The preparation method of edible magnesium chloride
A technology of magnesium chloride and potassium chloride, which is applied in the field of food chemistry, can solve problems such as the destruction of the ecological environment of salt lakes, the waste of magnesium resources, and the impurity content of products is easy to exceed the standard, and achieves the effect of easy operation and preparation and loose control conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] This embodiment discloses a preparation method of edible magnesium chloride, specifically refer to the following steps:
[0019] In step 1, take 100mL of secondary water as dissolved water, place 300g of solid ore in it and stir, and filter when the dissolution-precipitation equilibrium is reached to obtain the first filter residue and the first filtrate, and use the first filtrate as the first mother liquor for primary evaporation.
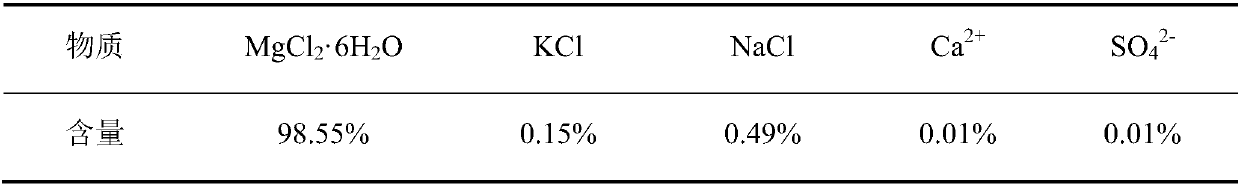
[0020] In this embodiment, the solid ore is a by-product bischofite in the salt lake, which is derived from the Chaerhan Salt Lake; obtained simultaneously in the process.
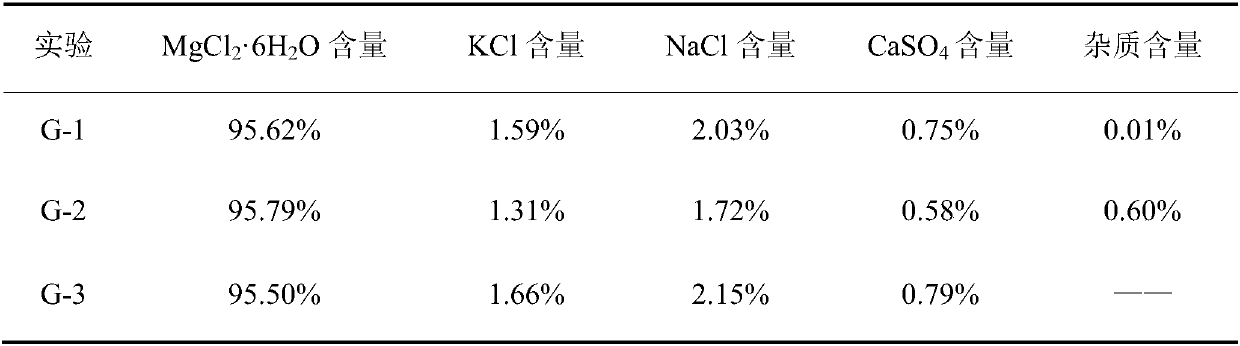
[0021] Specifically, the component analysis of the solid ore was carried out. In this embodiment, three parallel experiments were carried out for testing, which were recorded as G-1 to G-3 respectively; the analysis results are shown in Table 1.
[0022] Table 1 Full analysis results of solid ore components (in mass percent)
[0023]
[0024] Note: In Table 1, "—...
Embodiment 2
[0043] In the description of Embodiment 2, the similarities with Embodiment 1 will not be repeated here, and only the differences with Embodiment 1 will be described. The difference between Example 2 and Example 1 is that in step 1, 100mL of secondary water is taken as dissolved water, 350g of solid ore is placed in it and stirred, and filtered when the dissolution-precipitation equilibrium is reached to obtain the first Filter residue and the first filtrate, take the first filtrate as the first mother liquor; the quality of the obtained first mother liquor is 388.56g; the content analysis results of the main ions of the first mother liquor of this embodiment are shown in Table 4.
[0044] Table 4 Analysis results of main ions in the first mother liquor (in mass percent)
[0045]
[0046] In the first mother liquor, in addition to the above-mentioned ions, the rest are H 2 O.
[0047] In step 2, the mass of water lost through evaporation from the first mother liquor is 17...
Embodiment 3
[0054] In the description of Embodiment 3, the similarities with Embodiment 1 will not be repeated here, and only the differences with Embodiment 1 will be described. The difference between Example 3 and Example 1 is that in step 1, 100mL of secondary water is taken as dissolved water, 500g of solid ore is placed in it and stirred, and filtered when the dissolution-precipitation equilibrium is reached to obtain the first For the filter residue and the first filtrate, take the first filtrate as the first mother liquor; the quality of the obtained first mother liquor is 390.03g; the content analysis results of the main ions of the first mother liquor of this embodiment are shown in Table 6.
[0055] Table 6 Analysis results of main ions in the first mother liquor (in mass percent)
[0056]
[0057] In the first mother liquor, in addition to the above-mentioned ions, the rest are H 2 O.
[0058] In step 2, the mass of water lost through evaporation from the first mother liqu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com