Fully fitting esophageal stent complying with esophageal peristalsis
A full-fit, esophagus technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of restenosis, only prevent falling off, and the esophageal stent cannot fully fit the esophagus wall, so as to avoid pushing the trachea and enhance the resistance to displacement. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
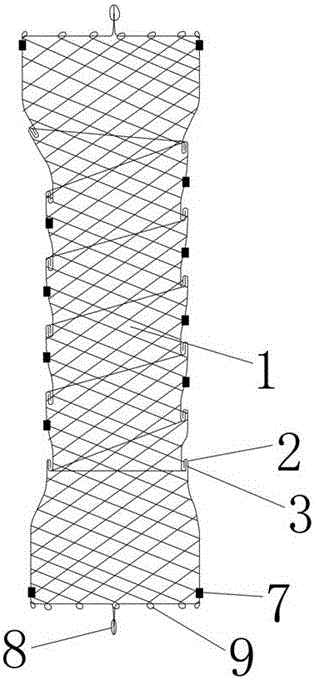
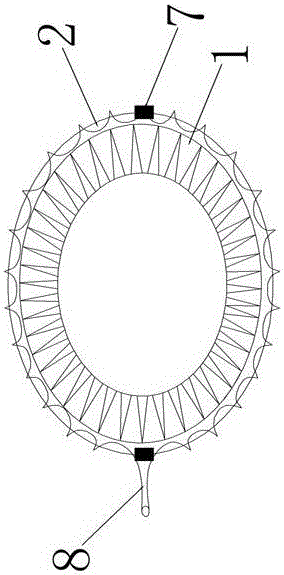
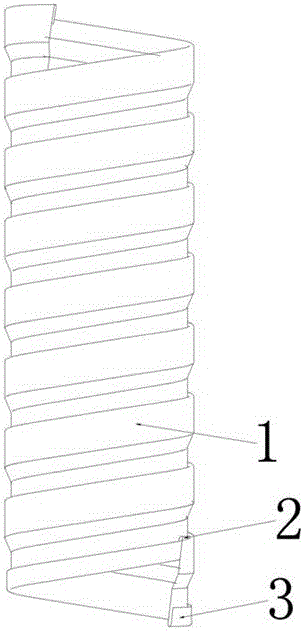
[0024] An esophageal stent conforming to the peristaltic function of the esophagus and the elliptical anatomical structure of the esophagus according to the present invention. The esophageal stent is composed of three sections with thick ends and thin middle sections smoothly connected. It is formed into a cylindrical shape, and the middle section is spirally wound by a long wire mesh 1 of equal width. The upper end of the long wire mesh 1 is provided with an upper hook 2, and the lower end of the long wire mesh 1 is provided with a lower hook 3. The long wire mesh 1 is provided with a lower hook 3....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com