Mobile robot path planning and obstacle avoidance method and system
A mobile robot and path planning technology, applied in control/regulation systems, instruments, non-electric variable control, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitable local planning in dynamic environments and easy loss of target points, etc., to improve path search efficiency and storage space Small, realize the effect of autonomous navigation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
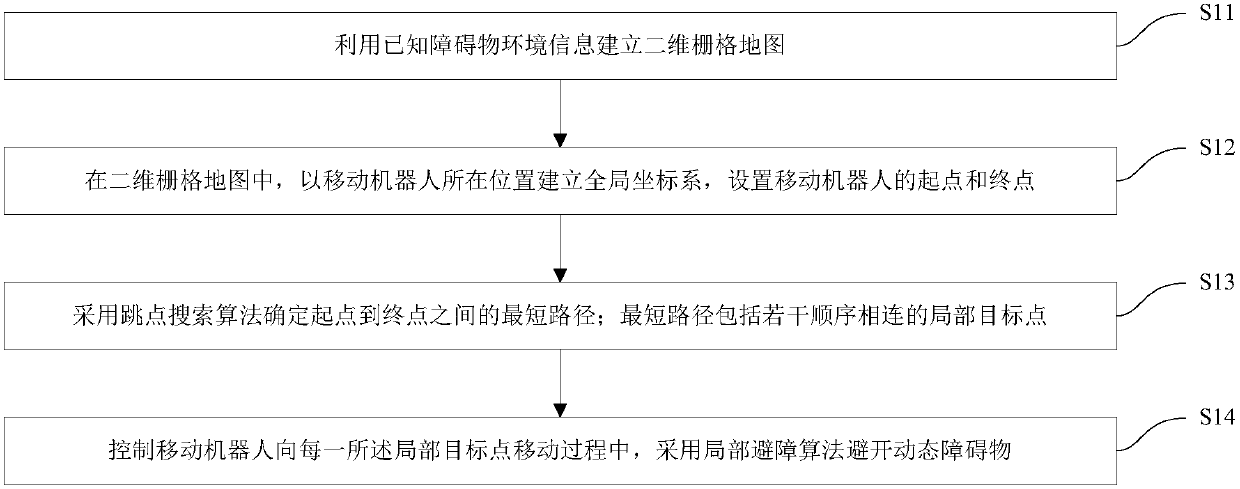
[0061] figure 1 The path planning and obstacle avoidance methods of the mobile robot in this embodiment are shown. Such as figure 1 As shown, the mobile robot path planning and obstacle avoidance method includes the following steps:
[0062] S11: Create a two-dimensional grid map using known obstacle environment information. In this embodiment, a two-dimensional array is used to store the existing obstacle environment information, and a two-dimensional grid map is established. In the two-dimensional grid map, 1 represents an obstacle grid with obstacles, and 0 represents a freedom without obstacles. grid. Wherein, the two-dimensional grid map may be pre-input manually. Understandably, it can also be combined with mapping and positioning technology to establish a two-dimensional grid map through slam (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, real-time positioning and map construction), and set the position that the mobile robot has passed to 0, and the position that has not p...
Embodiment 2
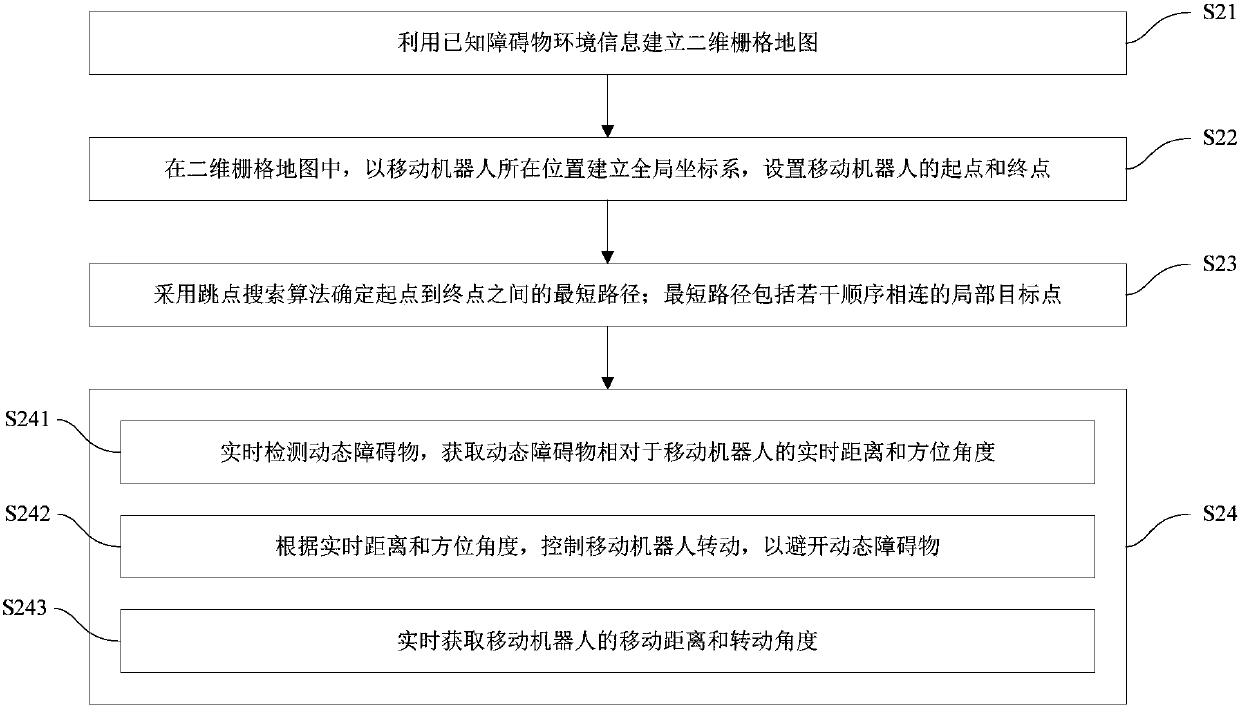
[0068] figure 2 The path planning and obstacle avoidance methods of the mobile robot in this embodiment are shown. Such as figure 2 As shown, the mobile robot path planning and obstacle avoidance method includes the following steps:
[0069] S21: Create a two-dimensional grid map by using known obstacle environment information. In this embodiment, a two-dimensional array is used to store the obstacle environment information and establish a two-dimensional grid map. In the two-dimensional grid map, 1 indicates an obstacle grid with obstacles, and 0 indicates a free grid without obstacles. grid. Wherein, the two-dimensional grid map may be pre-input manually. Understandably, it can also be combined with mapping and positioning technology to establish a two-dimensional grid map through slam (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, real-time positioning and map construction), and set the position that the mobile robot has passed to 0, and the position that has not passed The...
Embodiment 3
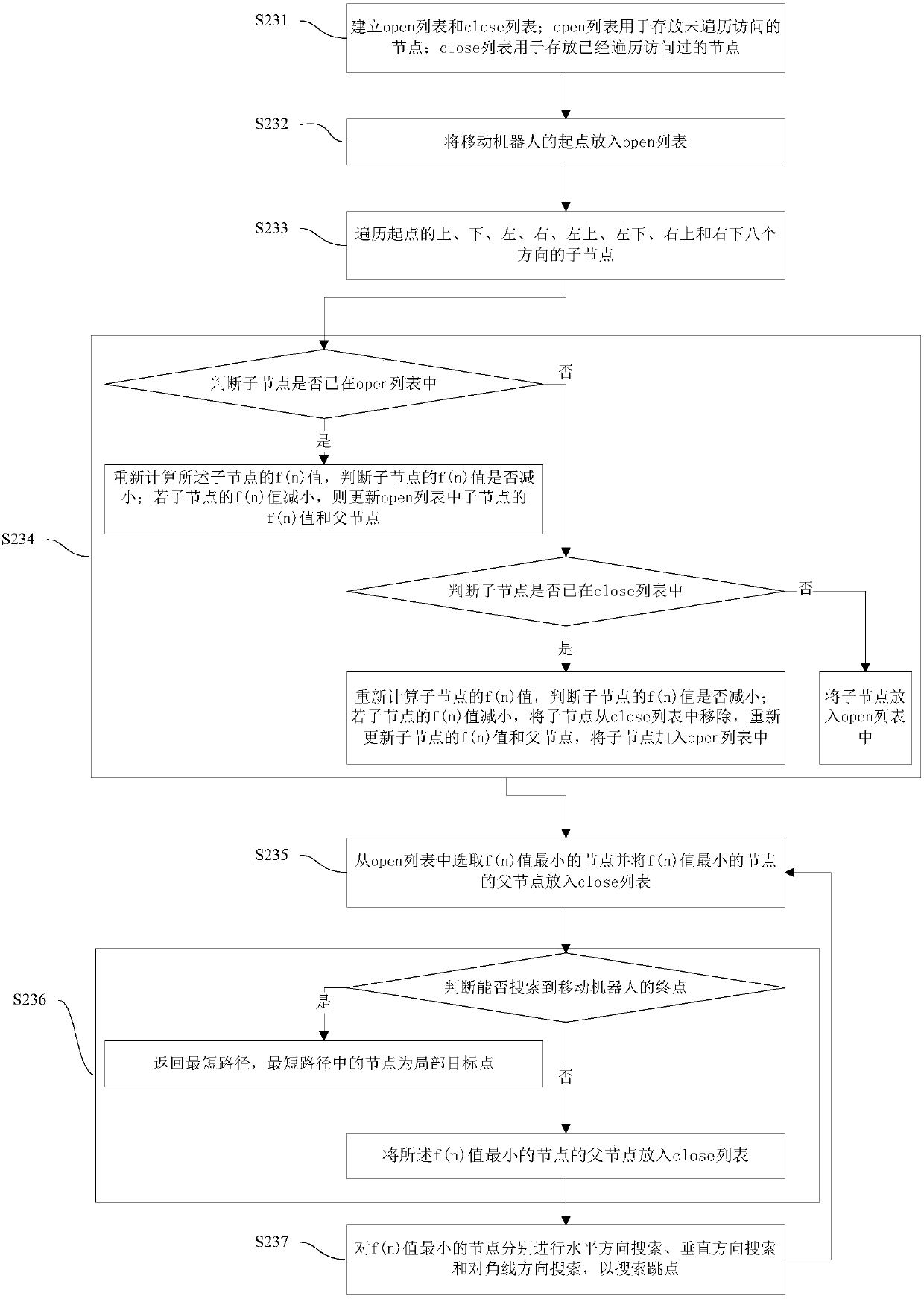
[0099] Figure 8 The path planning and obstacle avoidance system of the mobile robot in this embodiment is shown. Such as Figure 8 As shown, the mobile robot path planning and obstacle avoidance system includes:
[0100] Map building unit 10: used to create a two-dimensional grid map using known obstacle environment information. In this embodiment, a two-dimensional array is used to store the existing obstacle environment information, and a two-dimensional grid map is established. In the two-dimensional grid map, 1 represents an obstacle grid with obstacles, and 0 represents a freedom without obstacles. grid. Wherein, the two-dimensional grid map may be pre-input manually. Understandably, it can also be combined with mapping and positioning technology to establish a two-dimensional grid map through slam (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, real-time positioning and map construction), and set the position that the mobile robot has passed to 0, and the position that has ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com