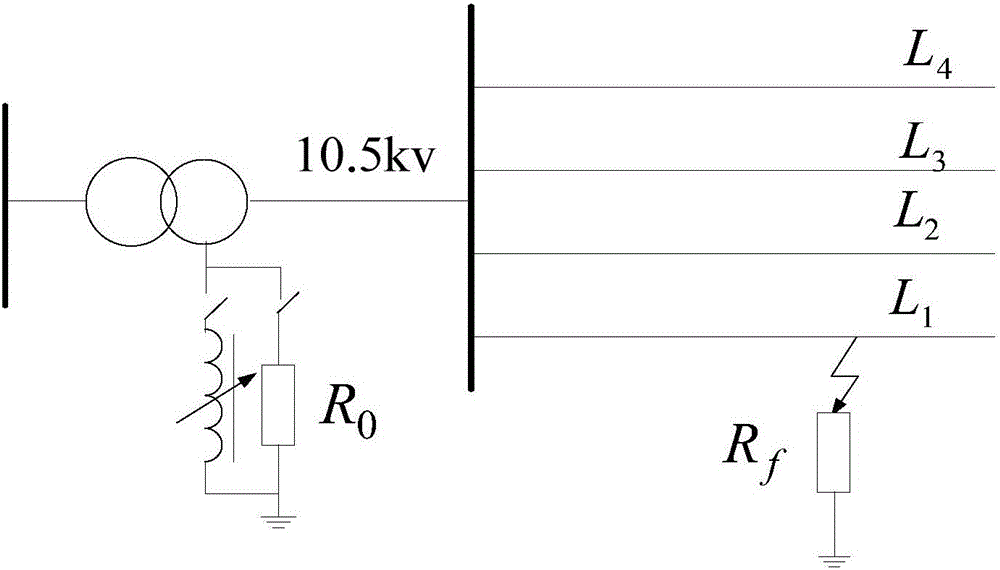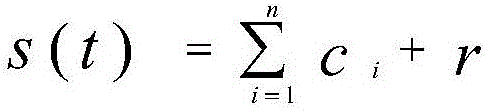Ground fault line selection method based on high-frequency component correlation
A technology for high-frequency components and ground faults, which is applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring devices, and measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient analysis of fault transient characteristics, lack of adaptability of wavelet analysis, lack of comprehensive analysis, etc., to achieve Easy to implement, strong practicability, and the effect of eliminating power frequency components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
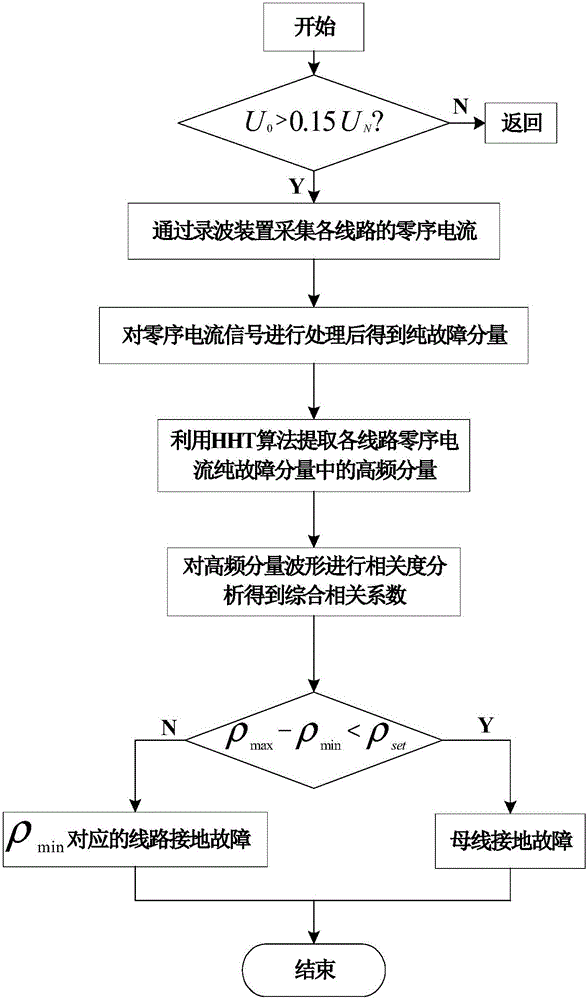
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, the ground fault line selection method based on high-frequency component correlation of the present invention, its steps are:
[0036] S1: Real-time monitoring of the zero-sequence voltage value at the outlet of the distribution line; if the zero-sequence voltage value is greater than the limit value, it is determined that a ground fault has occurred in the distribution network, and the zero-sequence current of each line is collected through the FTU; the zero-sequence voltage mutation moment is a fault the moment of occurrence;
[0037] S2: After denoising the zero-sequence current of each line, the pure fault component is obtained;
[0038] S3: Perform EMD decomposition on pure fault components to obtain various transient frequency components IMF1, IMF2, ..., and then through instantaneous frequenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com