A constant-contact method for preventing steel spring from breaking and vertical stop
A vertical stop, steel spring technology, applied in the direction of bogies, railway car body parts, axle box installation, etc., can solve the problem of greatly improving the fracture resistance of steel springs, without adjusting the stiffness, and it is difficult to effectively reduce the steel spring metal Fatigue and other problems, to achieve the effect of tight structure, reducing wear and preventing steel spring from breaking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
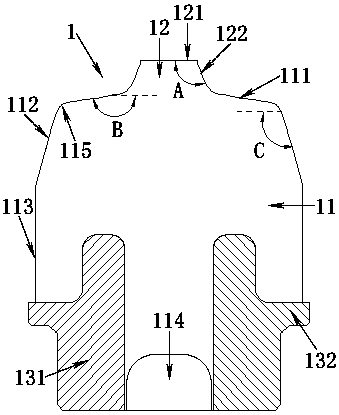
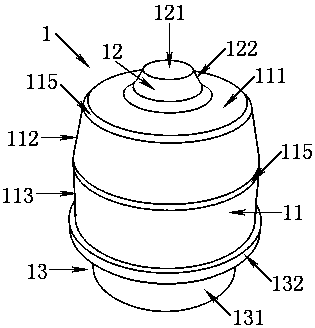
[0041] Such as Figure 5 As shown, a positioning base 4 is fixed above the axle box 5, and a double-volume spiral steel spring 2 is arranged above the positioning base 4, and the steel spring 2 supports the weight of the locomotive above the bogie frame 6. In order to reduce the vertical load borne by the steel spring 2 and reduce the metal fatigue generated by the steel spring 2 during locomotive operation, thereby preventing the steel spring 2 from breaking, a vertical stop 1 is provided in the steel spring 2 . The base flange 132 of the vertical stop 1 abuts against the positioning base 4 , and since the vertical stop 1 and the positioning base 4 are both revolving bodies, the vertical stop 1 can be stuck in the positioning base 4 . A frame guide cylinder 3 is arranged directly above the vertical stop 1. When the locomotive is unloaded, the rubber boss 12 of the vertical stop 1 is in contact with the frame guide cylinder 3, and the locomotive moves from no load to the maxim...
Embodiment 2
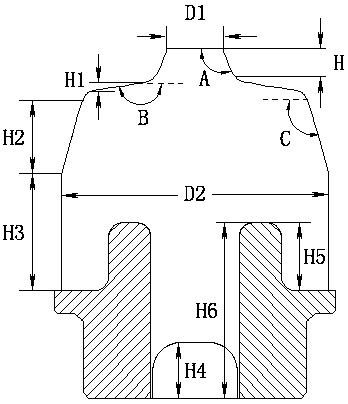
[0063] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the rotator-shaped rubber boss 12 above the rubber body 11 is no longer conical, but the generatrix 123 of the rotator-shaped rubber boss 12 is outward. Extruded smooth curves. Such as Figure 7 As shown, the diameter D3 of the rubber boss 12 refers to the diameter of the bottom of the rubber boss 12 , which is different from the diameter D1 of the rubber boss 12 in Embodiment 1, which refers to the diameter of the top of the rubber boss 12 . The preferred value of the diameter D3 of the rubber boss 12 in this embodiment is 20mm-60mm.
[0064] The busbar 123 is a gyratory-shaped rubber boss 12 protruding outwards with a smooth curve. When the locomotive load increases and the frame guide cylinder 3 is pressed down, the stiffness curve of the vertical stop 1 can be made smoother, thereby It can more effectively prevent the rigidity of the vertical stop 1 from increasing suddenly, and can better absor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com