A Parallel Method for Domain Decomposition Efficient for Unconditionally Stable Finite-Difference Time-Domain Methods
A finite difference method and domain decomposition technology, applied in the field of large-scale parallel computing, can solve the problems of prolonged simulation time, inability to enlarge the time step, and restrictions on large-scale efficient parallel computing, so as to enlarge the time step and reduce the calculation time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0014] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0015] The present invention is a kind of region decomposition parallel method effective to the unconditional stable time domain finite difference method, and the steps are as follows:
[0016] In the first step, MPI (message passing interface) is initialized, and the three-dimensional computing space is divided into regions according to each direction, the total number of processes is determined, and each process is numbered;
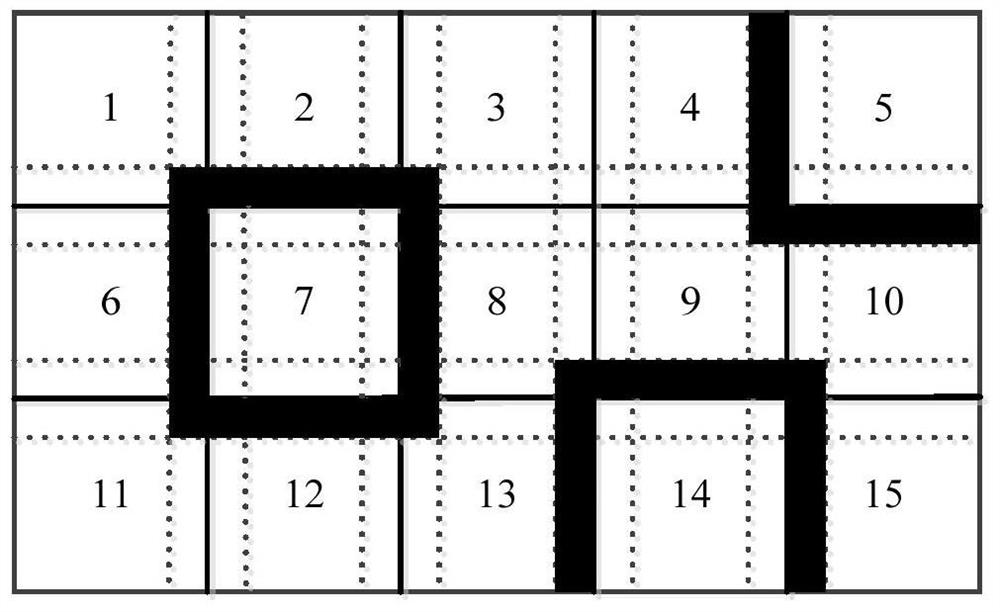
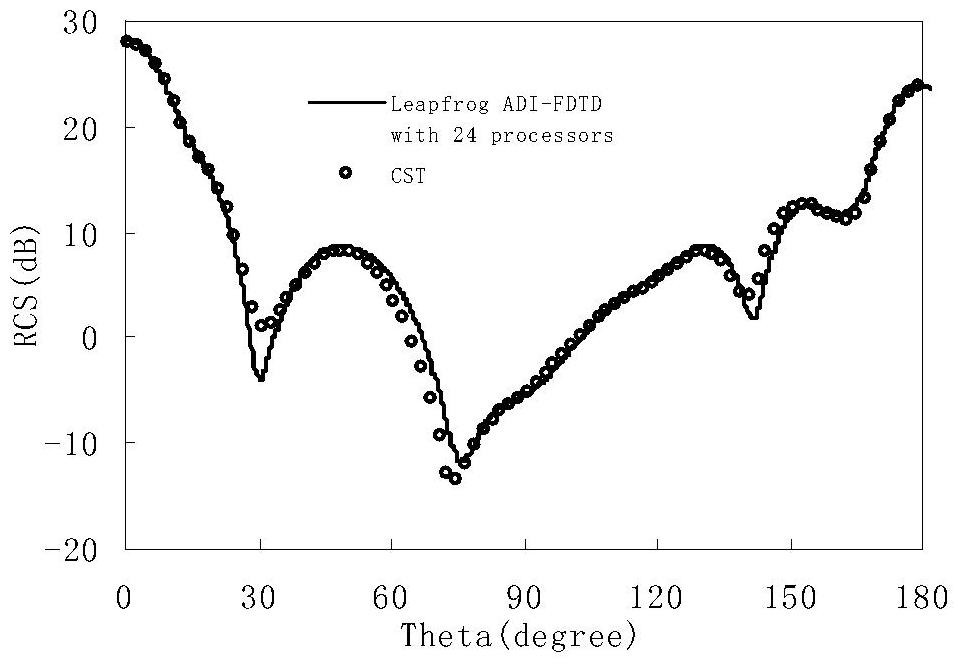
[0017] The second step is to execute the pre-processing of the program, and set the simulation parameters, including the setting of absorbing boundary conditions, the addition of plane waves, etc. attached figure 1 The solid line in is the boundary of the calculation area division in step 1. Each calculation area is expanded outwards to make it intersect with the adjacent calculation area to form a buffer area. For example, the actua...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com