Dynamic root key generating method
A technology for dynamically generating and rooting keys, applied in electrical components, wireless communications, security devices, etc., can solve problems such as key leakage, and achieve the effect of security protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
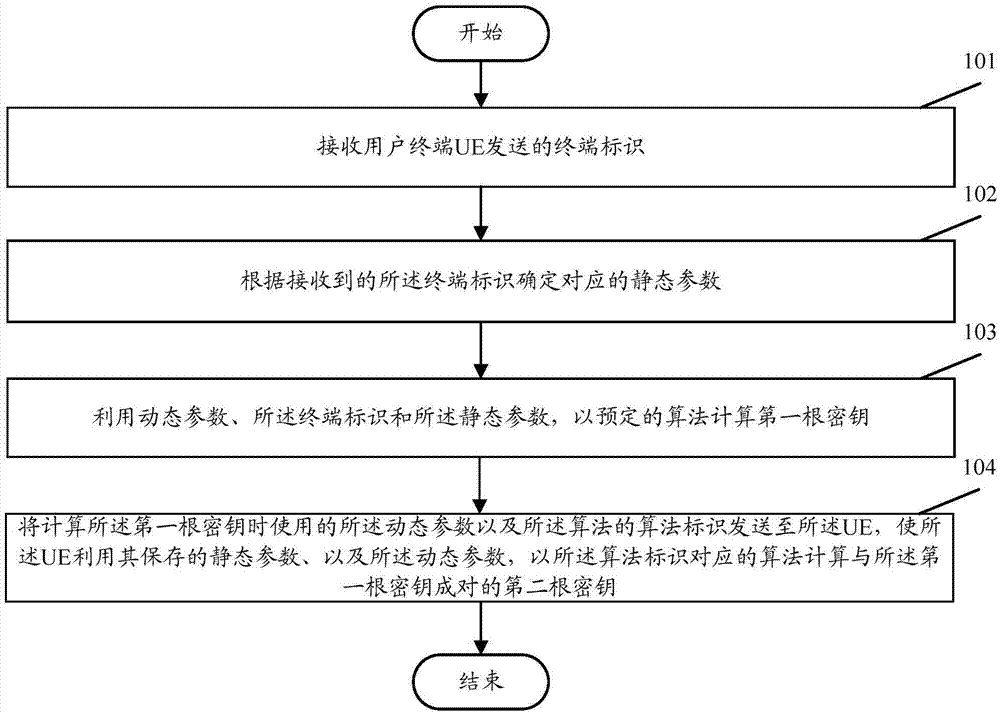
[0034] figure 1 It is a flowchart of an embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 1 As described, this embodiment includes the following steps performed in the core network:
[0035] Step 101: Receive a terminal identifier sent by a user terminal UE.
[0036] In this step, the core network receives the terminal identifier sent by the UE, and the terminal identifier is carried in the request message.
[0037] Wherein, the terminal identifier of the UE can uniquely identify the UE, preferably, an International Mobile Subscriber Identification Number (IMSI) can be used as the terminal identifier of the UE.
[0038] Step 102: Determine corresponding static parameters according to the received terminal identifier.
[0039] In this step, the core network determines the corresponding static parameters according to the received terminal identification of the UE. Specifically, the core network has pre-saved the correspondence table between the terminal identification of th...
Embodiment 2
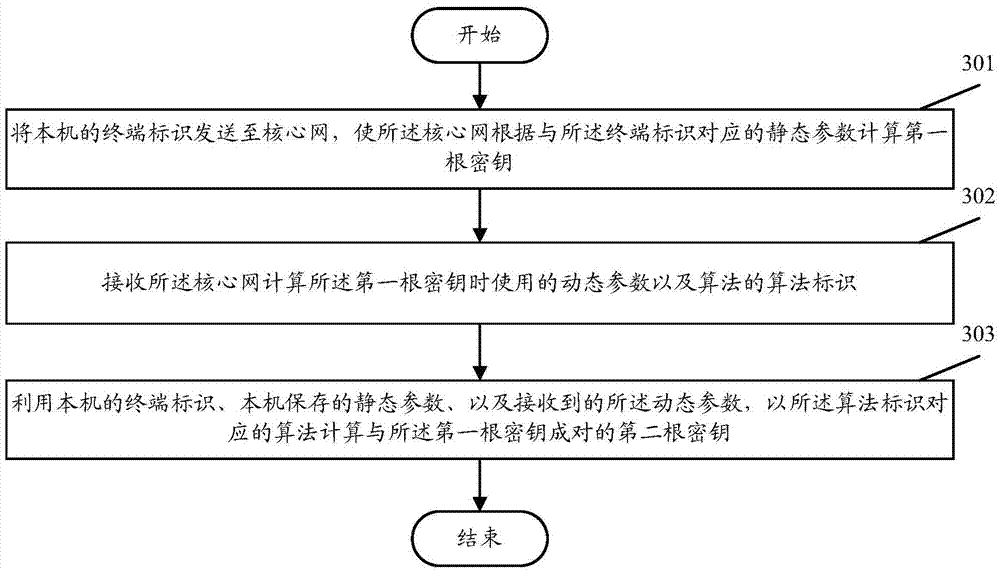
[0050] image 3 is another embodiment of the present invention, such as image 3 As mentioned above, this embodiment includes the following steps performed at the user terminal UE:
[0051] Step 301: Send the terminal identification of the local machine to the core network, so that the core network calculates the first root key according to the static parameters corresponding to the terminal identification.
[0052] In this step, it is embodied in that the UE initiates the authentication and authentication process with the core network, and sends the local terminal identification to the core network, so that the core network calculates the first root key according to the static parameters corresponding to the terminal identification . The steps for the core network to calculate the first root key are detailed in Embodiment 1 and will not be repeated here.
[0053] In actual implementation, the UE may send its own terminal identifier to the core network by carrying its own t...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Figure 4 Be the flow chart of this embodiment, such as Figure 4 shown, including the following steps:
[0064] Step 401: UE sends a request packet carrying its own IMSI to the core network.
[0065] Step 402: The core network receives the request message, and determines the corresponding public key according to the IMSI carried in the request message.
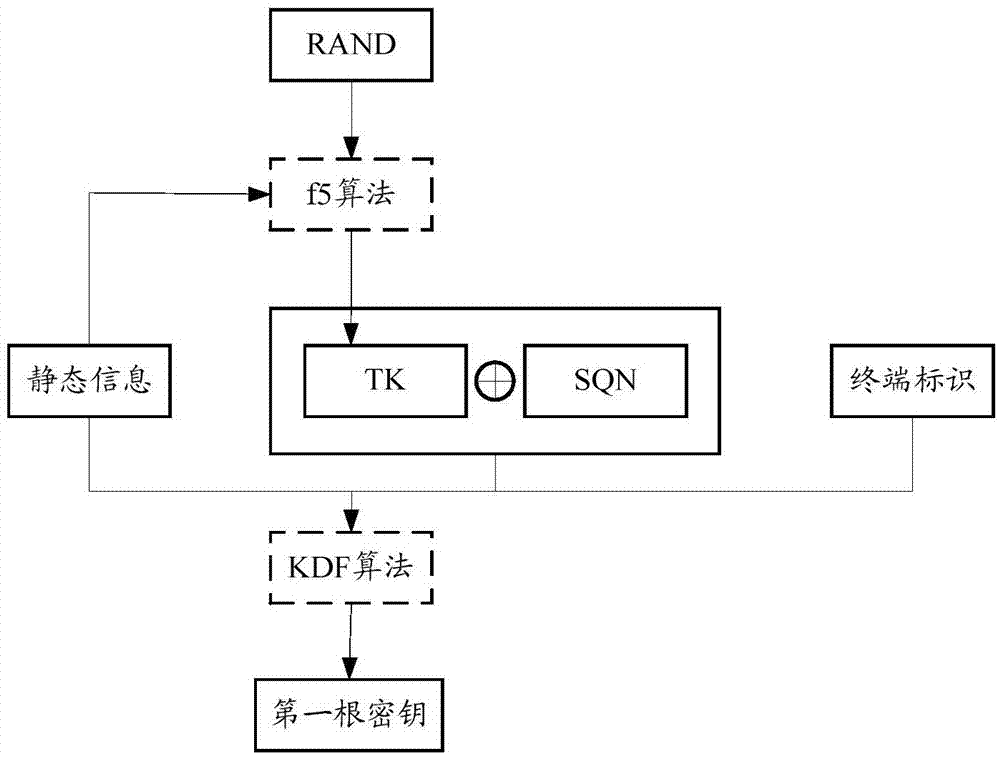
[0066] Step 403: The core network dynamically generates an original random number R1, calculates R1 and IMSI through the f5 algorithm to obtain a random number TK1, and determines another dynamic parameter SQN.
[0067] Step 404: Using TK1, SQN, the received IMSI and the determined public key, calculate the first root key with the KDF algorithm.
[0068] Step 405: Establish its own key system according to the calculated first root key.
[0069] Step 406: Delete the first root key.
[0070] Step 407: Send an acknowledgment message to the UE, the acknowledgment message carrying the algorithm identification S of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com