Obstacle avoidance method for soft landing of object outside earth under multi-obstacle constraint environment
A technology for obstacles and celestial bodies, applied in the field of optimal guidance for obstacle avoidance in a multi-obstacle constrained environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
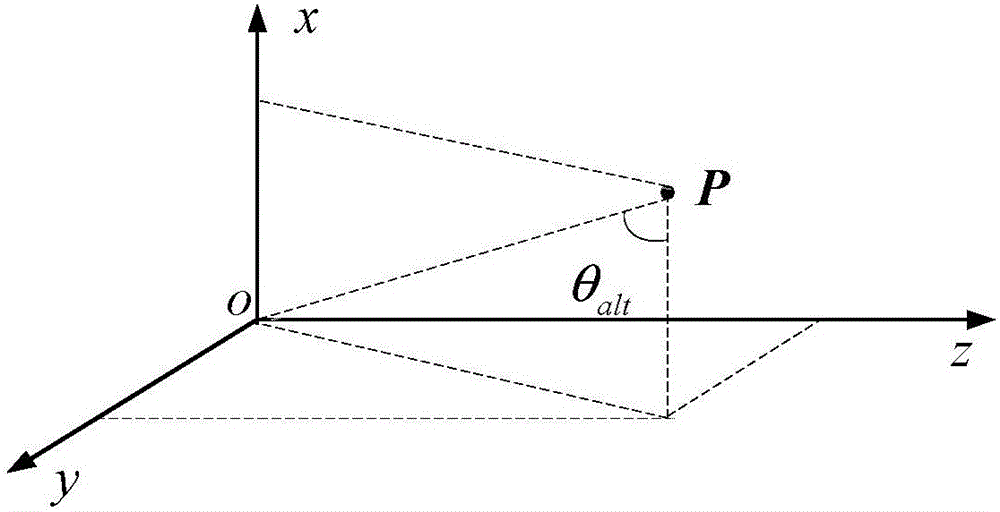
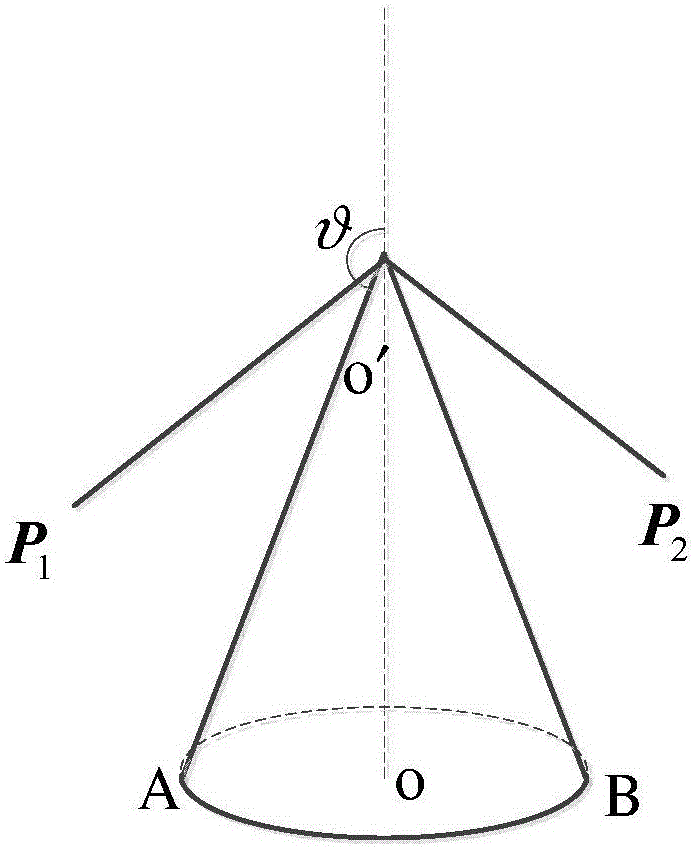
[0078] Specific implementation one: as Figures 2 to 4 As shown, the implementation process of an obstacle avoidance method for an extraterrestrial celestial body soft landing in a multi-obstacle constrained environment described in this embodiment is as follows:
[0079] Step 1. Analyze the convex obstacles on the surface of extraterrestrial celestial bodies and build a mathematical model of the convex obstacles;
[0080] Step 2, performing linear transformation on the mathematical model of the convex obstacle, and transforming the non-convex constraint into a convex constraint;
[0081] Step 3: Integrate the linearly transformed mathematical model of convex obstacles into the second-order cone programming problem, and establish a complete optimal second-order cone programming model considering obstacle constraints;
[0082] Step 4: Using a complete optimal second-order cone programming model considering obstacle constraints to achieve optimal obstacle avoidance under the mu...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0083] Specific embodiment 2: In this embodiment, the convex obstacles on the surface of extraterrestrial celestial bodies described in step 1 are analyzed and a mathematical model of convex obstacles is constructed. The specific process is:
[0084] Step 11. Raised obstacle model selection
[0085] The selected raised obstacle model generally conforms to the constrained outline and has the ability to describe most of the raised obstacles;
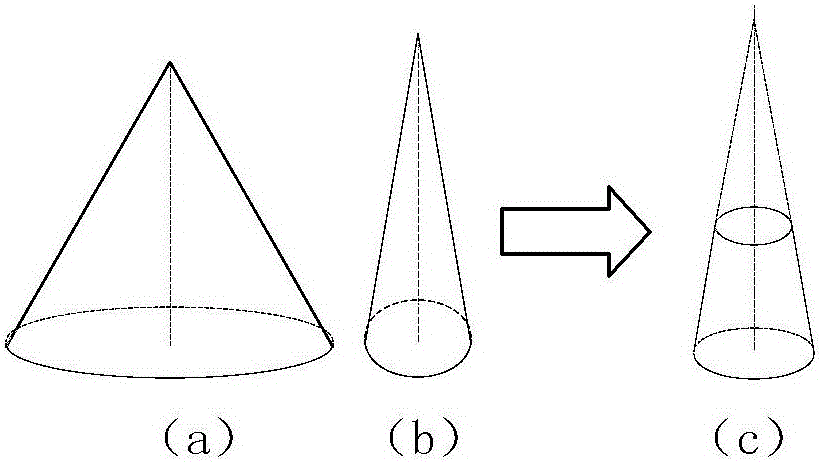
[0086] Using the convex optimization method to avoid obstacles, the selected 3D geometric model can be converted into convex constraints, and the convex obstacles on the lunar surface can be described as conical constraints;
[0087] By adjusting the height of the cone and the size of the half-apex angle, most of the convex obstacles on the lunar surface are approximately described, and it is universal to describe the convex obstacles as conical constraints;
[0088] Steps 1 and 2, Mathematical description of the raised obstacle model
...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0101] Specific implementation three: as Figures 2 to 4 As shown, in the second step of this embodiment, the mathematical model of the convex obstacle is linearly transformed, and the non-convex constraint is transformed into a convex constraint (the obstacle constraint convex transformation), and the specific process is:
[0102] Convex the non-convex obstacle constraint to transform the whole problem into a convex optimization problem, or more accurately, into a second-order cone programming problem;
[0103] The general idea of transforming the non-convex constraint shown in equation (8) into a convex constraint is to take the first-order Taylor expansion term for the norm constraint contained, so that the entire constraint becomes a linear constraint, because the linear constraint is a convex constraint. One, so the obstacle constraint is converted into a convex constraint;
[0104] To facilitate the solution, first write the vector in its component form:
[0105] P-H...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com