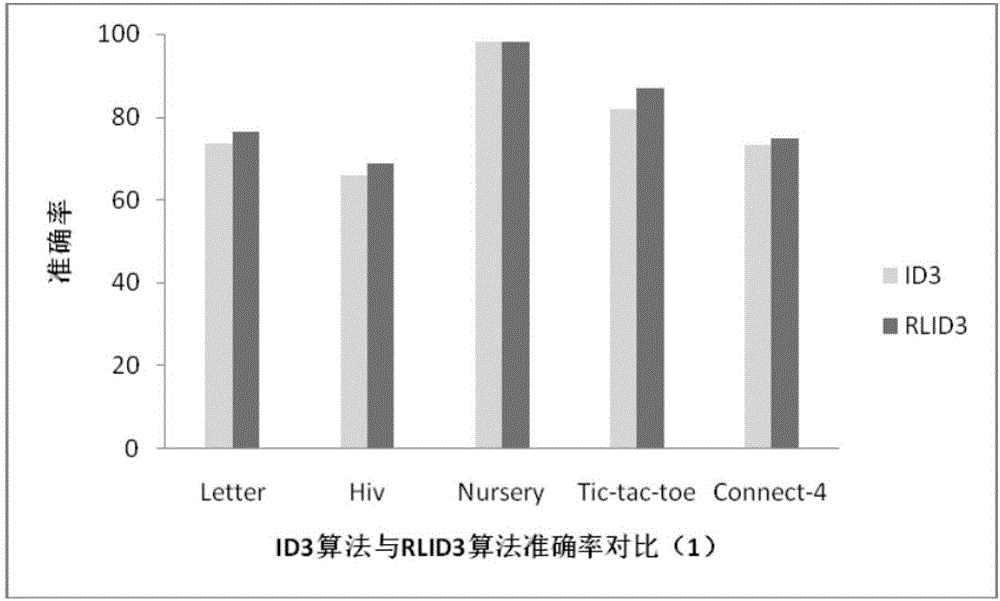
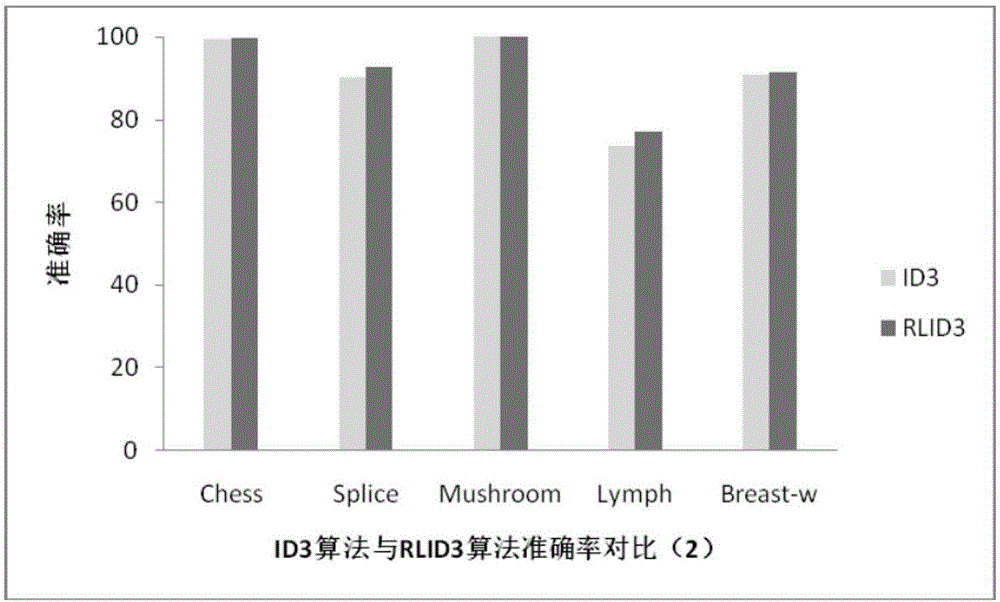
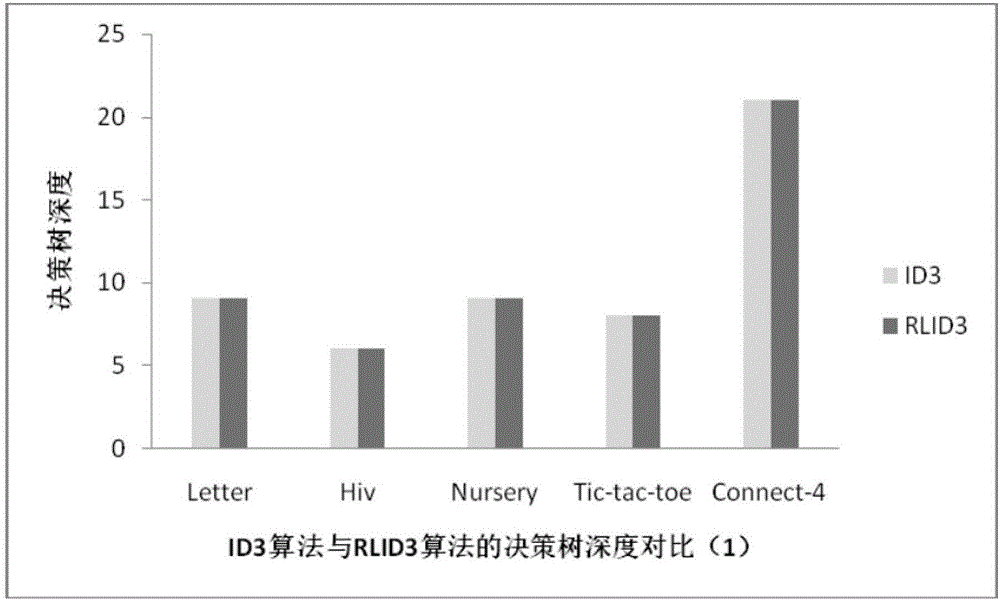
RLID3 data classification method based on decision tree optimization rate
A data classification and decision tree technology, applied in the direction of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer parts, etc., can solve the problem of low accuracy of decision tree data classification, and achieve the effect of simplifying the structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0053] Specific implementation mode one: a kind of RLID3 data classification method based on the decision tree optimization rate of the present embodiment is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
[0054] Step 1: Optimizing the information gain to obtain the optimization rate of the decision tree, the formula is as follows:
[0055] D T O R ( S , A ) = G a i n ( S , A ) L e a f N u m ( S , A ) - - ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0058] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: in the step one, the information gain is optimized to obtain the decision tree optimization rate; the specific process is:
[0059] The formula for calculating information gain is as follows:
[0060] Gain(S,A)=Entropy(S)-Entropy(S,A) (4)
[0061] In the formula, Gain(S,A) represents the information gain of attribute A on the training set S, Entropy(S) represents the information entropy of training set S, Entropy(S,A) represents the information entropy of attribute A, A is the attribute, S is the training set;
[0062] In the ID3 algorithm, information entropy can be understood as uncertainty. If Entropy(S) is understood as the uncertainty on the training set S, Entropy(S,A) is understood as the uncertainty of the A attribute on the training set S, and their difference represents the selection of the A attribute. , the reduction in uncertainty. ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0073] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is: the RLID3 algorithm is obtained based on the decision tree optimization rate in the said step two; the specific process is:
[0074] 2.1 RLID3 Algorithm
[0075] The category attribute refers to the attribute used to identify the category of the sample in the data set.
[0076] Non-category attributes refer to the attributes used to identify a certain aspect of the sample in the data set.
[0077] For example: In Table 1, outlook and humidity represent non-category attributes, and play represents category attributes. Examples of data sets are shown in Table 1.
[0078] Table 1 Data Set Example
[0079]
[0080] With the theoretical basis of the previous section, the proposed
[0081] The RLID3 algorithm is shown below.
[0082] Algorithm 1: makeRLID3Tree (training set)
[0083] Input the training set S, and output the decision tree...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com