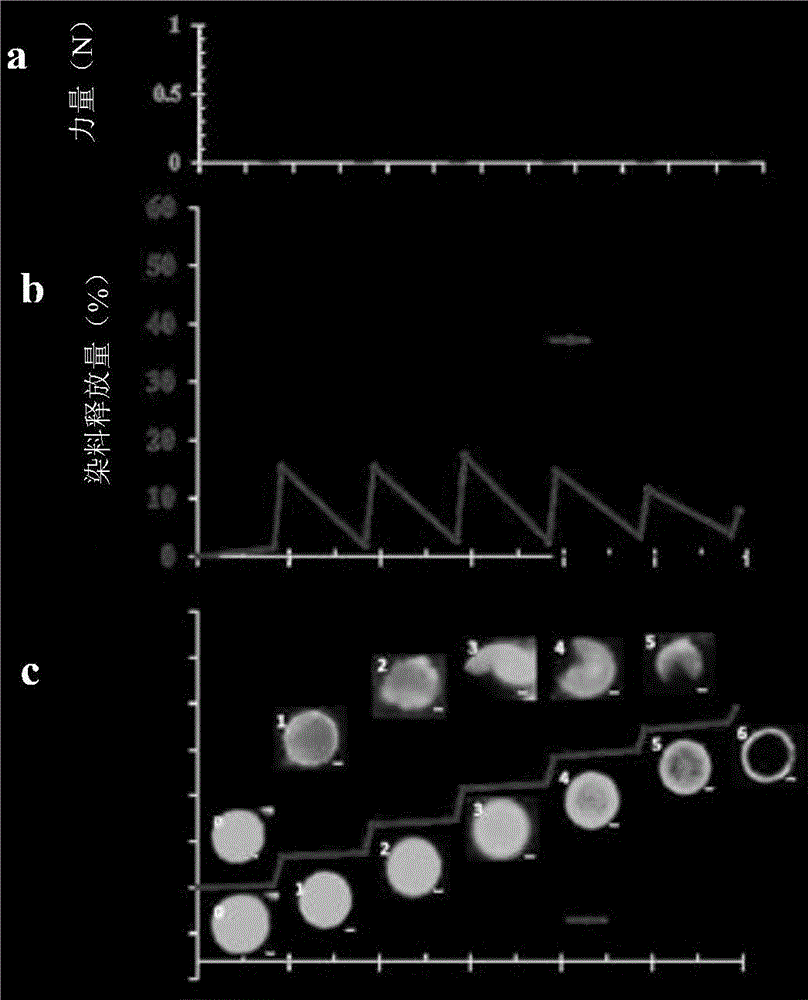
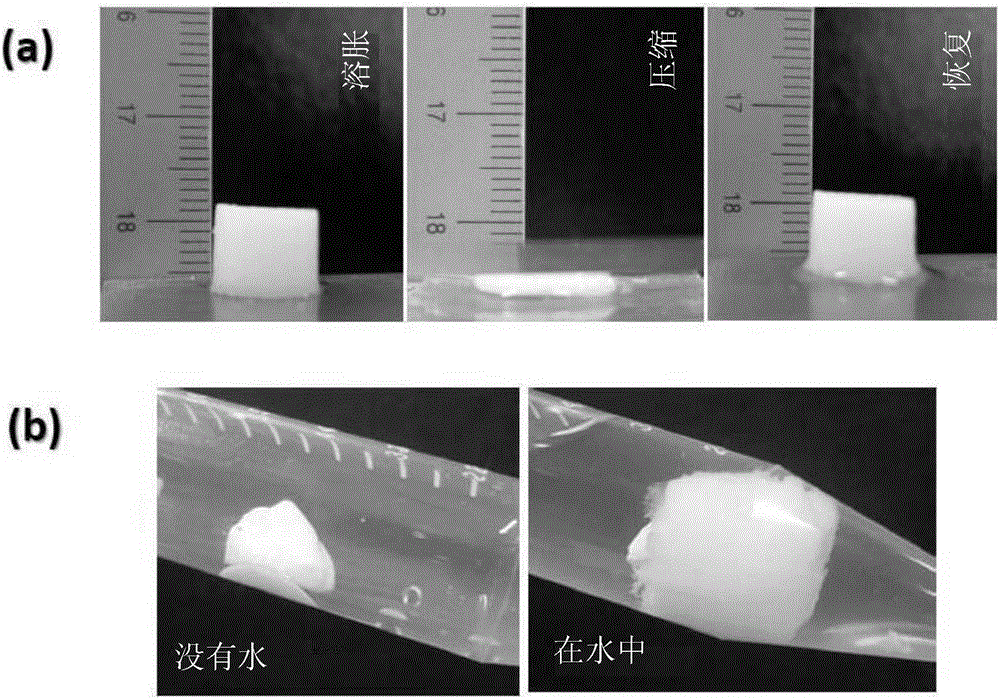
Hybrid hollow microcapsule, scaffold for soft tissue including same, and methods of preparing same
A microcapsule and hollow technology, applied in the field of soft tissue scaffold and its preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0079] Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a method for preparing hollow microcapsules. The method for preparing hollow microcapsules includes: Step (A), in ① a positively charged sacrificial core material or ② modified into a negatively charged sacrificial core material Forming a core polymer layer on the core material; step (B), ① in the case that the above-mentioned sacrificial core material is a positively charged sacrificial core material, alternately forming inorganic nanoparticle layers and capsules on the above-mentioned core polymer layer more than once The polymer layer for coating, ② In the case where the above-mentioned sacrificial core material is a sacrificial core material modified to be negatively charged, the above-mentioned core polymer layer is alternately formed on the above-mentioned core polymer layer for one or more times to coat the inorganic nanoparticle coating combination Inorganic nanoparticle layer and polymer layer for capsule co...
Embodiment 1
[0090] Example 1: Hydroxyphosphorus crosslinked by 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide crosslinker Preparation and Characterization of Stone / Gel Scaffolds (Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles Covered with Citrate@1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethyl Aminopropyl) carbodiimide-crosslinked gum )
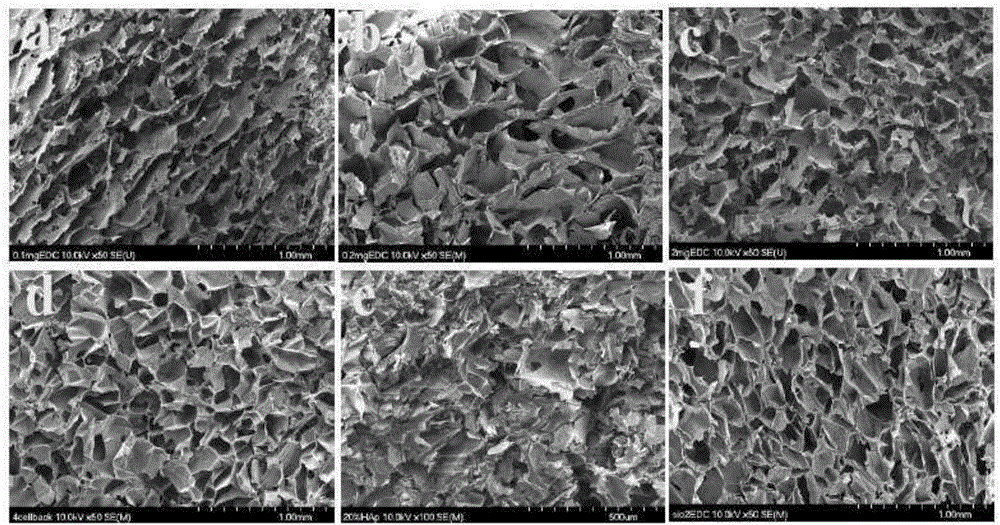
[0091] Soft and elastically recoverable macroporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles were cross-linked at -18°C by crosslinking citrate-coated and glue-coated (type B glue from porcine) hydroxyapatite nanoparticles Limestone / Gum Brackets. In the final solution before being frozen, the weight percent of polymer to particle was maintained at 1:10. That is, in 0.6 ml of deionized water, 6 mg of glue is applied to 60 mg of particles, and the amount of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide is set to 0.1 mg , 0.5mg, 2mg and 4mg (refer to figure 2 a to figure 2 d’s scanning electron micrograph). figure 1 a is a digital image of a 4 mg 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide scaffol...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Example 2: Preparation of carbon dioxide crosslinked with 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide crosslinking agent Silicone / gel scaffold (silica @ 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide cross-linked glue )
[0101] 10% by weight of silica nanoparticles with a size of 500 nm were vortexed in the e-tube and coated with 1% glue. The final volume of the solution was 0.6 ml, and the amounts of particles and polymers were 60 mg and 6 mg, respectively. 4 mg of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide crosslinker was added to the final solution, and the crosslinking was completed by freezing at -18°C for 24 hours. The mechanical properties of the obtained scaffold are similar to the hydroxyapatite 10% / glue 1% / 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide 4mg scaffold of Example 1 ( figure 2 f). The walls of the stent are mainly composed of silica particles.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com