Projection system with multi-luminous-spot packaging semiconductor laser alignment structure
A laser collimation and light-emitting point technology, applied in the field of projection systems, can solve problems such as lens spatial layout structure volume problems, and achieve the effect of ensuring the collimation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
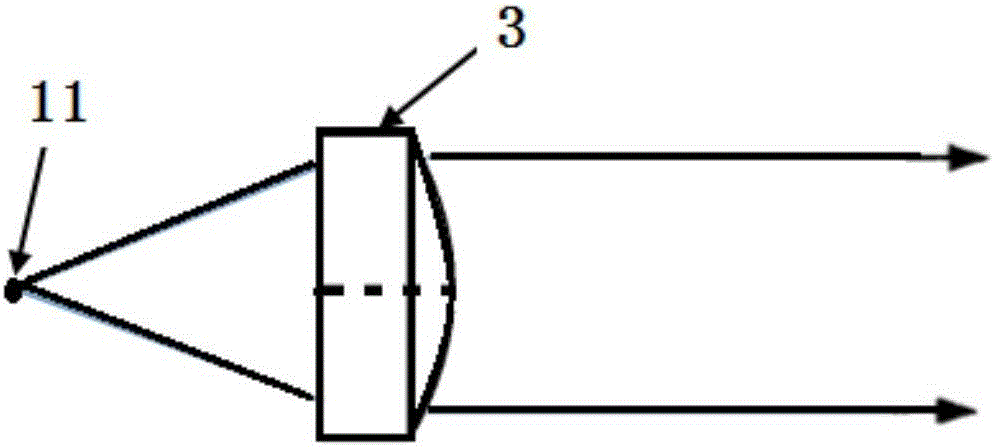
[0033] Embodiment 1, as Figure 4 , the multi-light-emitting point packaged semiconductor laser collimation device described in this example has a multi-light-point packaged diode 1 as an emission light source, and the multi-light-point packaged diode 1 has two light-emitting points; and is arranged on the multi-light-point packaged diode The collimating optical system on the beam exit path, the collimating optical system includes a microlens array composed of 2 microlenses 1 arranged in an array on the multi-spot package diode beam exit path and arranged on On the beam signal output path of each microlens I, there is a lens II capable of cooperating with the microlens I to collimate the emitted beam so as to output parallel light. Further, the center of any microlens I is located on the optical axis of the corresponding luminous point, and the distance between the microlens I and the luminous point is d=0.260mm, wherein the distance between the luminous point and the adjacent...
Embodiment 2
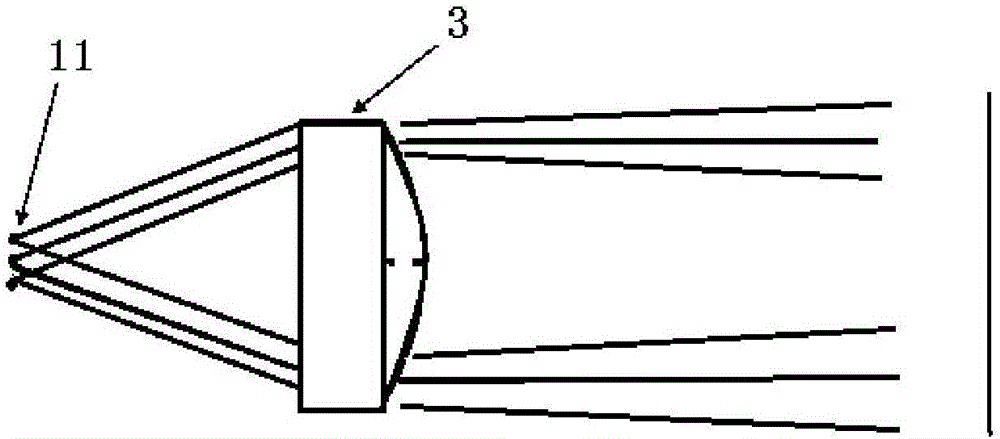
[0034] Embodiment 2, as Figure 5 , the multi-light-spot packaging semiconductor laser collimation device described in this example has a multi-light-spot package diode 1 as an emission light source, and the multi-light-spot package diode 1 has 4 light-emitting points; and is arranged on the multi-spot package diode The collimating optical system on the beam exit path, the collimating optical system includes a microlens array composed of 4 microlenses 1 arranged in an array on the multi-spot packaged diode beam exit path and arranged on On the light beam output path of each lens I, there is a lens II capable of collimating the emitted light beam with the micro lens I to output parallel light. Further, the center of any microlens I is located on the optical axis of the corresponding light-emitting point, and the distance between the lens I and the light-emitting point is d=0.179mm, wherein the distance a between the light-emitting point and the adjacent light-emitting point is...
Embodiment 3
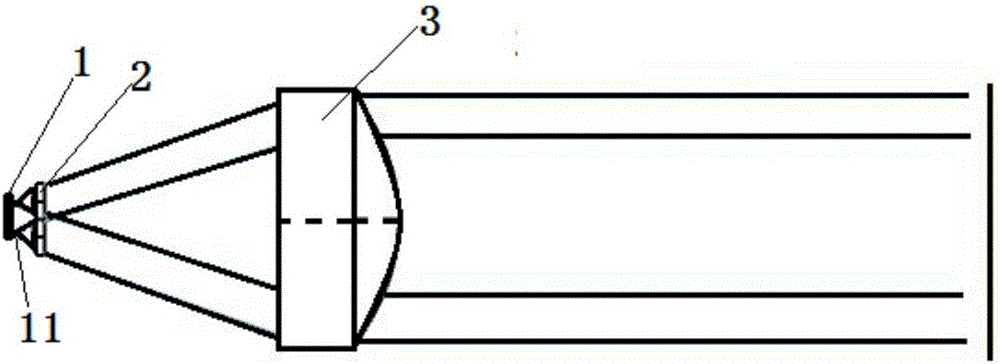
[0035] Embodiment 3, the laser projector described in this example, which is provided with the multi-light-emitting point packaging semiconductor laser collimation device in the optical structure, and the multi-light-emitting point packaging semiconductor laser collimation device includes a multi-light-emitting point package as the emission light source Diode 1, the multi-spot packaged diode 1 has 4 light-emitting points; The microlens array formed by the microlens I arranged in an array on the beam exit path of the point-package diode and the microlens array arranged on the beam exit path of each microlens I can cooperate with the lens I to collimate the emitted beam to output Lens II for Parallel Light. Further, the center of any one of the microlenses I is located on the optical axis of the corresponding luminous point, and the distance between the lens I and the luminous point is d=0.179mm, wherein the distance between the luminous point and the adjacent luminous point a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com