Spatial-temporal fragment storage method for distributed spatial database
A spatial data, distributed technology, applied in database indexing, data processing input/output process, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems affecting database storage performance, difficult to meet high-performance storage requirements for massive spatial data, etc. Meet the requirements of query performance, good social and economic benefits, and high feasibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The present invention will be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which exemplary embodiments of the invention are illustrated.
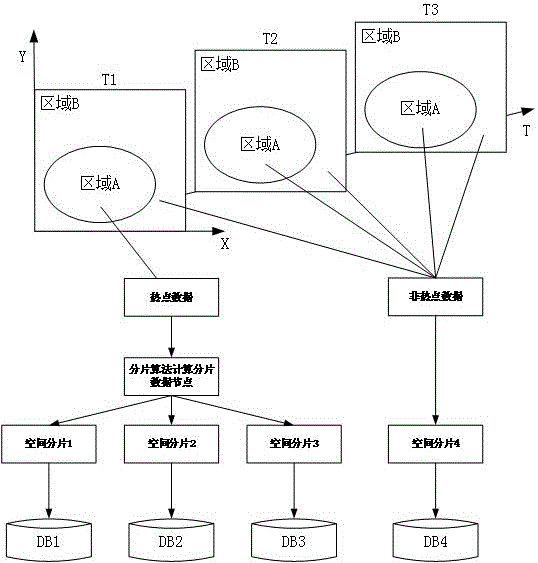
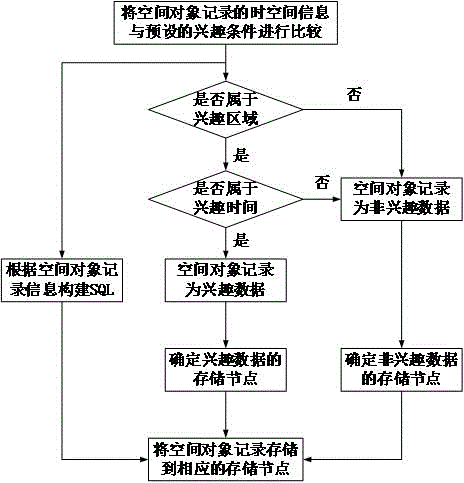
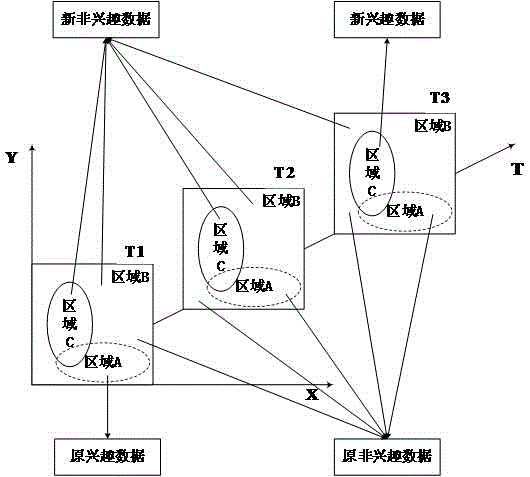
[0041]The technical solution adopted by the present invention to solve the above-mentioned technical problems is: use the time information and spatial information of the spatial object as the basis for data fragmentation, determine the interest area and interest time of the spatial data according to the use frequency of the data, and simultaneously The interest data satisfying the interest area and interest time are stored in fragments on multiple storage nodes, and the rest of the data is stored on a certain storage node. During data query, the frequently used interest data is stored on multiple storage nodes, so that multi-node parallel query can be realized. In addition, the less frequently used non-interest data is stored on a single storage node, which will not Affects query performance on dat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com