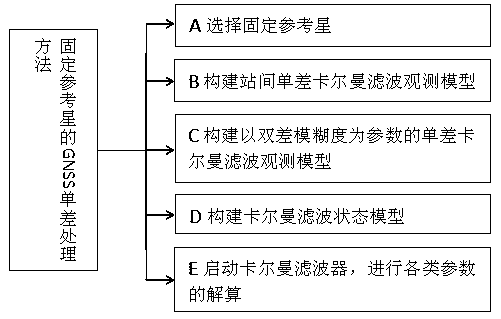
GNSS single-difference processing method with fixed reference star
A processing method and technology of reference satellites, which are applied to satellite radio beacon positioning systems, instruments, measurement devices, etc., and can solve the problem of discontinuous transmission of ambiguity parameters and clock error parameters between epochs, weak GNSS service capabilities, and low computational efficiency. and other problems, to achieve the effect of strong GNSS service capability, solving the continuous transmission of ambiguity parameters and clock error parameters between epochs, and high computational efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
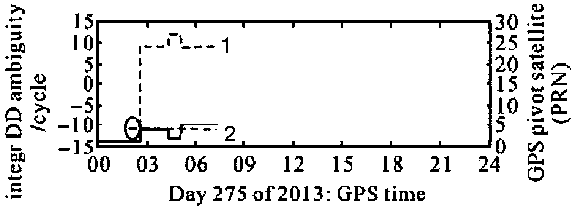
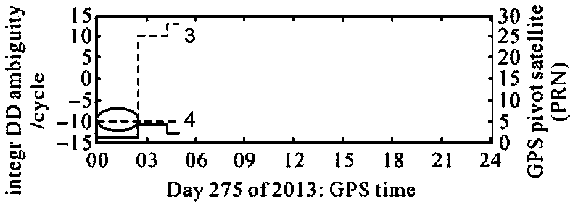
[0059] Example 1: Using a short baseline to analyze the impact of reference star fixation and replacement on double-difference ambiguity estimation
[0060] Data description and processing plan: In 2013, DOY275 days (DOY: Day Of Year, annual cumulative days) collected 24 hours of continuous GPS observation data at CUAA and CUT3 stations to form a baseline CUAA-CUT3, with a length of about 8.4km, used for related calculations See Table 1 for information. Among them, the cut-off elevation angle is set to 20° in order to eliminate the influence of multipath on the observed values as much as possible. The single-difference processing scheme of fixing the reference star and the double-difference processing scheme of replacing the reference star are adopted to compare the influence of changing and fixing the reference star on the ambiguity continuity.
[0061] Table 1 Observation information and parameter settings used in the baseline calculation
[0062]
[0063] see figure...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2: Using medium and long baselines to analyze the impact of reference satellite fixation and replacement on receiver clock error estimation
[0089] Data description and processing plan: In 2014, DOY collected observation data of STAR and LALB for 21 hours in 190 days to form a baseline STAR-LALB with a length of about 105 km. The information used in the calculation is shown in Table 2.
[0090] Table 2 The baseline solution uses observation information and parameter settings
[0091]
[0092] The GNSS single-difference processing method of the fixed reference star in this embodiment is the same as that in Embodiment 1. The baseline is relatively long, and the correlation of atmospheric errors is relatively weak. In the single-difference Kalman filter observation model, the state parameters include the residual ionospheric delay error and the tropospheric zenith delay error, and the residual ionospheric delay error and the tropospheric sky The top delay erro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com