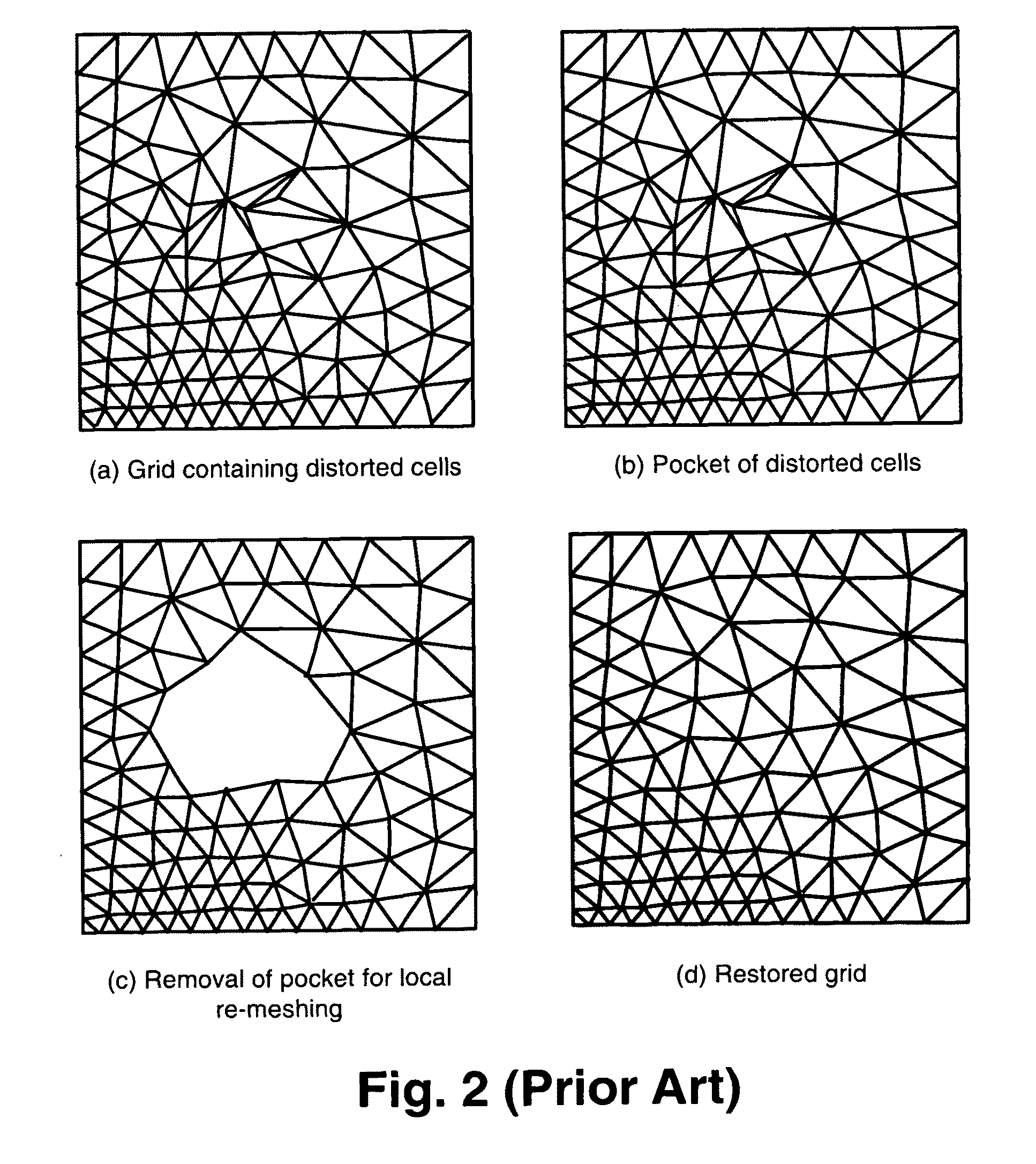
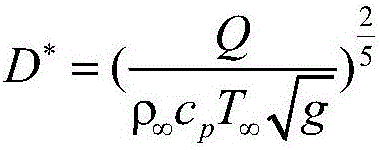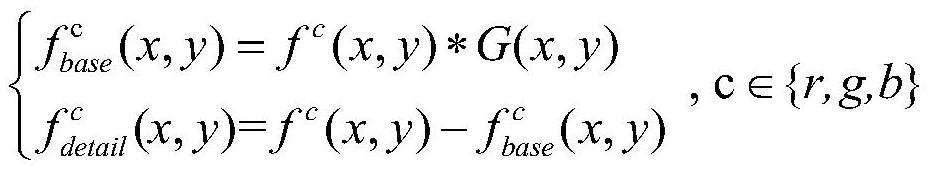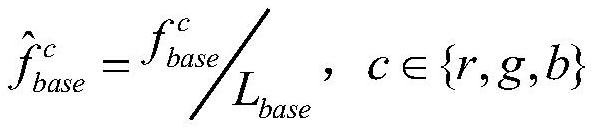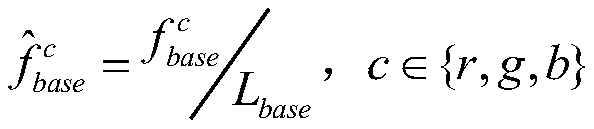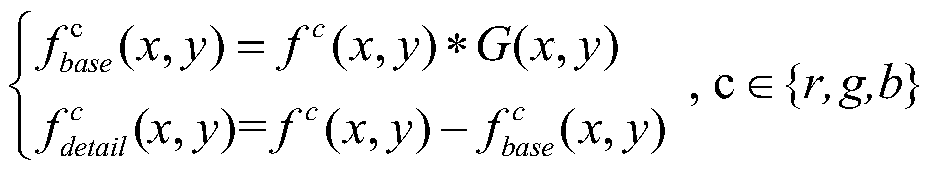Patents
Literature
31 results about "Domain decomposition methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, numerical analysis, and numerical partial differential equations, domain decomposition methods solve a boundary value problem by splitting it into smaller boundary value problems on subdomains and iterating to coordinate the solution between adjacent subdomains. A coarse problem with one or few unknowns per subdomain is used to further coordinate the solution between the subdomains globally. The problems on the subdomains are independent, which makes domain decomposition methods suitable for parallel computing. Domain decomposition methods are typically used as preconditioners for Krylov space iterative methods, such as the conjugate gradient method or GMRES.
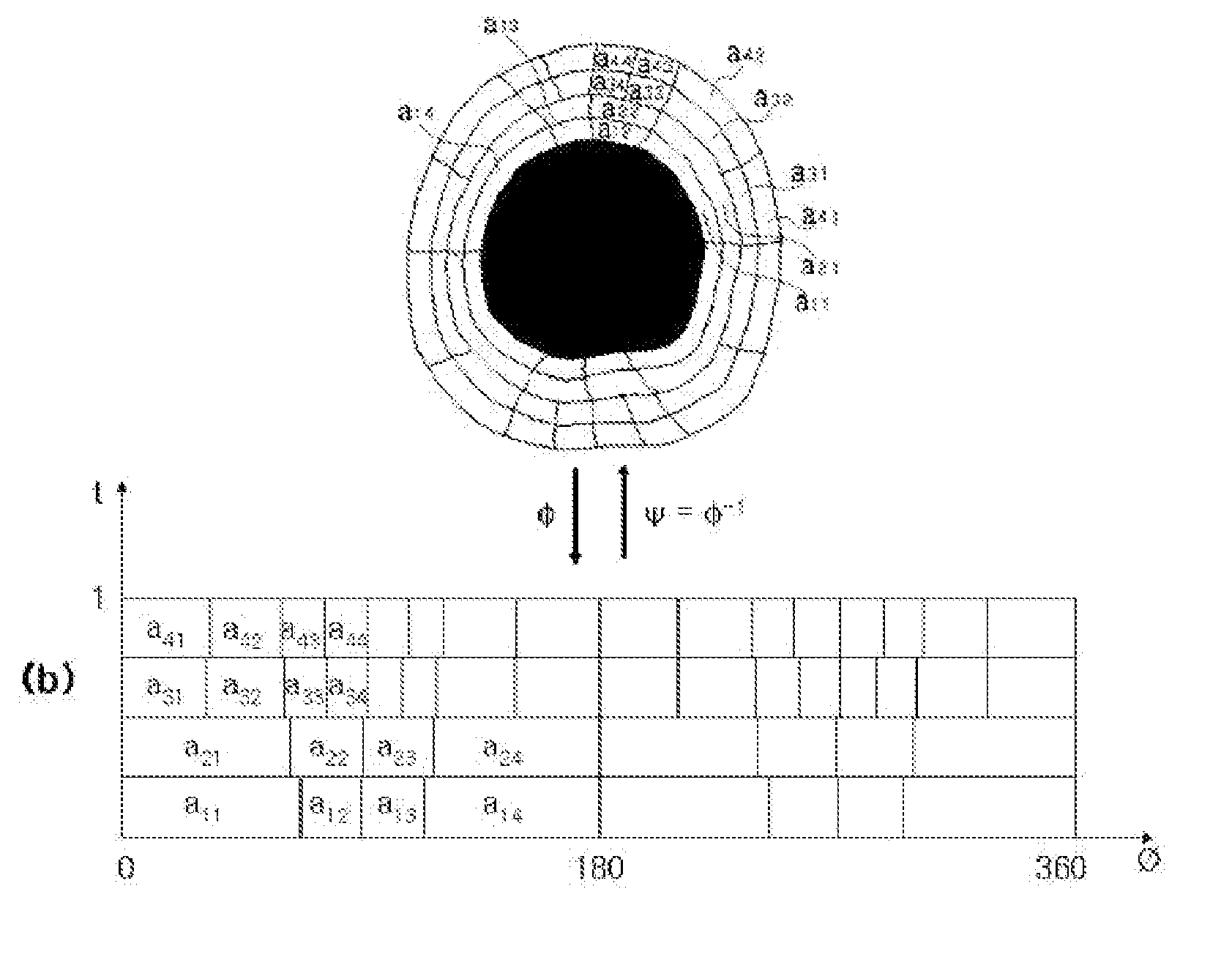
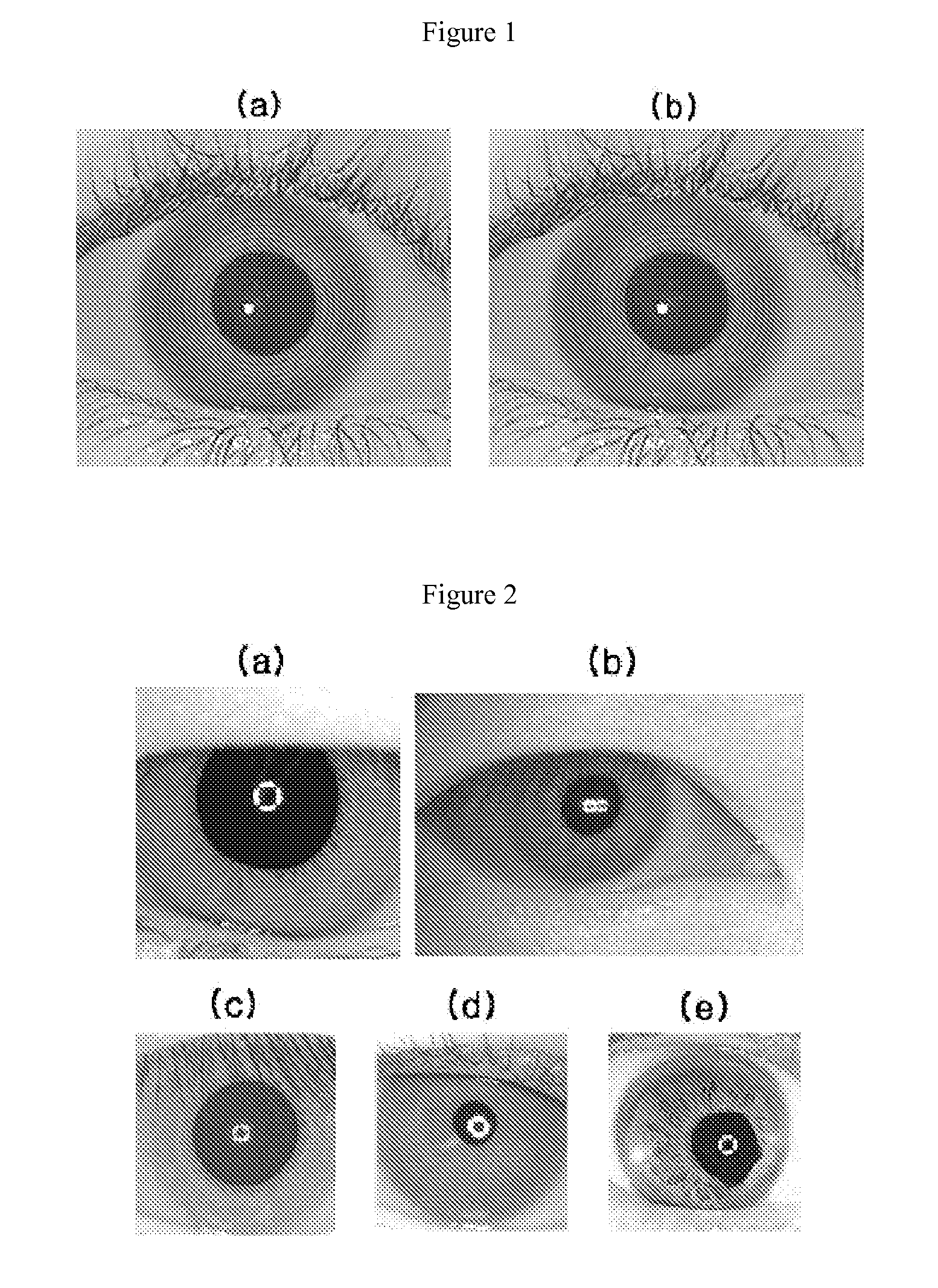
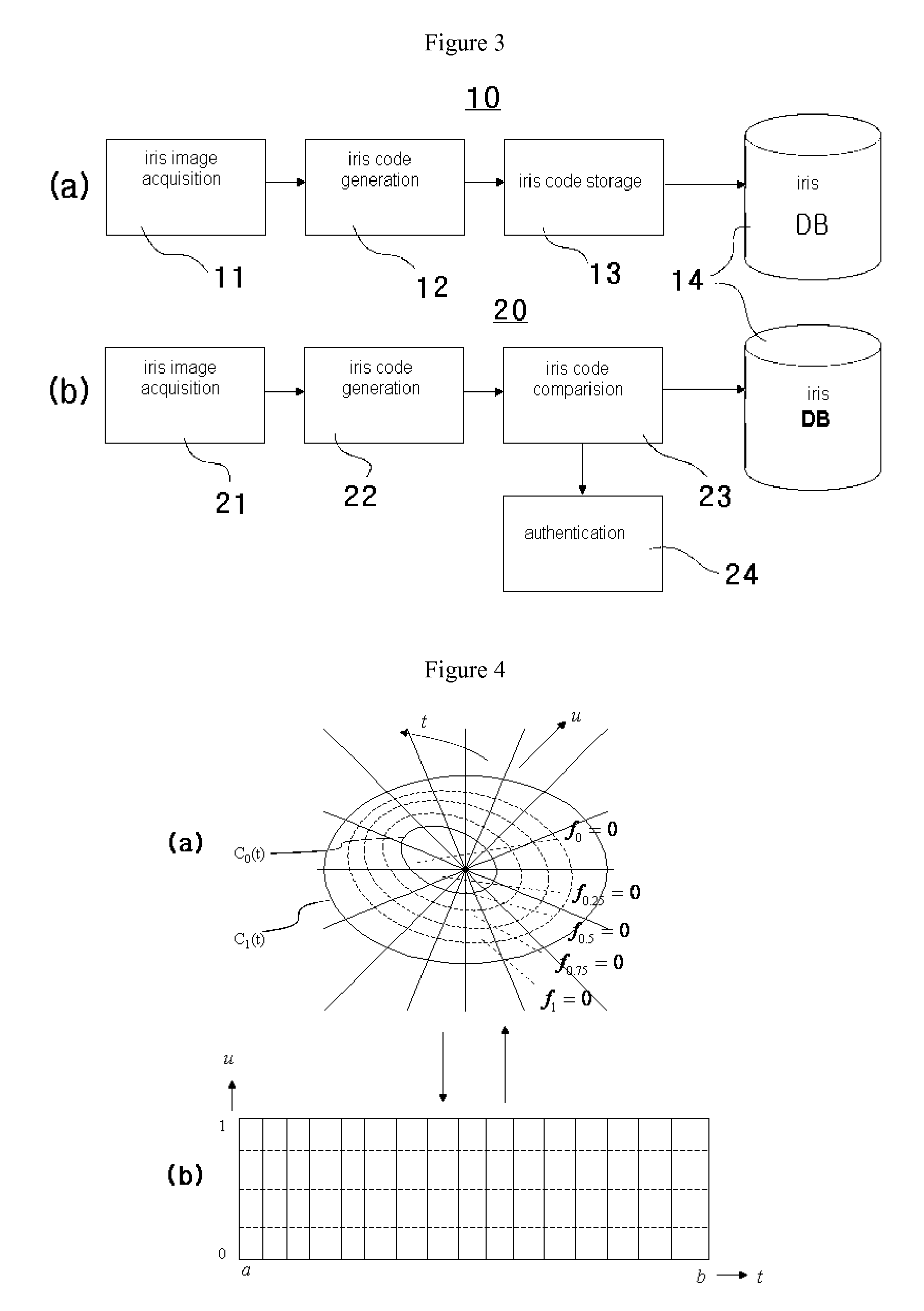
Multi-scale Variable Domain Decomposition Method and System for Iris Identification
InactiveUS20090169064A1Quick identificationDrawing from basic elementsAcquiring/recognising eyesComputer hardwareIris code
The present invention relates to an iris identification method and system, which divide an iris image, which is acquired for personal identification, into a plurality of equal / unequal and multiscale regions, generate a corresponding code corresponding to the respective regions, organizing codes into a database, generate a code at the time of authentication in the same manner, and identify a person by comparing this code with the codes stored in the database, thus improving identification speed and rate.The present invention provides an iris identification method including iris code registration and iris code authentication, the iris code registration including the steps of acquiring iris images by capturing iris using cameras or receiving image files, generating iris codes from the acquired iris images, and storing the generated iris codes in a database, the iris code authentication including the steps of acquiring an iris image in a manner identical to that of the iris code registration, generating an iris code from the acquired iris image, and identifying the generated iris code by comparing the generated iris code with the iris codes stored in the database, wherein the iris code generation step is performed in such a way as to determine the inner and outer boundaries of an iris region by approximating the inner and outer boundaries with general curves based on actual shapes of the inner and outer boundaries, divide a part or all of a region between the inner and outer boundaries into one or more unit sectors, and generate an iris code corresponding to the respective sectors, and the iris code identification step is performed in such a way as to measure the distances of the generated code to the existing codes stored in the database and determine whether each of the distances falls within a threshold value.
Owner:IRITECH
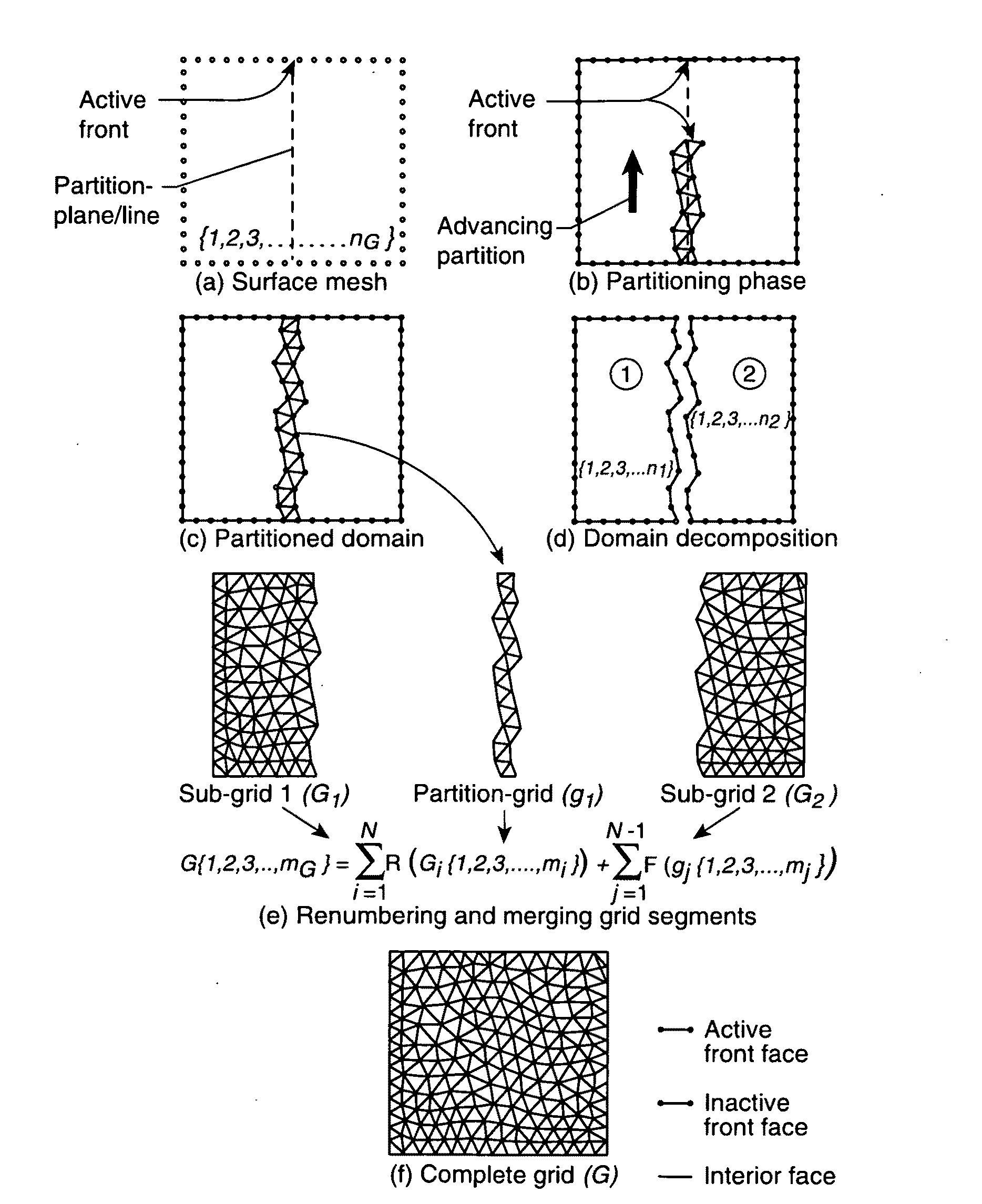
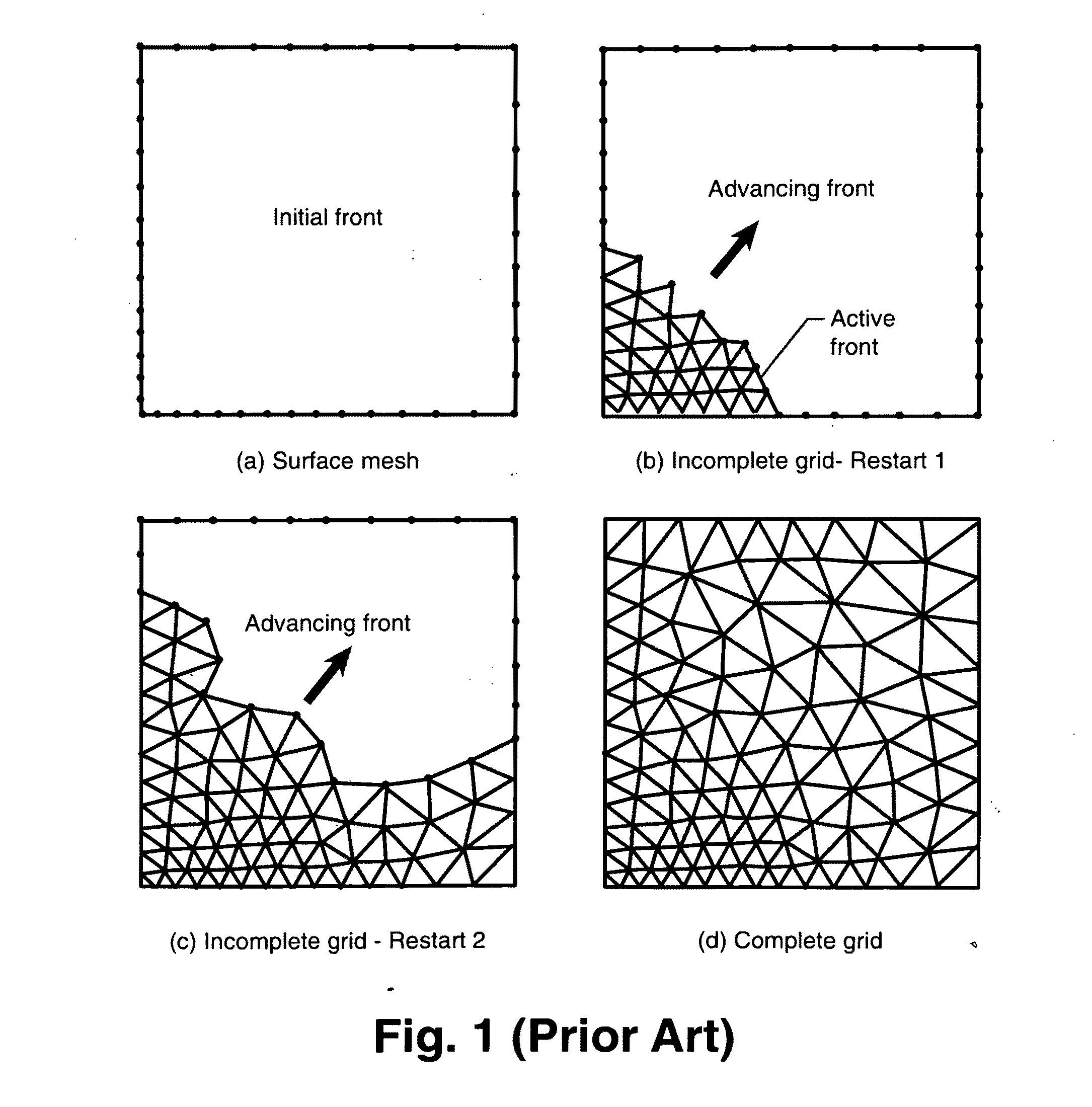
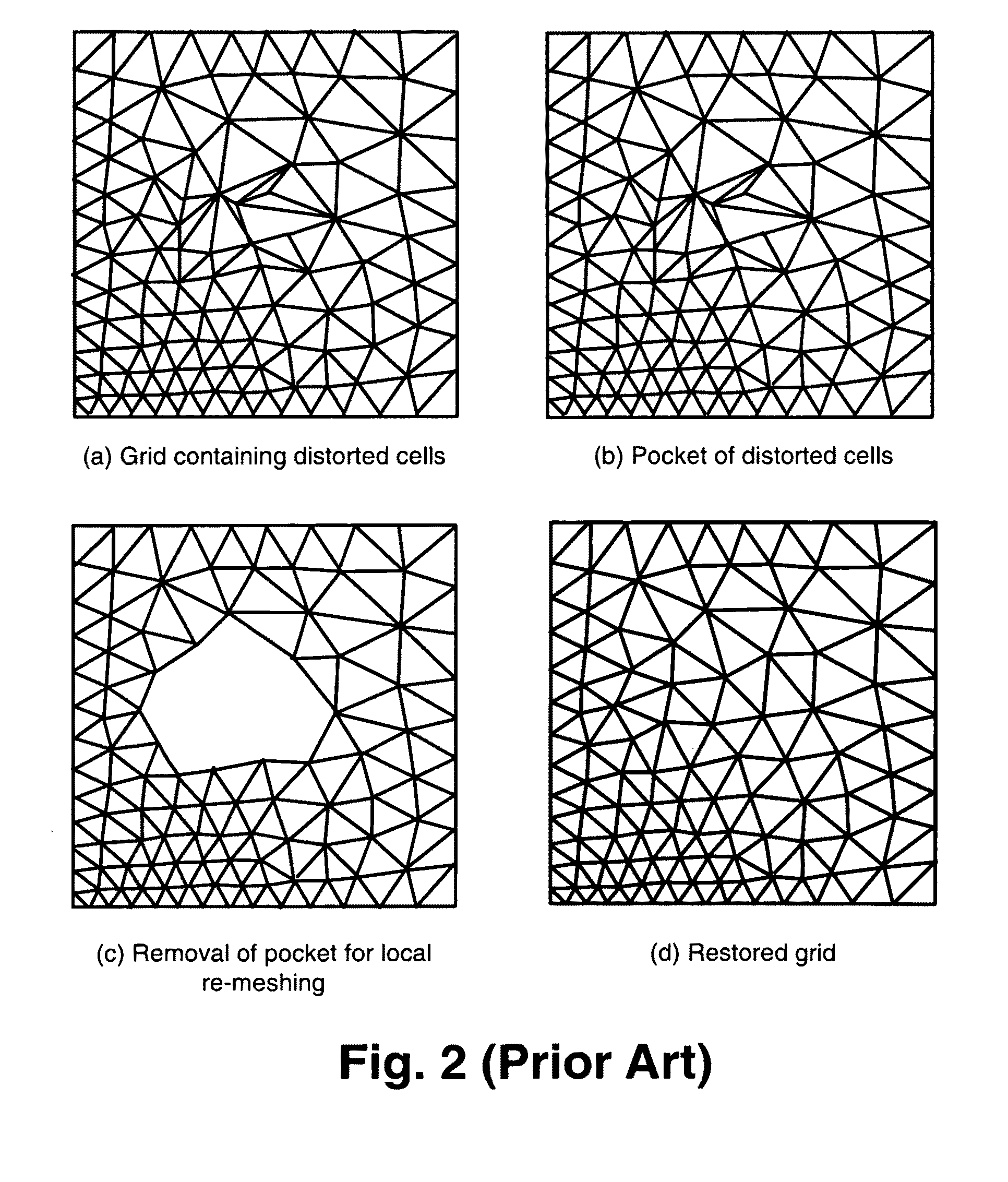
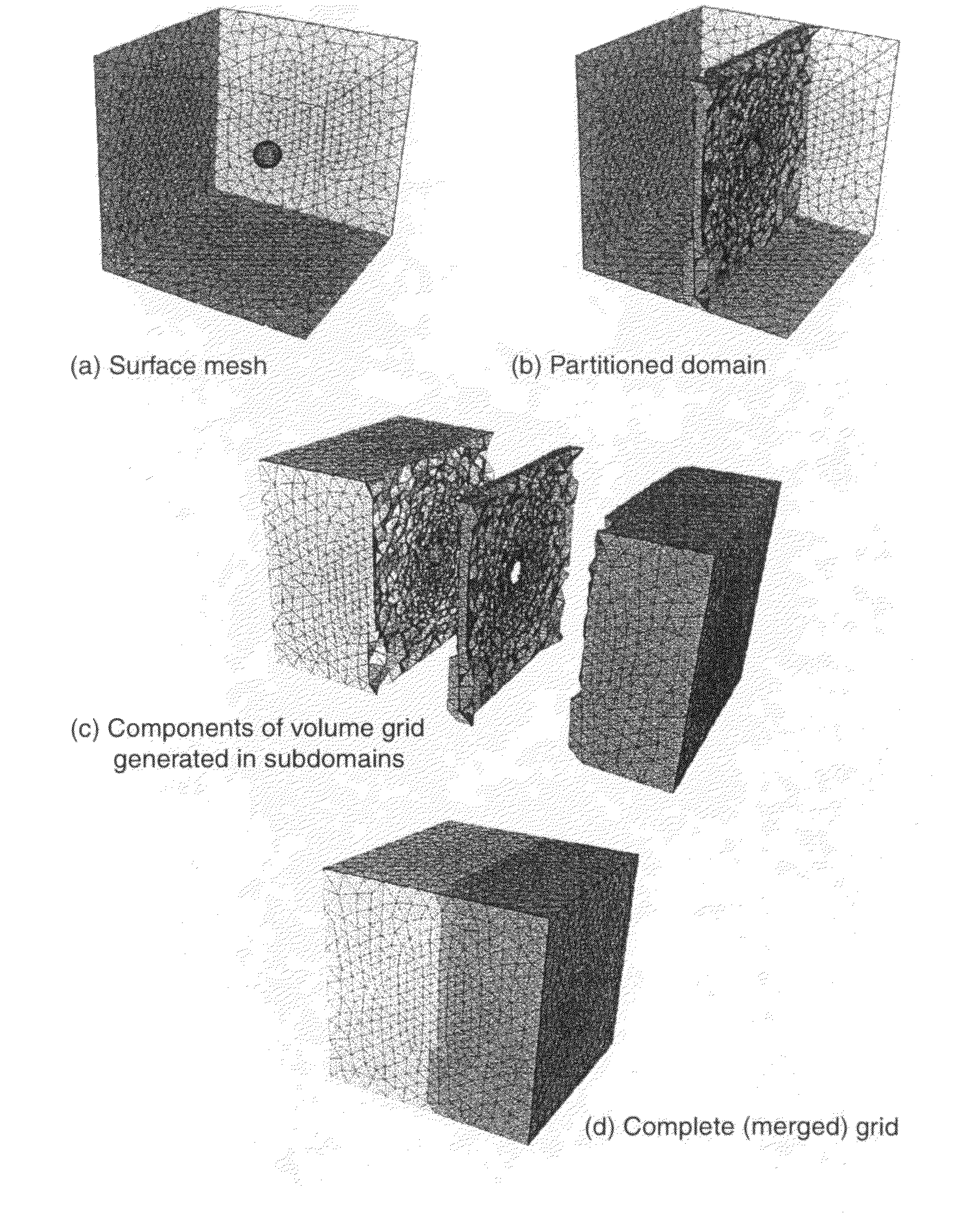
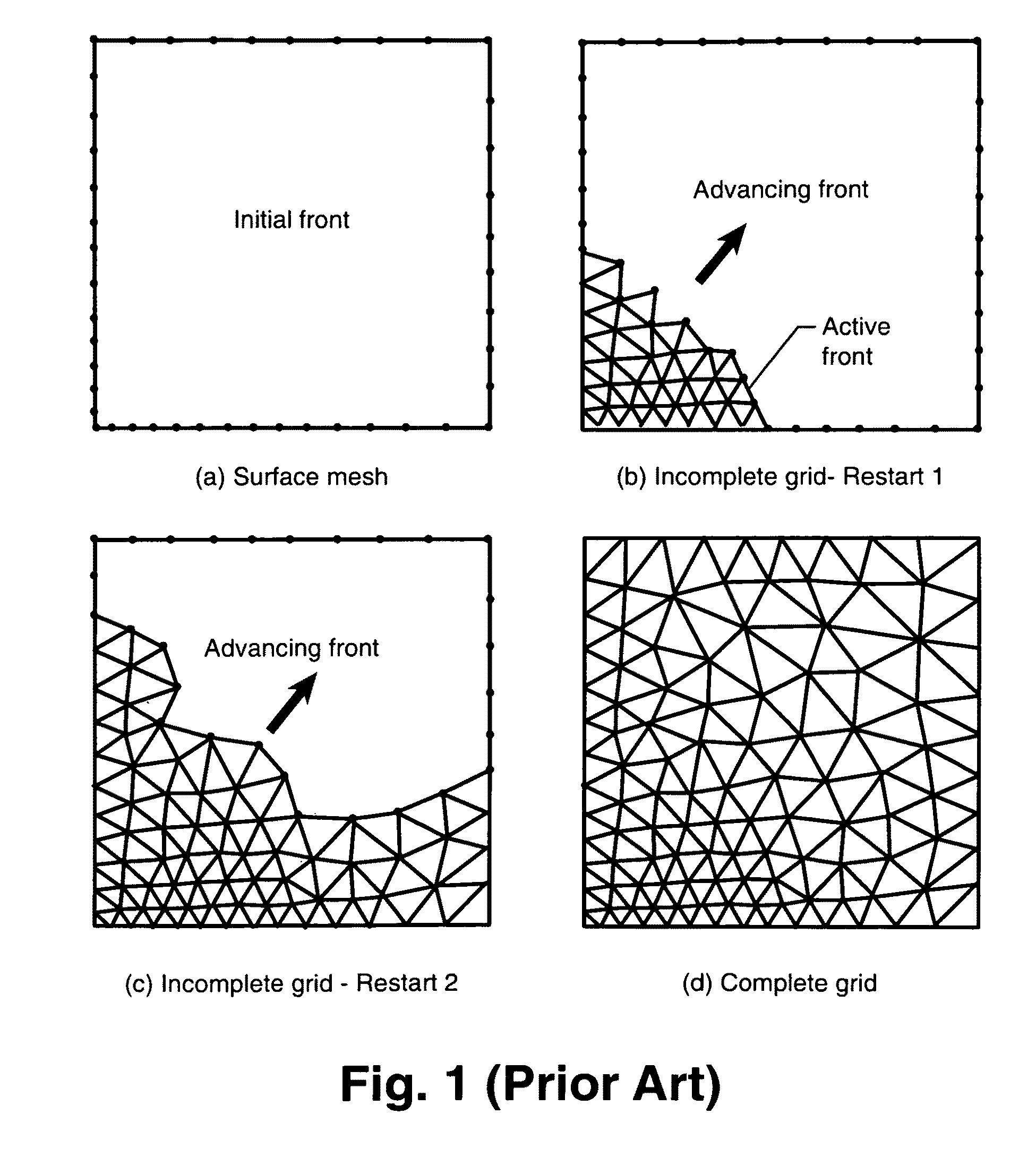
Domain Decomposition By the Advancing-Partition Method for Parallel Unstructured Grid Generation
InactiveUS20100134498A1Drawing from basic elements3D-image renderingDecompositionDomain decomposition methods
In a method for domain decomposition for generating unstructured grids, a surface mesh is generated for a spatial domain. A location of a partition plane dividing the domain into two sections is determined. Triangular faces on the surface mesh that intersect the partition plane are identified. A partition grid of tetrahedral cells, dividing the domain into two sub-domains, is generated using a marching process in which a front comprises only faces of new cells which intersect the partition plane. The partition grid is generated until no active faces remain on the front. Triangular faces on each side of the partition plane are collected into two separate subsets. Each subset of triangular faces is renumbered locally and a local / global mapping is created for each sub-domain. A volume grid is generated for each sub-domain. The partition grid and volume grids are then merged using the local-global mapping.
Owner:NASA
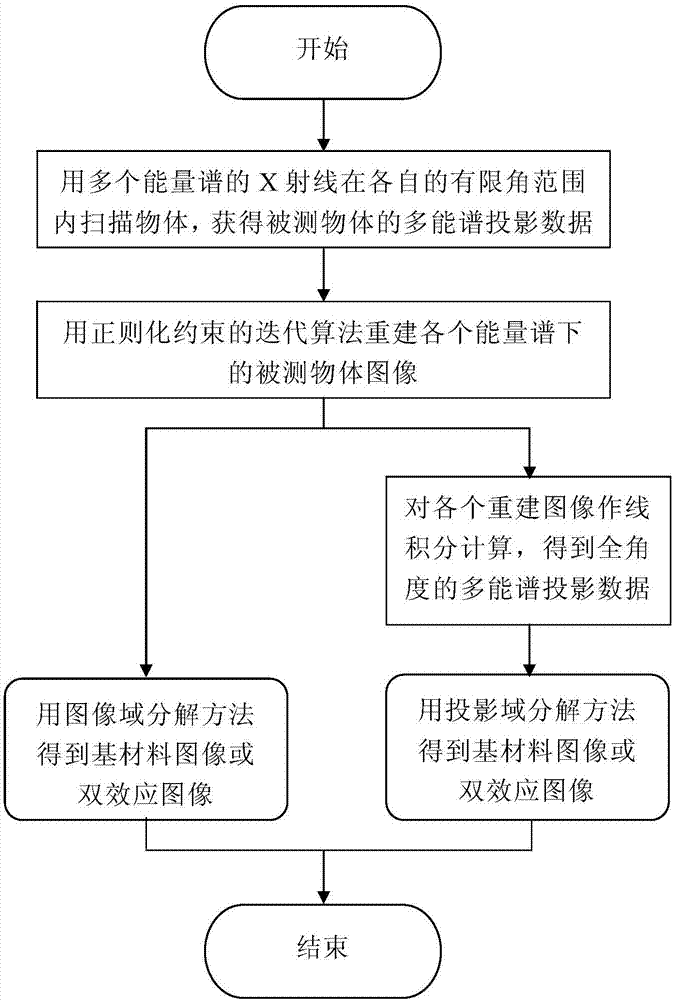
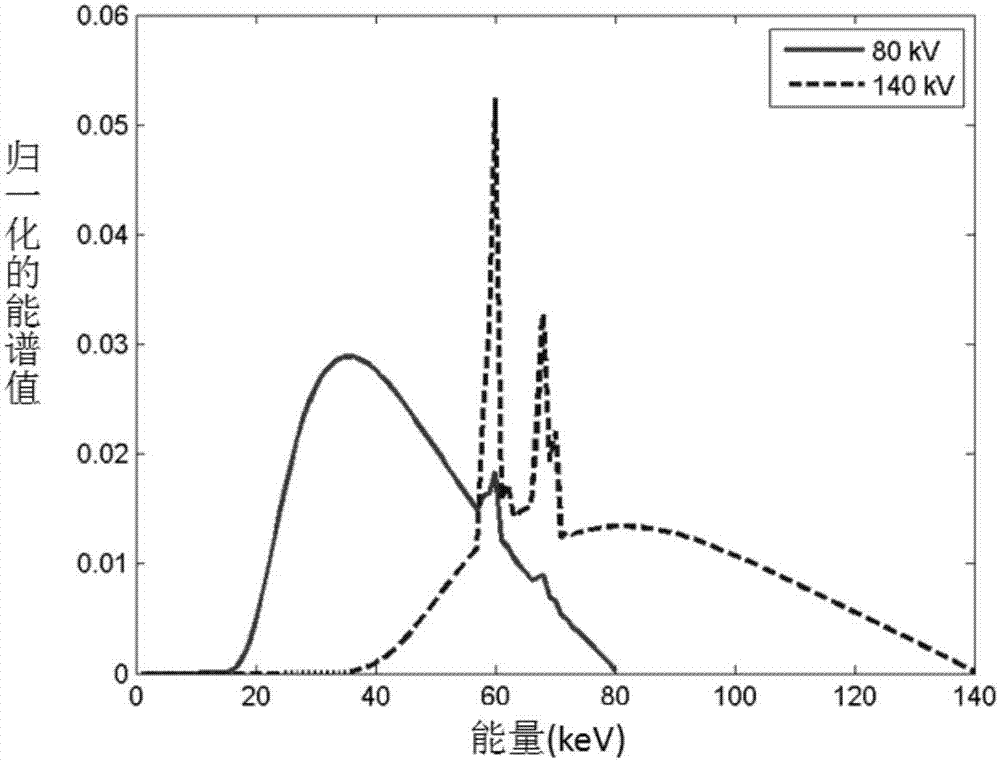
X ray multi-energy-spectrum CT (Computed Tomography) finite angle scanning and image iterative reconstruction method
ActiveCN108010099AReduce radiation doseReduce scan timeImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionHigh rateX-ray
The invention discloses an X ray multi-energy-spectrum CT (Computed Tomography) finite angle scanning and image iterative reconstruction method, which comprises the following steps that: applying theX rays of a plurality of energy spectrums to scan an object in a respective finite angel range, and obtaining the projection data of a tested object under each energy spectrum; on the basis of the projection data, independently reconstructing the image of each tested object under each energy spectrum; utilizing the consistency of the tested object and the complementarity of the reconstructed imageunder each energy spectrum, designing a combined regularization method to effectively remove an artifact caused by finite angle scanning in the reconstructed image under each energy spectrum, and calculating to obtain a high-quality reconstructed image; and therefore, applying an image domain decomposition method or a projection domain decomposition method to calculate to obtain the base materialimage or the dual-effect image of the tested object. The method is suitable for the image reconstruction of the multi-energy-spectrum CT under a finite angle scanning condition, the dosage of the X ray is lowered, scanning time is shortened, and the method has the advantages of high reconstructed image quality, high rate of convergence and the like.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
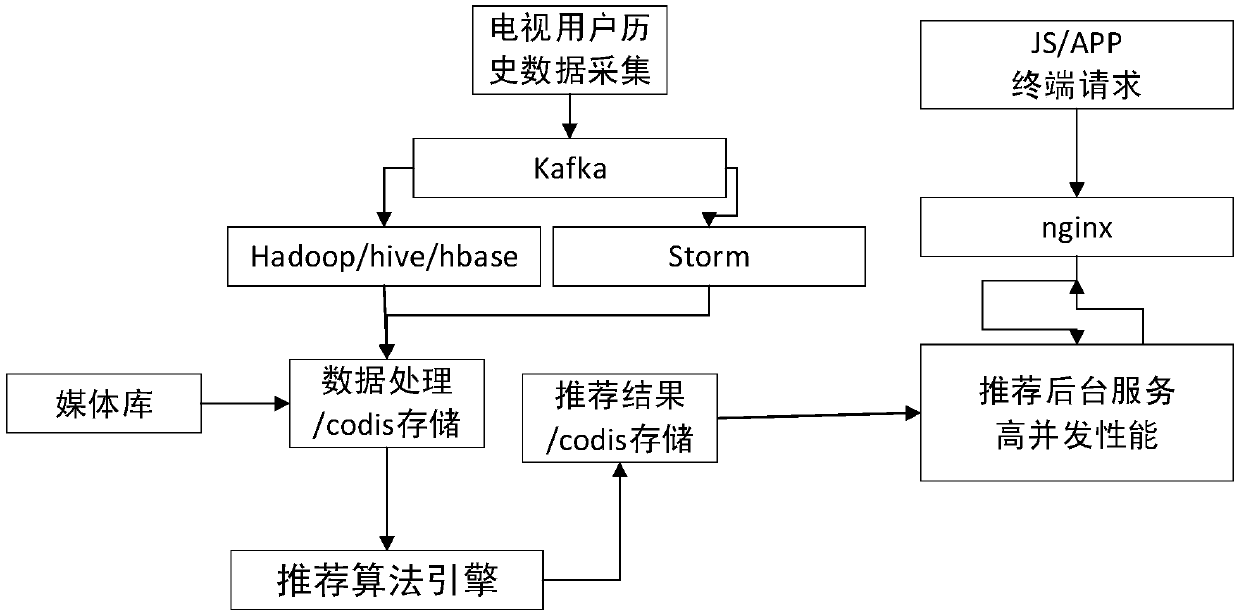
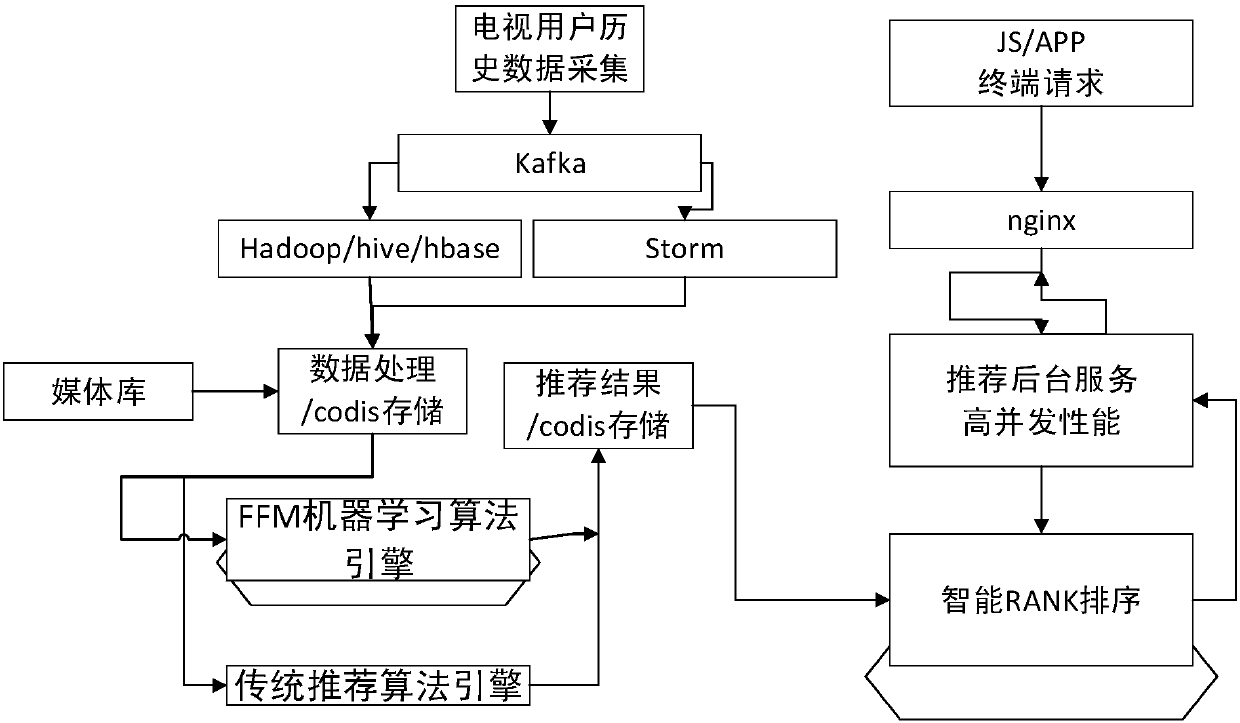
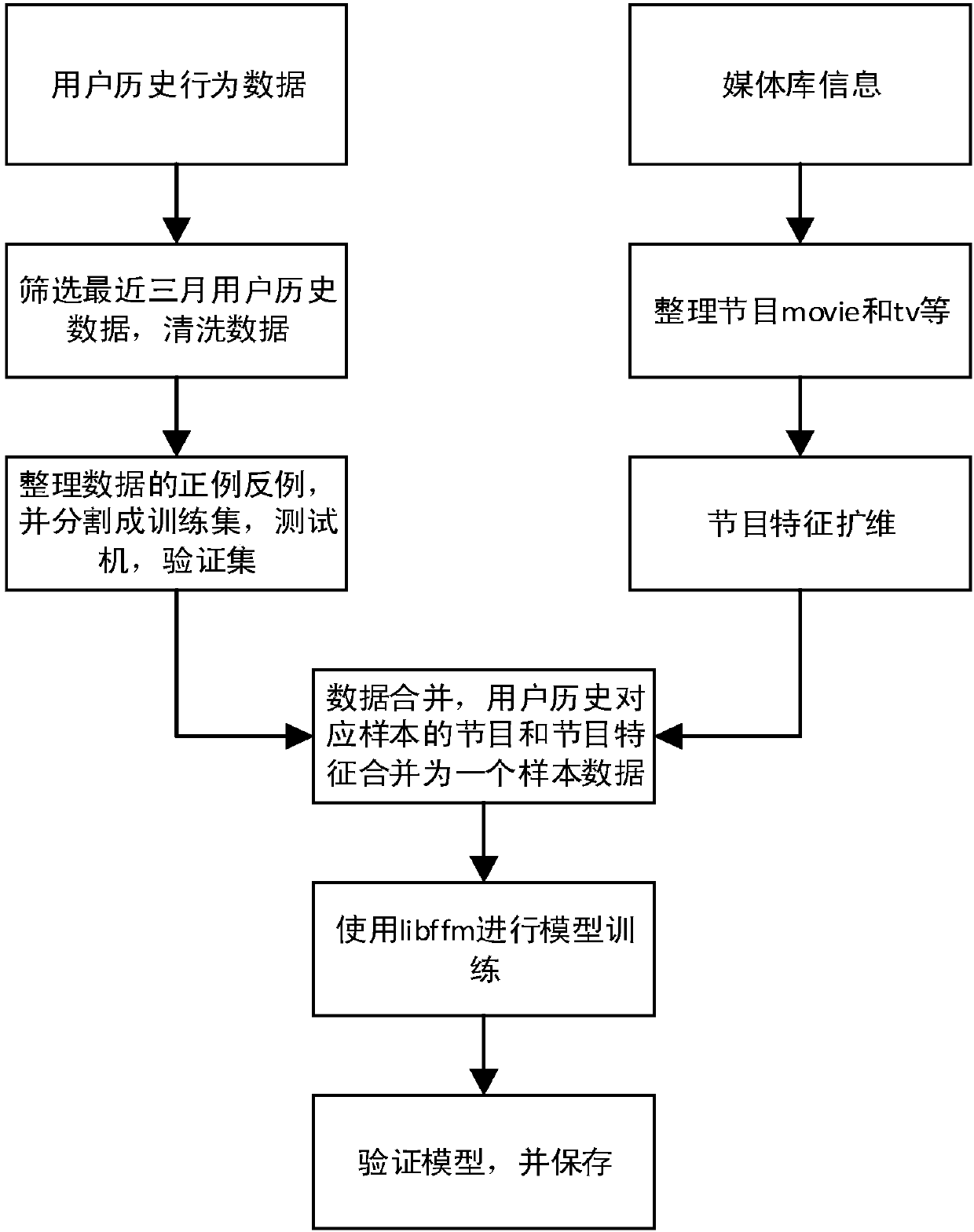
Machine learning TV program recommendation method based on domain decomposition machine
InactiveCN107635151APersonalizedImprove recommended TV showsSelective content distributionSpecial data processing applicationsRecommendation modelDecomposition
The invention relates to the field of big data technology, and discloses a machine learning TV program recommendation method based on a domain decomposition machine, aiming at solving the problems that a program recommendation scheme in a traditional technology has more human interventions, is not applied by only taking the historical behavior data of users as the basis, and is poor in recommendation effect. The method comprises the following steps: a, arranging the historical behavior data of the users and feature information of programs; b, constructing an FFM algorithm recommendation modelby taking the arranged data as basic data of the model; c, calculating recommendation results by adopting a logistic regression algorithm based on the constructed FFM algorithm recommendation model; and d, sorting the recommendation results, and pushing the sorted recommendation results to the users.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
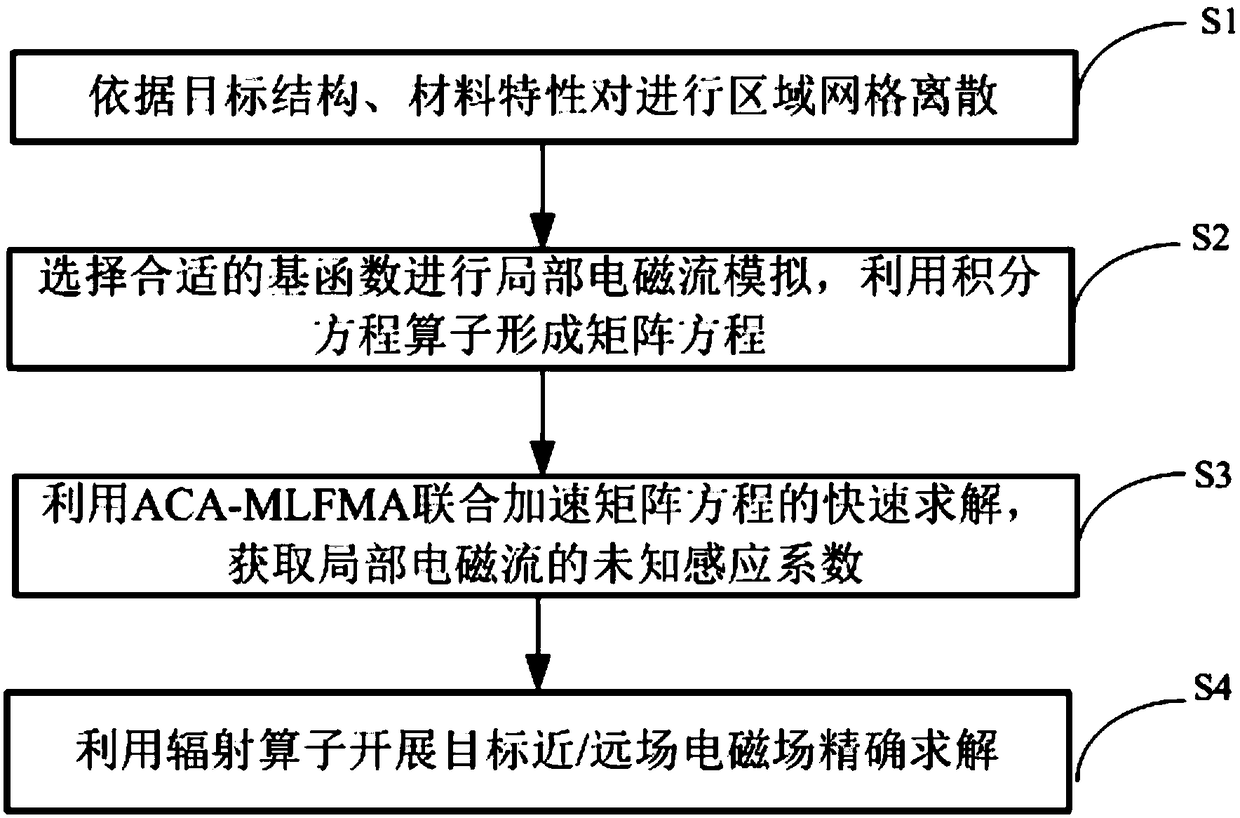
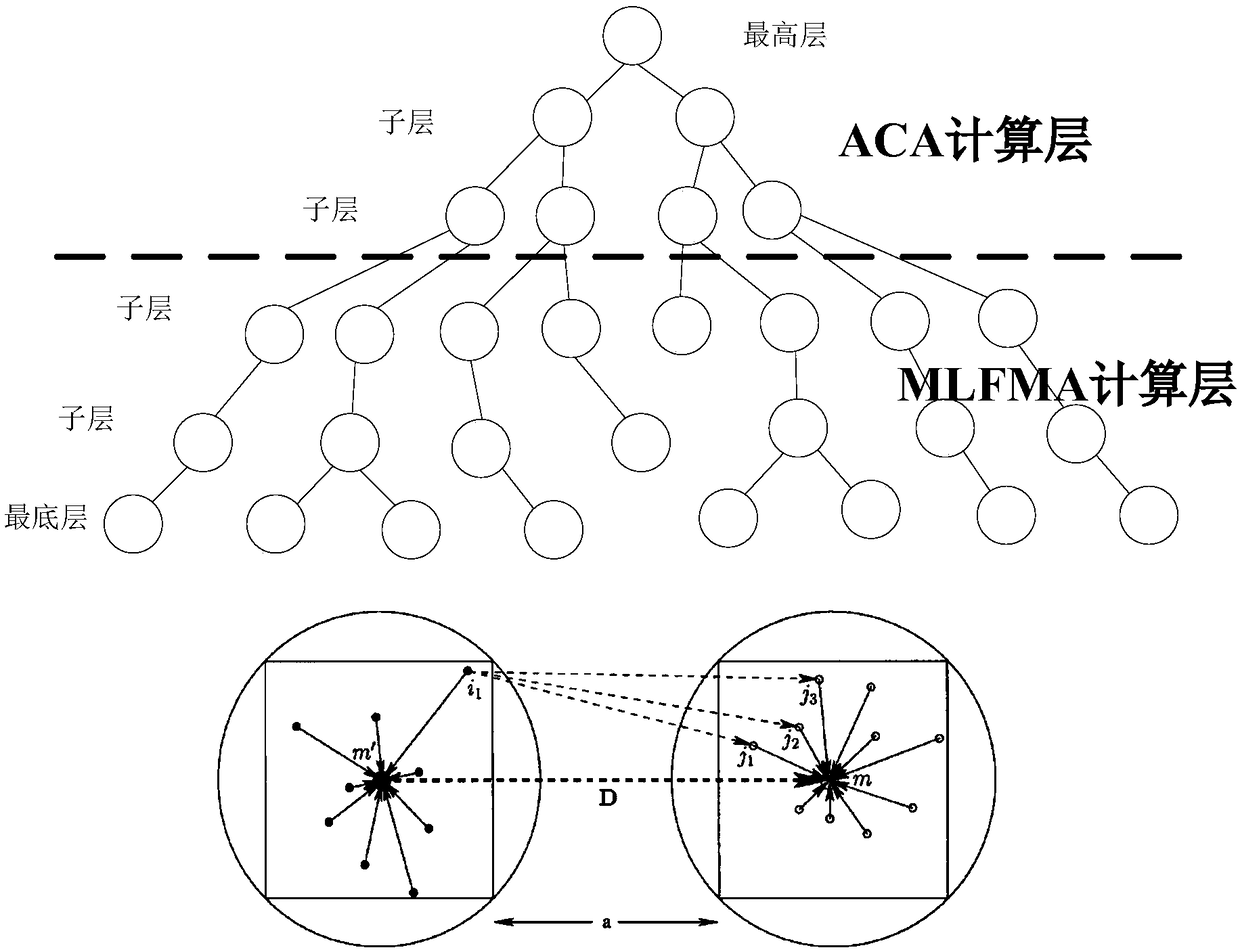
A fast simulation modeling method based on ACA-MLFMA accelerated domain decomposition non-conformal mesh
PendingCN109376485AImprove the ability to solve electromagnetic field characteristicsImprove the efficiency of electromagnetic field solutionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFormation matrixSecondary radiation
ACA based-MLFMA-accelerated fast simulation modeling method for domain decomposition non-conformal mesh comprises the following steps: S1, according to the structure and material characteristics of the target, the target is divided into regions, and discretizing then the mesh on each different region, and separately dividing the mesh between adjacent regions to form non-conformal mesh; S2, separating the mesh between adjacent regions to form non-conformal mesh; S2, selecting appropriate basis function to simulate local electromagnetic current, and using integral equation operator to form matrix equation; S3, using ACA-MFLMA algorithm compresses the matrix equation and iterates quickly to accelerate the solution of the matrix equation, obtains the position induction coefficients of the local electromagnetic current, and then obtains the distribution of the induced electromagnetic current on the target. S4, taking the induced electromagnetic current as the secondary radiation source, theelectromagnetic field distribution in the near region and the scattering characteristics of the far field are calculated, and the electromagnetic field response characteristics of the target are analyzed. The advantages of the method are that it makes full use of the advantages of ACA and MLFMA, and greatly improves the capability of solving the engineering electromagnetic field characteristics.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
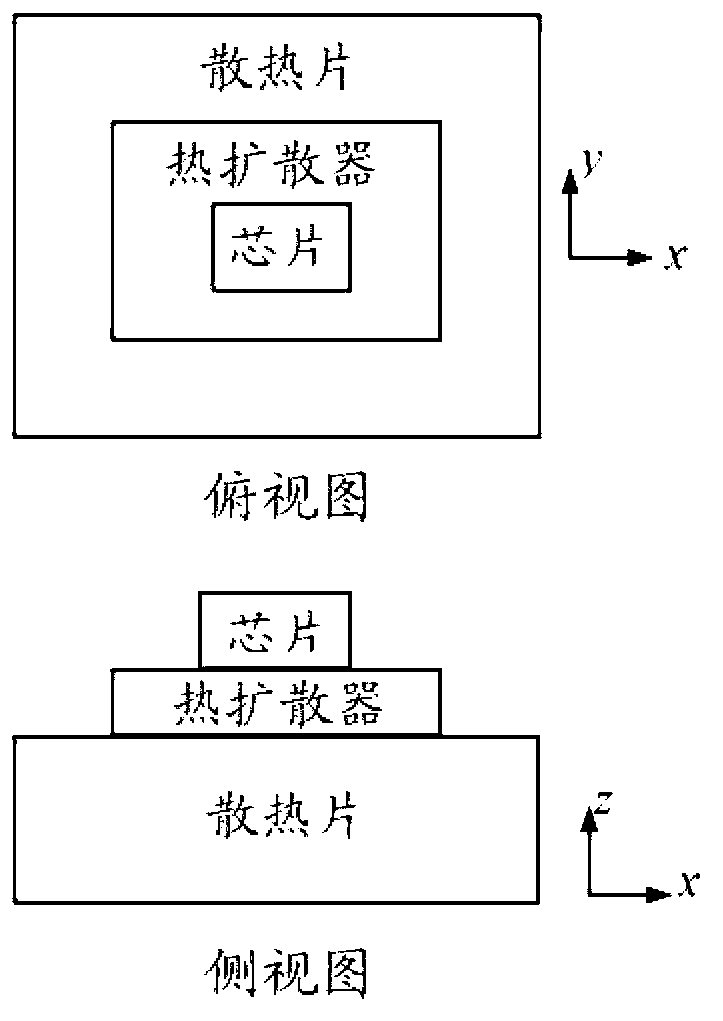
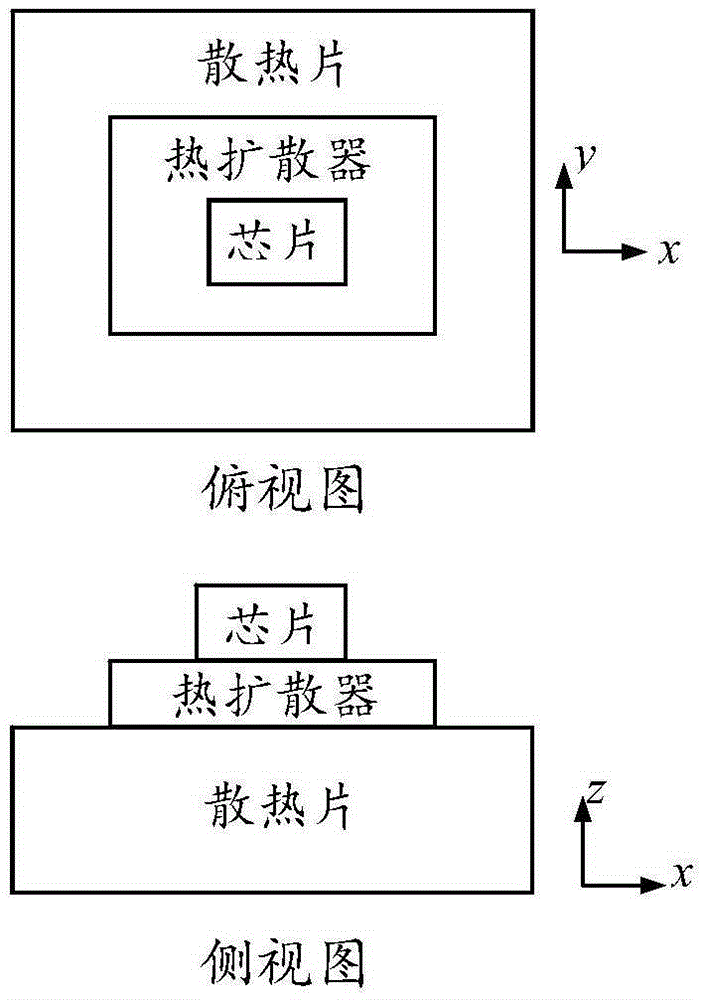
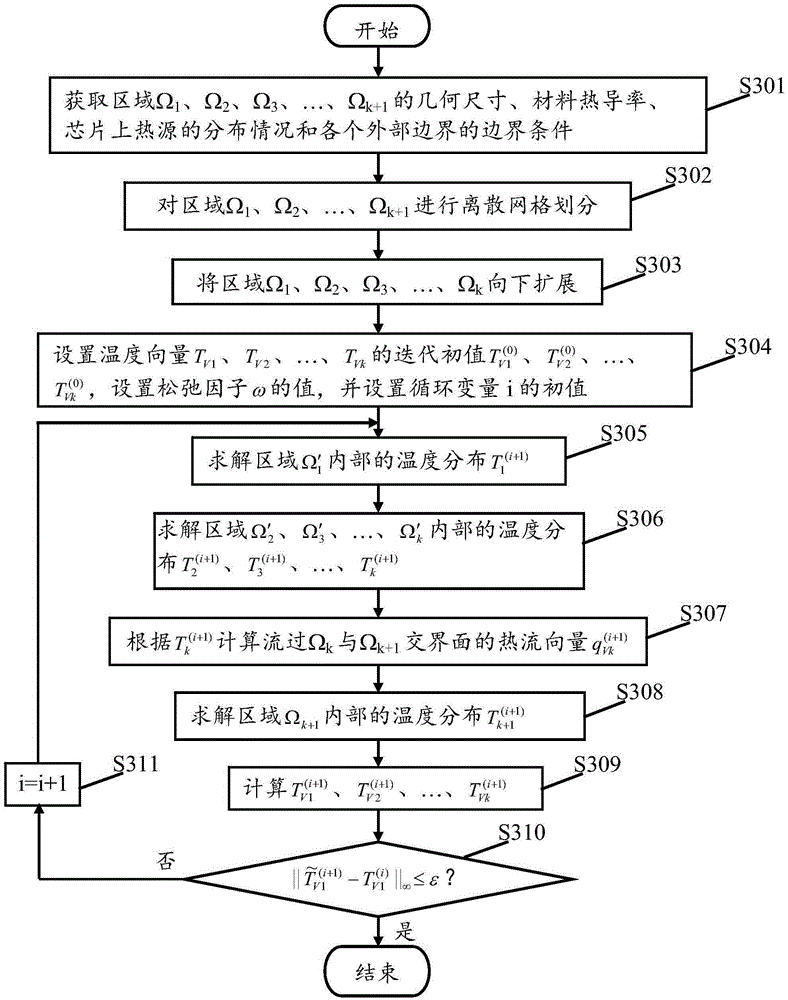
Chip thermal analysis method based on three-dimensional domain decomposition
InactiveCN103324836AAccurate temperatureCalculation speedSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionDomain decomposition methods
A chip thermal analysis method based on three-dimensional domain decomposition comprises the steps of adopting a non-overlapping domain decomposition method to perform thermal analysis of a chip system including a chip and a heat-radiating part, performing discrete grid division of different domains of the chip system respectively, setting an appropriate condition at each domain interface position to solve the domains and achieving convergence of a computed result of the interface position of the chip and the heat-radiating part through multiple overall iterations. By means of the chip thermal analysis method based on the three-dimensional domain decomposition, temperature distribution of the chip in the chip system can be quickly calculated.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Domain decomposition by the advancing-partition method for parallel unstructured grid generation
In a method for domain decomposition for generating unstructured grids, a surface mesh is generated for a spatial domain. A location of a partition plane dividing the domain into two sections is determined. Triangular faces on the surface mesh that intersect the partition plane are identified. A partition grid of tetrahedral cells, dividing the domain into two sub-domains, is generated using a marching process in which a front comprises only faces of new cells which intersect the partition plane. The partition grid is generated until no active faces remain on the front. Triangular faces on each side of the partition plane are collected into two separate subsets. Each subset of triangular faces is renumbered locally and a local / global mapping is created for each sub-domain. A volume grid is generated for each sub-domain. The partition grid and volume grids are then merged using the local-global mapping.
Owner:NASA
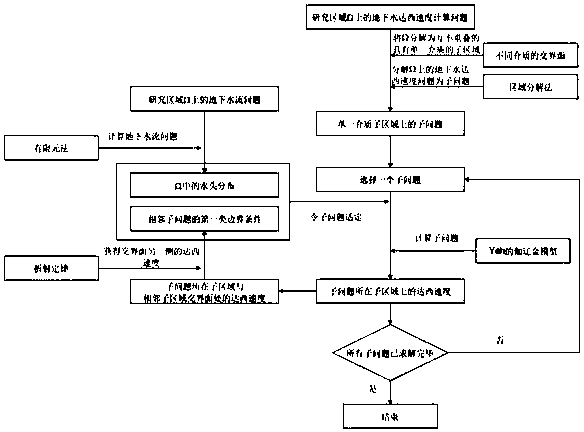
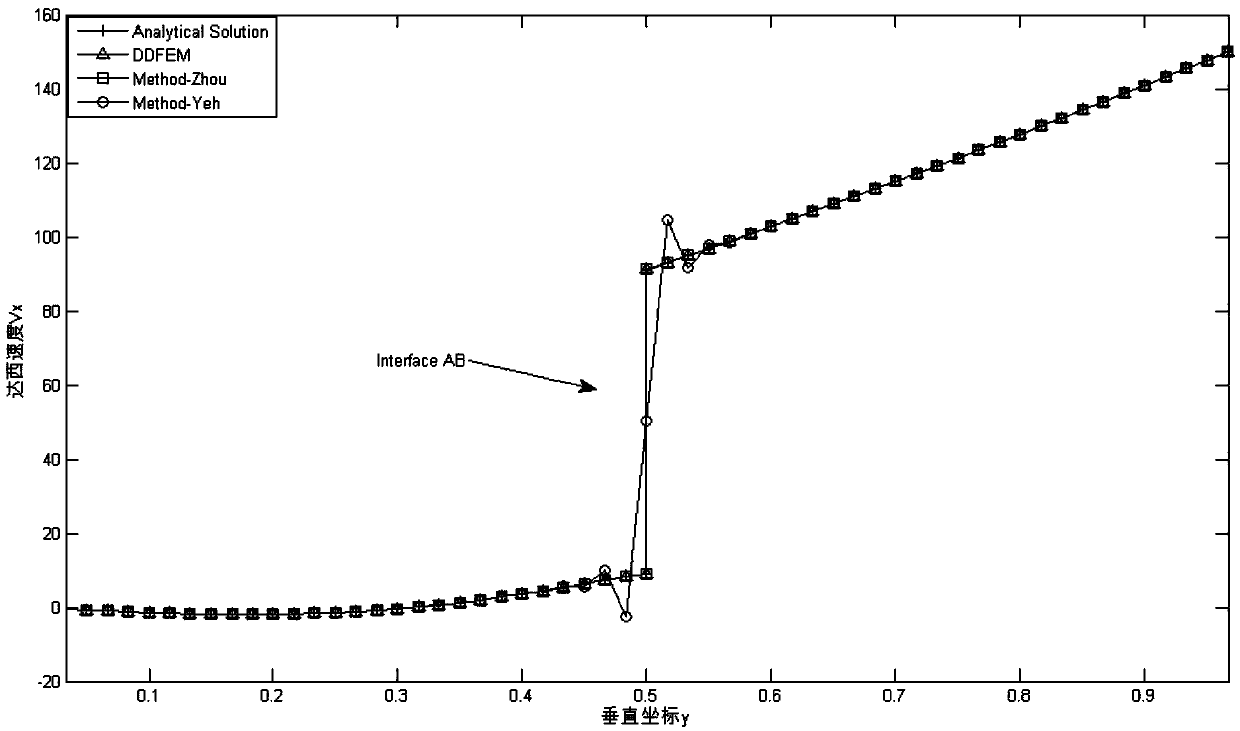
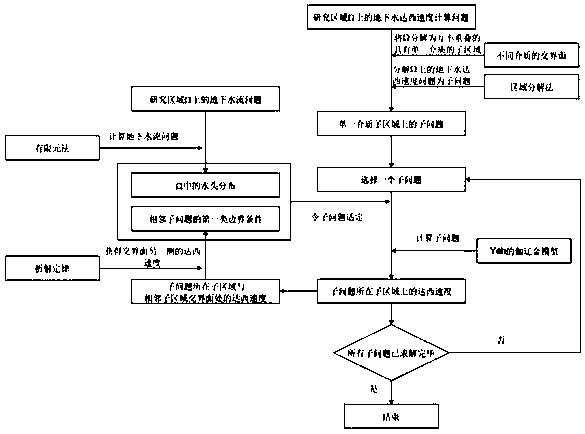
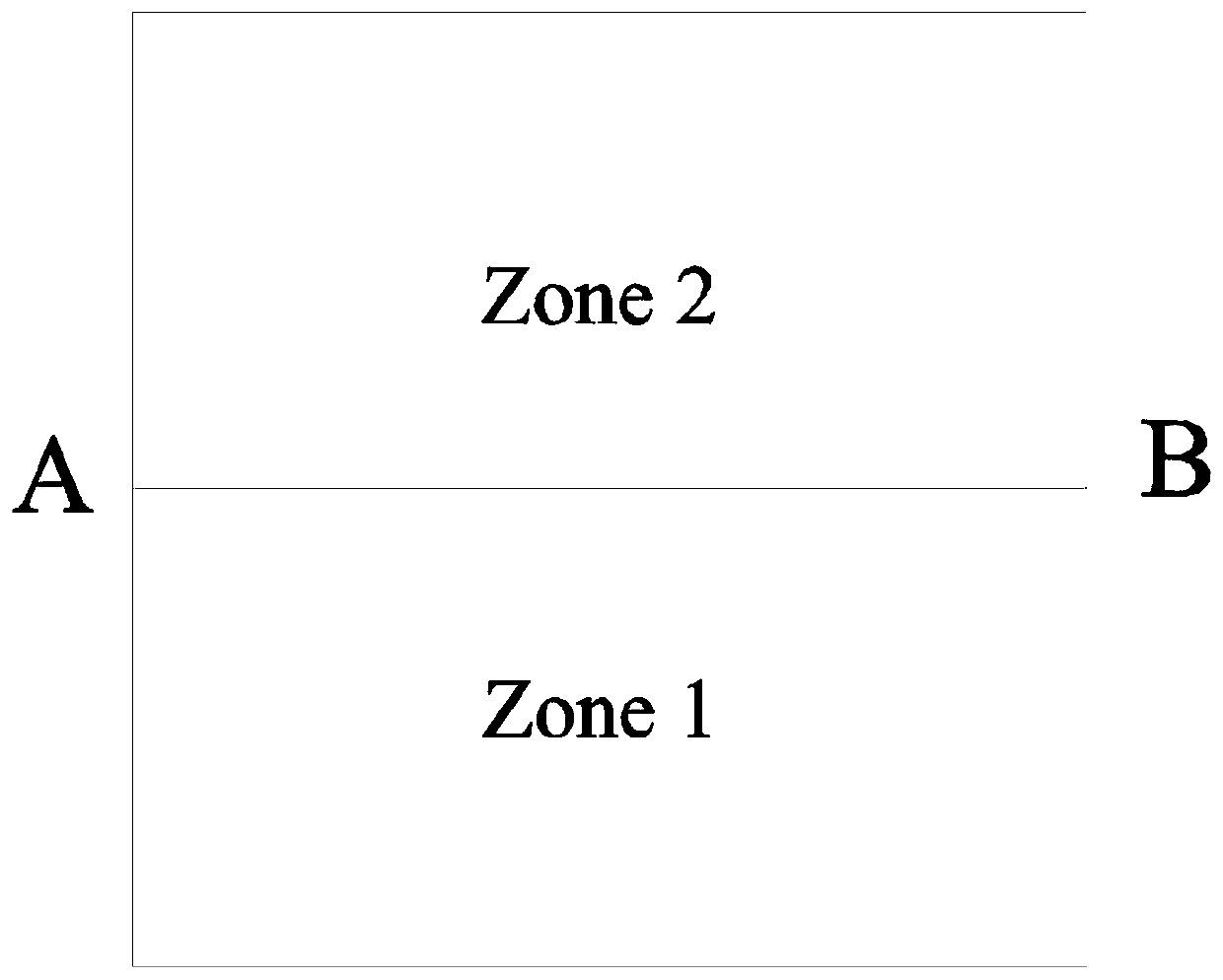
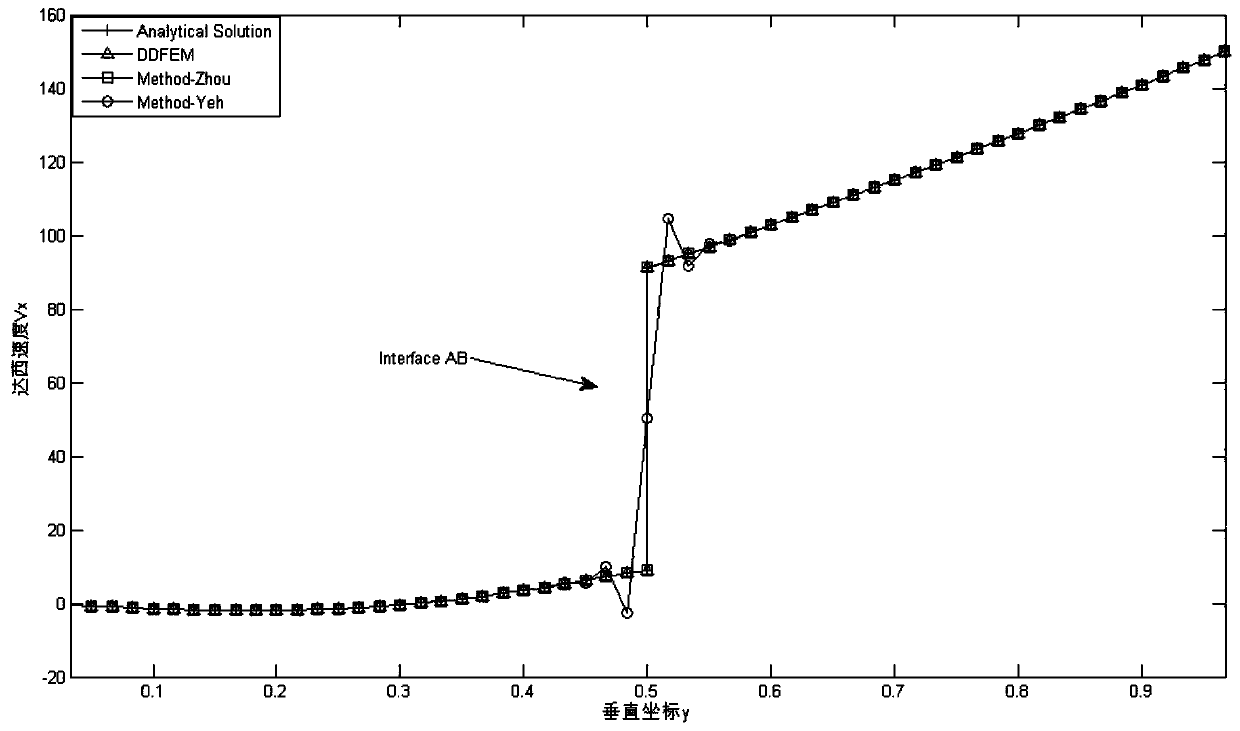
Domain decomposition finite element method for simulating Darcy speed at underground medium interface
ActiveCN107657075AImprove computing efficiencyGuaranteed accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionExtended finite element method
The invention discloses a domain decomposition finite element method for simulating Darcy speed at an underground medium interface. The method comprises the following steps: performing variation on anunderground flow problem by using a Galerkin method, sub-dividing a research domain, and acquiring waterhead by applying the finite element method; decomposing the research domain into a plurality ofsingle-medium sub-domains by applying interfaces of different mediums according to the medium composition of the research domain, and decomposing an underground Darcy speed solution problem on the research domain into sub-problems on the sub-domain by applying the domain decomposition method; selecting one sub-problem, performing variation by using the Galerkin method, and acquiring the Darcy speed by applying a Galerkin model of the Yeh, acquiring the Darcy speed at the other side of the interface of the sub-domain and other sub-domain by combining with the refraction law as the first classof boundary condition of the adjacent sub-problem; selecting the next sub-problem to solve, and repeating this process until all sub-problems are completely solved. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the computing consumption of the Darcy speed is reduced through the domain decomposition method, and the precision of the Darcy speed at the interface is guaranteed by using the refraction law.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
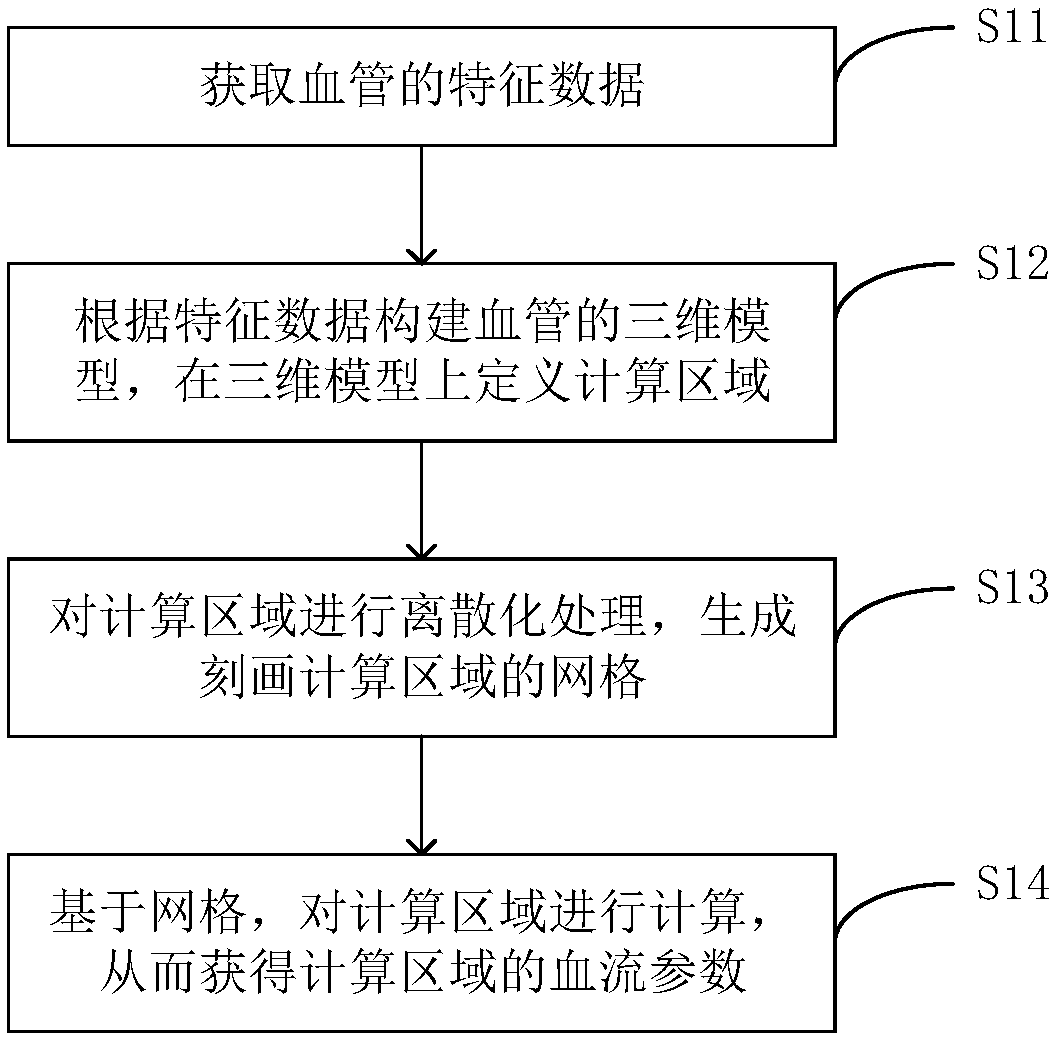
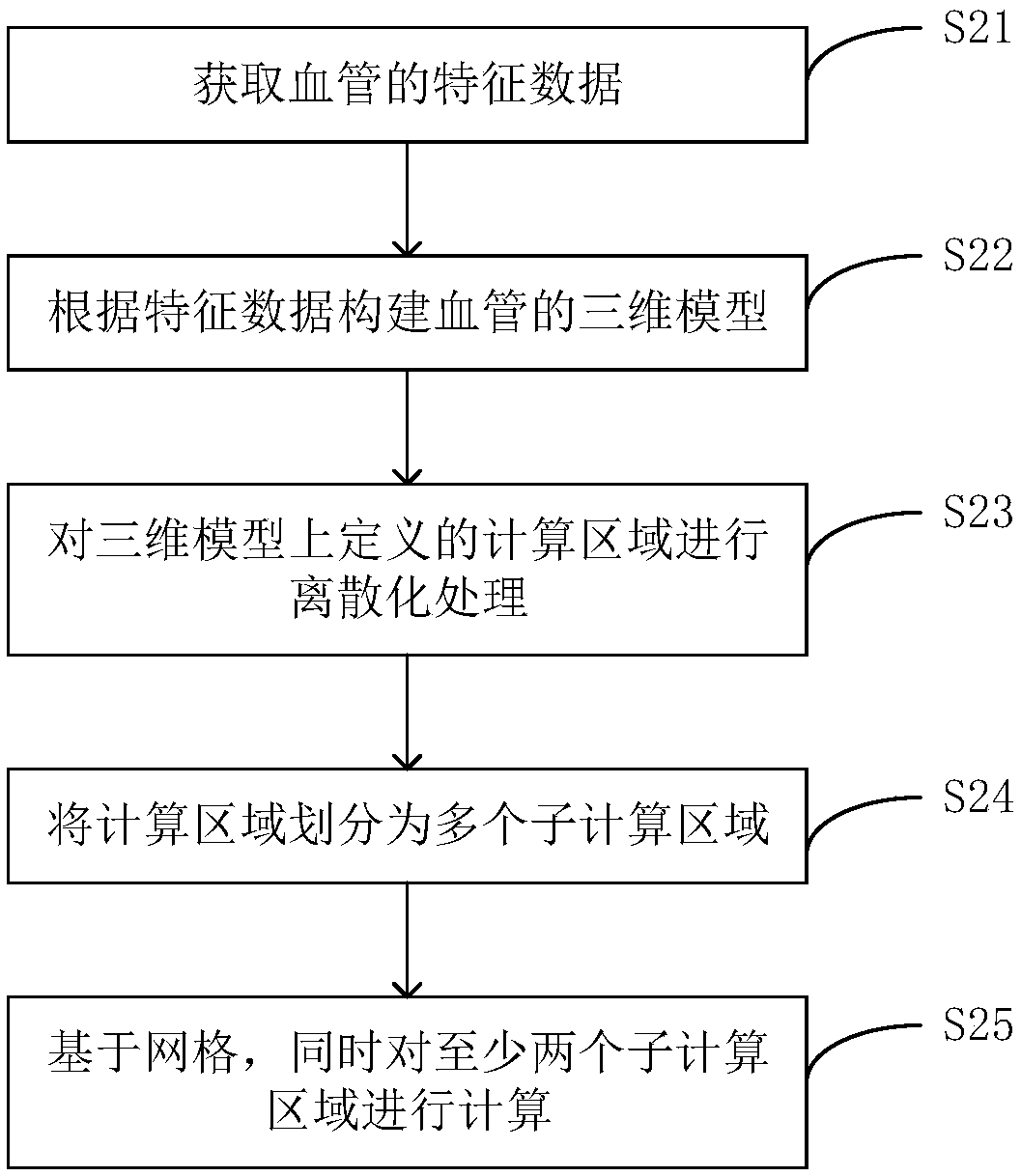
Vascular blood flow simulation method based on domain decomposition and related device
PendingCN109102568AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyMedical simulation3D modellingBlood flowDecomposition
The invention discloses a blood flow simulation method of blood vessel based on domain decomposition, a blood flow simulation device and a computer-readable storage medium, wherein the method comprises acquiring characteristic data of blood vessel; a three-dimensional model of blood vessel being constructed according to the characteristic data, wherein the three-dimensional model defines a computational region; the computational region being discretized to generate a grid describing the computational region; the computational area being divided into several sub-computational areas, wherein thenumber of grid points in each sub-computational area is identical; at least two sub-compute regions being simultaneously computed based on a grid to obtain blood flow parameters of that compute regions. The present application enables accurate and efficient simulation of blood flow in blood vessels.
Owner:杭州阿特瑞科技有限公司
Domain decomposition order stepping time domain integration method based on equivalence principle
ActiveCN104915326AIncrease condition numberOvercome the weakness of backward tense instabilityComplex mathematical operationsTime domainStable state
The invention discloses a domain decomposition order stepping time domain integration method based on an equivalence principle. The method includes the steps that interaction between a scattering object and equivalence faces surrounding the object is solved; interaction between the equivalence faces is solved, equivalence scattering electromagnetic current on one equivalence face senses corresponding equivalence scattering electromagnetic current on other equivalence faces, and the equivalence scattering electromagnetic current on the surfaces of the equivalence faces is constantly updated through coupling between all the equivalence faces until a stable state is achieved; according to the obtained interaction relation between the scattering object and the equivalence faces surrounding the object and the interaction relation between the equivalence faces, an iteration method is adopted for solving final equivalence scattering electromagnetic current on the equivalence faces; according to the final equivalence scattering electromagnetic current on the equivalence faces, the radar scattering sectional area is solved based on a reciprocal principle. Rapid electromagnetic scattering simulation can be performed on scattering characteristics of multiple objects, the implementation process is flexible and free, and the method has great actual engineering application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
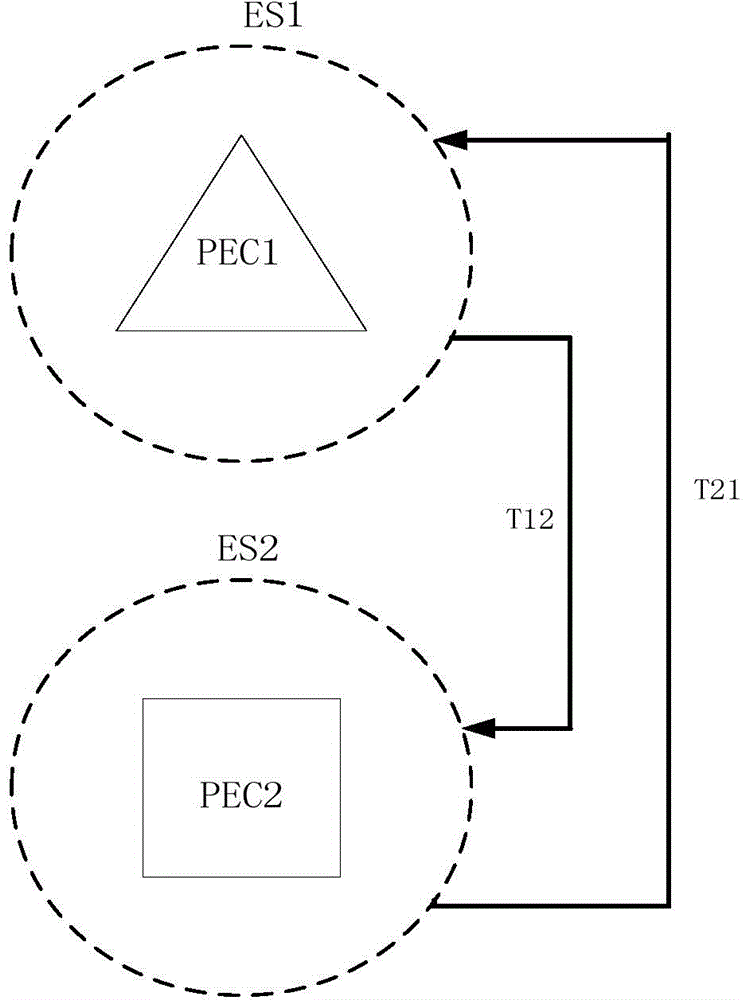
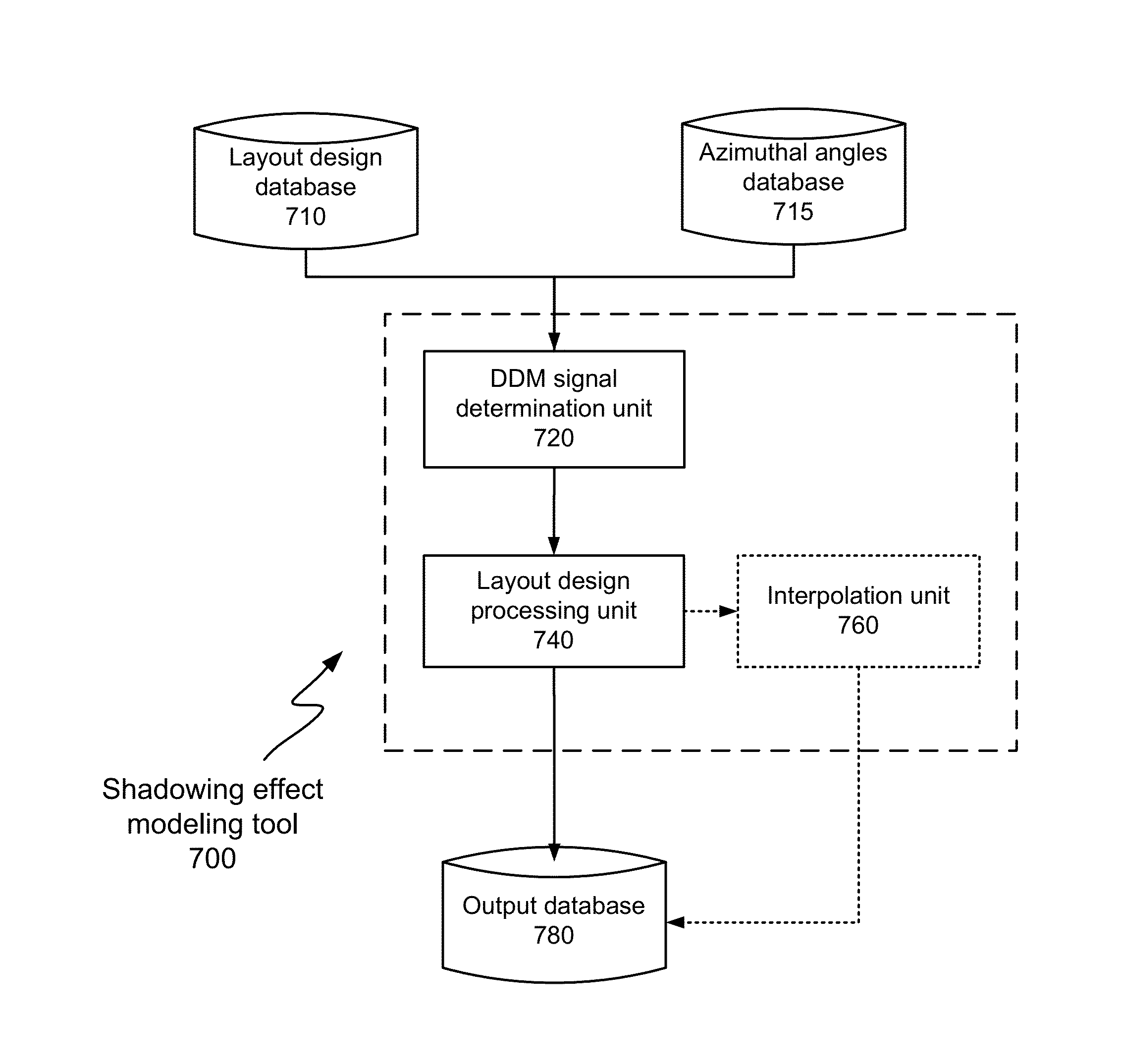
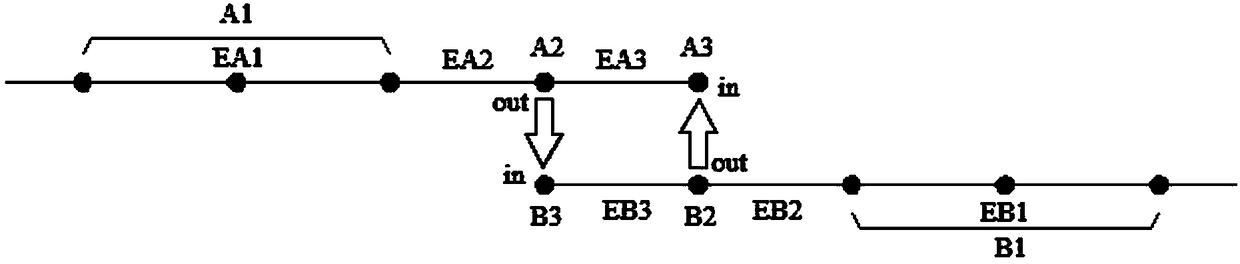
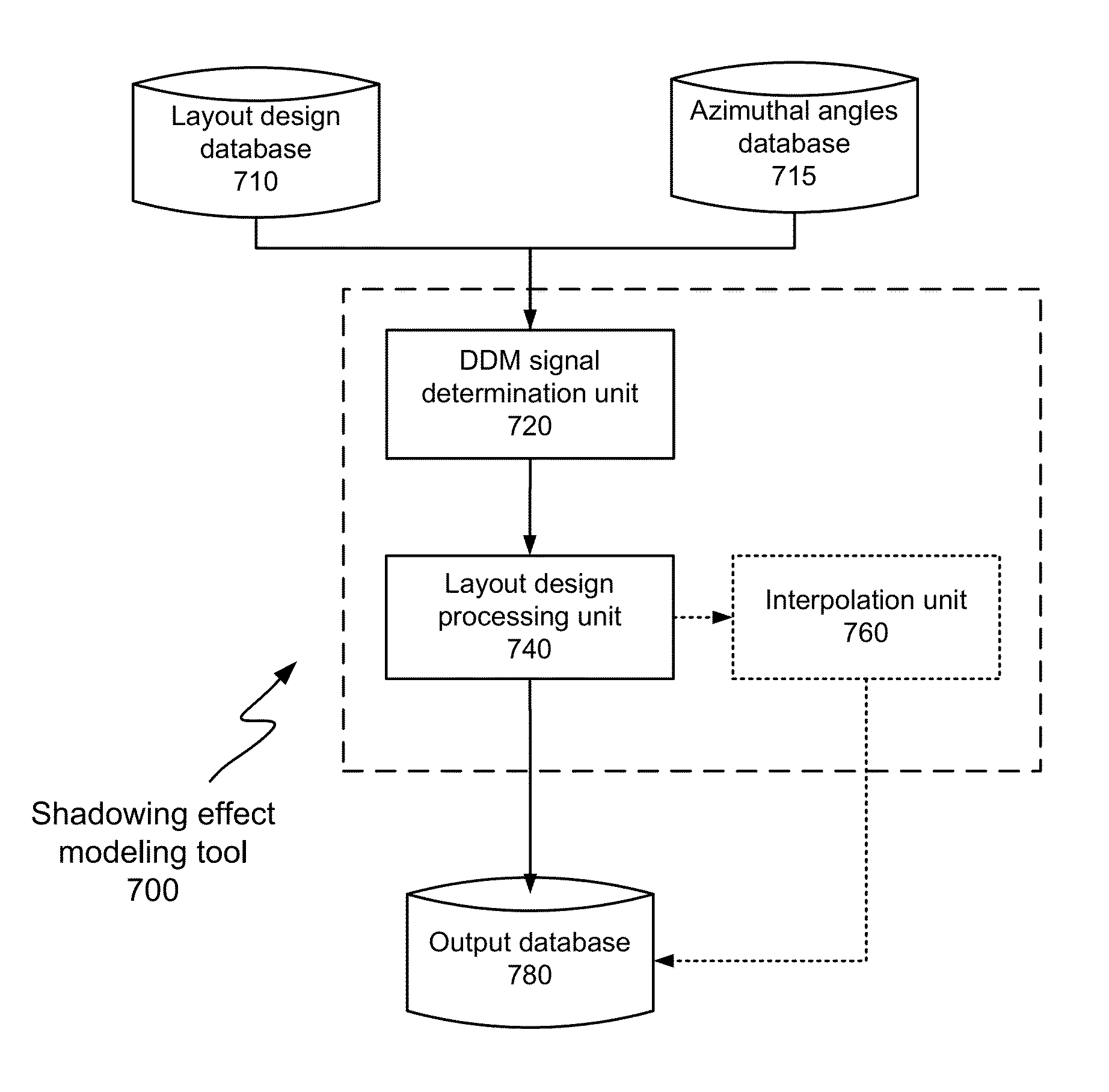
Simulation And Correction Of Mask Shadowing Effect
ActiveUS20130080982A1Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithographic artistDomain decomposition methods
Disclosed are techniques for simulating and correcting the mask shadowing effect using the domain decomposition method (DDM). According to various implementations of the invention, DDM signals for an extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography mask are determined for a plurality of azimuthal angles of illumination. Base on the DDM signals, one or more layout designs for making the mask may be analyzed and / or modified.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Finite difference stencil parallelizing method based on iteration space sticks
InactiveCN102200962AAchieve parallelizationImprove data localitySpecial data processing applicationsIterative methodologyIteration space
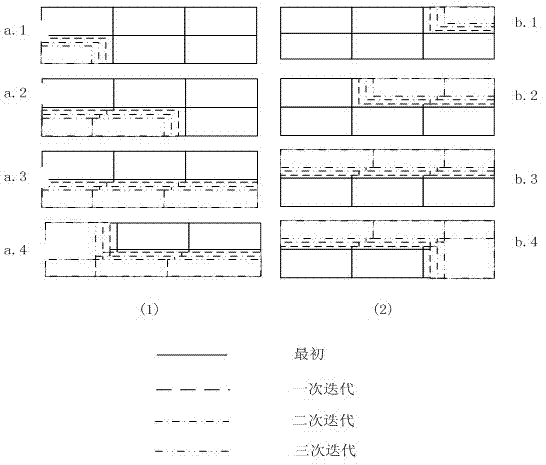
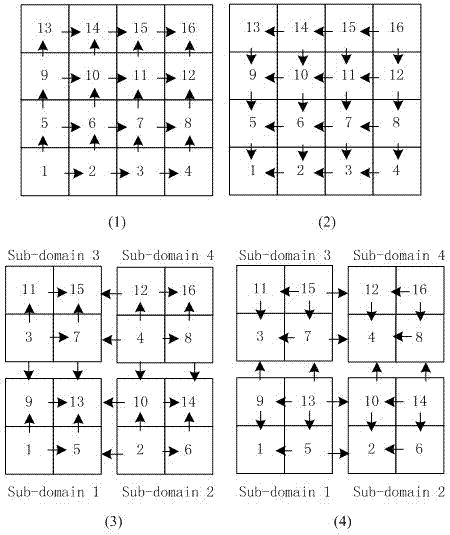
The invention relates to a finite difference stencil parallelizing method based on iteration space sticks. In the traditional parallel iterative method, synchronous operation for maintaining the data dependence relation is needed both in iteration and among the iterations. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: dividing an iteration space into grid sticks in a time-axis direction to realize multiple recursion-type iteration-step updates on the same grid block, thereby improving the data locality in the sticks at the same time of not changing the property of a serial stencil iterative method; and then reordering the grid sticks to realize the parallelization of staggered sticks in the finite difference stencil method. Compared with the traditional domain decomposition method and a red-black ordering parallel method, the method provided by the invention has better data locality, parallelization efficiency and extensibility.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Analysis method for pumped storage generator damper winding magnetic field characteristics
InactiveCN107169237AOmit divisionEasy procedureDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMagnetic tension forceElement model
The invention discloses an analysis method for pumped storage generator damper winding magnetic field characteristics, and belongs to the technical field of pumped storage generator magnetic field analysis. In order to solve the problem that an effective method capable of accurately analyzing a specific relationship between the pumped storage generator magnetic field and a damper winding does not exist at present, the method comprises the following steps that: S1: establishing a mathematical model and a finite element model, and finishing simulation; S2: simplifying a physical model; S3: determining the mathematical model; S4: calculating electromagnetic force borne by damping bars, exciting windings, pole bodies and pole shoes in different working condition conversion and transition processes; S5: coupling a domain decomposition method with a radial basis element-free method; S6: obtaining a function relationship between a loading rate and a damper winding dynamic conversion current; and S7: analyzing a result. By use of the analysis method for pumped storage generator damper winding magnetic field characteristics, dependency on elements can be gotten rid of, and the method has the advantages of high accuracy, simpleness in calculation and the like.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
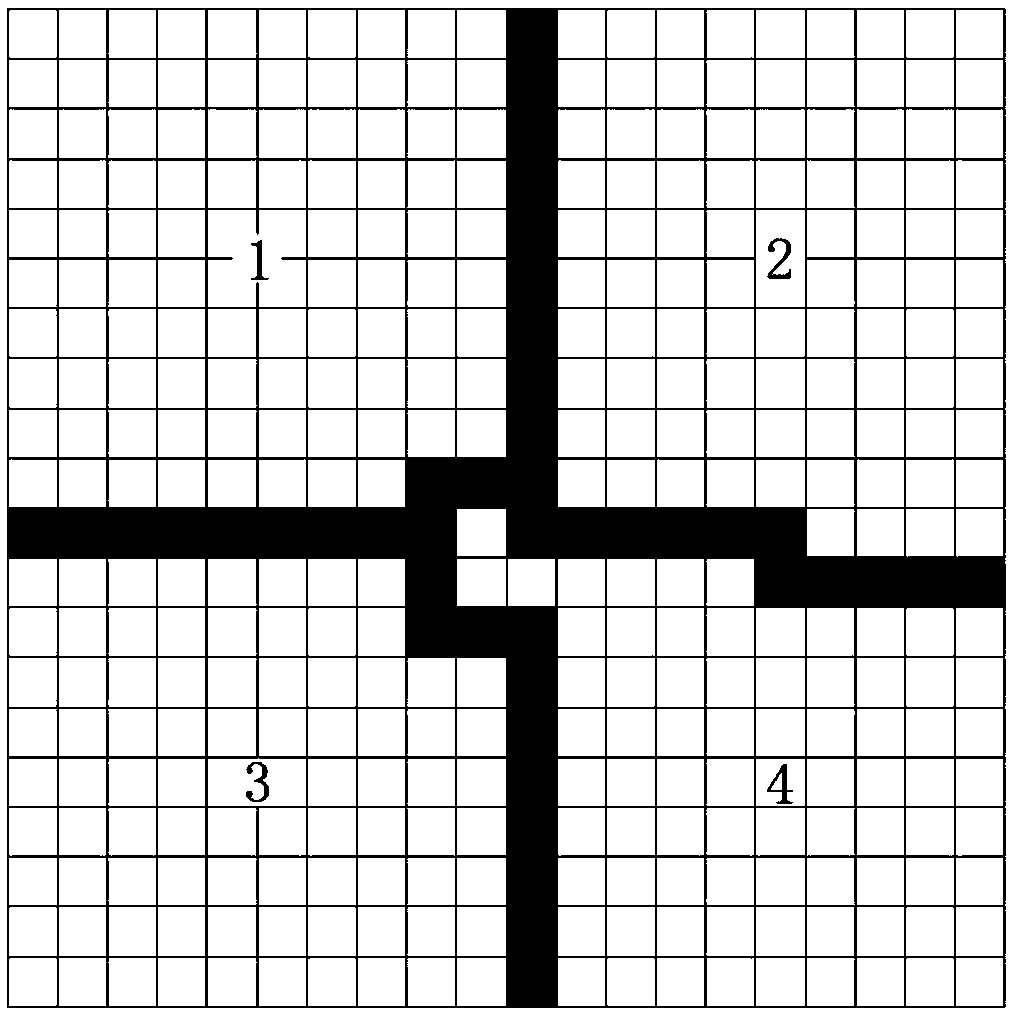
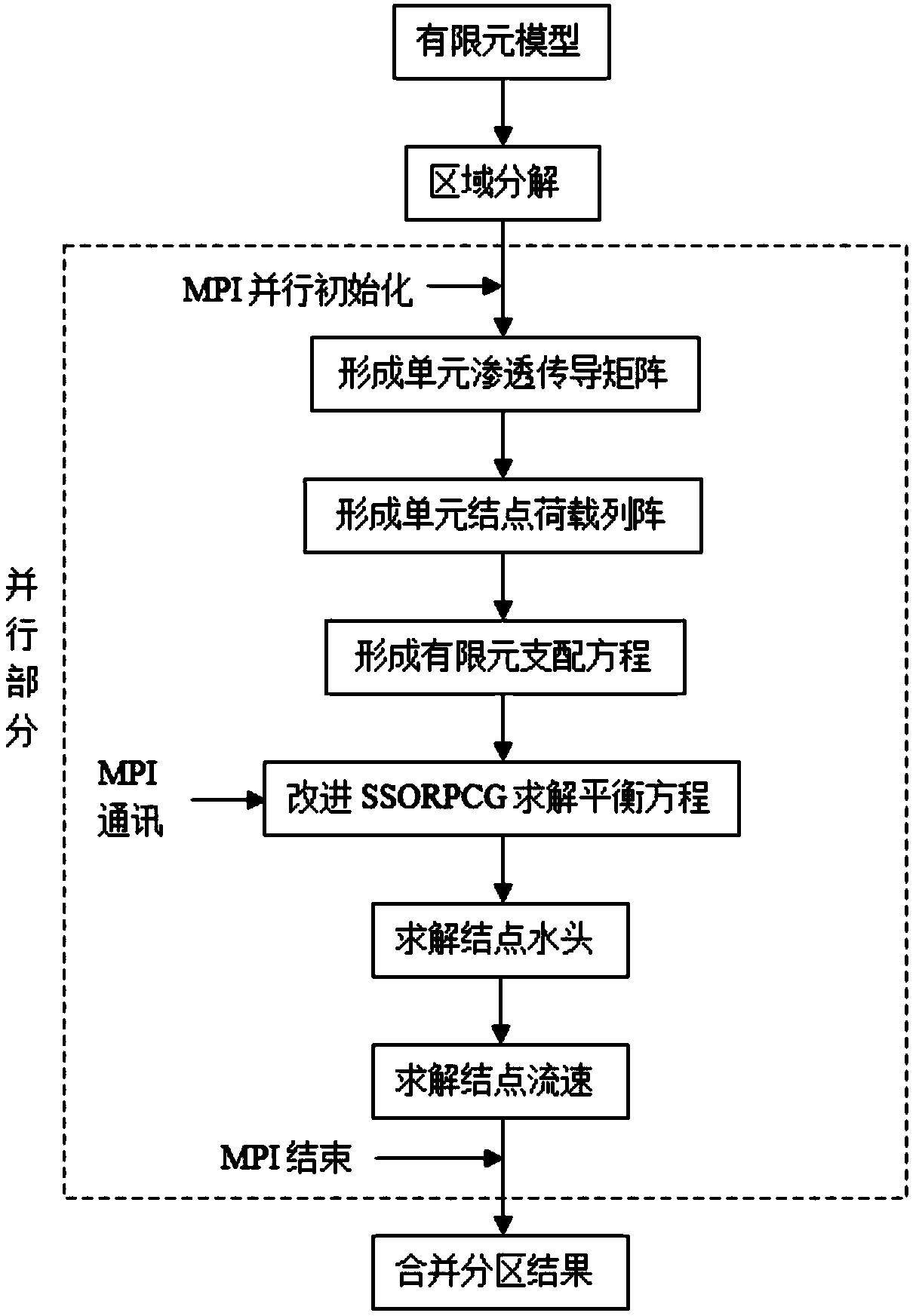
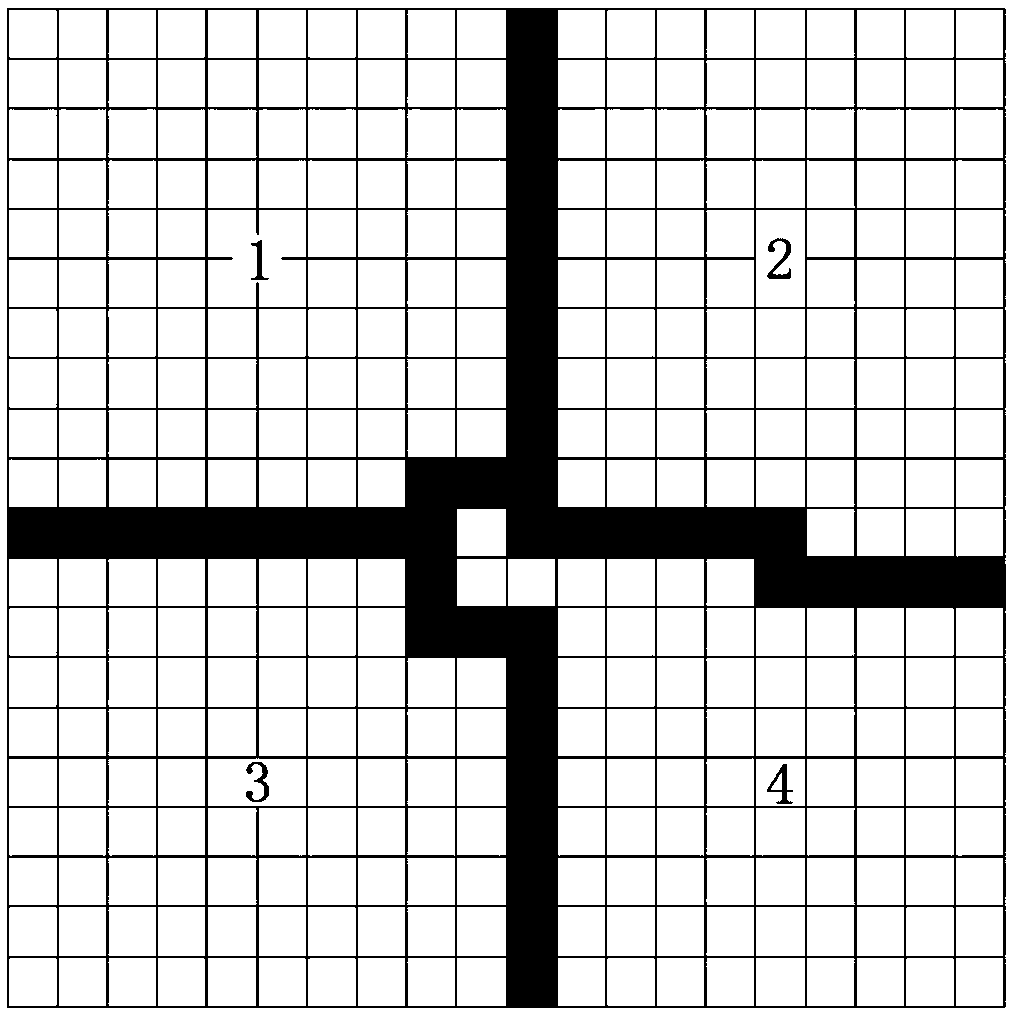
Improved SSORPCG parallel method based on domain decomposition of finite element for solving temperature field
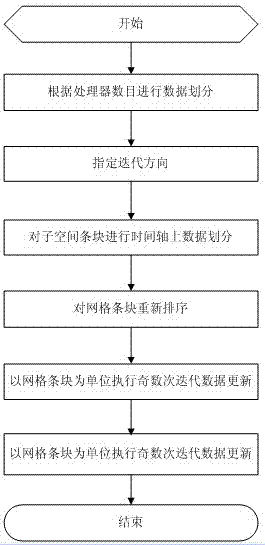
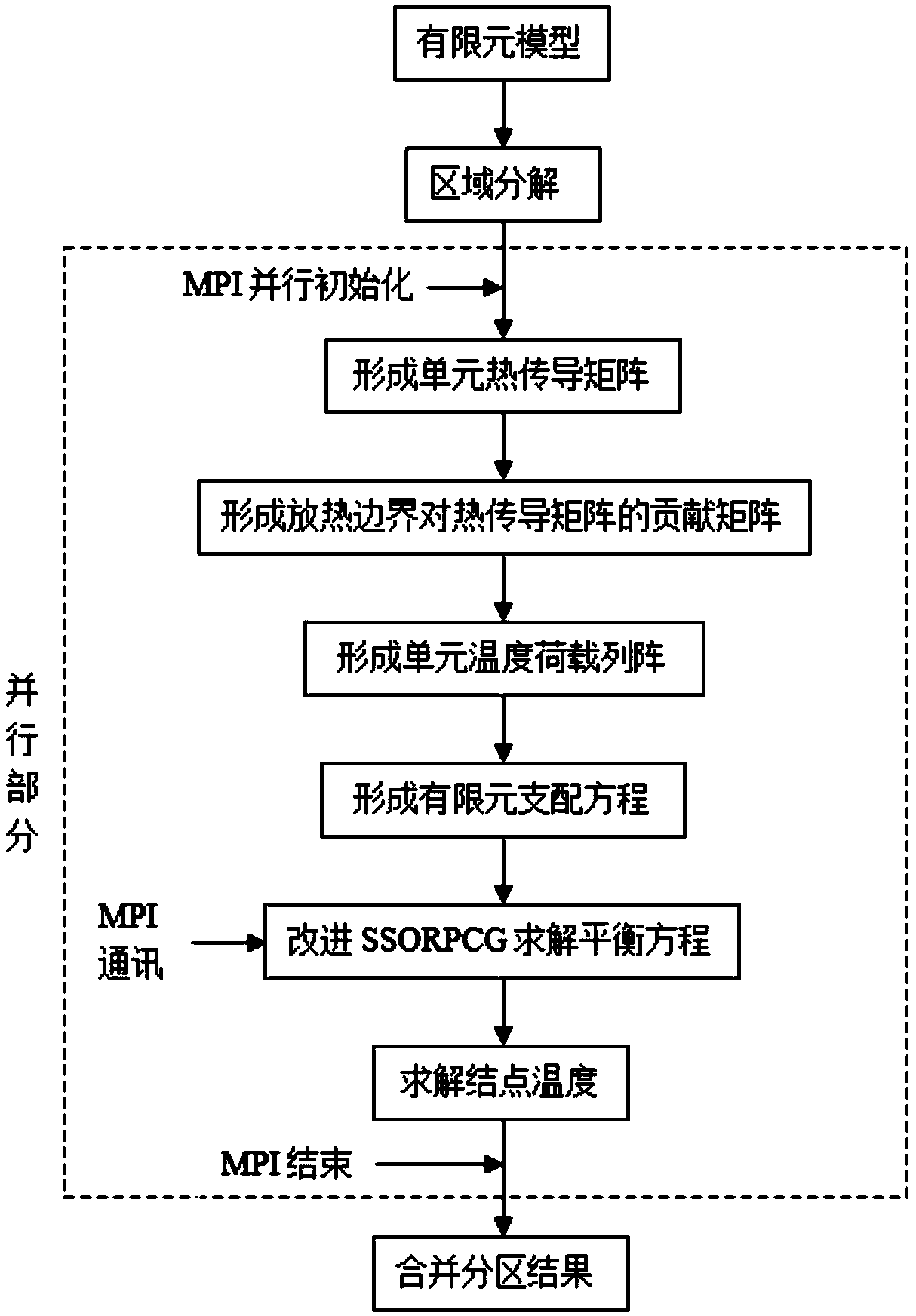
ActiveCN109033733AAvoid restrictionsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionGoverning equation
The invention provides a parallel method for solving temperature field by improved SSORPCG of finite element domain decomposition, which comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a solution model, carrying out finite element discretization on the model, and obtaining structural information of the model; (2) dividing the model into a certain number by using domain decomposition method under serial computation, and distributing the unit information and message passing index of each partition; (3) the element heat conduction matrix, the contribution matrix of exothermic boundary to the heatconduction matrix and the element temperature load array being formed independently in each processor, thus the governing equation of finite element being formed; (4) improved SSORPCG solver being called to solve the temperature of each unknown node, and the temperature field of each partition being obtained; (5) the calculation results of the whole model being obtained. Advantages: the inventioncan effectively improve the ability of solving large-scale sparse coefficient matrix equation group of the temperature field, and can improve the quality and efficiency of the finite element analysisand parallel calculation of the temperature field.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
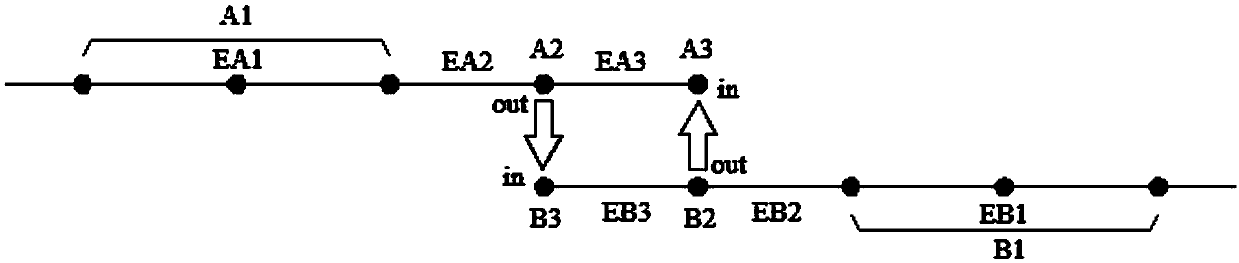
A parallel method for solving seepage field by improved SSORPCG of finite element domain decomposition
ActiveCN109359397AAvoid restrictionsImprove computing efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement analysisDecomposition
The invention discloses a parallel method for solving seepage field by improved SSORPCG of finite element domain decomposition, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps:a solution model is established, the finite element discretization is carried out on the model, and the structural information of the model is obtained; The domain decomposition method is used to partition the model, and the corresponding data files of P sub-regions and each sub-region are obtained. Message passing interface MPI is initialized, finite element governing equation is formed by variational principle; According to Darcy's law, the seepage field of each zone is obtained. Step 5, the results of the P sub-regions are merged to obtain the calculation results of the whole model. Advantages: all processors are independent of each other in the calculation of partition, each process is equal, thus effectively avoiding the limitation of the main process, can maximize the capacity of the computation node, to carry out larger-scale parallel computing; The computational efficiency of solving large sparse coefficient matrix equations is effectively improved in the finite element analysis.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Simulation and correction of mask shadowing effect
ActiveUS8539393B2Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithographic artistDomain decomposition methods
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
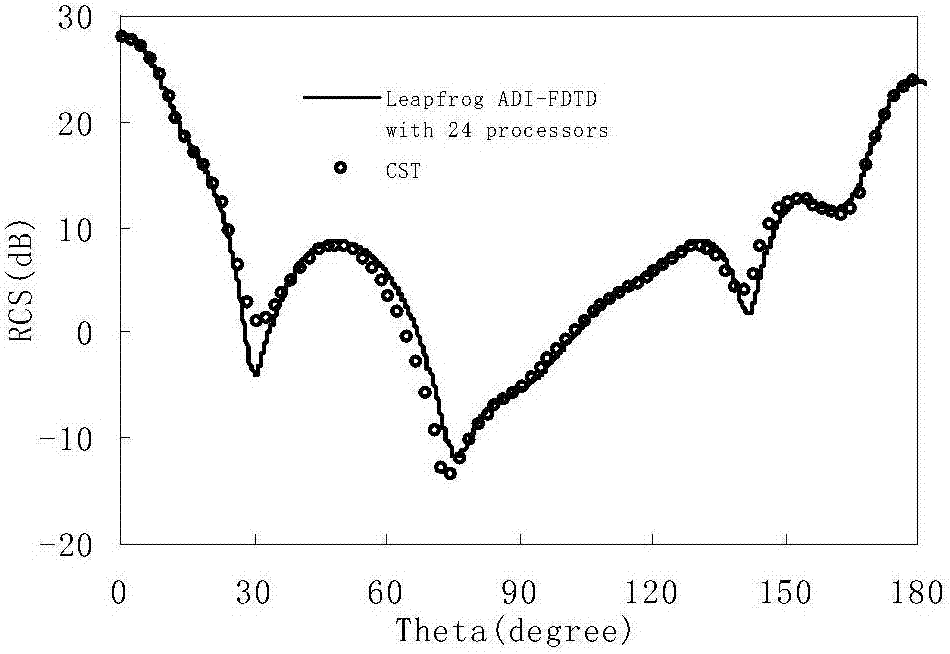
Domain decomposition parallel method effective for unconditional stable time-domain finite difference method
ActiveCN107239586AAchieving Massively Parallel ComputingImplement parallel computingInterprogram communicationDesign optimisation/simulationTime domainDecomposition
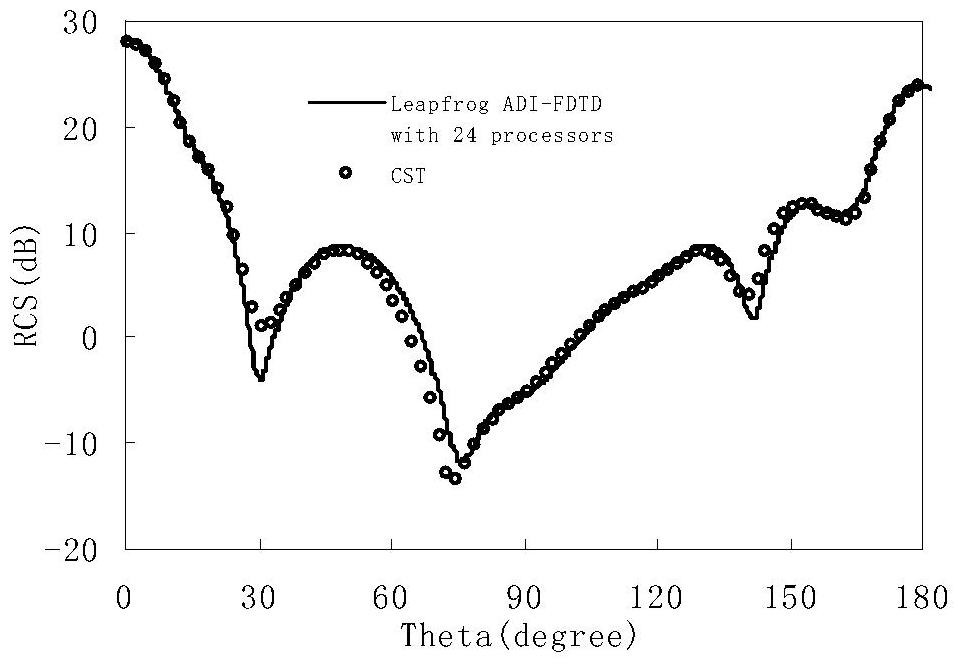
The present invention discloses a domain decomposition parallel method effective for an unconditional stable time-domain finite difference method. In the present invention, the causal domain decomposition method is used to realize the height parallelization of the frog jump alternating direction implicit scheme time-domain finite difference method, and height parallel calculation can be carried out while the unconditional stability is maintained. According to the method disclosed by the present invention, the simulating calculation time on the time-domain finite difference method can be effectively saved, and the programming is simple and the method has a strong practical engineering application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Domain decomposition optimizing method for numerical simulation of structure fire
InactiveCN106815075AHigh speedAutomatic detection of load balancingResource allocationSupercomputerComputer cluster
The invention provides a domain decomposition optimizing method for numerical simulation of structure fire. The method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing a building model, calculating an overall grid size of the building model according to a characteristic diameter of the flame and an empirical formula, and dividing the overall grid; 2) acquiring hardware configuration; 3) dividing the building model into sub-domains, of which the quantity is equal to the quantity of modes used in a cluster or the quantity of CPU used in a super computer, according to an influence factor of load balance; 4) verifying the load balance of each divided sub-domain; if balancing, allocating to a corresponding node and calculating; and if not, adopting a mode searching method for adjusting the volume of each sub-domain, wherein the node means the node used in the computer cluster or the usable CPU. According to the invention, the load balance of each computer node can be automatically detected and adjusted; the method is suitable for high-performance super computers and individual clusters; and the speed of numerical simulation is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
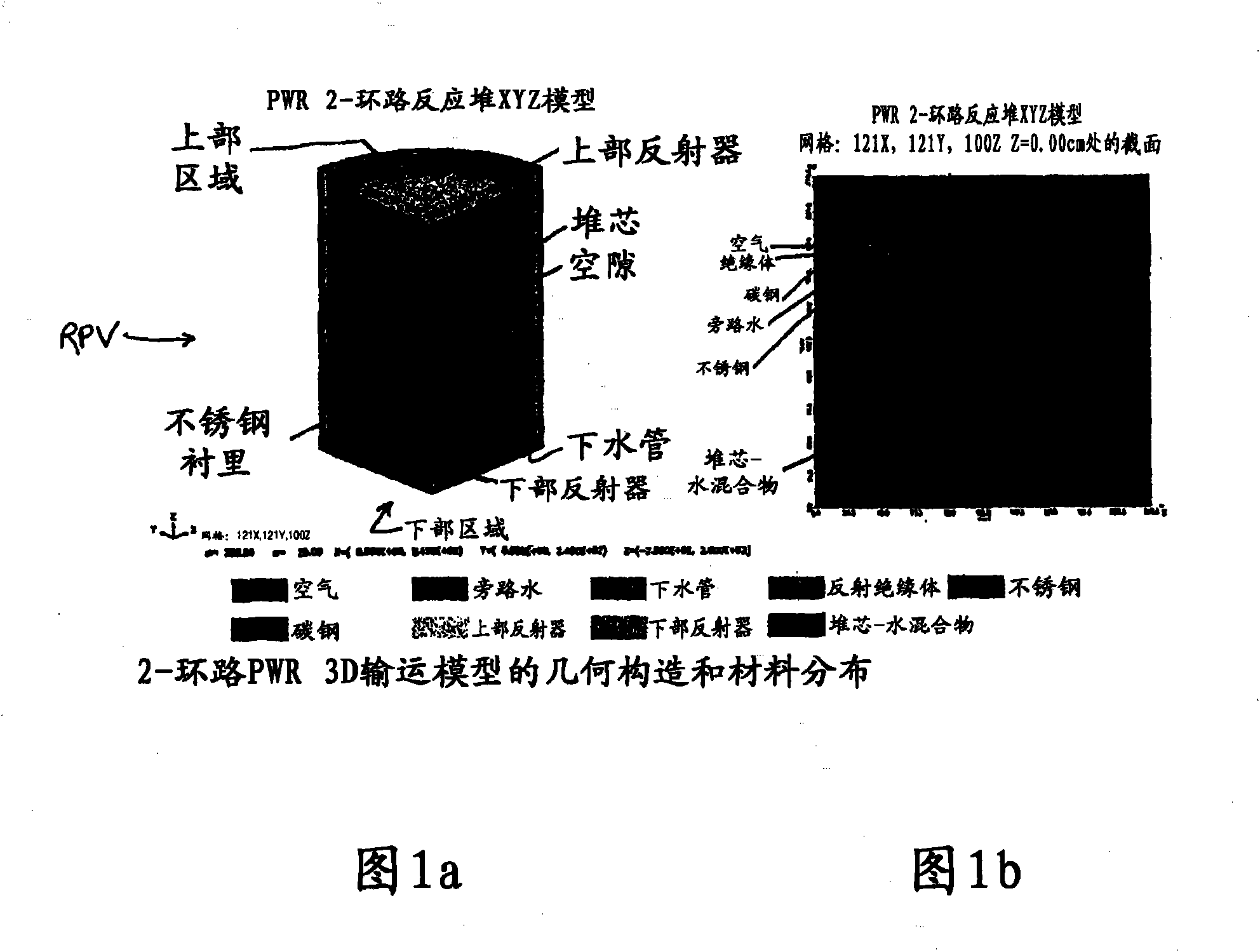
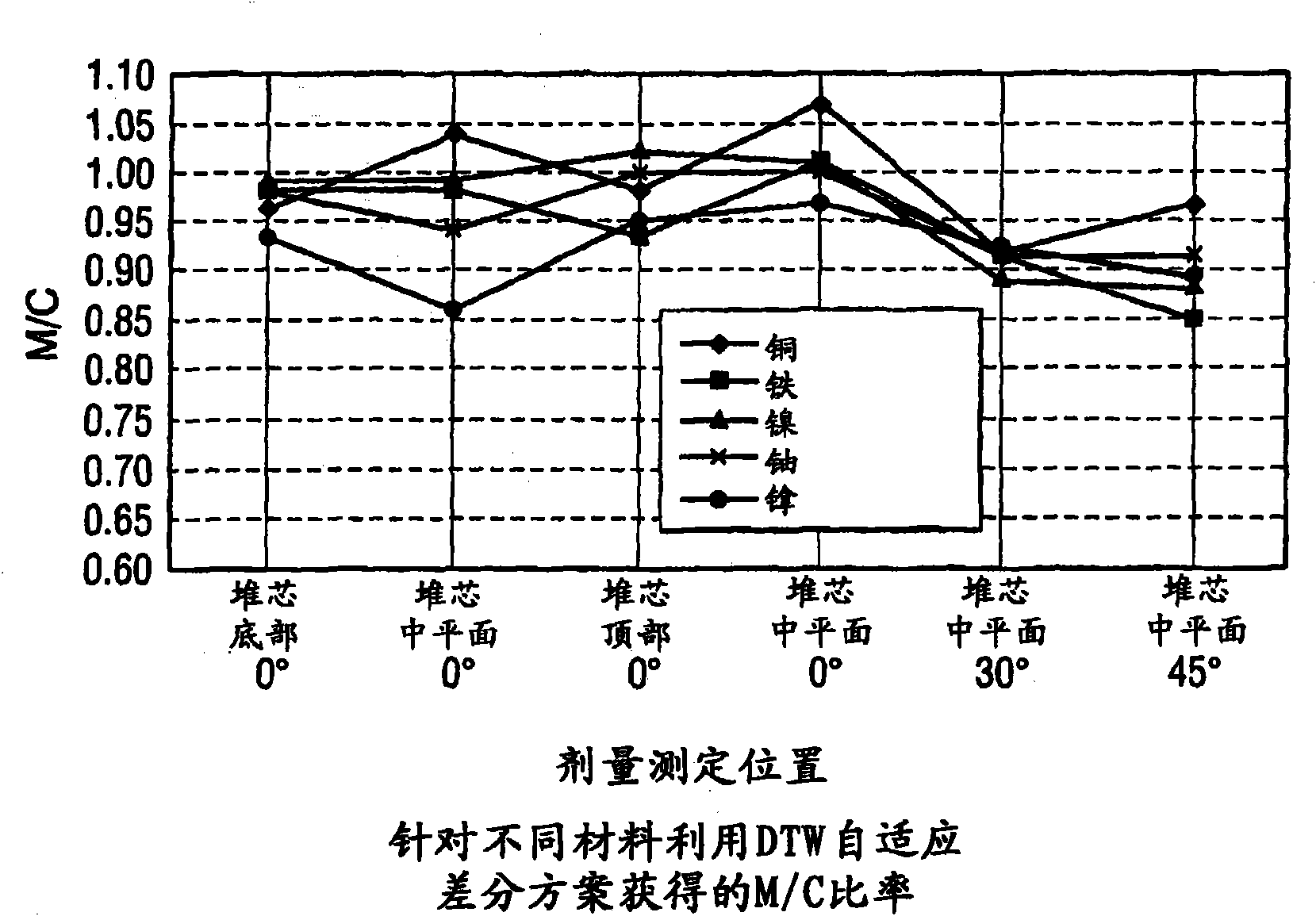
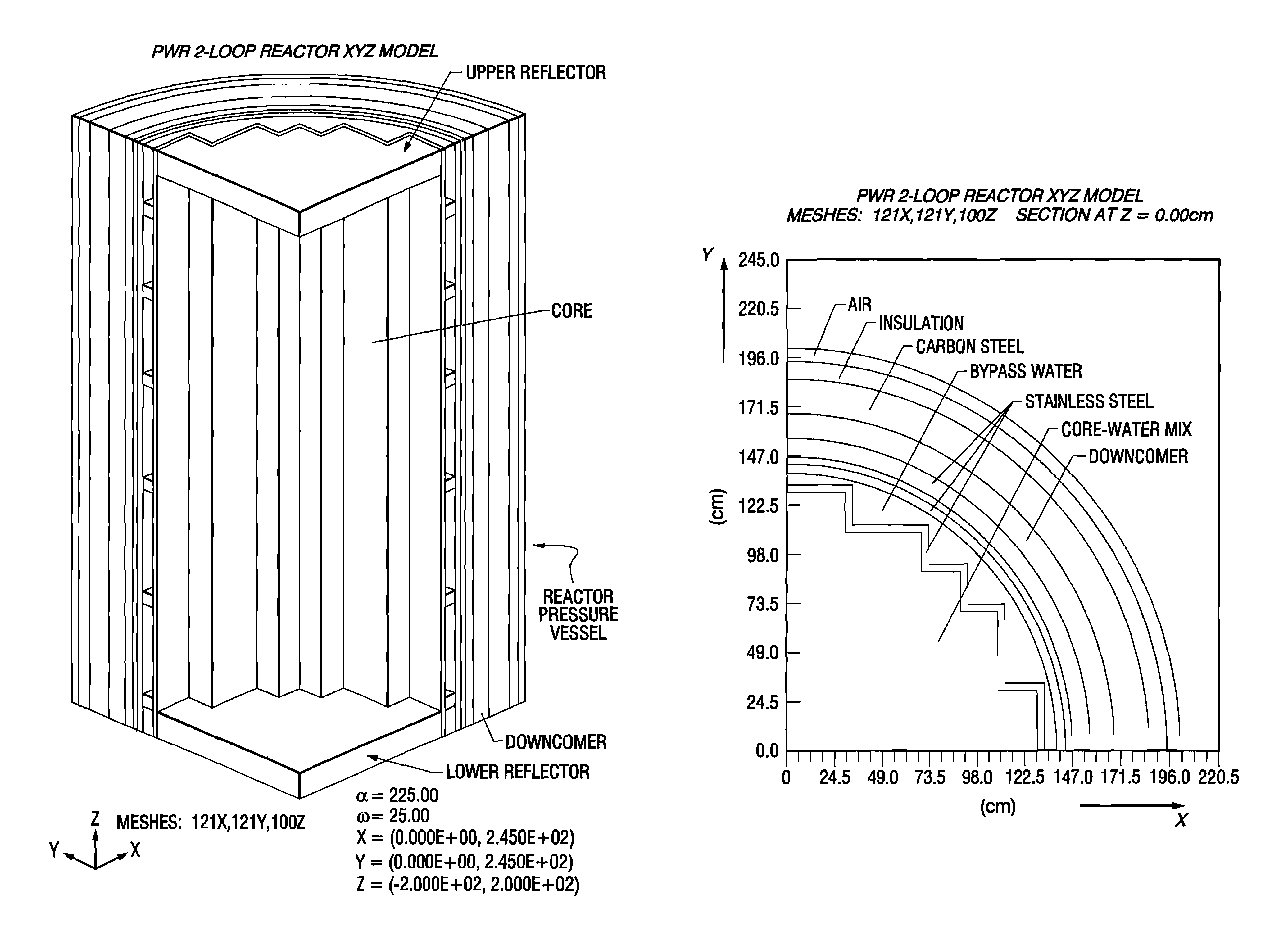
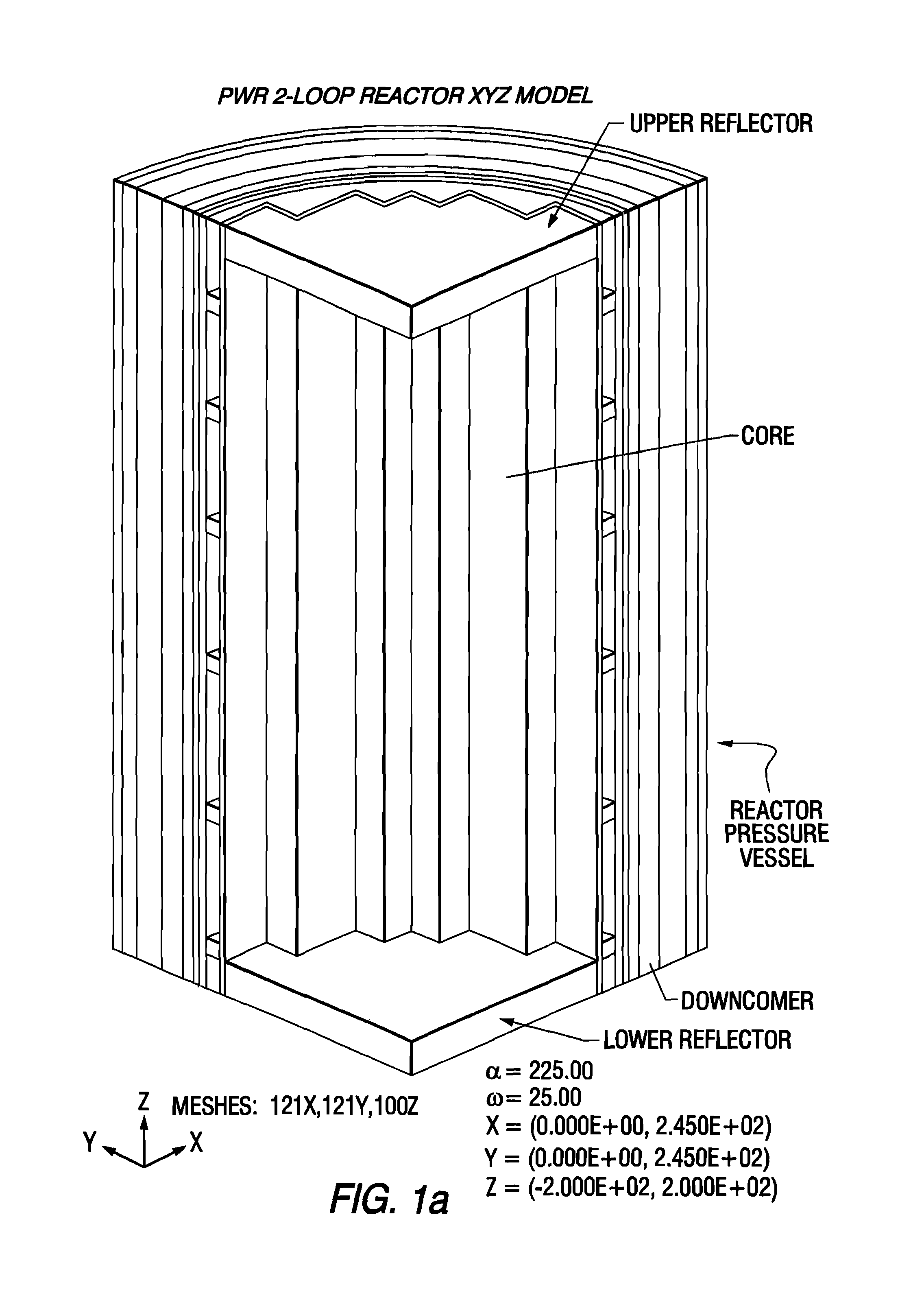
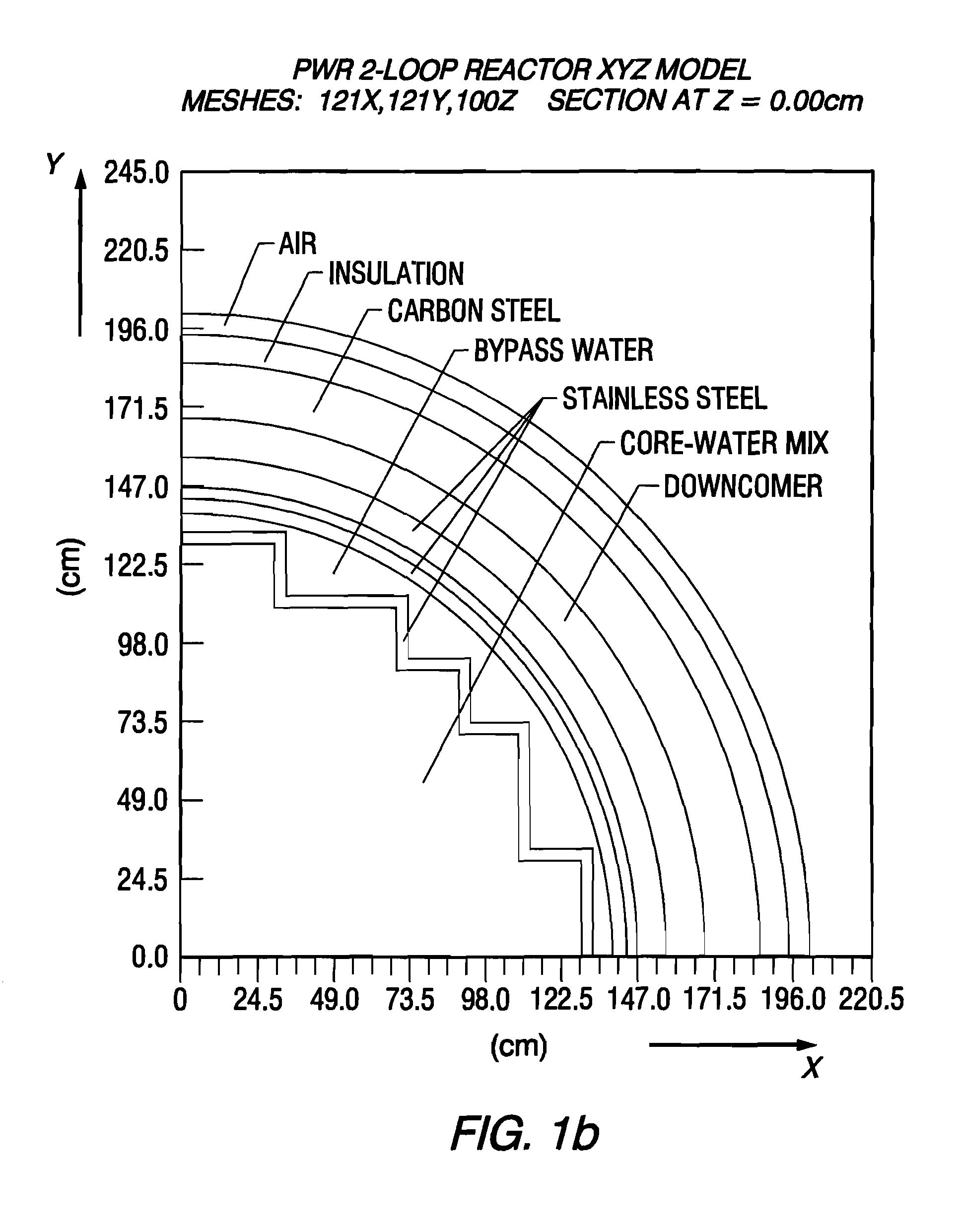
Reactor dosimetry applications using a parallel 3-D radiation transport code
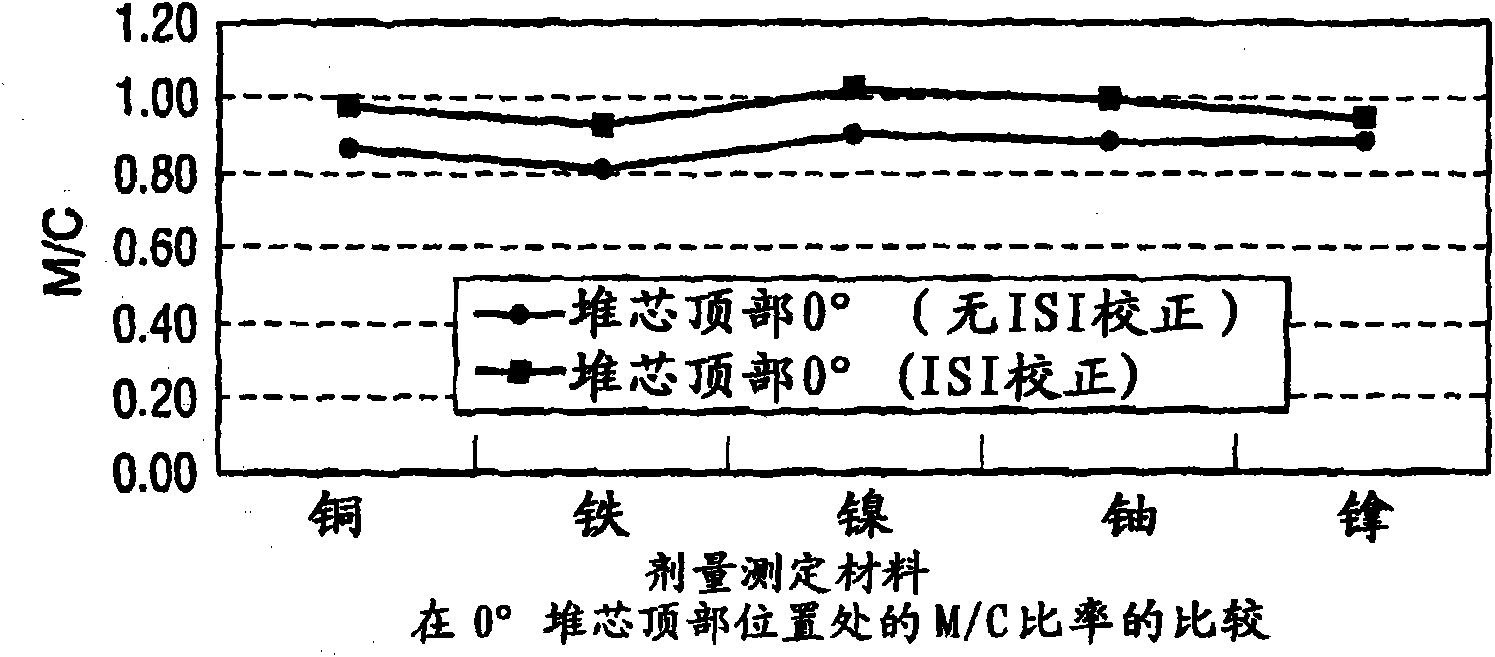
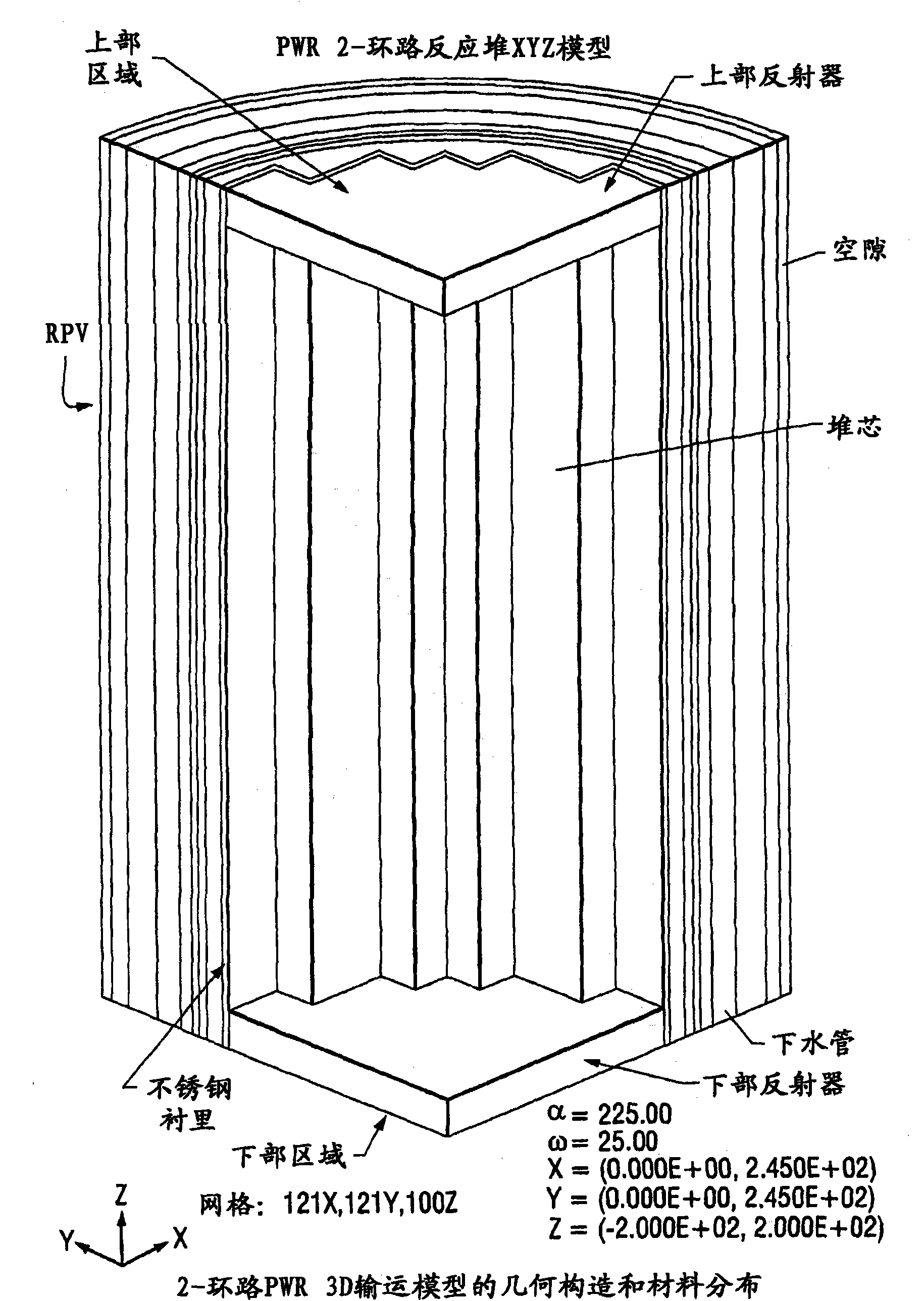
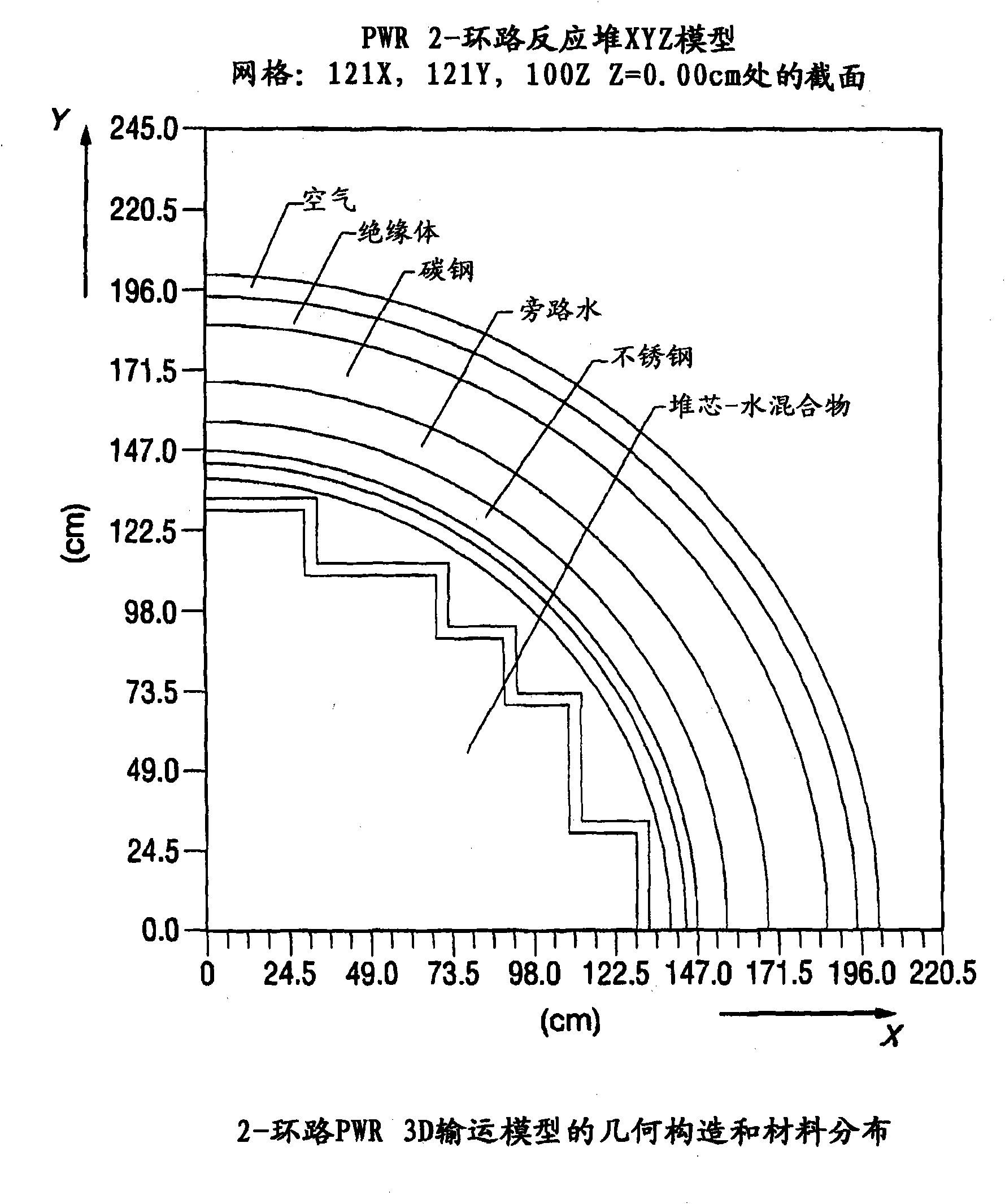
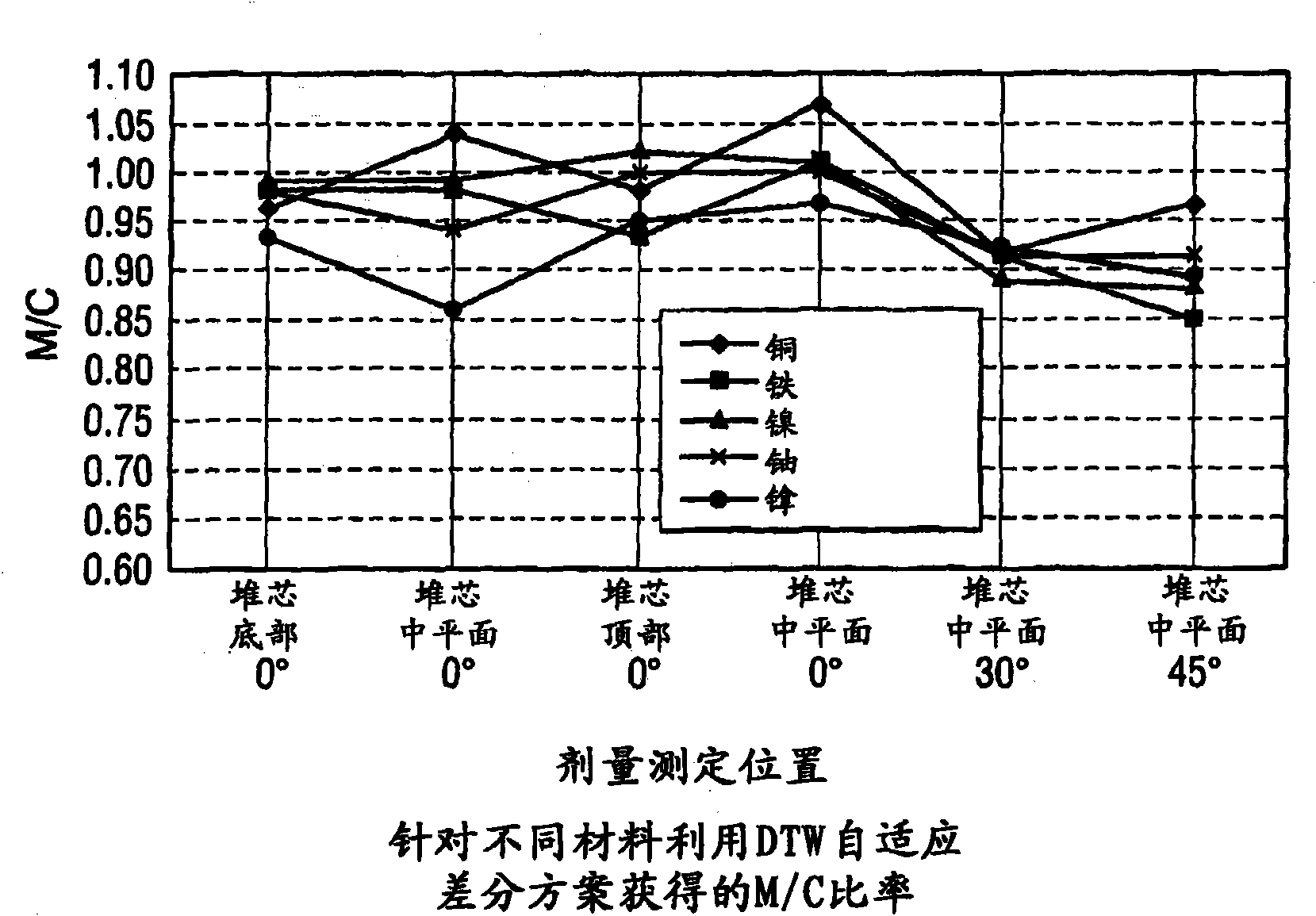
ActiveCN101861609ACosmonautic condition simulationsInterprogram communicationMulti processorDecomposition
The invention relates generally to a method for the calculation of radiation field distributions employing a new parallel 3-D radiation transport code and, a multi-processor computer architecture. The code solves algorithms using a domain decomposition approach. For example, angular and spatial domains can be partitioned into subsets and, the subsets can be independently allocated and processed.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Dynamic load spectrum compilation method based on time domain extrapolation technology
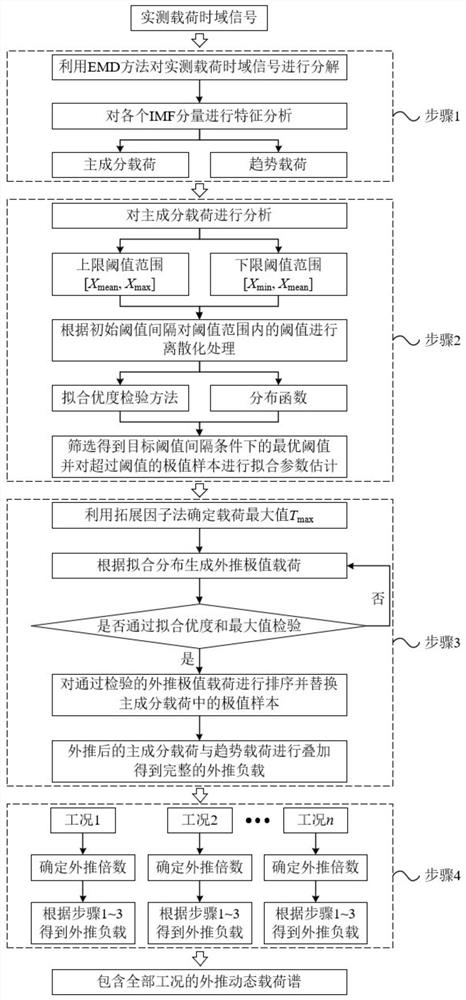
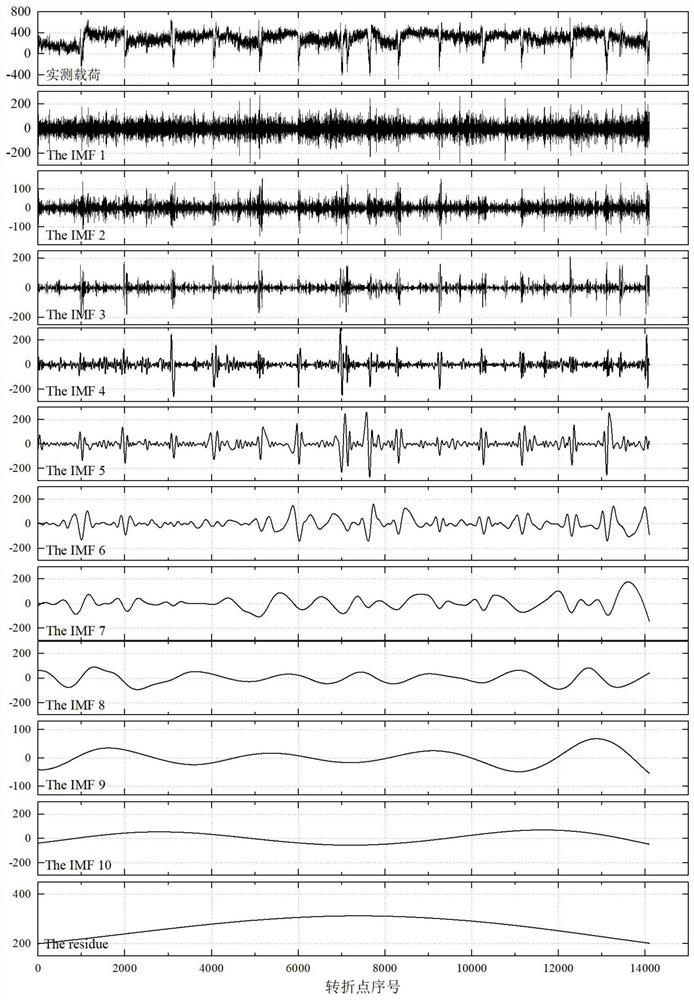
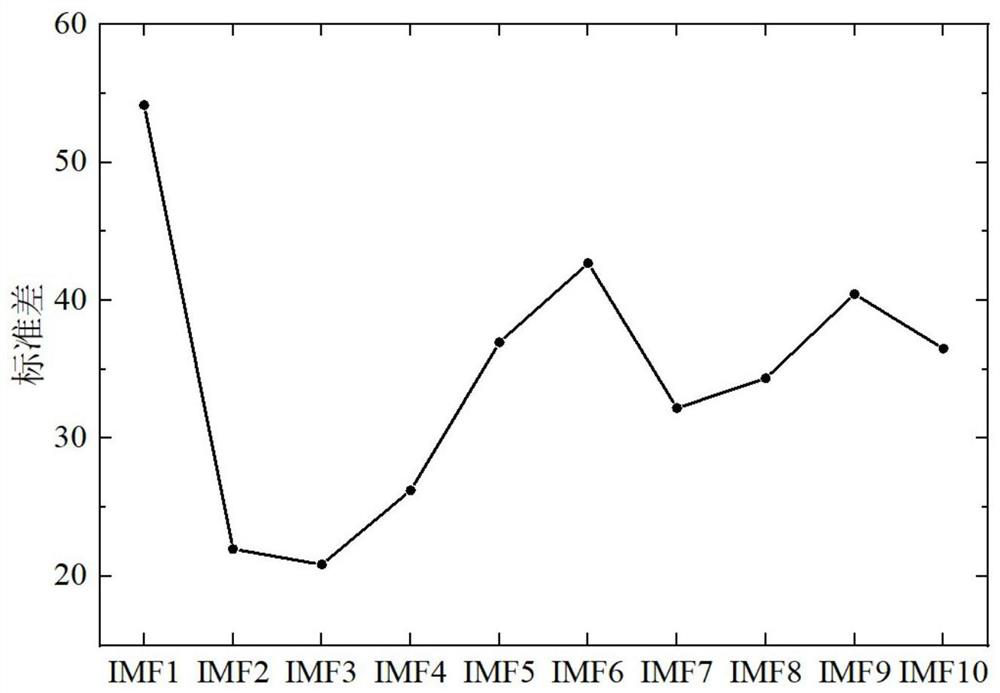
PendingCN113095192AImprove preparation efficiencySolve the problem of distorted extrapolation resultsCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainComponent Load
The invention relates to a dynamic load spectrum compilation method based on a time domain extrapolation technology, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, processing an actually measured load time domain signal through employing a load time domain decomposition method of empirical mode decomposition, and obtaining a principal component load and a trend load; step 2, calculating an upper and lower limit optimal threshold value based on a threshold value screening method, and obtaining a fitting distribution function consistent with extreme value sample distribution exceeding the threshold value; 3, extrapolating and reconstructing the extreme value sample exceeding the threshold value on the basis of the step 2 to obtain a complete extrapolation load; and 4, compiling a dynamic load spectrum based on an improved time domain extrapolation method. According to the method, more accurate load input can be provided for simulation analysis and reliability tests in the field of mechanical engineering, and the precision of load spectrum compilation is further improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Reactor dosimetry applications using a parallel 3-D radiation transport code
The invention relates generally to a method for the calculation of radiation field distributions employing a new parallel 3-D radiation transport code and, a multi-processor computer architecture. The code solves algorithms using a domain decomposition approach. For example, angular and spatial domains can be partitioned into subsets and, the subsets can be independently allocated and processed.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
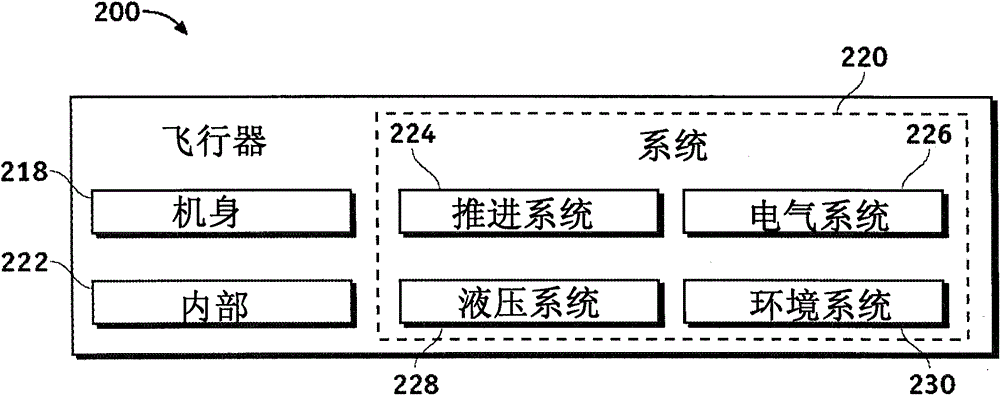
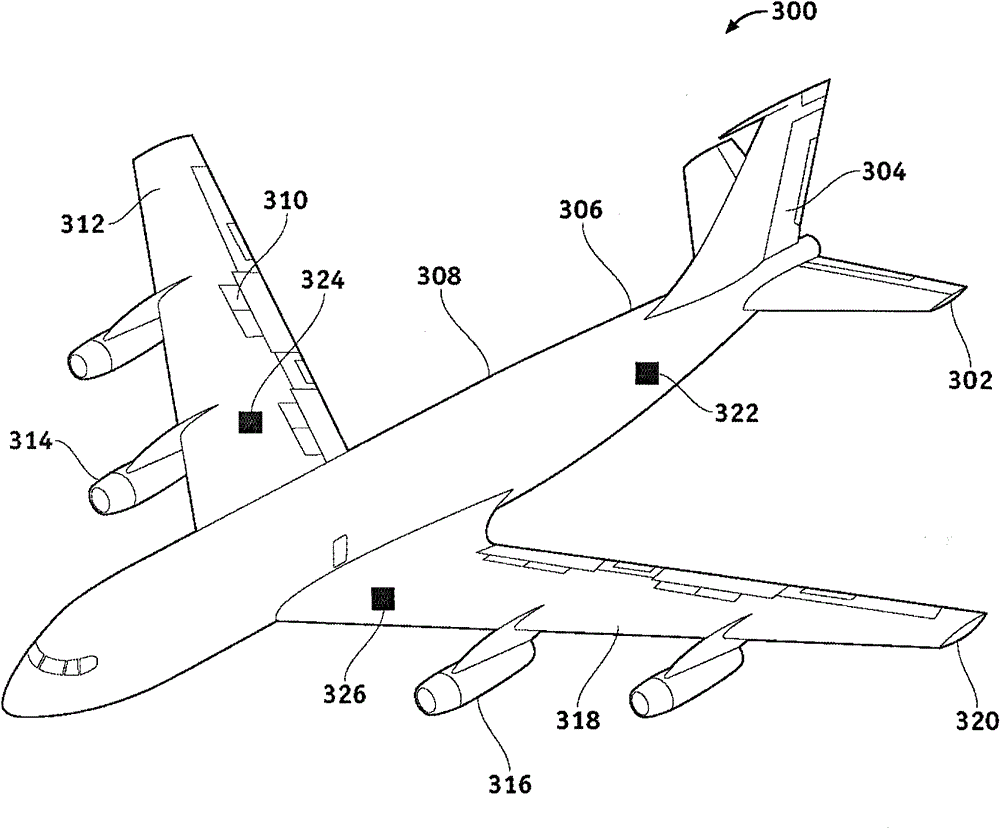
Processor Feature Optimization and Large-Scale System Optimization via Domain Decomposition
ActiveCN102446238BOptimizing Processor RequirementsForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionDomain decomposition methods
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Domain decomposition finite element method for simulating Darcy velocity at interface of groundwater medium
ActiveCN107657075BImprove computing efficiencyGuaranteed accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionProton
The invention discloses a domain decomposition finite element method for simulating Darcy speed at an underground medium interface. The method comprises the following steps: performing variation on anunderground flow problem by using a Galerkin method, sub-dividing a research domain, and acquiring waterhead by applying the finite element method; decomposing the research domain into a plurality ofsingle-medium sub-domains by applying interfaces of different mediums according to the medium composition of the research domain, and decomposing an underground Darcy speed solution problem on the research domain into sub-problems on the sub-domain by applying the domain decomposition method; selecting one sub-problem, performing variation by using the Galerkin method, and acquiring the Darcy speed by applying a Galerkin model of the Yeh, acquiring the Darcy speed at the other side of the interface of the sub-domain and other sub-domain by combining with the refraction law as the first classof boundary condition of the adjacent sub-problem; selecting the next sub-problem to solve, and repeating this process until all sub-problems are completely solved. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the computing consumption of the Darcy speed is reduced through the domain decomposition method, and the precision of the Darcy speed at the interface is guaranteed by using the refraction law.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
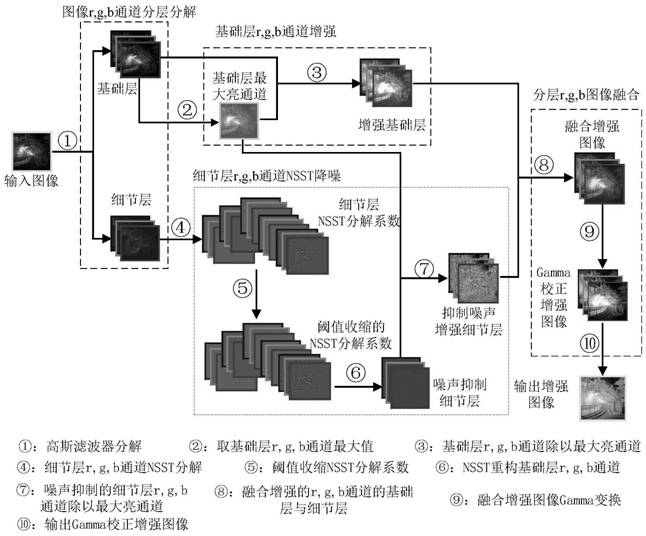
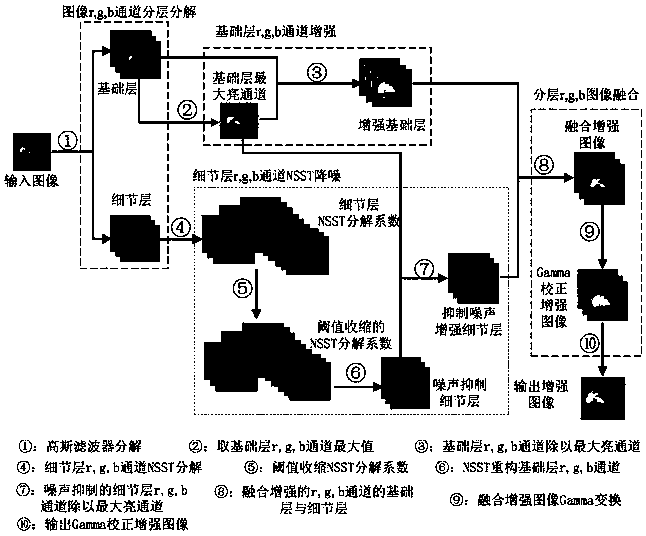
An Enhancement Method of Underground Noisy Image Based on Dual Domain Decomposition
ActiveCN110634112BIncrease contrastImage enhancementImage analysisDomain decomposition methodsMaterials science
The invention discloses a dual-domain decomposition method for enhancing noise-containing images in underground mines. The method first uses a Gaussian filter in space to decompose the noise-containing images in underground mines in layers to realize the decoupling of image contrast improvement and noise suppression; The maximum bright channel image of the base layer obtained by the layer is used as the illuminance component estimation of the Retinex model. According to the Retinex enhancement principle, the contrast of the base layer is improved; The shearlet transform domain implements hard threshold shrinkage on the decomposition coefficients to achieve noise suppression in the detail layer. The non-subsampled shearlet inverse transform shrinks the decomposition coefficients to obtain the noise suppression detail layer. Using the same enhancement ratio as the base layer, the noise suppression detail layer is achieved. Enhancement; finally, the fusion enhanced image is obtained by fusing the enhanced base layer and the noise-suppressed enhanced detail layer, and Gamma fine-tuning is performed on the fusion-enhanced image to obtain the final noise-suppressed and contrast-enhanced enhanced image.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
A Parallel Method for Domain Decomposition Efficient for Unconditionally Stable Finite-Difference Time-Domain Methods
ActiveCN107239586BAchieving Massively Parallel ComputingImplement parallel computingInterprogram communicationDesign optimisation/simulationComputational scienceTime domain
The present invention discloses a domain decomposition parallel method effective for an unconditional stable time-domain finite difference method. In the present invention, the causal domain decomposition method is used to realize the height parallelization of the frog jump alternating direction implicit scheme time-domain finite difference method, and height parallel calculation can be carried out while the unconditional stability is maintained. According to the method disclosed by the present invention, the simulating calculation time on the time-domain finite difference method can be effectively saved, and the programming is simple and the method has a strong practical engineering application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chip Thermal Analysis Method Based on 3D Domain Decomposition
InactiveCN103324836BAccurate temperatureCalculation speedSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionDomain decomposition methods
A chip thermal analysis method based on three-dimensional domain decomposition comprises the steps of adopting a non-overlapping domain decomposition method to perform thermal analysis of a chip system including a chip and a heat-radiating part, performing discrete grid division of different domains of the chip system respectively, setting an appropriate condition at each domain interface position to solve the domains and achieving convergence of a computed result of the interface position of the chip and the heat-radiating part through multiple overall iterations. By means of the chip thermal analysis method based on the three-dimensional domain decomposition, temperature distribution of the chip in the chip system can be quickly calculated.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
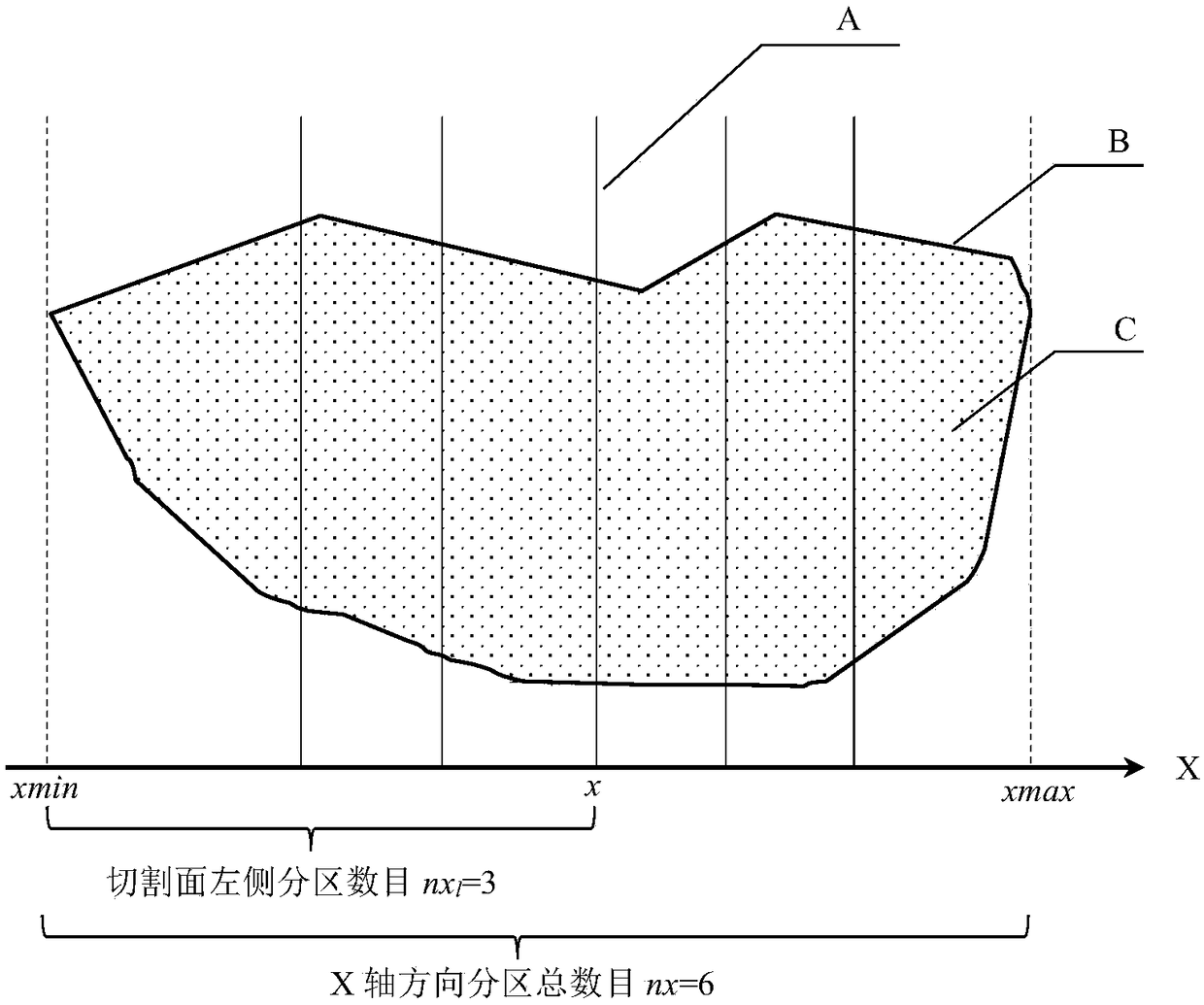
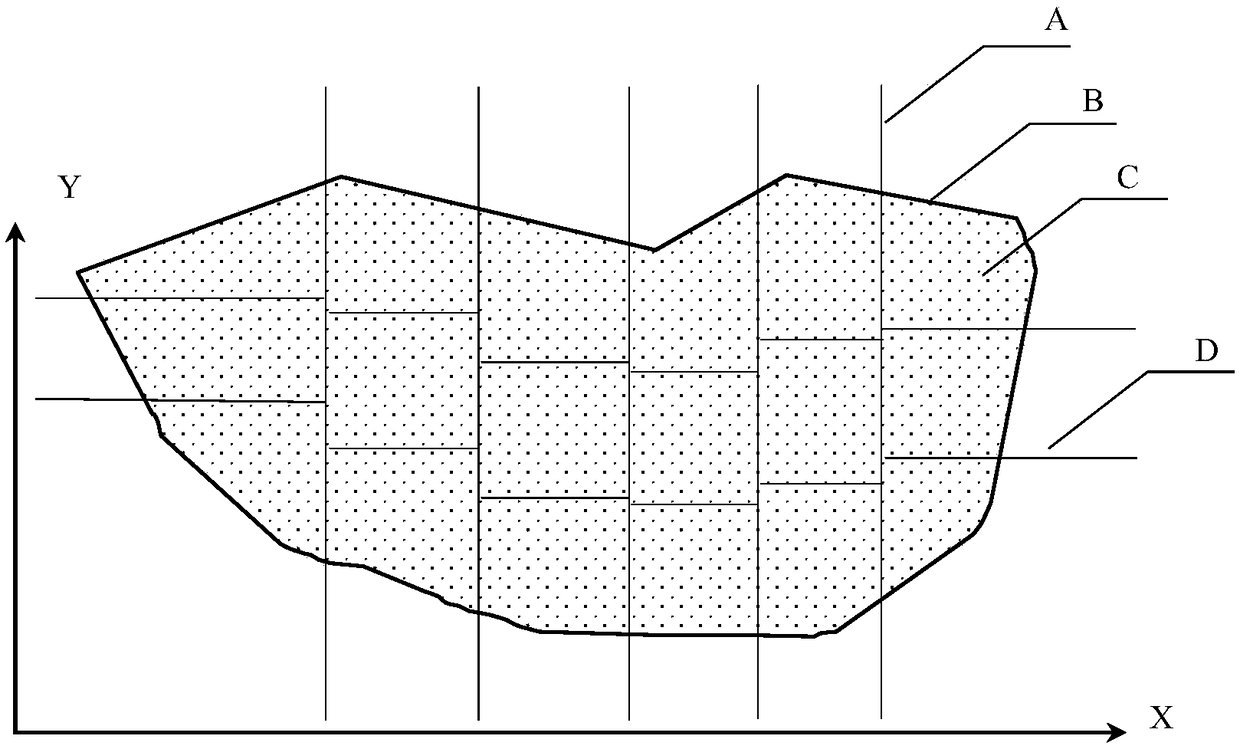
A fast cutting surface search method for domain decomposition in parallel numerical simulation
ActiveCN109002651AQuick searchImprove search efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionDistribution characteristic
The invention relates to a fast cutting surface search method for region decomposition of parallel numerical simulation, which comprises the following steps: according to the distribution characteristics of particles or grids in the simulation region, a monotonic decreasing function about the cutting surface is constructed, so that when the cutting surface is in the correct position, the monotonicdecreasing function value is 0; then the benchmark function is constructed to measure the relative error of the cutting surface. The expected cutting surface is obtained by iterative method using monotonic decreasing function and benchmark function. The invention continuously narrows the searching range of the cutting surface through an iterative algorithm and can quickly converge to the cuttingsurface.
Owner:中国空气动力研究与发展中心超高速空气动力研究所
Dual-domain decomposition mine noise-containing image enhancing method
The invention discloses a dual-domain decomposition mine noise-containing image enhancing method, which comprises the following steps: firstly, hierarchically decomposing a mine noise-containing imageby using a spatial domain Gaussian filter to realize decoupling of image contrast improvement and noise suppression; secondly, taking the maximum bright channel image, obtained through layering, of the base layer as illuminance component estimation of a Retinex model, and improving the contrast of the base layer according to the Retinex enhancement principle; decomposing a detail layer obtained by layering by using non-subsampled shear wave transformation; carrying out hard threshold shrinkage on the decomposition coefficient in the shear wave transform domain, realizing detail layer noise suppression and non-subsampled shear wave inverse transform shrinkage decomposition coefficients, obtaining a noise suppression detail layer, and realizing enhancement of the noise suppression detail layer by using the same enhancement proportion of the base layer; and finally, fusing the enhanced base layer and the enhanced detail layer for noise suppression to obtain a fused enhanced image, and performing Gamma fine adjustment on the fused enhanced image to obtain a final enhanced image for noise suppression and contrast improvement.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Reactor dosimetry applications using parallel 3-D radiation transport code
ActiveCN101861609BCosmonautic condition simulationsInterprogram communicationDosimetry radiationMulti processor
The invention relates generally to a method for the calculation of radiation field distributions employing a new parallel 3-D radiation transport code and, a multi-processor computer architecture. The code solves algorithms using a domain decomposition approach. For example, angular and spatial domains can be partitioned into subsets and, the subsets can be independently allocated and processed.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
A Fast Algorithm for Coupling High-Precision Complicated Flow Field Based on Domain Decomposition
ActiveCN104036095BImprove adaptabilityEasy to handleSpecial data processing applicationsProblem domainDecomposition
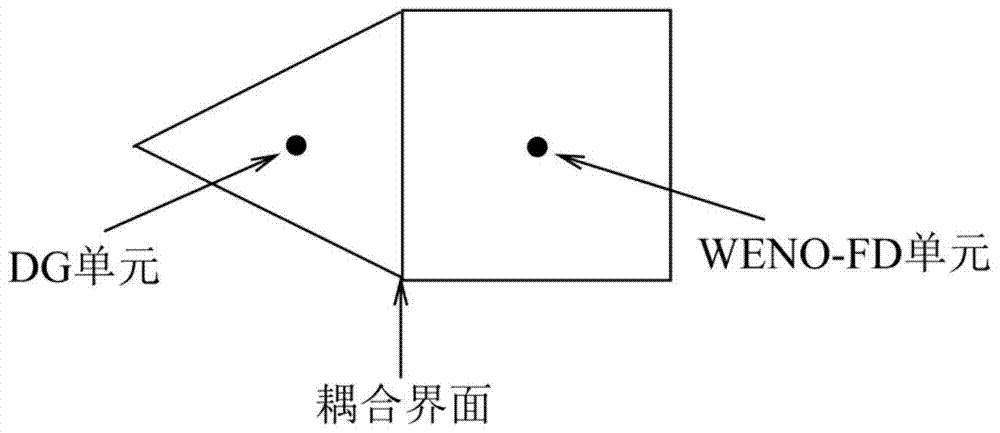
The invention provides a fast calculation method for solving hyperbolic conservation law equations and Euler equations based on domain decomposition coupled high-precision DG and WENO methods. The method first performs domain decomposition on the original problem, that is, adopts a structure in the area near the physical boundary Or the unstructured discontinuous finite element method (DG), using the finite body difference weighted intrinsically non-oscillating (WENO) scheme under the structured mesh in the remaining regular regions. In the process of dealing with the domain coupling interface, there are two processing methods, one is the conservative coupling processing method; the other is the non-conservative coupling processing method. In the actual calculation process, we use the bad element indicator to judge whether the solution near the interface is sufficiently smooth. If the solution is sufficiently smooth, the non-conservative coupling method is used at the interface, otherwise, the conservative coupling method is used.
Owner:三多(杭州)科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com