Heterogeneous image change detection method based on non-supervision depth neural network
A deep neural network and image change detection technology, applied in the field of remote sensing image processing, can solve problems such as complex implementation and inability to meet requirements, and achieve excellent feature learning ability, excellent effect, and stable results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
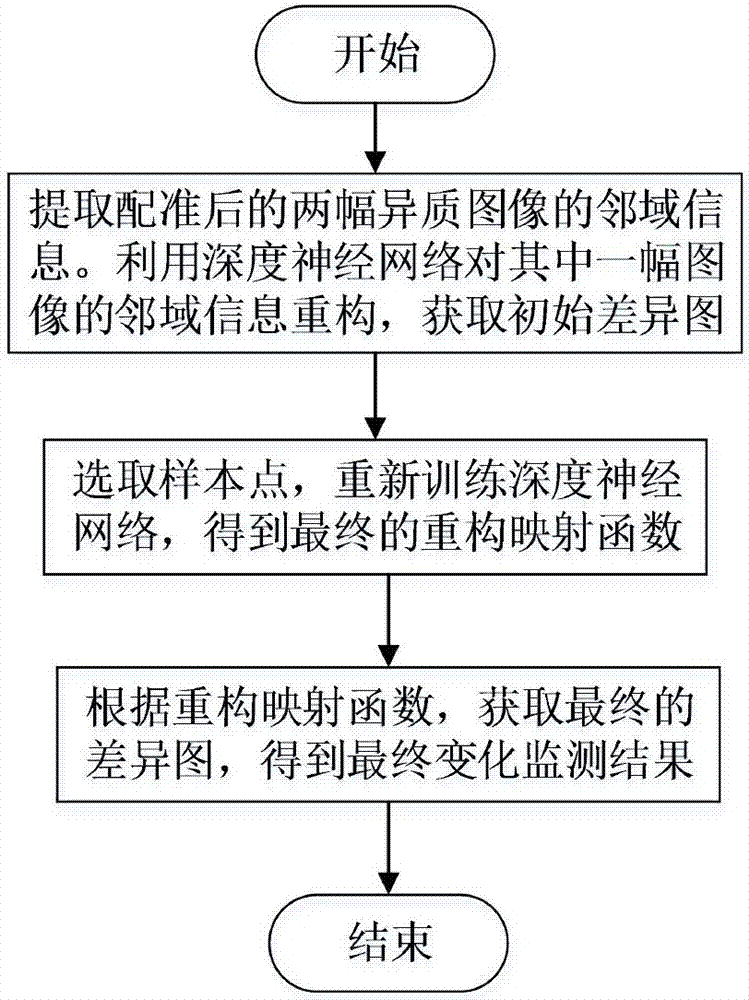
[0042] This embodiment provides a heterogeneous image change detection method based on an unsupervised deep neural network, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0043] Step 1: Select two heterogeneous images of the same region with different phases, denoted as image I 1 and image I 2 , using a deep neural network to image I 1 The neighborhood information of all points is input, and the reconstructed image I 2 Neighborhood information, get the initial reconstruction mapping function f 1 (x), get the initial difference map DI 1 ;
[0044] Step 2: The initial difference map DI obtained in Step 1 1Select sample points in , retrain the deep neural network, and obtain the final reconstructed mapping function f(x);
[0045] Step 3: Use the final reconstruction mapping function f(x) obtained in Step 2 to obtain the difference map DI to obtain the final change detection result.
[0046] The present invention breaks through the traditional heterogeneous image...
Embodiment 2
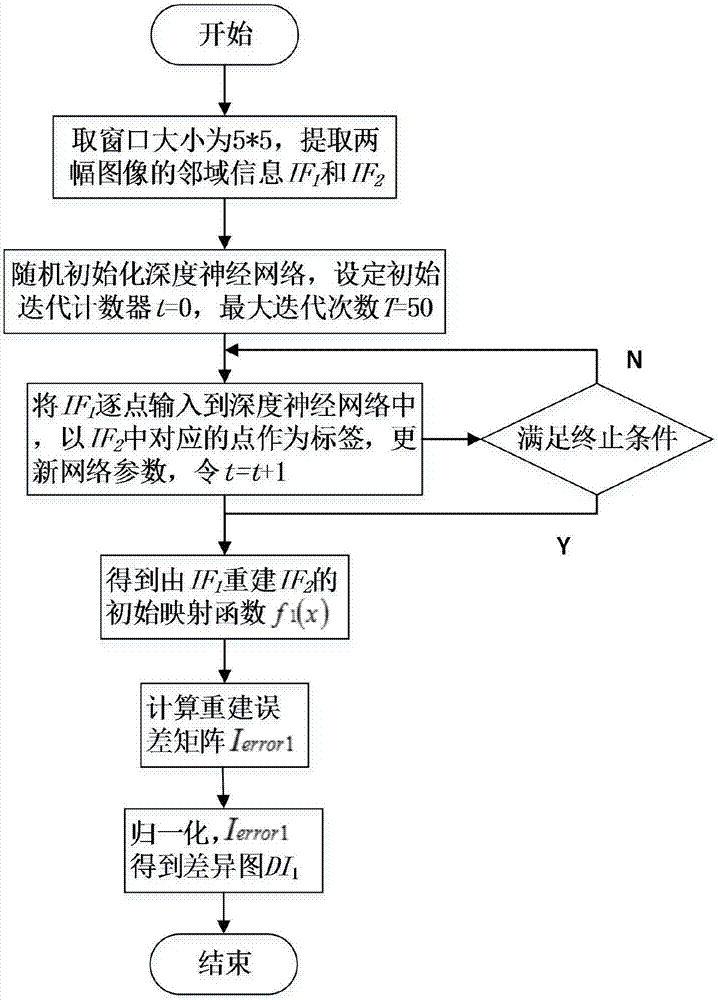
[0048] This embodiment further describes step 1 in detail on the basis of embodiment 1, as figure 2 As shown, step one specifically includes the following steps:
[0049] Step 101: Select two heterogeneous images of the same region with different phases, denoted as image I 1 and image I 2 , take the position (i, j) pixel as the center pixel, take a window whose size is 5×5, and the total number of pixels is N=25, extract two images I 1 , I 2 Neighborhood information IF 1 , IF 2 ;
[0050] Step 102: Randomly initialize the deep neural network, initialize the iteration counter t=0, and the maximum number of iterations T=50;
[0051] Step 103: Convert the image I 1 Neighborhood information IF 1 Input point by point in the deep neural network of step 102, with image I 2 Neighborhood information IF 2 The corresponding points of are used as labels, and the network parameters are updated using the conjugate gradient algorithm based on the minimum cross-entropy, t=t+1;
[...
Embodiment 3
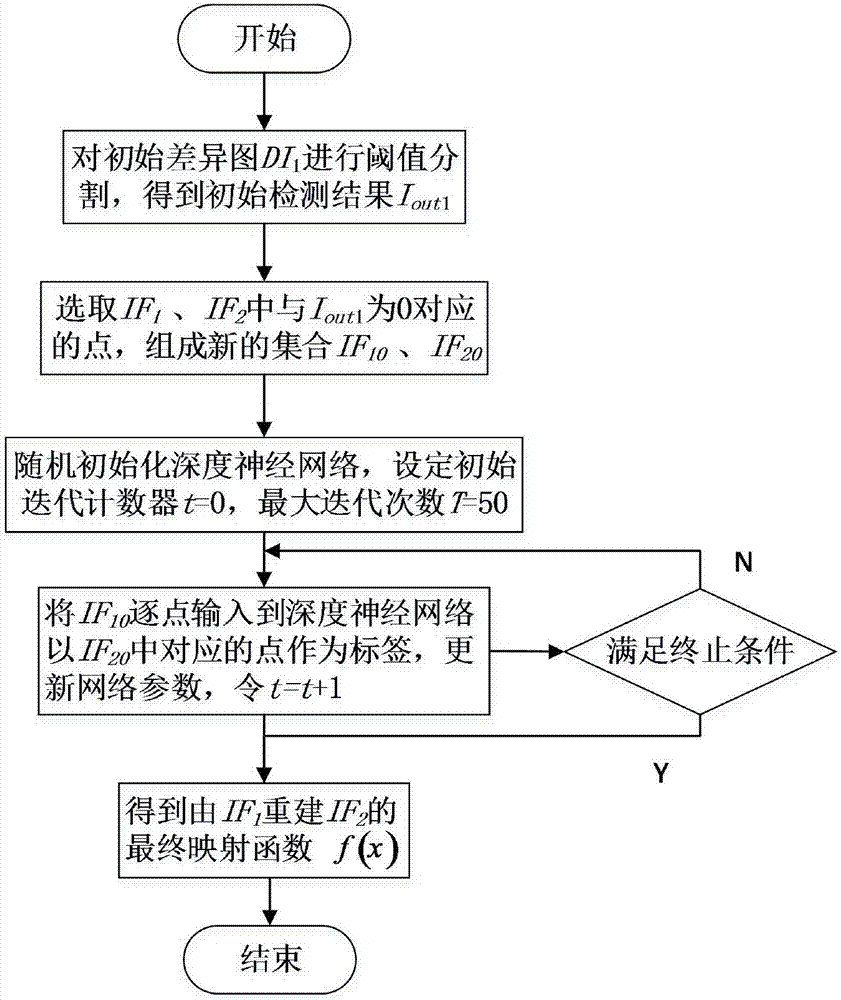
[0056] This embodiment further describes step 2 in detail on the basis of embodiment 1 and embodiment 2, as image 3 As shown, step two specifically includes the following steps:
[0057] Step 201: The initial difference map DI obtained in step 1 1 Perform threshold segmentation to obtain the initial detection result Iout 1 ;
[0058] Step 202: Select IF 1 , IF 2 The corresponding Iout in 1 The points that are 0 in form a new set IF 10 , IF 20 ;
[0059] Step 203: Randomly initialize the deep neural network, initialize the iteration counter t=0, and the maximum number of iterations T=50;
[0060] Step 204: set IF 10 Input point by point into the deep neural network of step 203, with IF 20 The corresponding points of are used as labels, and the network parameters are updated using the conjugate gradient algorithm based on the minimum cross-entropy, t=t+1;
[0061] Step 205: Repeat step 204 until the error is smaller than the specified threshold or t>T, and a new mapp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com