Mixed integer programming-based multi-objective distributed generation locating and sizing method
A technology of distributed power supply, location selection and capacity determination. It is applied in resources, data processing applications, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as short-circuit current increase, voltage fluctuation, and idle distribution network assets.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
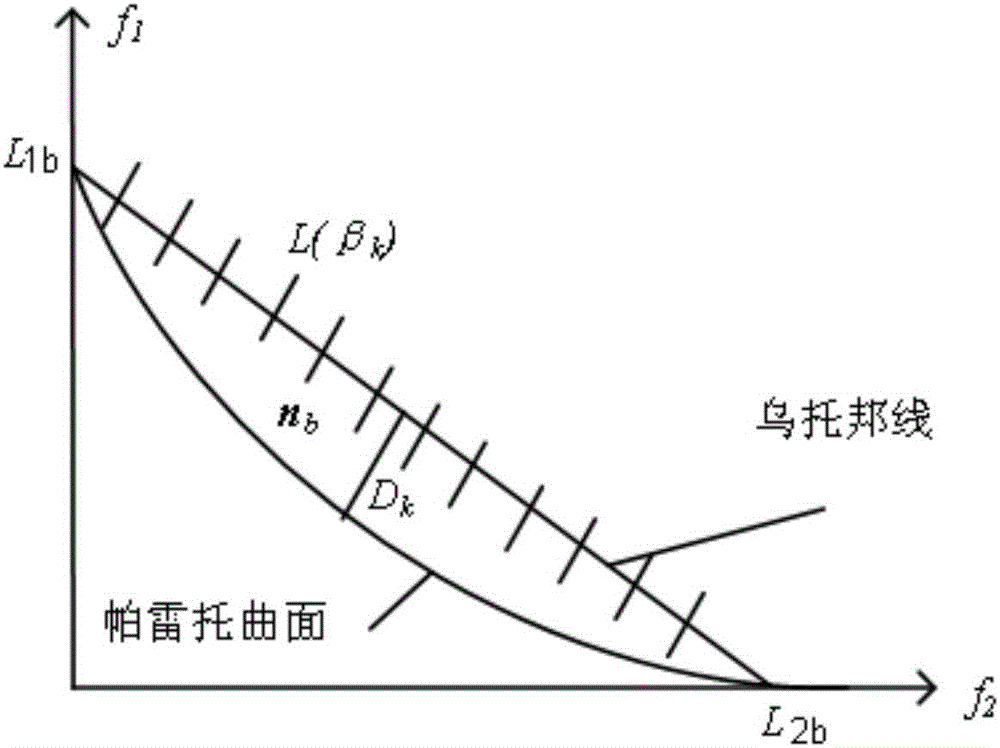
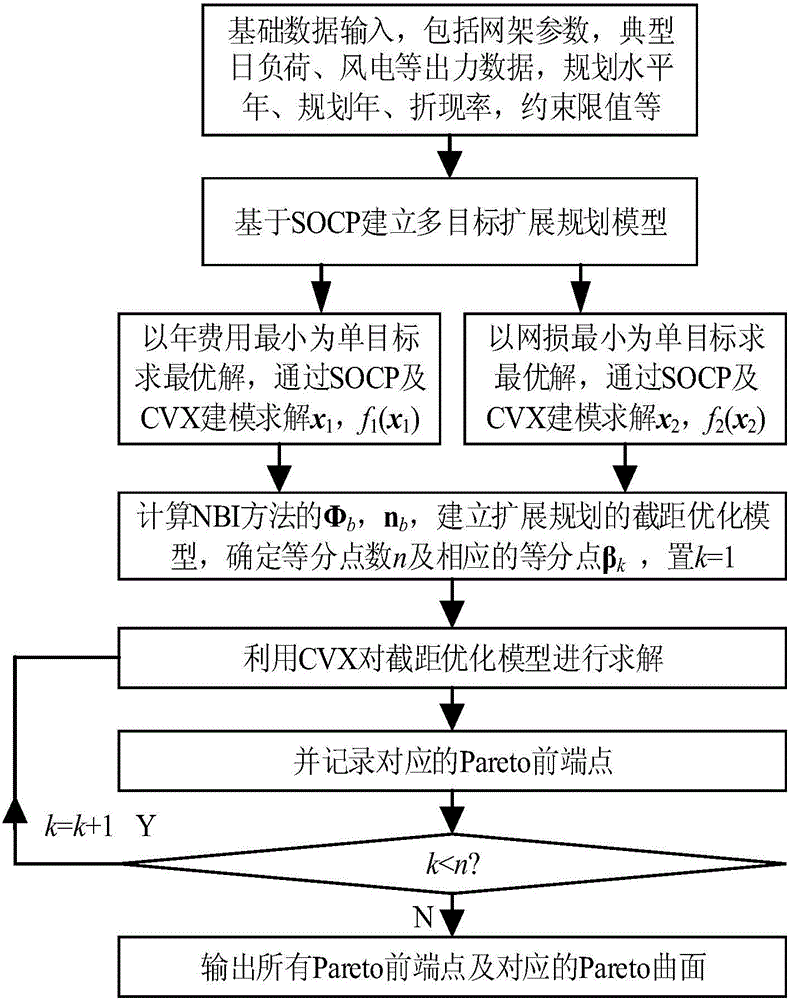
[0014] Based on the DG timing characteristics, the present invention establishes a multi-objective DG site selection model considering DG investment, operation and maintenance costs, and network loss costs. In order to obtain a uniformly distributed Pareto front-end solution, the multi-objective problem is dealt with by using the Normal Boundary Intersection (NBI). The DG site selection and capacity planning model is transformed into a second-order cone programming model by using the power distribution network forward and backward generation equation and the constraint relaxation strategy, and the CVX platform and GUROBI solver are used to solve the problem.
[0015] The present invention is realized through the following approaches:
[0016] 1) Establish DG site selection and capacity setting as a multi-objective planning model. The objective function includes: minimizing the total investment, operation and maintenance costs during the planning period, and minimizing the tota...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com