient a of each frame of data to be encoded ii , including:
[0095] The Yule-Walker equation for p-order linear prediction is as follows:
[0096]
[0097] in, is the autocorrelation coefficient;
[0098] There are p+1 equations in the Yule-Walker equation,
[0099] When k=0,1,2,...,p When known, solve a pk [k=1, 2, . . . , p] and Sample p+1 unknowns, where a pk predictive coefficient, is the minimum error power;
[0100] Autocorrelation Coefficient in Yule-Walker Equation for Linear Prediction Calculating the minimum forecast error power of the second-order forecast based on the Levinson-Durbin algorithm
[0101] The recursive formula of Levinson-Durbin algorithm is
[0102]
[0103] where [k=1, 2, . . . , p];
[0104] For two-stage pred...
Embodiment 3
[0139] The adaptive mixed data lossless compression method described in this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1, also includes a decoding step, such as figure 2 As shown, the decoding step specifically includes:
[0140] S1 extracts the flag bit of each frame coded stream.
[0141] S2 judges whether the encoded stream of each frame is linearly predicted during the encoding process,
[0142] If linear prediction is performed, then
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com