An image depth estimation system and method based on hole convolution and semi-supervised learning
A semi-supervised learning and image depth technology, applied in the field of computer vision, can solve problems such as ignoring the spatial information dependence of depth estimation tasks, reducing spatial resolution, and limiting prediction accuracy, achieving large spatial perception range, strong spatial dependence, The effect of removing noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Existing image depth estimation methods based on deep learning ignore the dependence of depth estimation tasks on spatial information. When using a deep convolutional network, a large number of pooling operations reduces the spatial resolution of the features, which leads to the loss of spatial information and has a non-negligible impact on the output results.
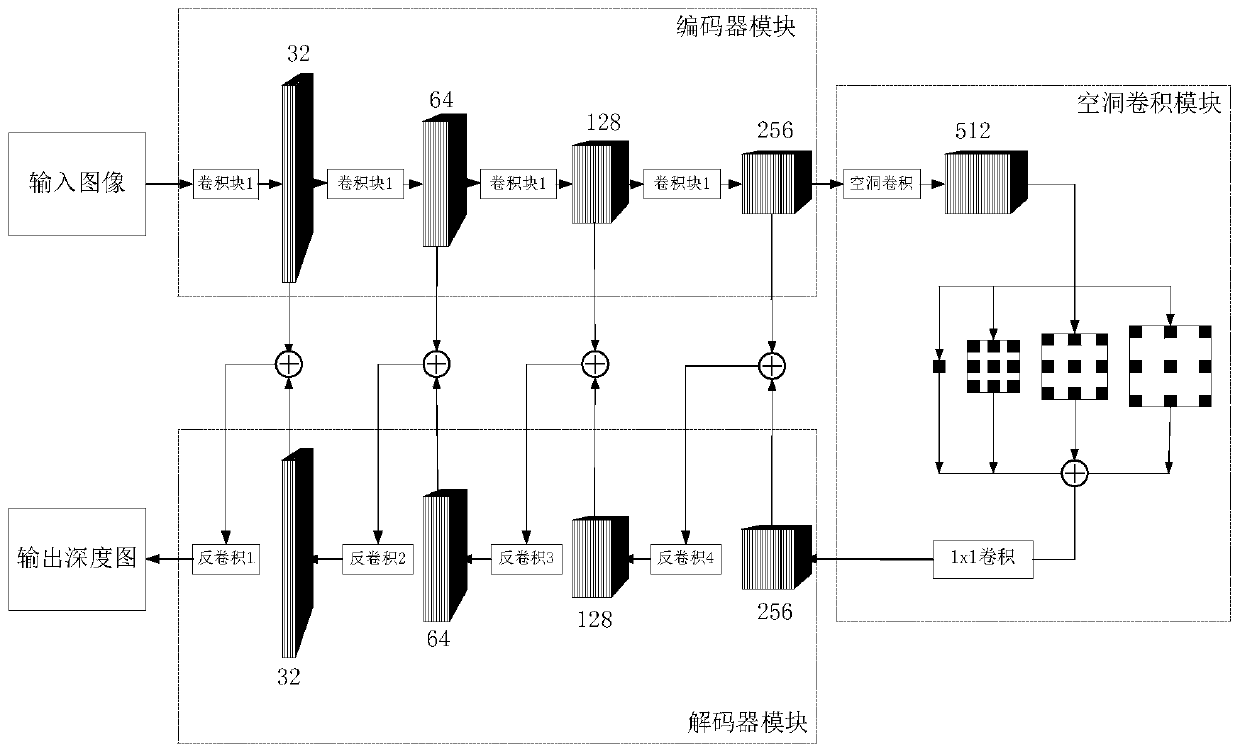
[0027] The present invention conducts research on the above-mentioned status quo, and proposes an image depth estimation system based on atrous convolution and semi-supervised learning, including a decoder module and a decoder module symmetrically connected to it. The decoder module inputs the image to be estimated, decodes The module obtains and outputs the image after depth estimation, see figure 1 , the present invention adds a dilated convolution module between the decoder module and the decoder module. The main body of the dilated convolution module of the present invention is a dilated convolution pyramid...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The image depth estimation system based on hole convolution and semi-supervised learning is the same as embodiment 1, see figure 1 , the main body of the atrous convolution module in the present invention is an atrous convolution pyramid model containing four parallel-connected convolution kernels with different expansion rates, the output of the encoder module in the present invention is used as the input of the atrous convolution module, and the atrous convolution The output of the product module is used as the input of the decoder module. The encoder module of the present invention is composed of 4 convolution blocks, each convolution block contains two convolution layers, the decoder module is composed of 4 deconvolution layers, the decoder module and the decoder module have a symmetrical structure, and Make skip connections.
[0031] The encoder module of the present invention reduces the spatial resolution of the input step by step through operations of different...
Embodiment 3
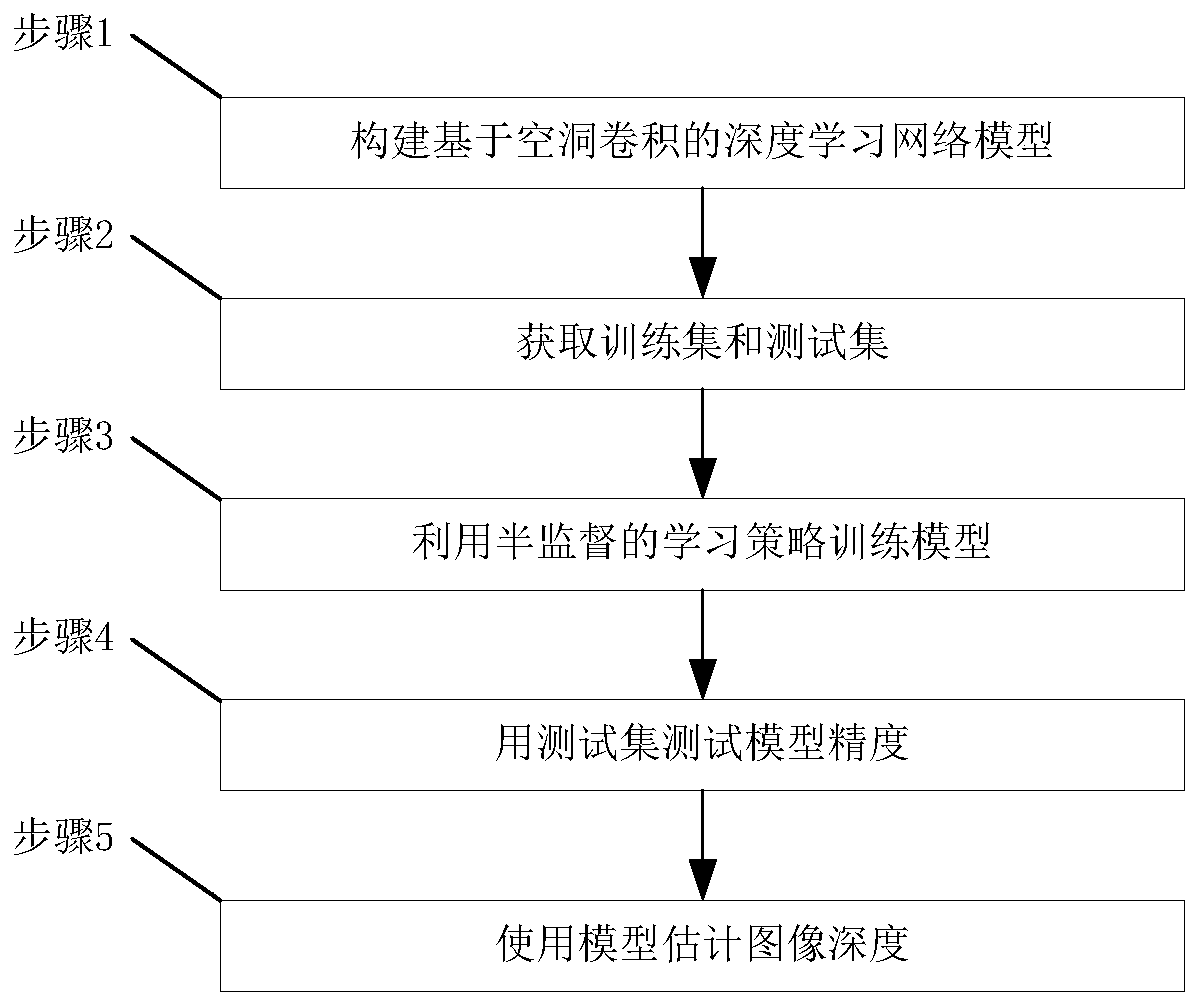
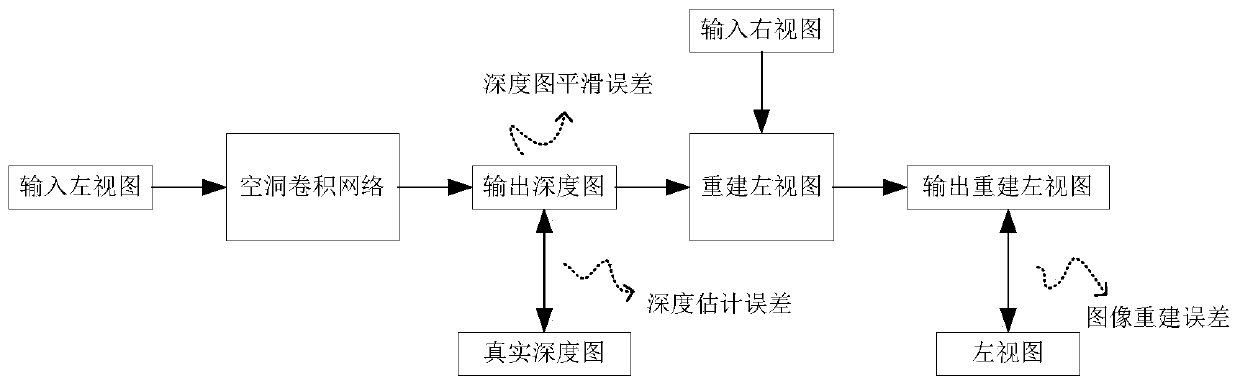
[0035] The present invention is also an image depth estimation method based on atrous convolution and semi-supervised learning, which utilizes deep learning to estimate the depth of an input single image. Realized on the system, the image depth estimation system based on hole convolution and semi-supervised learning is the same as embodiment 1-2, see figure 2 , including the following steps:
[0036] Step 1: Build a deep learning network model based on hole convolution: use hole convolution in the model to form a network structure composed of a decoder module, a hole convolution module and a decoder module; the network structure is characterized by The atrous convolution module, encoder module and decoder module have a symmetrical structure and are skip-connected.
[0037]Step 2: Obtain training set and test set: the training set and test set are composed of stereo image pairs and corresponding depth maps, and the number of training sets is expanded; the acquisition of train...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com