Fast simulation method for non-stationary random process
A stochastic process and simulation method technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems that two-dimensional FFT cannot be used, and non-stationary stochastic process simulation cannot be directly applied
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0167] Example 1: Simulation of non-stationary and heterogeneous ground motion
[0168] Assuming that the distance between two earthquake simulation points is 10m, and a total of 401 points are simulated. The evolution power spectrum of an earthquake adopts an inseparable form, and its formula is as follows:
[0169]
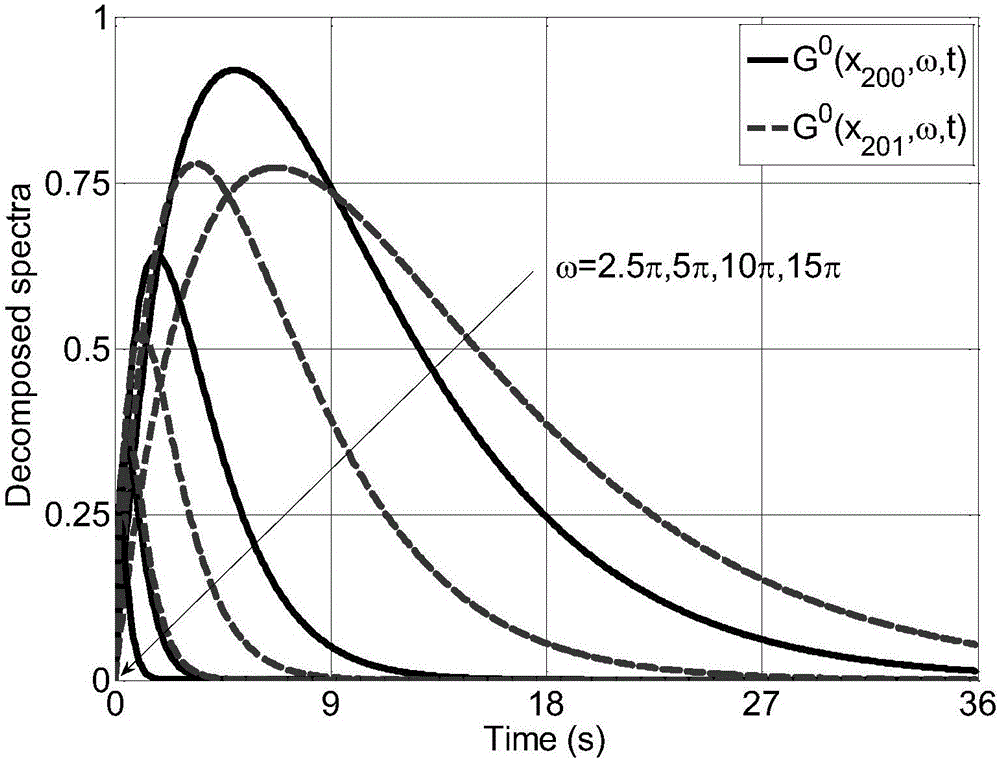
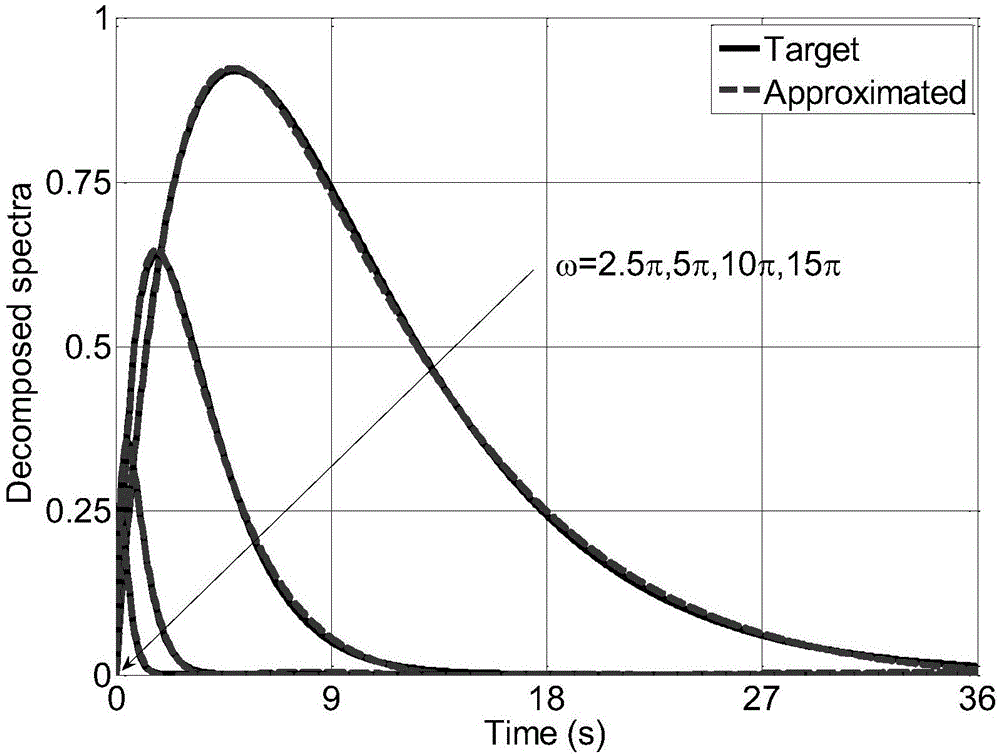
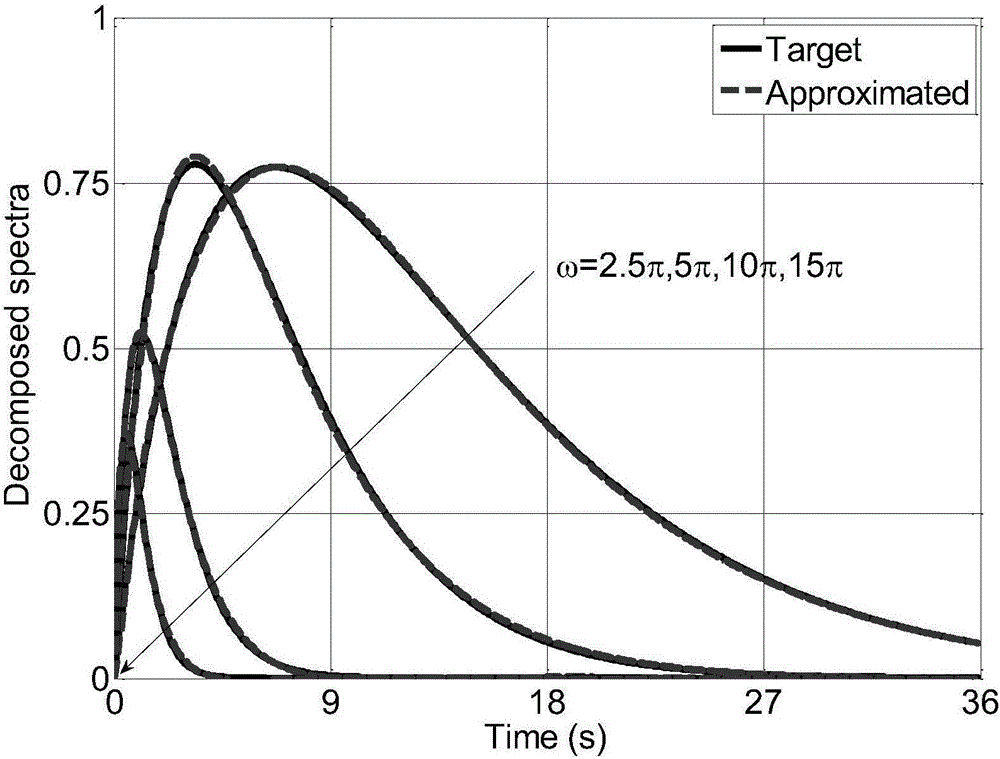
[0170] In the formula: S 0 =1. For simulation points j=1,2…,200, parameter C j = 2.5 and D j = 0.15. For simulation points j=201,202…,401, parameter C j = 4 and D j = 0.2. figure 1 Decomposed spectrum G at four selected frequencies is shown 0 (x 200 ,ω,t) and G 0 (x 201 ,ω,t) fluctuation curve. It can be seen that there is a relatively obvious difference between the evolution spectra of the simulation points 200 and 201 . Based on the POD method in the present invention, the decoupling and reconstruction of the evolutionary power spectrum are performed, when N q = 6, the comparison between the reconstructed evolution spectrum and the target evol...
example 2
[0181] Example 2: Simulation Efficiency Comparison
[0182] In 2015, Huang applied POD to the spectral representation method of non-stationary random processes, and proposed a fast simulation method for non-stationary random processes that can use FFT. In addition, the method is highly accurate and easy to implement. For convenience of comparison, this method is defined as a POD-based method. In this embodiment, the differences in efficiency and accuracy between the present invention and the POD-based method will be compared.
[0183] For comparison, these two methods are used simultaneously to simulate the random process of earthquake motion in Example 1. In the simulation, the number of discrete frequencies in both methods is set to 1024, while the number of simulation points varies from 32 to 512. The simulations of the two methods are calculated by Matlab programming, and run on a 64-bit computer with Intel(R) Xeon(R) E5-2609 v2 processor (frequency 2.50GHz) and 32GB me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com