Tapped balance reactor with secondary side winding rectification function
A technology for balancing reactors and secondary windings, applied in the direction of output power conversion devices and electrical components, which can solve the problem of increasing current harmonics, output voltage ripple and system loss, increasing the complexity of rectifying devices, and small load adaptation range and other issues, to achieve the effect of reducing input current harmonics, reliable and easy to control, and reducing the difficulty of processing technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
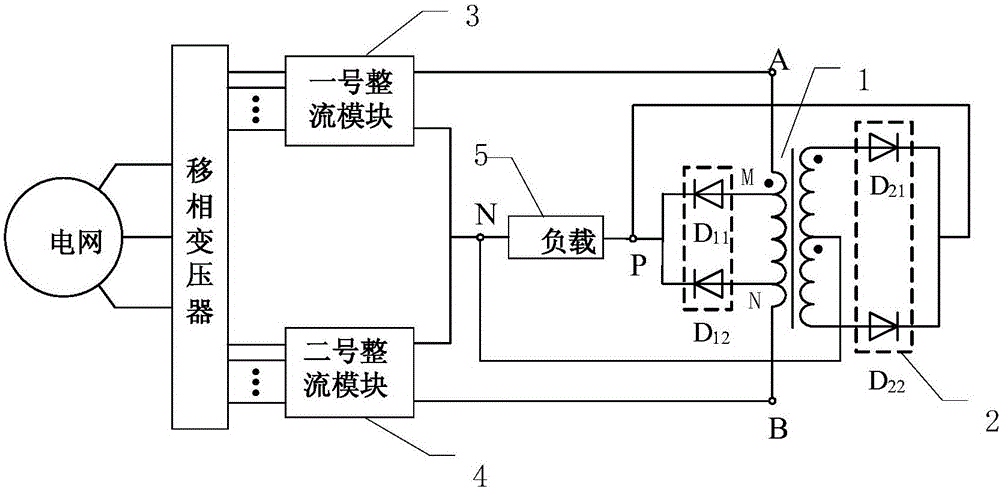
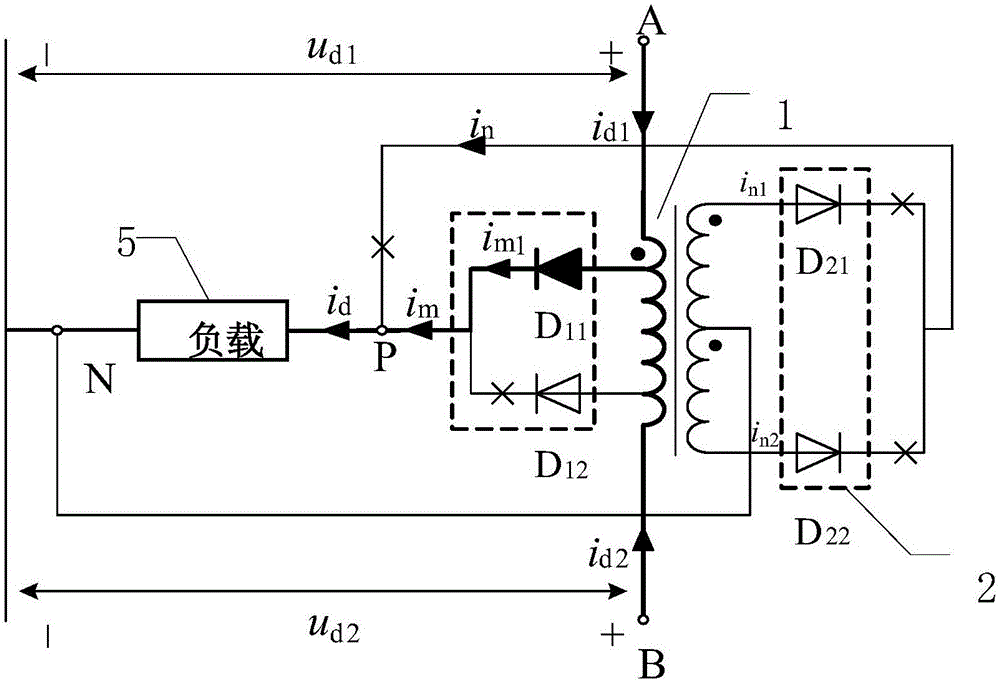
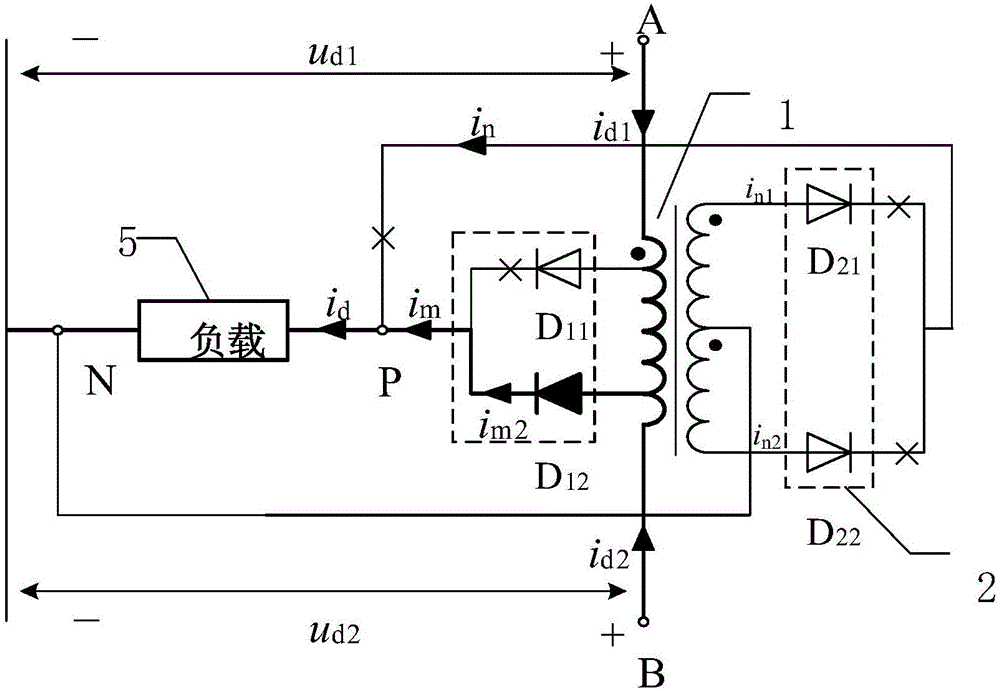
[0049] Specific implementation mode one: refer to figure 1 Describe this embodiment in detail. The tapped balance reactor with secondary winding rectification function described in this embodiment includes a balance reactor 1, a single-phase full-wave rectifier circuit 2, a diode D 11 and diode D 12 ,
[0050] The primary side coil of the balance reactor 1 has two taps, and the two tap points are point M and point N respectively, and the two taps are arranged symmetrically with the center of the primary side coil, and the secondary side of the balance reactor 1 The coil has a center tap,
[0051] The three-phase voltage input terminal of the grid is connected to the AC input terminal of the No. 1 rectifier module 3 and the AC input terminal of the No. 2 rectifier module 4 after passing through the phase-shifting transformer.
[0052] One end of the primary coil of the balance reactor 1 is connected to point A of the positive terminal of the No. 1 rectifier module 3, and the...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0059] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of the tapped balance reactor with secondary winding rectification function described in specific embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the single-phase full-wave rectification circuit 2 includes a diode D 21 and diode D 22 ,
[0060] Diode D 21 The anode of the balance reactor 1 is connected to one end of the secondary coil, and the diode D 22 The anode of the balance reactor 1 is connected to the other end of the secondary coil;
[0061] Diode D 21 the cathode and diode D 22 The cathode is connected as the output end of the single-phase full-wave rectification circuit 2.
[0062] In this embodiment, on the premise of realizing the same system pulse number, the primary side of the balanced reactor in the present invention adopts a two-tap structure, and only uses the diode D 11 and diode D 12 , no control circuit is required, and the structure is simpler.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0063] Specific embodiment 3: This embodiment is to further explain the tapped balance reactor with secondary winding rectification function described in specific embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the first rectification module 3 and the second rectification module 4 are both It is a three-phase half-bridge rectifier, a three-phase full-bridge rectifier, a rectifier group composed of a plurality of three-phase half-bridge rectifiers or a rectifier group composed of three-phase full-bridge rectifiers.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com