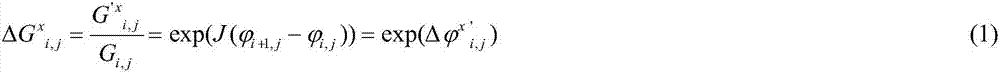Phase unwrapping method based on least square method
A least-squares method and unwrapping technology, applied in measurement devices, instruments, optical devices, etc., can solve the problems of too fast phase transformation in local areas, sharpening of the wrapped phase, and undersampling.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
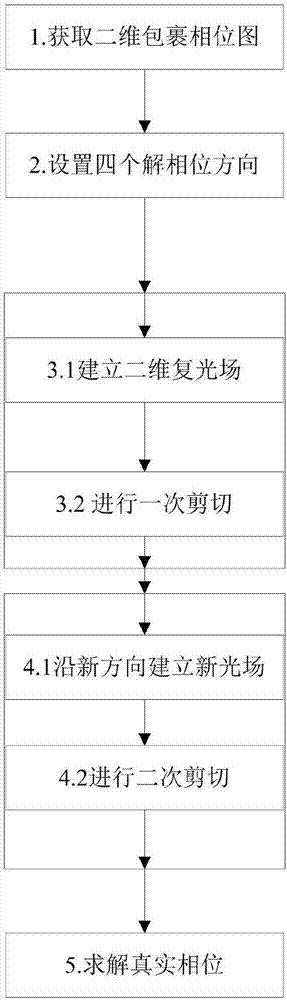
[0015] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples. It should be noted that the described examples are only intended to facilitate the understanding of the present invention, and have no limiting effect on it.
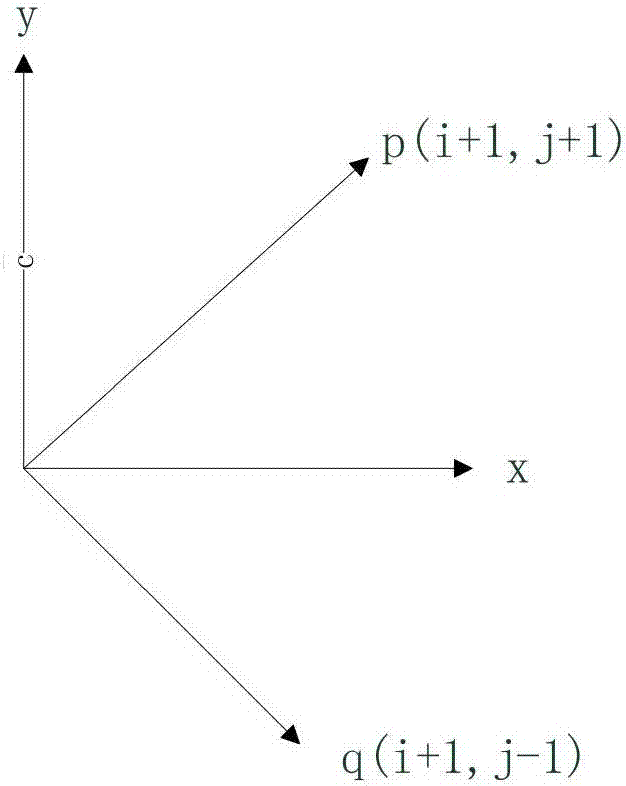
[0016] In this method, the parameter symbols are expressed in the following manner: M is the maximum value of the horizontal coordinate of the wrapped phase image pixel, and N is the maximum value of the vertical coordinate of the wrapped phase image pixel. The wrapping phase is The value range is Where i is the horizontal coordinate value of the wrapped phase image pixel, 0≤i≤M. j is the longitudinal coordinate value of the wrapped phase image pixel, 0≤j≤N. The true phase is φ i,j ,And a k i,j for the package cycle. Δ is the first-order difference of adjacent phases in a certain direction. G x i,j Represents the two-dimensional sheared complex light field, where G represents the complex ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com