A Quantitative Calculation Method for Unbalance Responsibility at Common Coupling Points in Power Distribution System
A public coupling point and power distribution system technology, applied in the direction of reducing asymmetry of multi-phase network, eliminating/reducing asymmetry of multi-phase network, etc., can solve problems such as three-phase voltage imbalance, and achieve the effect of simple and practical method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
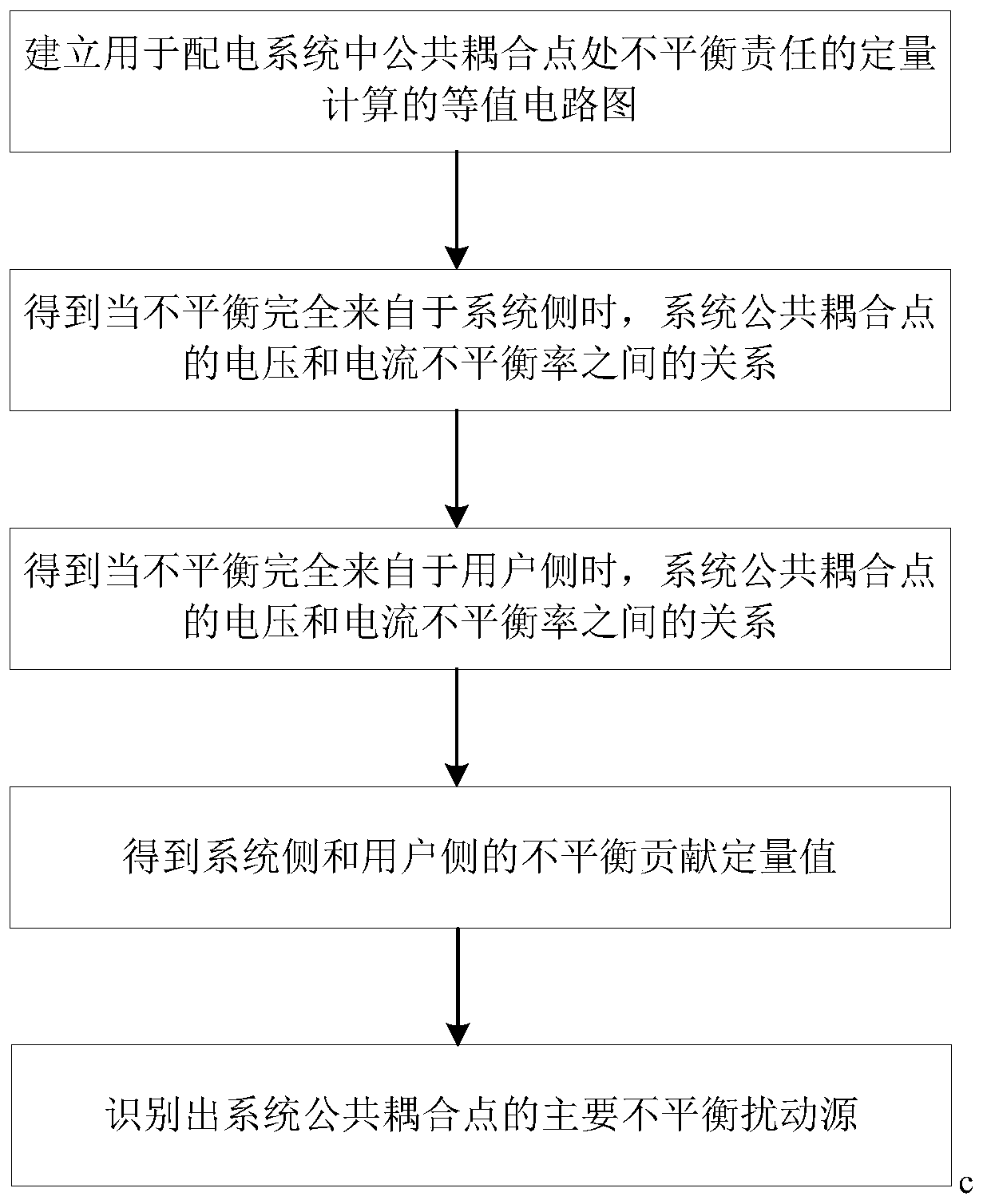
Embodiment
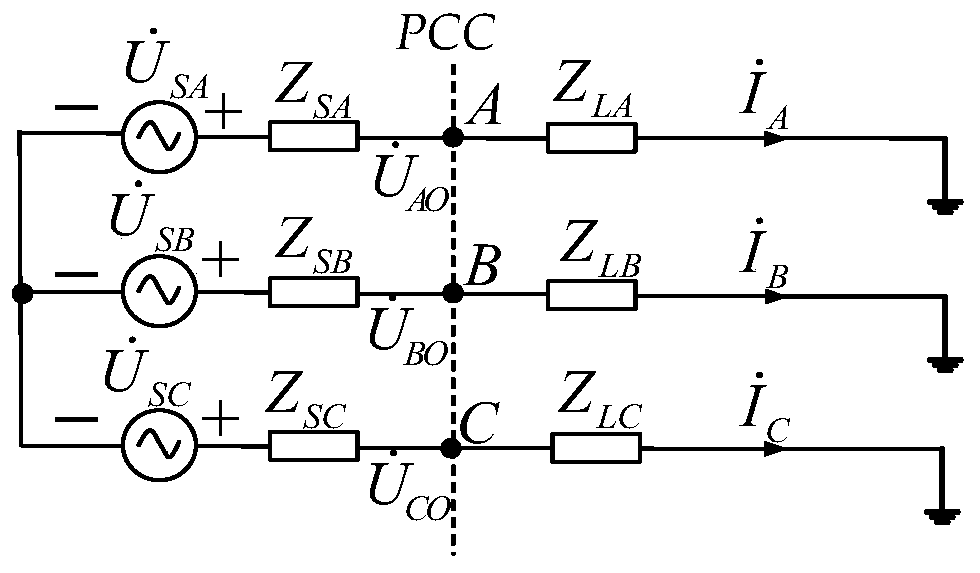
[0074] The system diagram of this embodiment is as follows Figure 4 shown. Among them, the PCC point is the common connection point, is the equivalent voltage source of the power supply system, Z System is the equivalent impedance on the system side, Z Line is the line impedance, Z PL stands for passive load, Z IM Represents a three-phase induction motor load.
[0075] Figure 4 The basic parameters of the system are:
[0076] Power supply system: 10kV, 50Hz, three-phase three-wire
[0077] System Impedance: Z System =(0.0365+j0.1966)Ω
[0078] Transmission line: the length is 5km, and the line impedance matrix (per km) is:
[0079]
[0080] Passive load: total capacity is 5MVA, power factor is 0.95
[0081] Induction motor load: the total capacity is 2.4MVA
[0082] Parameters of induction motor: 6.0kV, 200kW, 50Hz, R s =0.0464p.u.,X s =0.0585 p.u., R r =0.0132p.u.,X r =0.0585p.u.,X m = 1.2056p.u. and J = 398.0kg / m 2 .
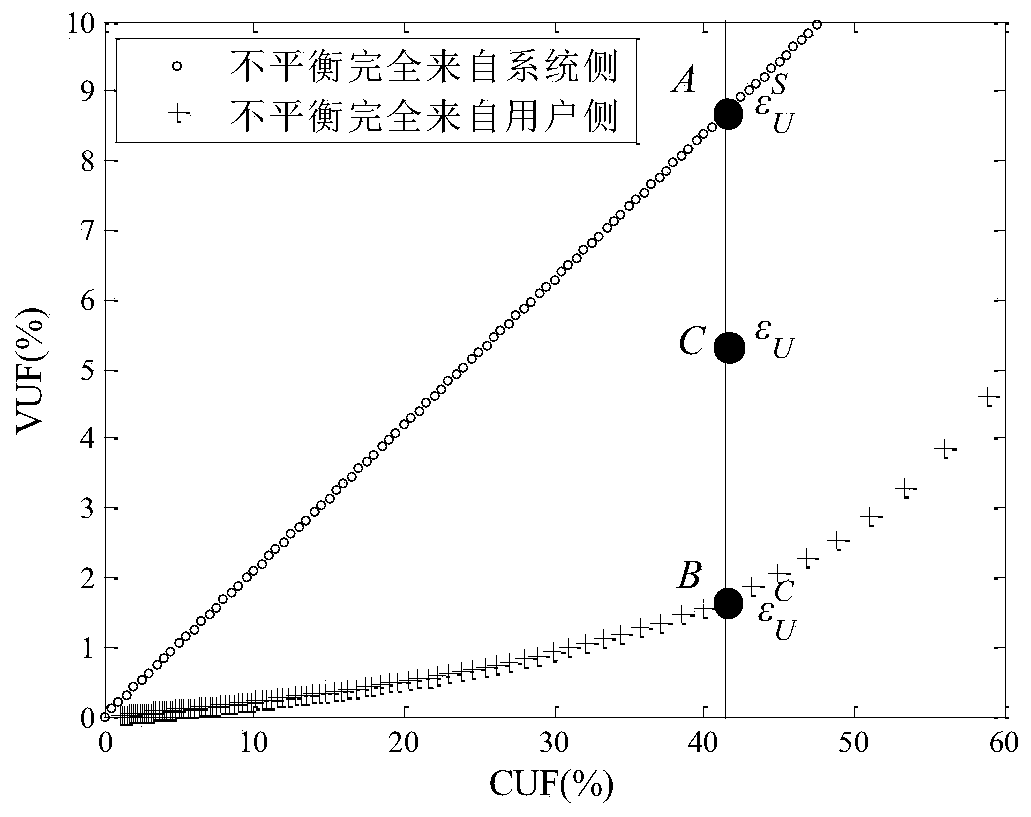
[0083] Change the load and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com