Multi-modal brain-computer interface (BCI) method and system based on synchronic compound limb imaginary movement
A brain-computer interface and synchronization technology, applied in computer components, mechanical mode conversion, user/computer interaction input/output, etc., can solve problems such as few optional categories, affecting flexibility, and not being able to satisfy multiple instruction outputs, etc. , to achieve the effect of satisfying the output of a large instruction set
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
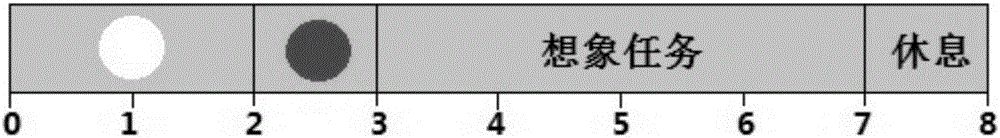
[0039] A multimodal brain-computer interface method based on synchronous compound limb imaginary actions, see figure 1 , the interface method includes the following steps:
[0040] 101: Design seven types of synchronous compound limb imagination movements involving hand-foot-body multi-limb participation;
[0041] 102: Using four-period task patterns to stimulate subjects, collect EEG data, and perform preprocessing;
[0042] 103: Use three different co-space pattern algorithms to perform feature extraction and pattern recognition on the preprocessed EEG data, and obtain a single task EEG feature vector;
[0043] 104: Input the single-task EEG feature vector into the support vector machine to train the classifier, and then predict the spatial features from the test set.
[0044] Wherein, the first type of synchronous compound limb imagining action in step 101 is: coordinated movement of both hands; the second type of synchronous compound limb imagining action is: left hand a...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Below in conjunction with specific accompanying drawing, calculation formula, the scheme in embodiment 1 is introduced in detail, see the following description for details:
[0066] 201: Design three types of synchronous compound limb imagination movements involving hand-foot-body multi-limb participation;
[0067] The embodiment of the present invention designs three types of synchronous compound limb imaginative actions involving hand-foot-body multi-limb participation, which are respectively the first type: the coordinated movement of both hands; the second type: the coordinated movement of the left hand and the opposite lower limb, and the third Class: coordinated movement of right hand and contralateral lower limb; three simple imaginary movements of limbs, respectively Class IV: left hand; Class V: right hand; Class VI: foot movement; and Class VII: resting state.
[0068] 202: Experimental Paradigm;
[0069] During the experiment, the subjects sat quietly on a c...
Embodiment 3
[0116] Below in conjunction with concrete test data, the scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is done feasibility verification, see the following description for details:
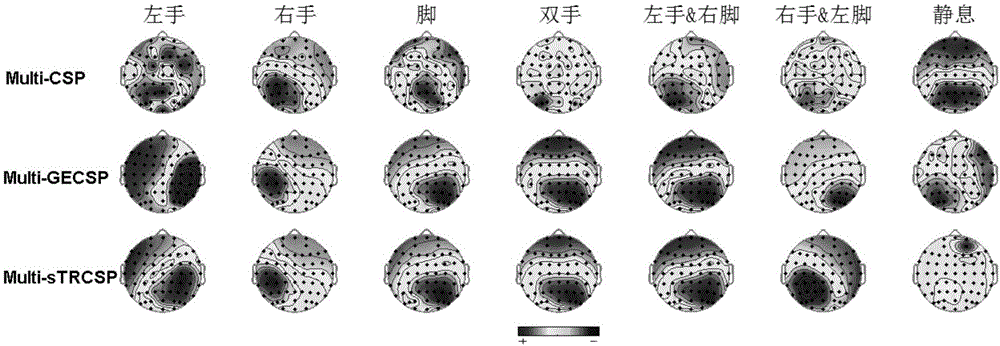
[0117] Table 1 shows the classification accuracy of ten subjects under three multi-category CSP algorithms for seven types of task patterns. It can be seen that the correct rate of the seven classifications of the second subject is the highest, reaching more than 80% under the three CSP algorithms, and 84.11% under the Multi-sTRCSP. Among them, the third subject performed the worst, with a correct rate of about 63%. Through the average accuracy rate of all subjects, it can be found that the classification accuracy rates of Multi-sTRCSP and Multi-CSP are both about 70%, and Multi-sTRCSP is slightly better than Multi-CSP, while Multi-GECSP performs the worst.
[0118] The above results show that the improved multi-classification CSP algorithm based on the binary classification CSP algorithm can be applied to the fea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com