MTOR-independent activator of TFEB for autophagy enhancement and uses thereof
A free and neurodegenerative technology, applied in the direction of active ingredients of ketones, nervous system diseases, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problems of poor blood-brain barrier penetration and achieve the elimination of MTOR-related complications, wide application fields, The effect of simple chemical structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0092] In the following examples, the following materials were used; various commercial sources of the materials are provided. Details of the various schemes are also set forth below:
[0093] Reagents and Antibodies
[0094]Test samples of monocarbonyl analogues of curcumin were kindly provided by Dr. Bo Zhou (Lanzhou University, China). Compound C1 ((1E,4E)-1,5-bis(2-methoxy-phenyl)pent-1,4-dien-3-one) was synthesized from 2-methoxybenzene in a single-step reaction Synthetic formaldehyde. The structure and purity of the compound were confirmed by 1H NMR and HPLC. Curcumin (08511), chloroquine (C6628), doxycycline (D9891), and anti-Flag M2 antibody (F1804) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Torin1(2273-5) was purchased from BioVision Company. Anti-phospho-AKT (ser473) antibody (9271), anti-AKT antibody (9272), anti-phospho-MTOR (Ser2448) antibody (2971), anti-MTOR antibody (2983), anti-phospho-P70S6K / RPS6KB1 (Thr389) antibody (9234 ), anti-P70S6K / RPS6KB1 antibody (9202)...
Embodiment I
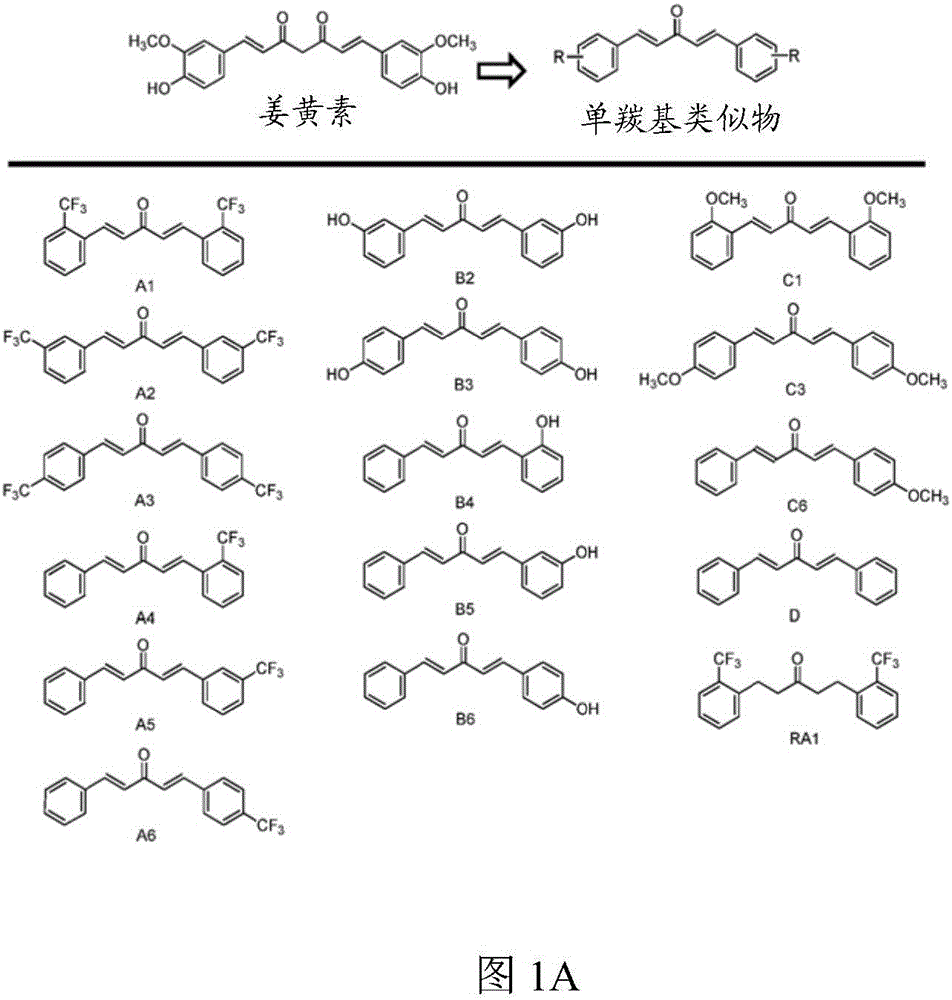
[0115] Novel autophagy enhancers identified from monocarbonyl analogs of curcumin.
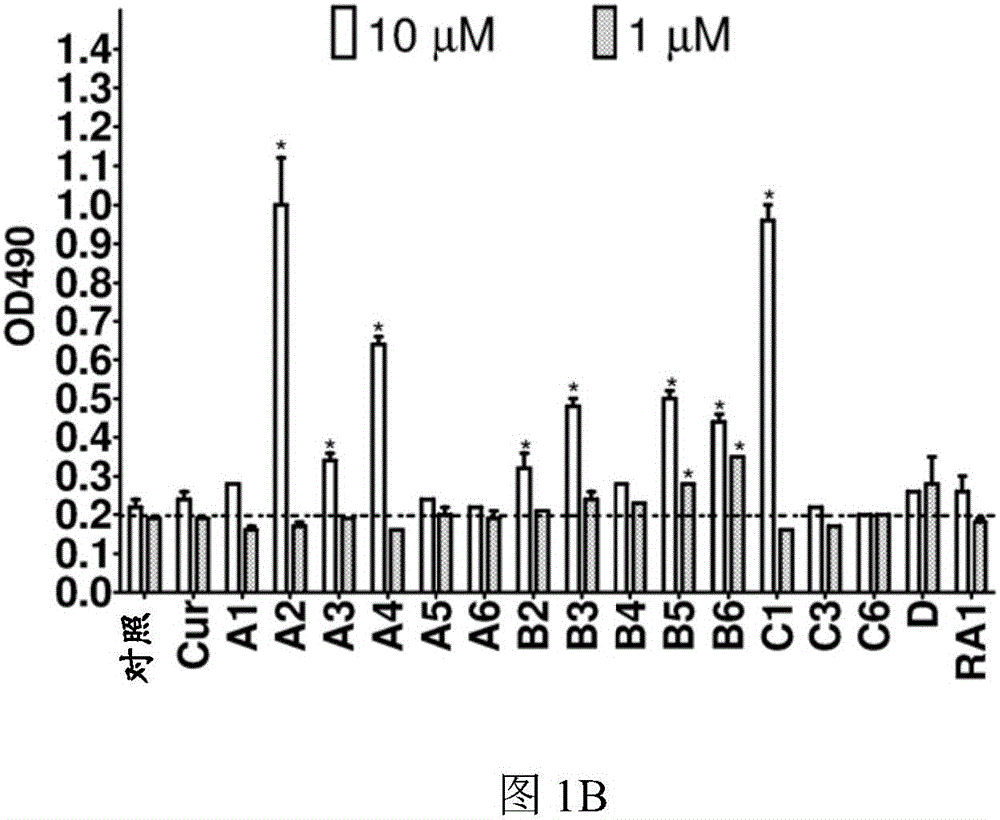
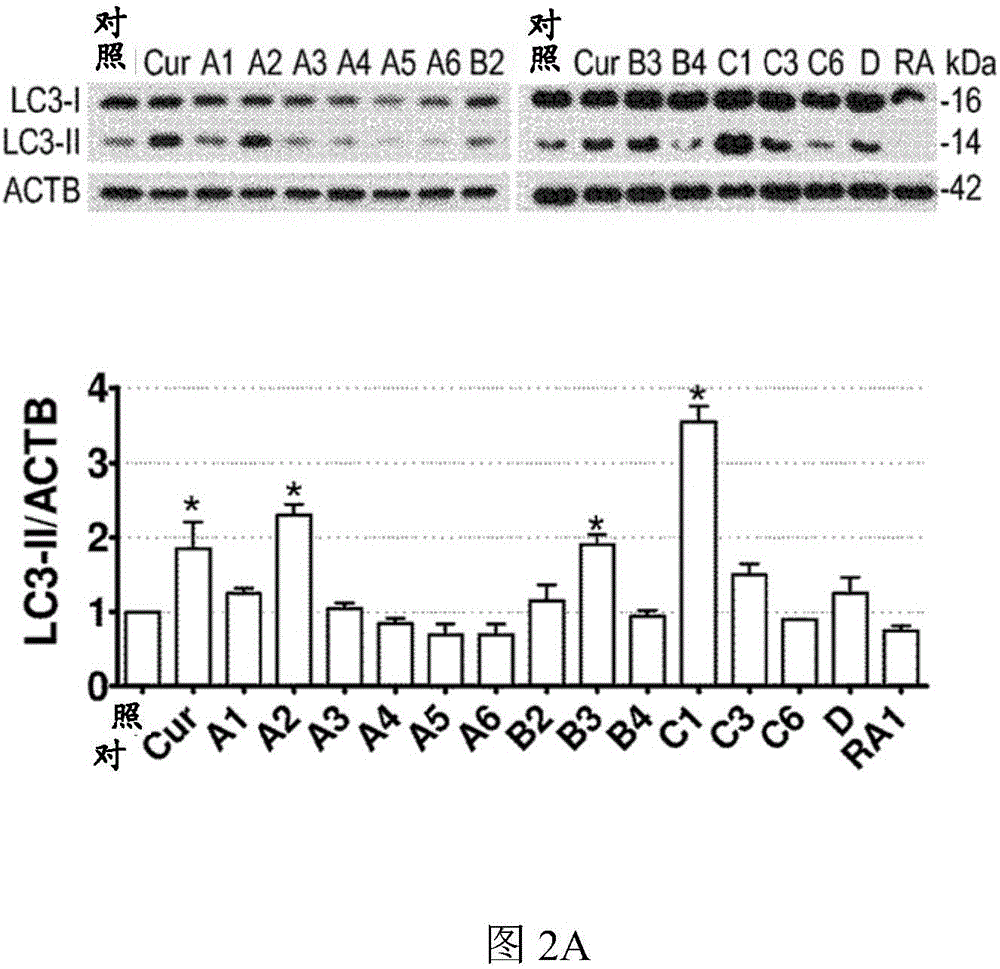
[0116] First, the inventors of the present application measured by LDH ( figure 1 B) tested the test compound (such as figure 1 Shown in A) Cytotoxicity at 1 μM and 10 μM over 24 hours and subsequently using a concentration of 1 μM. Compared with vehicle control (0.1% DMSO), curcumin (10 μM) and analogs A2, B3 and C1 (1 μM) significantly increased the level of microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3B (LC3B)-II in N2a cells ( figure 2 A). In the presence of the lysosomal inhibitor chloroquine (CQ), these analogs further increased LC3-II levels compared to CQ treatment alone ( figure 2 B). Furthermore, when the expression of autophagy-related gene 5 (Atg5) was interfered with by siRNA, these compounds could not increase the level of LC3-II ( figure 2 C). The data indicate that curcumin analogs A2, B3 and C1 enhance autophagy rather than prevent lysosomal degradation.
Embodiment II
[0118] Effects of curcumin analogues on the MTOR pathway
[0119] Since curcumin enhances autophagy via inhibition of the MTOR pathway, the effects of the three newly identified autophagy enhancers of the present invention on the MTOR pathway were confirmed. Similar to curcumin, A2 and B3 inhibited the phosphorylation of RPS6KB1 / p70S6K, MTOR and AKT ( image 3 A and image 3 B). Torin1, a potent MTOR inhibitor, was used as a positive control. C1 significantly promoted the phosphorylation of RPS6KB1, MTOR and AKT ( image 3 A and image 3 B).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com