Ad Hoc One-way Link Network Decentralized Distributed Fast Consensus Method
A one-way link and distributed technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as uncertainty of convergence accuracy, high energy consumption of nodes, and large amount of calculation of nodes, so as to reduce the number of nodes and the amount of information interaction, and avoid information redundancy. In addition, the effect of saving frequency band resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
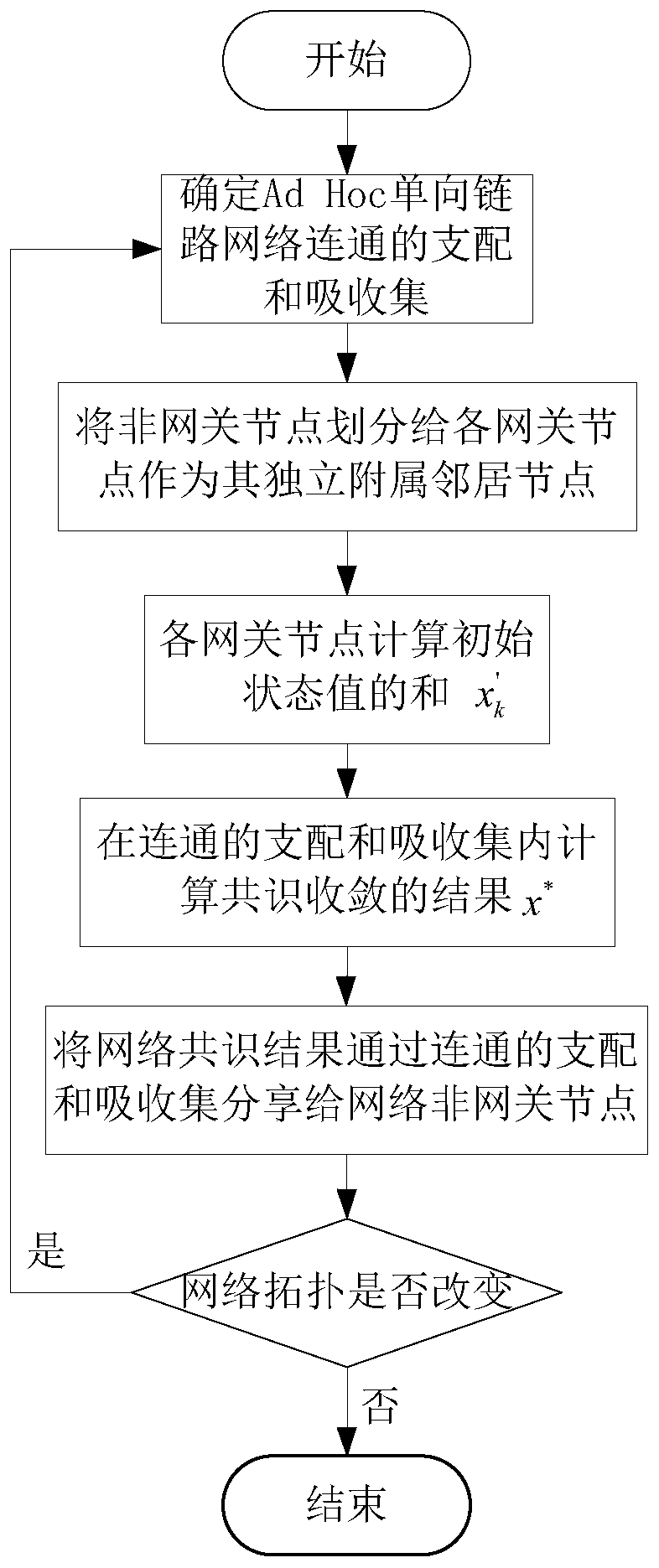
[0035] Ad Hoc network is a special wireless mobile network whose main characteristics are limited bandwidth, unconstrained mobility and low energy. In many cases, Ad Hoc network nodes are limited by available resources such as energy and limited bandwidth. The network often has no control center, and the distributed algorithm to be executed is simple and time-efficient.
[0036] However, in the information diffusion link and iterative calculation link of the existing algorithm, when the number of network nodes is large and the information diffusion path is very long, the information diffusion speed is slow, the algorithm convergence speed is slow, the node calculation amount is large, and the node energy consumption is high, resulting in a distributed network. The consensus algorithm has low efficiency, high energy consumption, and poor real-time performance. More importantly, there is uncertainty in the accuracy of the convergence link. The reduced reliability directly affects...
Embodiment 2
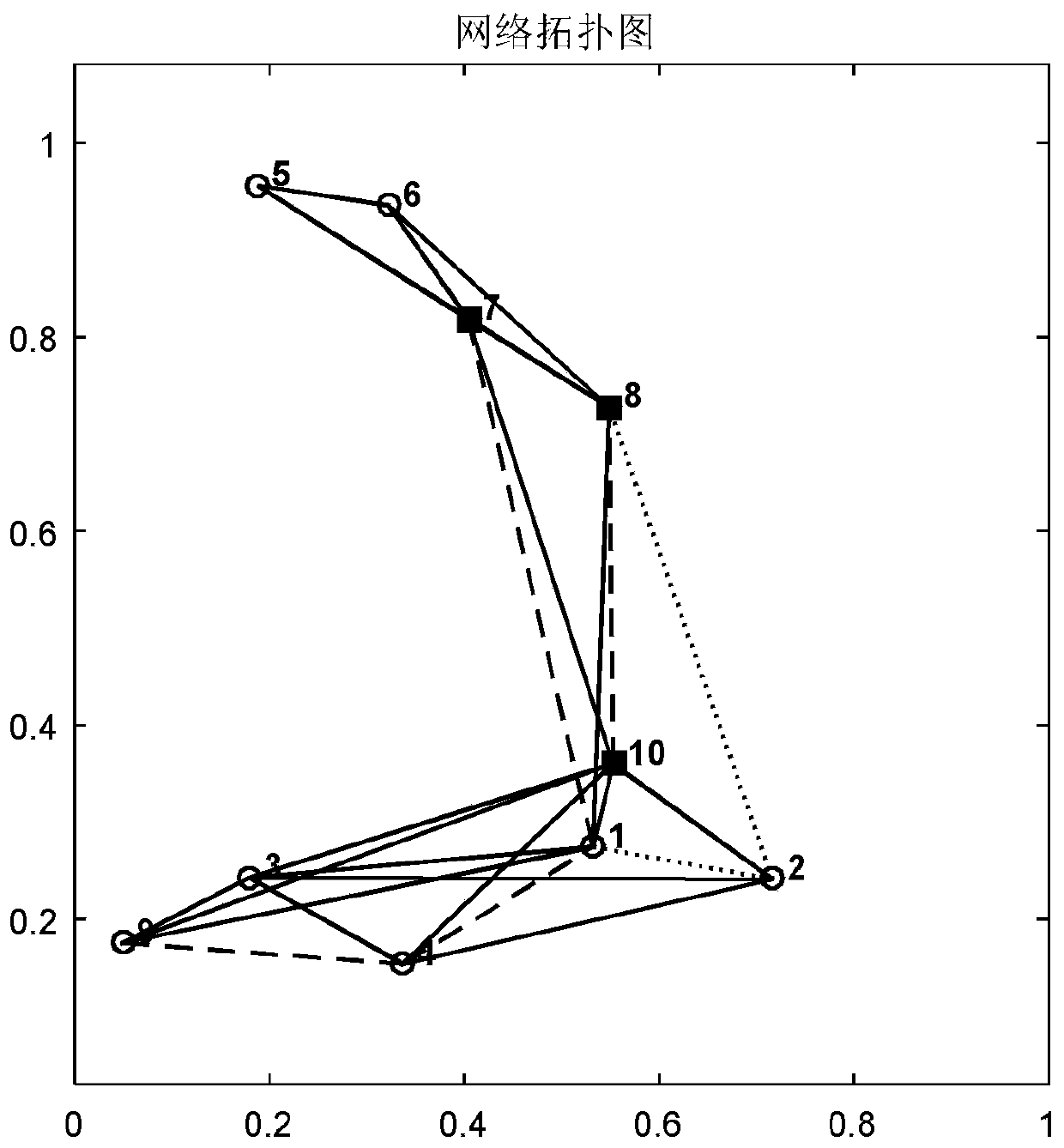
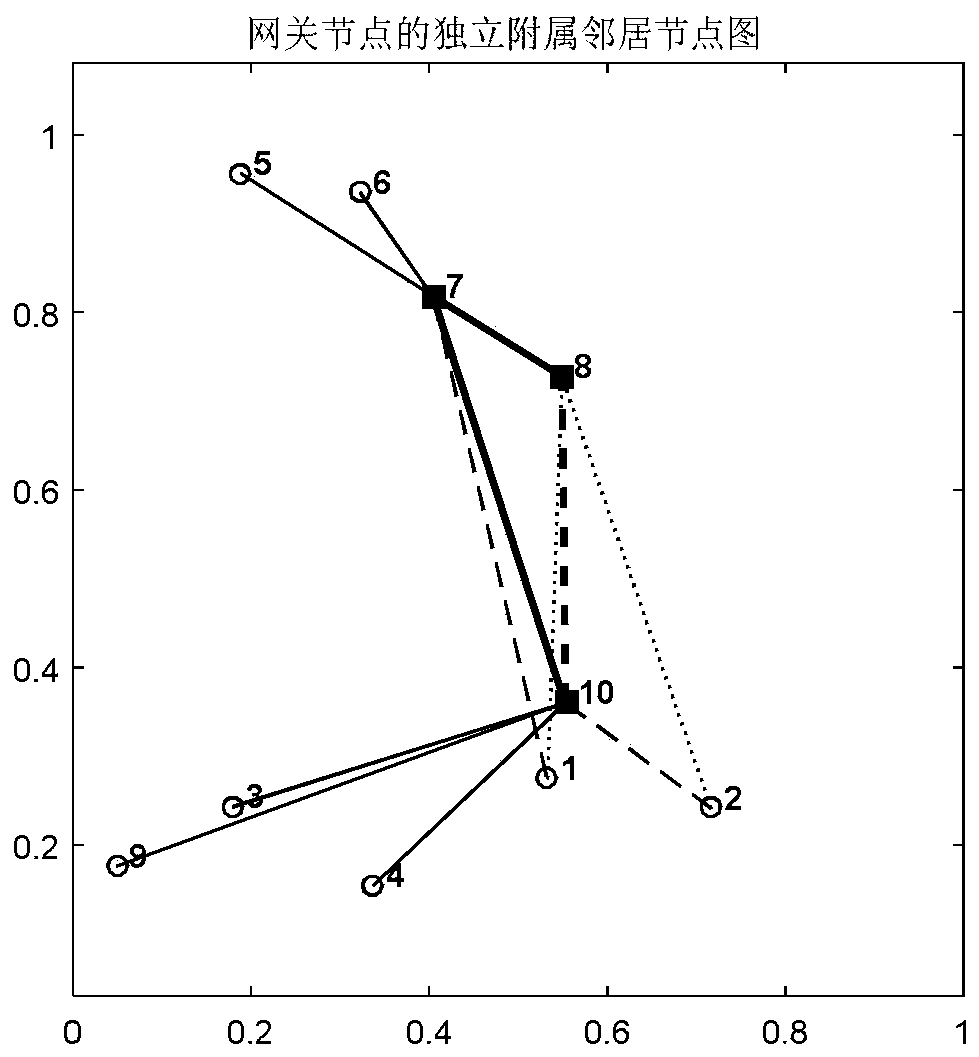
[0047] The centerless distributed fast consensus method for Ad Hoc unidirectional link network is the same as that of Embodiment 1. The independent subordinate dominant neighbor and the independent subordinate absorbing neighbor described in step 2 are respectively: if a non-gateway node has only one gateway dominant neighbor, then the non-gateway node has only one gateway dominant neighbor. A gateway node is divided into independent subordinate absorbing neighbors of the gateway node. If a non-gateway node has only one gateway absorbing neighbor, the non-gateway node is divided into independent subordinate dominating neighbors of the gateway node; if a non-gateway node has multiple gateway dominating neighbor nodes , then select one of the gateway nodes according to the criteria of proximity or link status, and divide the non-gateway node to the selected gateway node as its independent subordinate absorbing neighbor. If the non-gateway node has multiple gateway absorbing neighb...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Ad Hoc unidirectional link network centerless distributed fast consensus method is the same as embodiment 1-2. In step 3, the independent initial state collection value x' of gateway node k is obtained k , specifically using the state variable x i Represents the initial state value of network node i. For gateway node k=1,...,|V'|, |V'| is the number of nodes in the connected dominating absorbing set V', and the independent subordinate dominating neighbors of gateway node k represent for F k , |F k |represents the number of independent subordinate dominant neighbors of gateway node k; each gateway node k performs the calculation:
[0050]
[0051] where x' k Represents the independent initial state collection value of gateway node k, which is the initial state and value of all independent affiliated neighbors of gateway node k. and gateway node k initial state value x k The added sum value.
[0052] The invention utilizes network subsets to connect, dominate an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com