Lead storage battery matching method
A technology for lead-acid batteries and storage batteries, which is applied in the field of lead-acid storage batteries, and can solve the problems of not being able to remove batteries well, and not being able to fully reflect the differences of different single batteries.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Conduct a 2-hour volume inspection after formation.
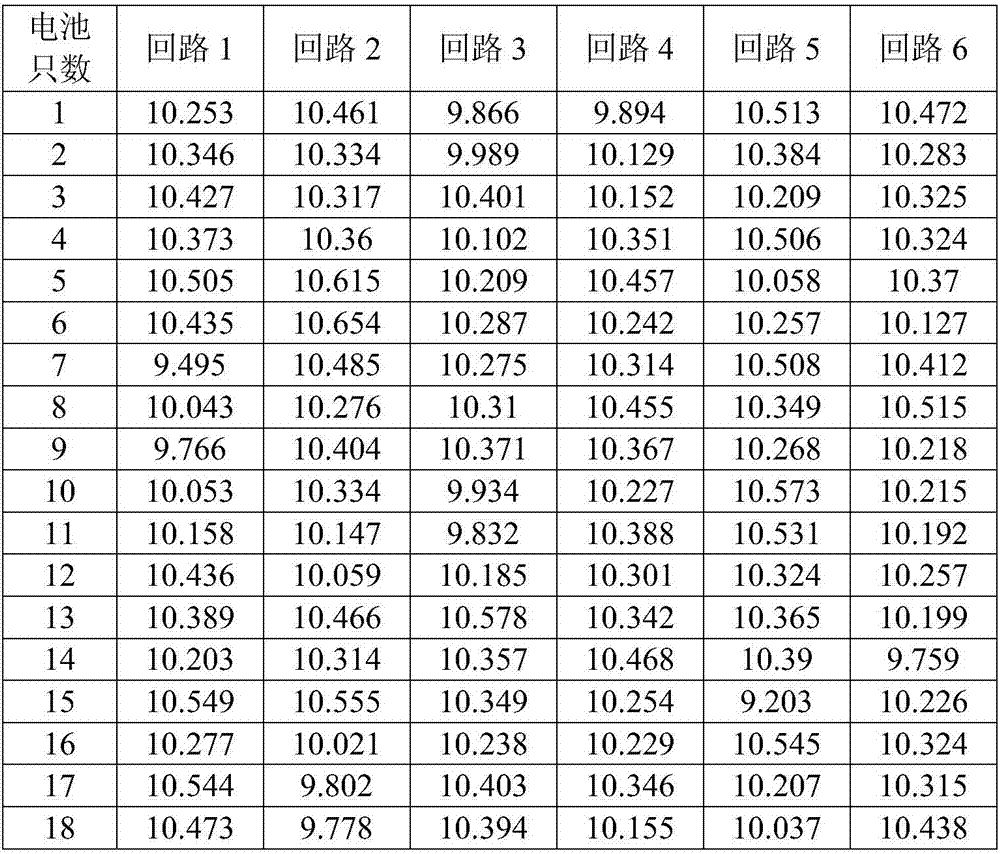
[0028] 6-DZM-20 battery, the number of formed batteries is 108 (a total of 6 circuits, 18 for each circuit). When the average voltage of the control circuit is 10.2V / piece, the discharge time is 124.5 minutes, and the voltage collected at this time is used for capacity inspection and classification, and the discharge time difference between each circuit is within 30 seconds).
[0029] Table 1
[0030]
[0031] (2) 2-hour capacity inspection and classification.
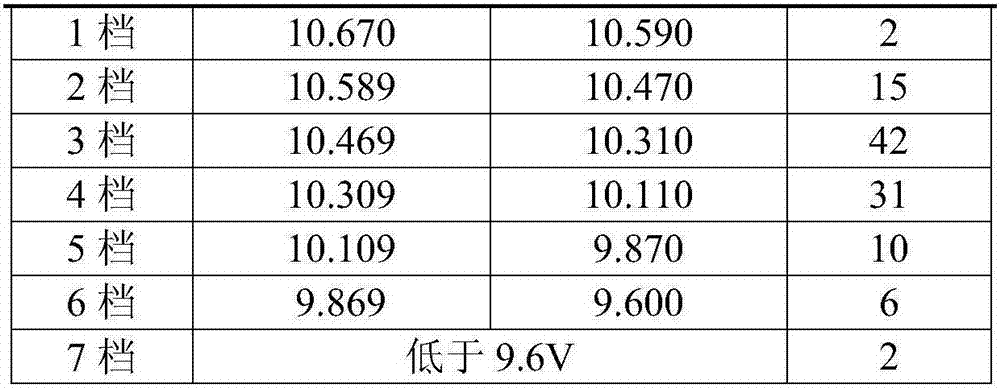
[0032] The above-mentioned 108 single batteries are classified according to the setting value of the classification, and are divided into 7 grades. The classification results are shown in Table 2. The two batteries lower than 9.6V do not enter the subsequent matching group.
[0033] Table 2
[0034]
[0035]
[0036] (3) Internal resistance detection and large current discharge.
[0037] After the completion of the formation, let it stand for...
Embodiment 2
[0047] (1) Conduct a 2-hour volume inspection after formation.
[0048] 6-DZM-20 battery, the number of formed batteries is 108 (a total of 6 circuits, 18 for each circuit). When the average voltage of the control circuit is 10.2V / piece, the discharge time is 124.5 minutes, and the voltage collected at this time is used for capacity inspection and classification, and the discharge time difference between each circuit is within 30 seconds).
[0049] Table 6
[0050]
[0051]
[0052] (2) 2-hour capacity inspection and classification.
[0053] The above-mentioned 108 single batteries are classified according to the setting value of the classification, and are divided into 10 grades. The classification results are shown in Table 7, and the two batteries lower than 9.6V do not enter the subsequent grouping.
[0054] Table 7
[0055]
[0056] (3) Internal resistance detection and large current discharge.
[0057] After the completion of the formation, let it stand for 36...
Embodiment 3
[0069] (1) Perform a 2-hour volume inspection after formation.
[0070] 6-DZM-12 battery, the number of formed batteries is 108 (a total of 6 circuits, 18 for each circuit). The formation process adopts a conventional three-day process. When the average voltage of the control circuit is 10.2V / piece, the discharge time is 125 minutes, and the voltage collected at this time is used for capacity inspection and classification, and the discharge time difference between each circuit is within 30 seconds).
[0071] Table 11
[0072]
[0073] (2) 2-hour capacity inspection and classification.
[0074] The above-mentioned 108 single batteries are classified according to the setting value of the classification, and are divided into 5 grades. The classification results are shown in Table 12, and the two batteries lower than 9.6V do not enter the subsequent grouping.
[0075] Table 12
[0076]
[0077] (3) Internal resistance detection and large current discharge.
[0078] After...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com