Data transmission method and device
A data transmission method and equipment technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of limited system capacity, low system spectrum utilization, waste of resources, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
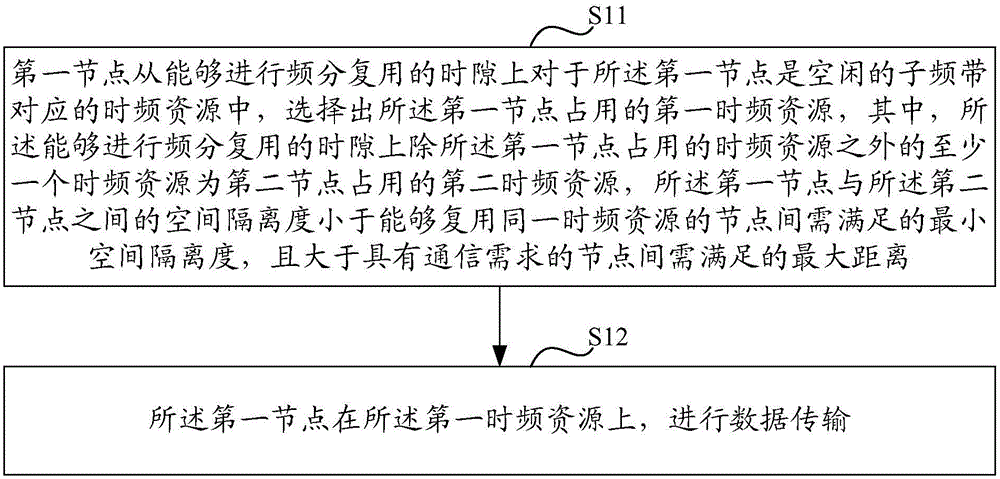
[0141] Embodiment 1: This embodiment selects the occupied time-frequency resource based on the received FI message, taking a partial frequency division method as an example.
[0142] It is assumed that each node retransmits once, that is, the transmission of each node includes an initial transmission and a retransmission. The initial / retransmission time-frequency resource pairs pre-configured by the system are shown in Table 1. X1 represents an initial / retransmission time-frequency resource pair, and X2 represents an initial / retransmission time-frequency resource pair.
[0143] Table 1
[0144] time slot 1 time slot 2 slot 3 slot 4 slot 5 Subband 1 Node A Node A X1 X1 X sub-band 2 Node B X2 Node B X2 X Subband 3 X X X X X
[0145] In the table, X represents an idle time-frequency resource, and there are two initial / retransmission time-frequency resource pairs X1 and X2 in the idle time-frequency resource, both of which...
Embodiment 2
[0155] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is used to illustrate the time-frequency resource maintenance process, taking the complete frequency division method as an example.
[0156] For the two nodes A and B that have been frequency-division multiplexed, the time-frequency resources occupied by them are shown in Table 2.
[0157] Table 2
[0158] time slot 1 time slot 2 slot 3 slot 4 slot 5 Subband 1 Node A Node A Node D Node D X sub-band 2 Node B Node B X X X Subband 3 X X X X X
[0159] In the table, X represents idle time-frequency resources. Since node A and node B occupy the same time slot by frequency division multiplexing, it means that node A and node B have no communication requirements with each other.
[0160] Whether node A and node B can continue frequency division multiplexing is determined by a third party (namely node D), as follows:
[0161] For node A, it is assumed that node D determines the received ...
Embodiment 3
[0165] Embodiment 3: This embodiment provides a scenario where retransmission is not considered when the number of subbands is relatively small.
[0166] The frequency division multiplexing between nodes is shown in Table 3. Node A and node B use frequency division multiplexing to occupy time slot 1, and node C and node D use frequency division multiplexing to occupy time slot 2. X in the table represents idle time audio resources.
[0167] table 3
[0168] time slot 1 time slot 2 slot 3 slot 4 slot 5 Subband 1 Node A Node C X X X sub-band 2 Node B Node D X X X
[0169] When node E selects time-frequency resources, it selects time slots occupied by nodes far away from itself for frequency division multiplexing. The principle of selecting time slots for frequency division multiplexing is consistent with the consideration of the retransmission mode, that is, it is determined according to the FI message or received power. The jud...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com