A silicon-based display based on fusion scanning strategy
A display, silicon-based technology, used in static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as high data bandwidth, reduce area requirements, reduce circuit scanning speed requirements, and improve conversion accuracy and conversion speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
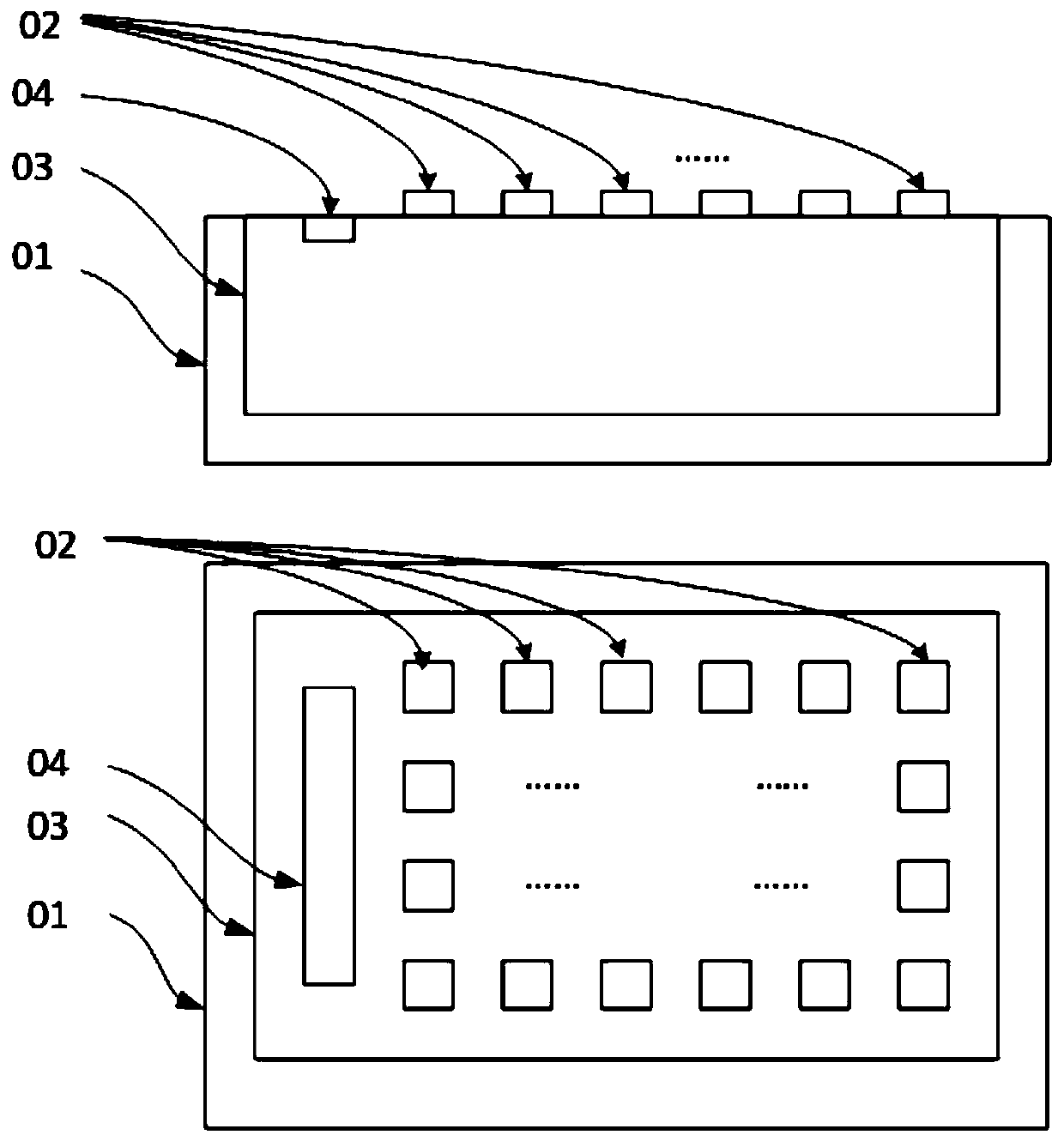
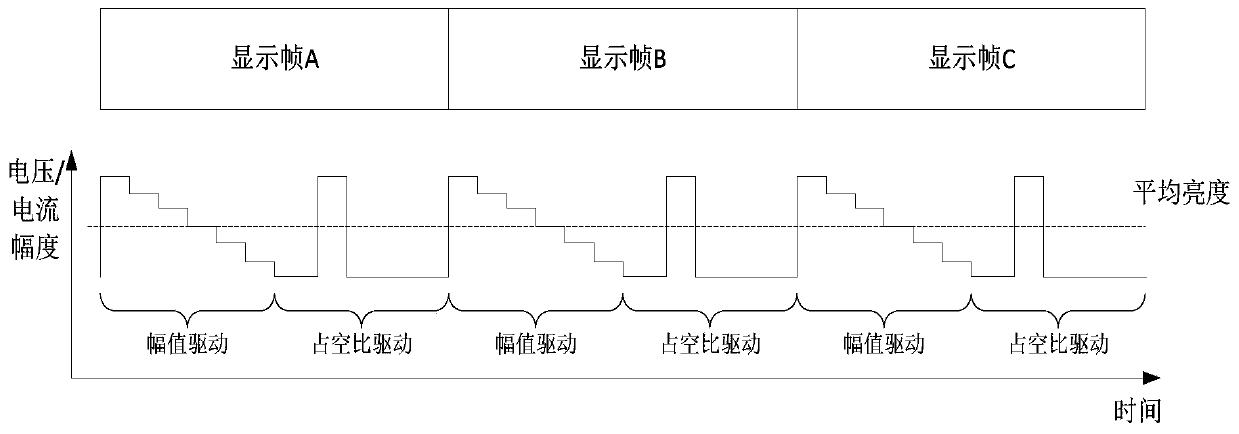
[0041] figure 1 The basic structure of a silicon-based microdisplay adopted in the present invention is illustrated, the upper part is a side view, and the lower part is a top view, which at least includes a semiconductor silicon substrate 01 and a pixel 02 on the surface of the silicon substrate and a driving circuit 03 contained in the silicon substrate and Interface 04, the drive circuit 03 at least includes a metal-oxide semiconductor field effect transistor and at least two metal layers; the brightness of the pixel 02 in a specific display frame is determined by the output current or voltage of the pixel in the display frame The amplitude of the pixel and the time duty cycle of the output current or voltage of the pixel in the display frame are jointly determined; the display frame includes the pixel grayscale information in a specific display area through the interface 04 through the drive circuit 03 is the process of transmitting to the pixel 02; the specific display fr...
Embodiment 2
[0045] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
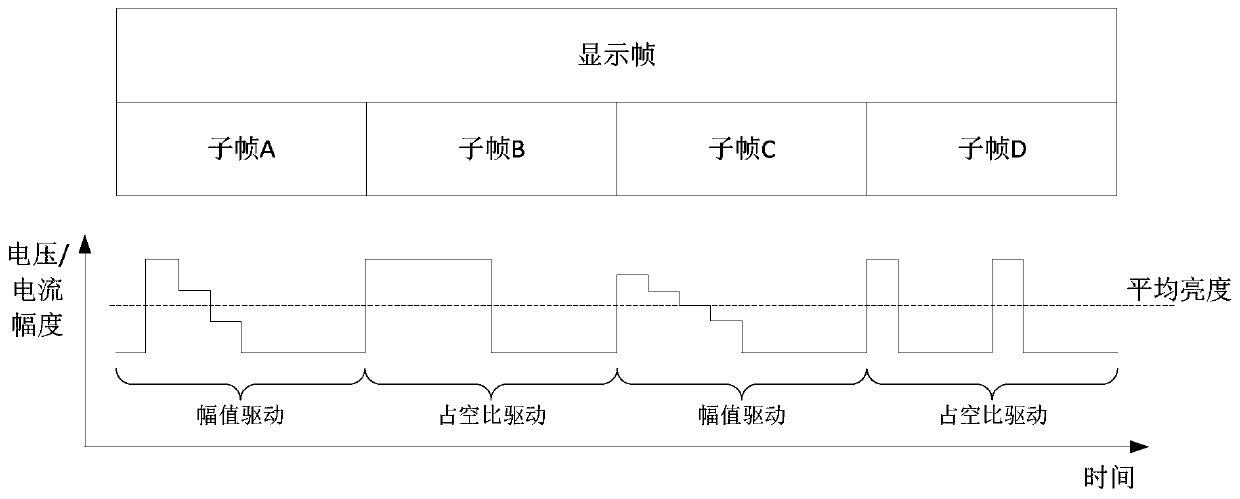
[0046] In any subframe, the brightness of a pixel is jointly determined by the magnitude of the output current or voltage of the pixel in the subframe and the time duty cycle of the output current or voltage of the pixel in the subframe. Brightness The brightness in the specific display frame is equivalent to the average brightness of the pixel in all sub-frames in the specific display frame.
[0047] The process is a sequential transmission process or a random transmission process. The sequential transmission means that the grayscale information is transmitted point by point in the order from row to column or from column to row. The random transmission means that the grayscale information Information is transmitted randomly in random row or random column order.
[0048] The specific subset is one or more bit planes of pixel grayscale data in the specific display area, the bit plane is a data ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
[0053] The subframe can be further divided into several repeated frames, the repeated frames include the process of repeatedly transmitting the same grayscale information to the pixel 02, and the grayscale information transmitted by each repeated frame is consistent with the The information required to be transmitted in a subframe is exactly the same, the sum of the time lengths of all repeated frames in each subframe is equal to the total time length of the subframe, and the time order of the repeated frames belonging to different subframes is in order within a display frame or randomly arranged. Figure 5 An example of displaying subframe repeating frame driving waveforms for silicon-based microdisplays, including two sets of repeating frames A1 / A2 and B1 / B2, where A1 and A2 are repeating frames of subframe A, and B1 and B2 are repeating frames of subframe A. For the repeated frames of frame...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com