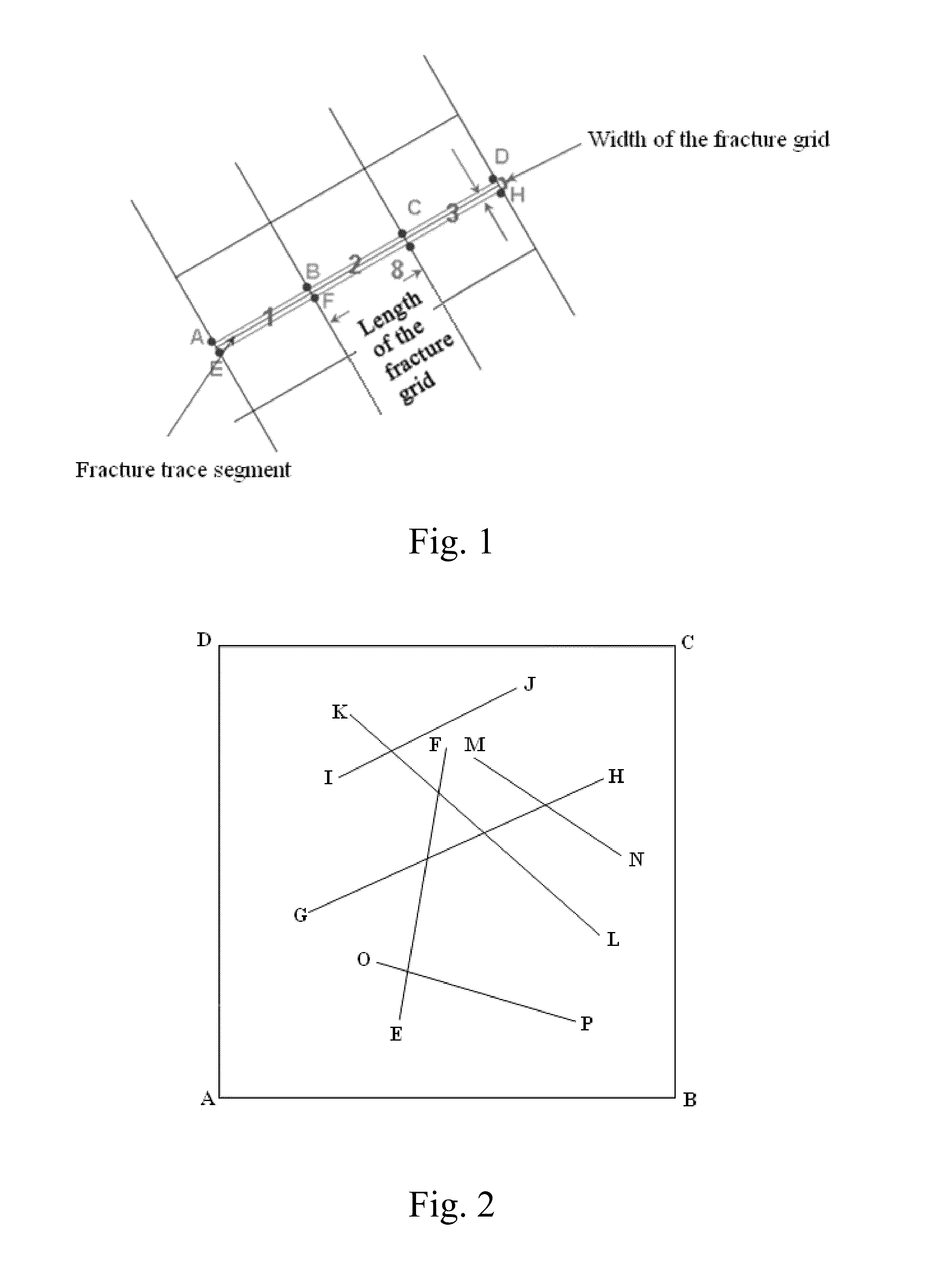
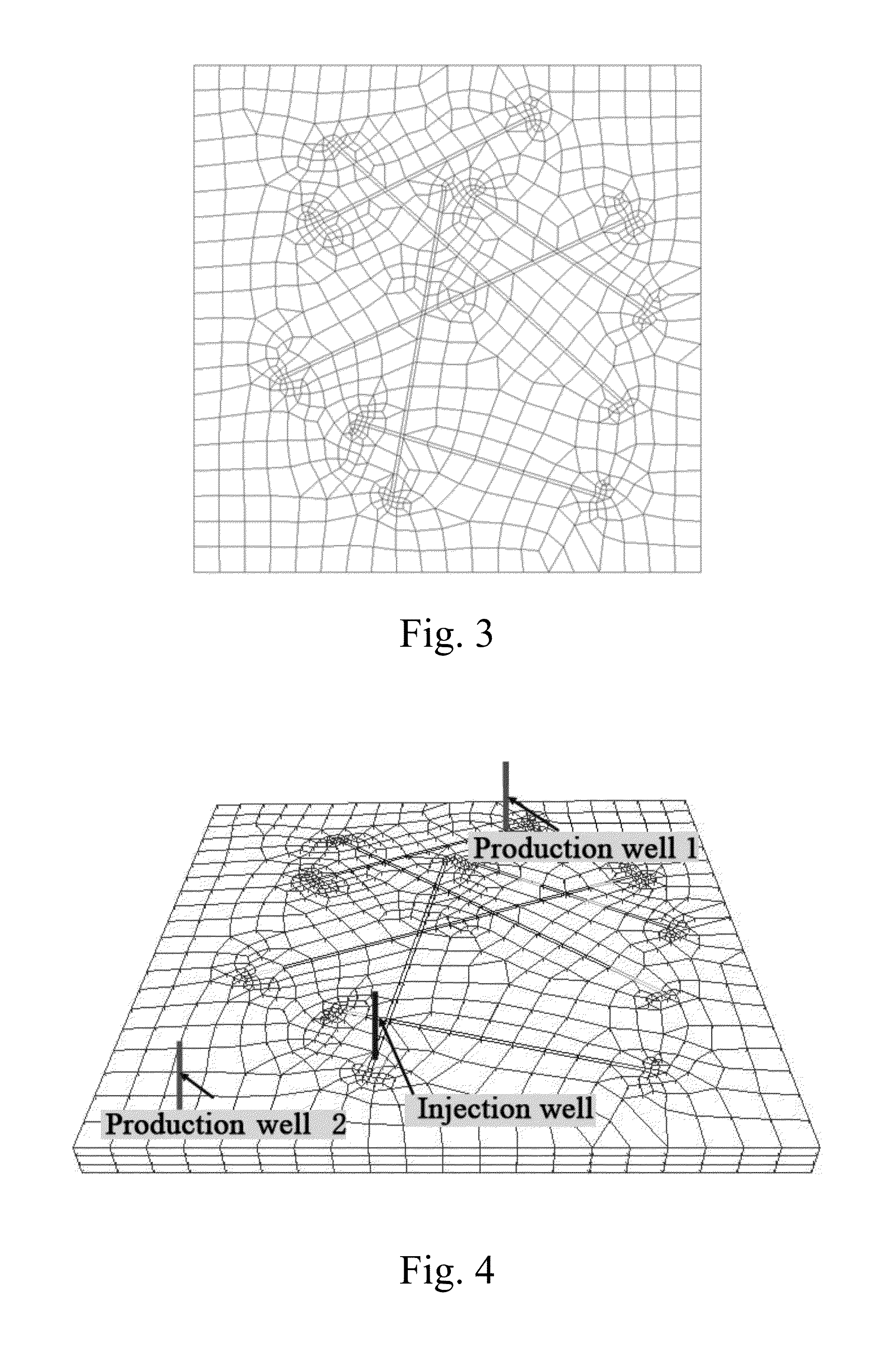
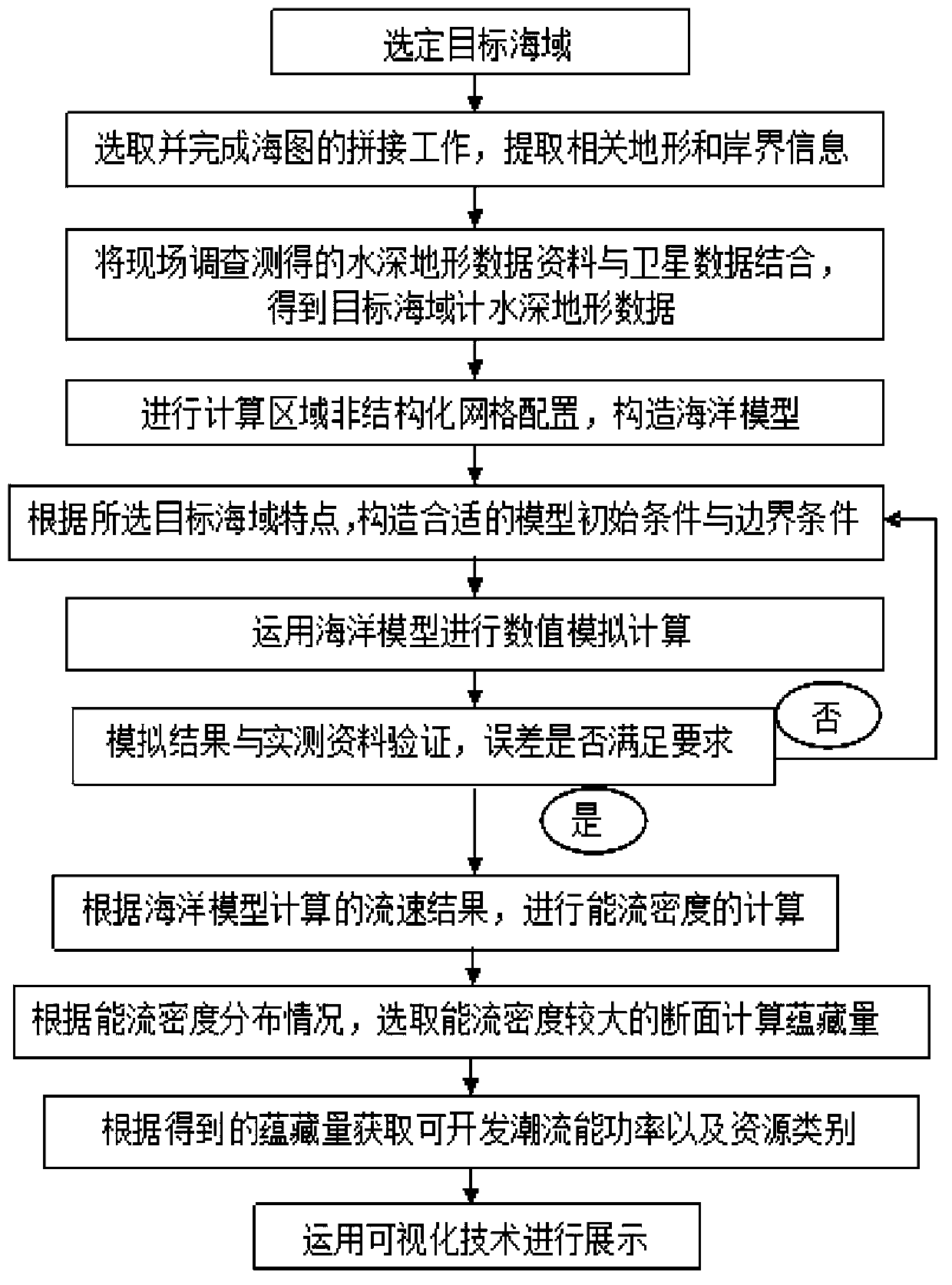
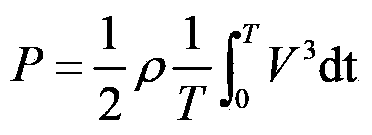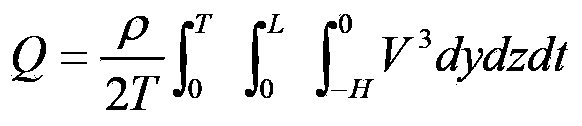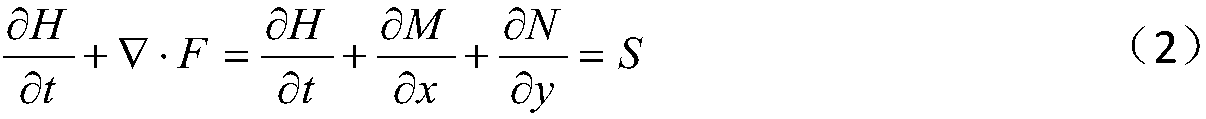Patents
Literature
111 results about "Unstructured mesh" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
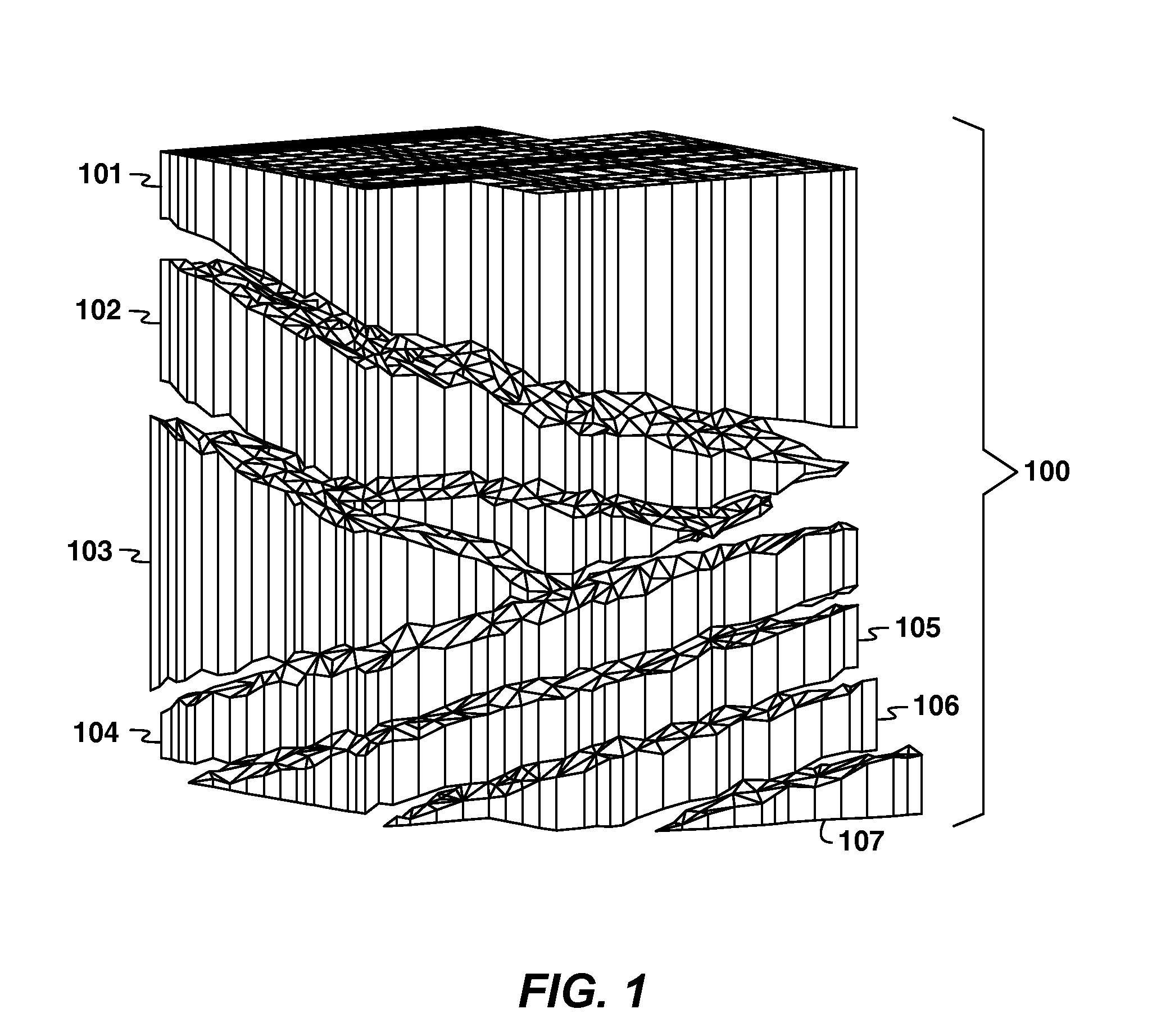
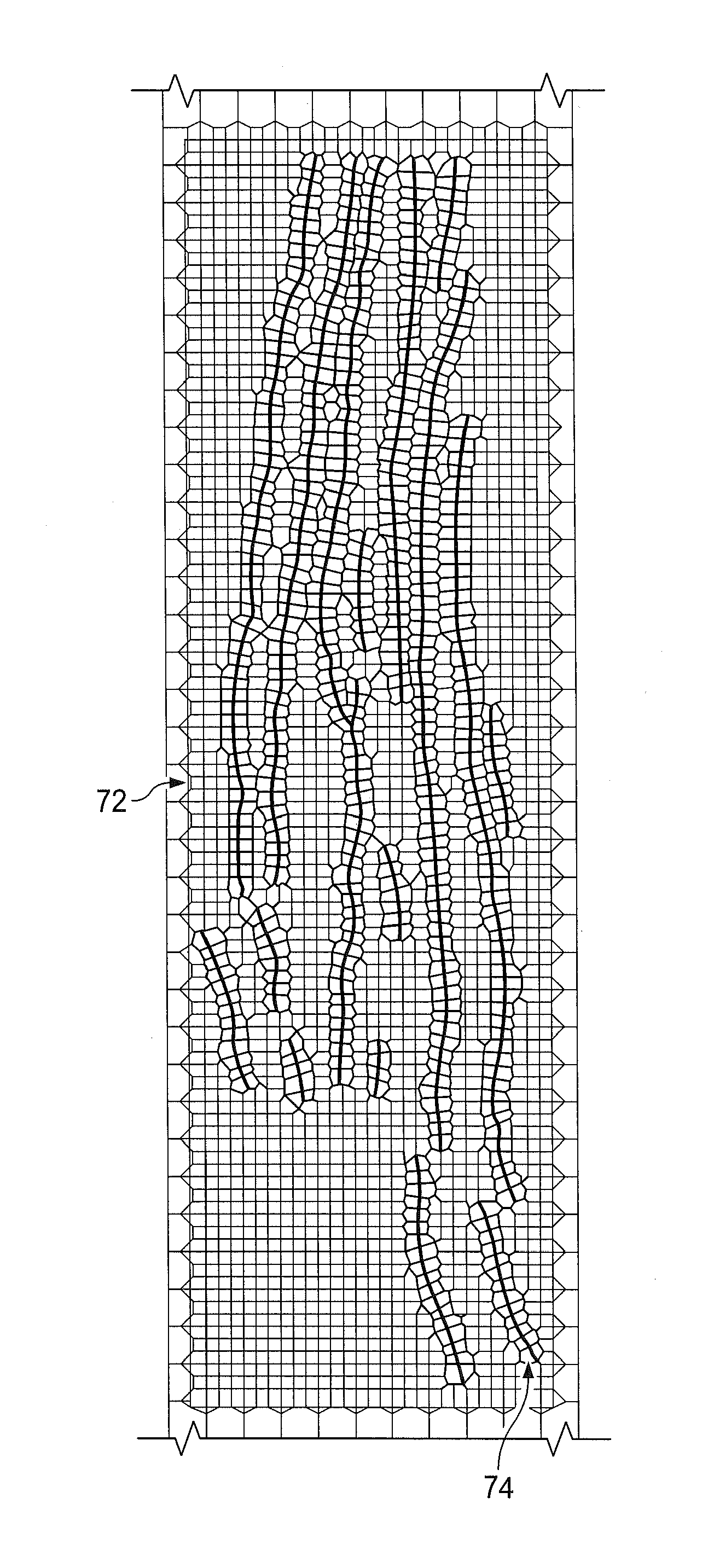
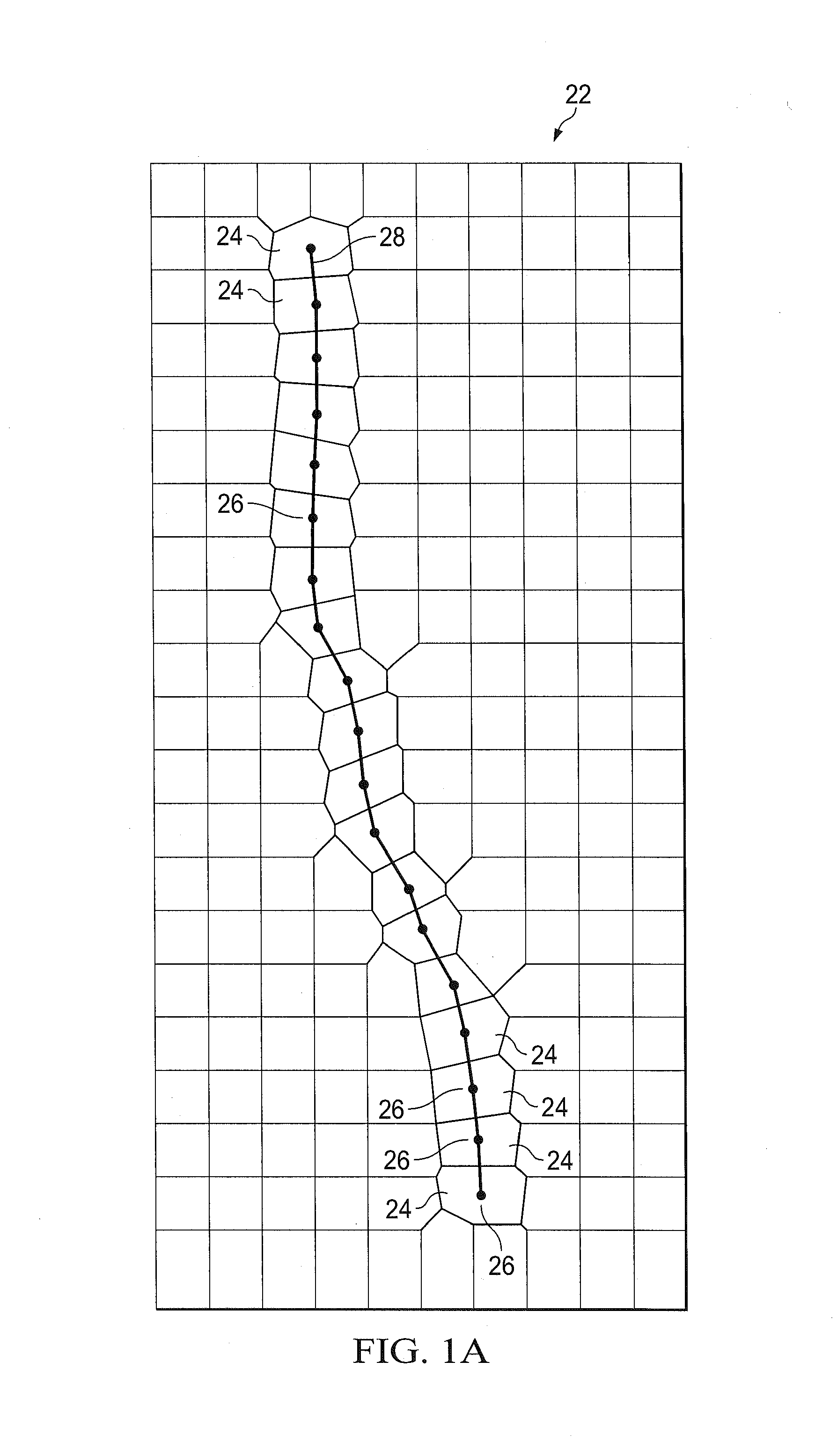
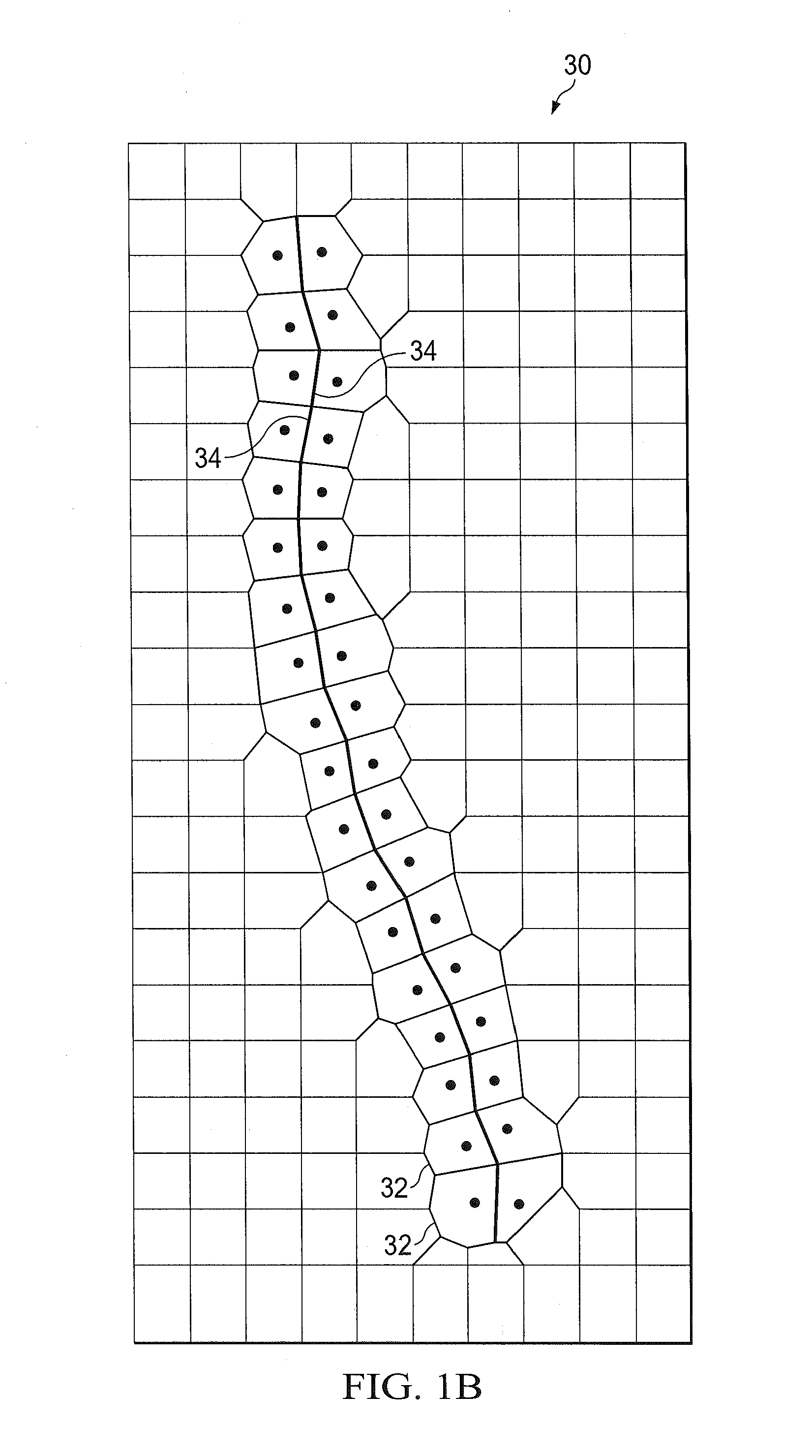
Solution method and apparatus for large-scale simulation of layered formations
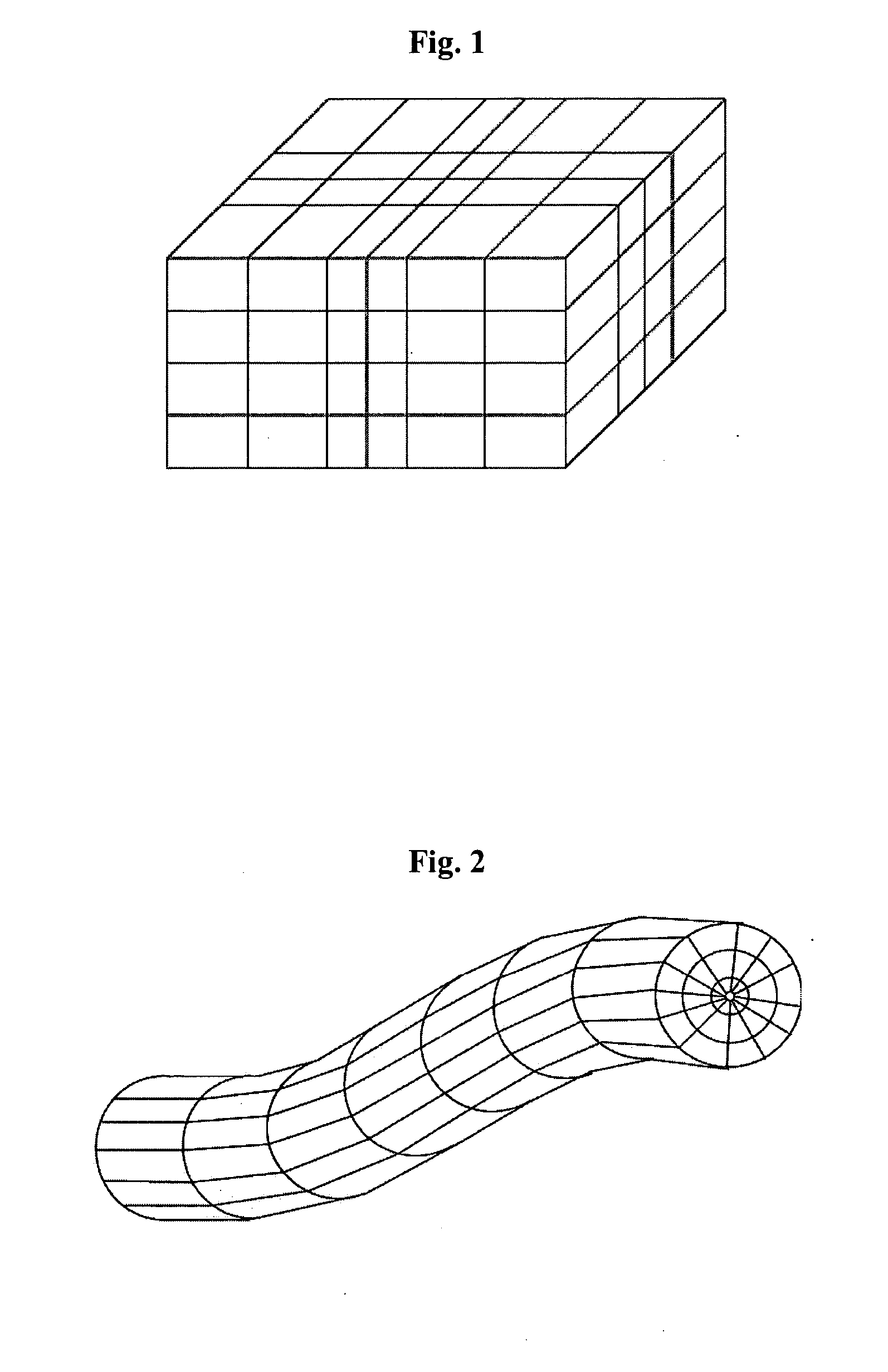
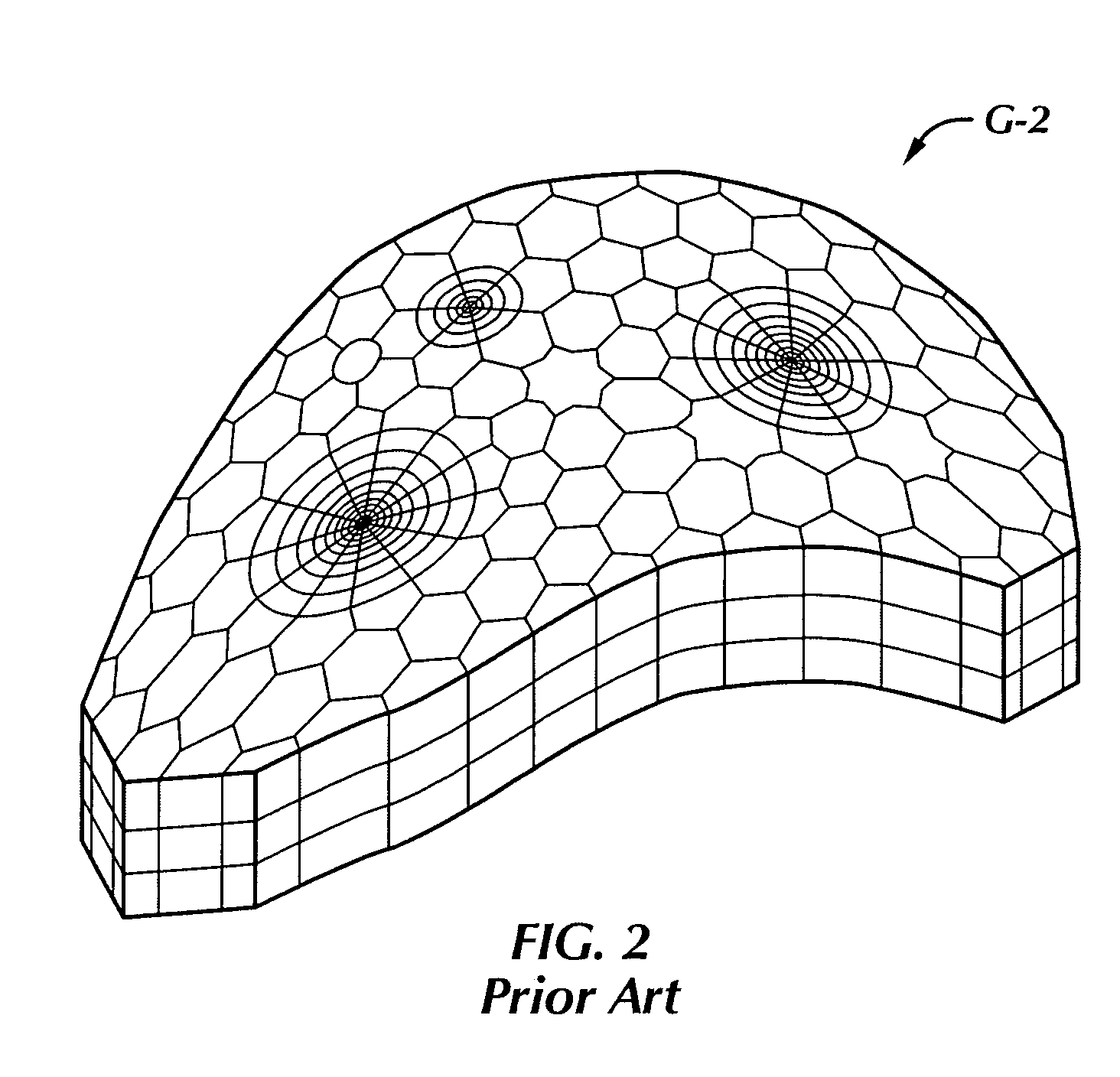
ActiveUS20060235667A1Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSupercomputerAngular point
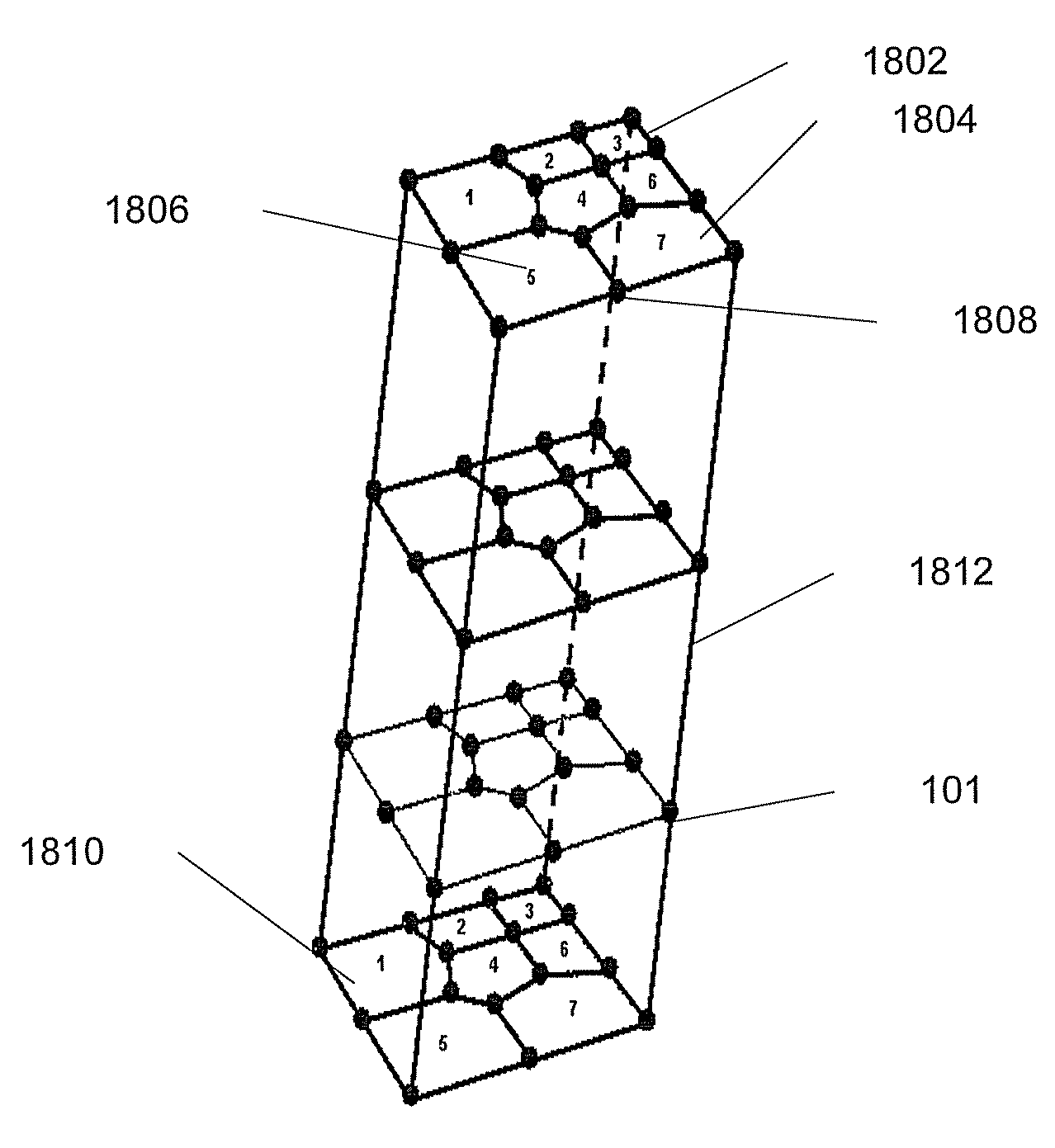
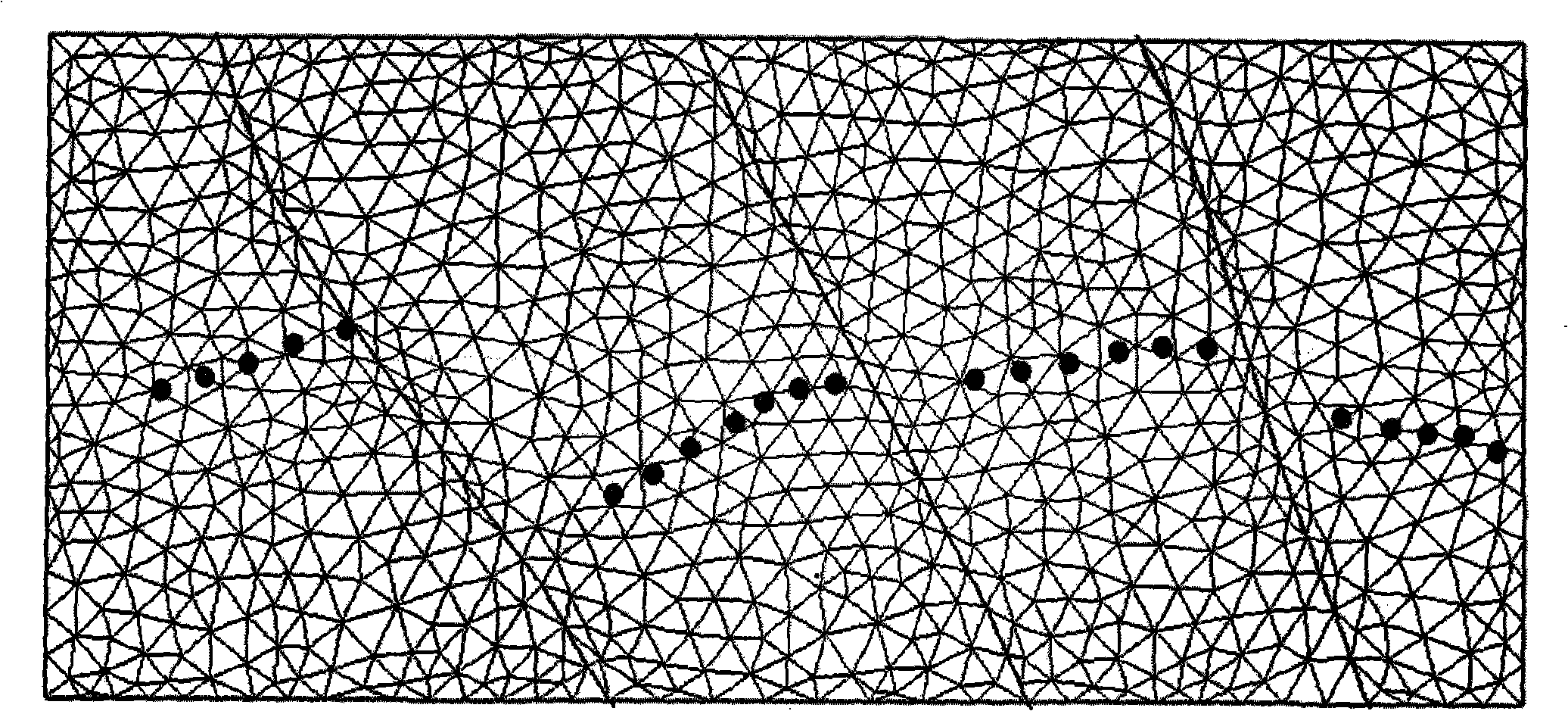
A targeted heterogeneous medium in the form of an underground layered formation is gridded into a layered structured grid or a layered semi-unstructured grid. The structured grid can be of the irregular corner-point-geometry grid type or the simple Cartesian grid type. The semi-unstructured grid is areally unstructured, formed by arbitrarily connected control-volumes derived from the dual grid of a suitable triangulation; but the connectivity pattern does not change from layer to layer. Problems with determining fluid movement and other state changes in the formation are solved by exploiting the layered structure of the medium. The techniques are particularly suited for large-scale simulation by parallel processing on a supercomputer with multiple central processing units (CPU's).
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
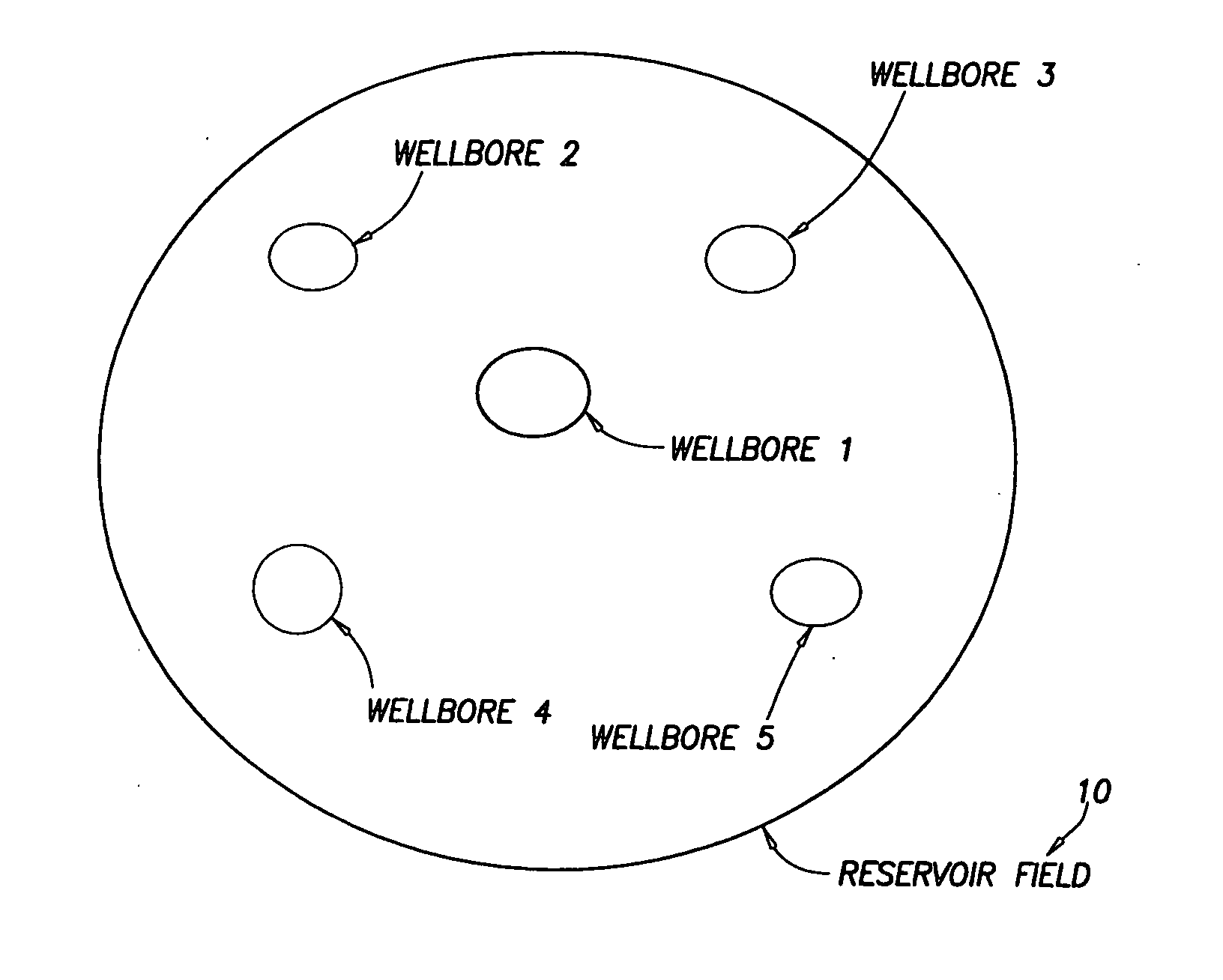
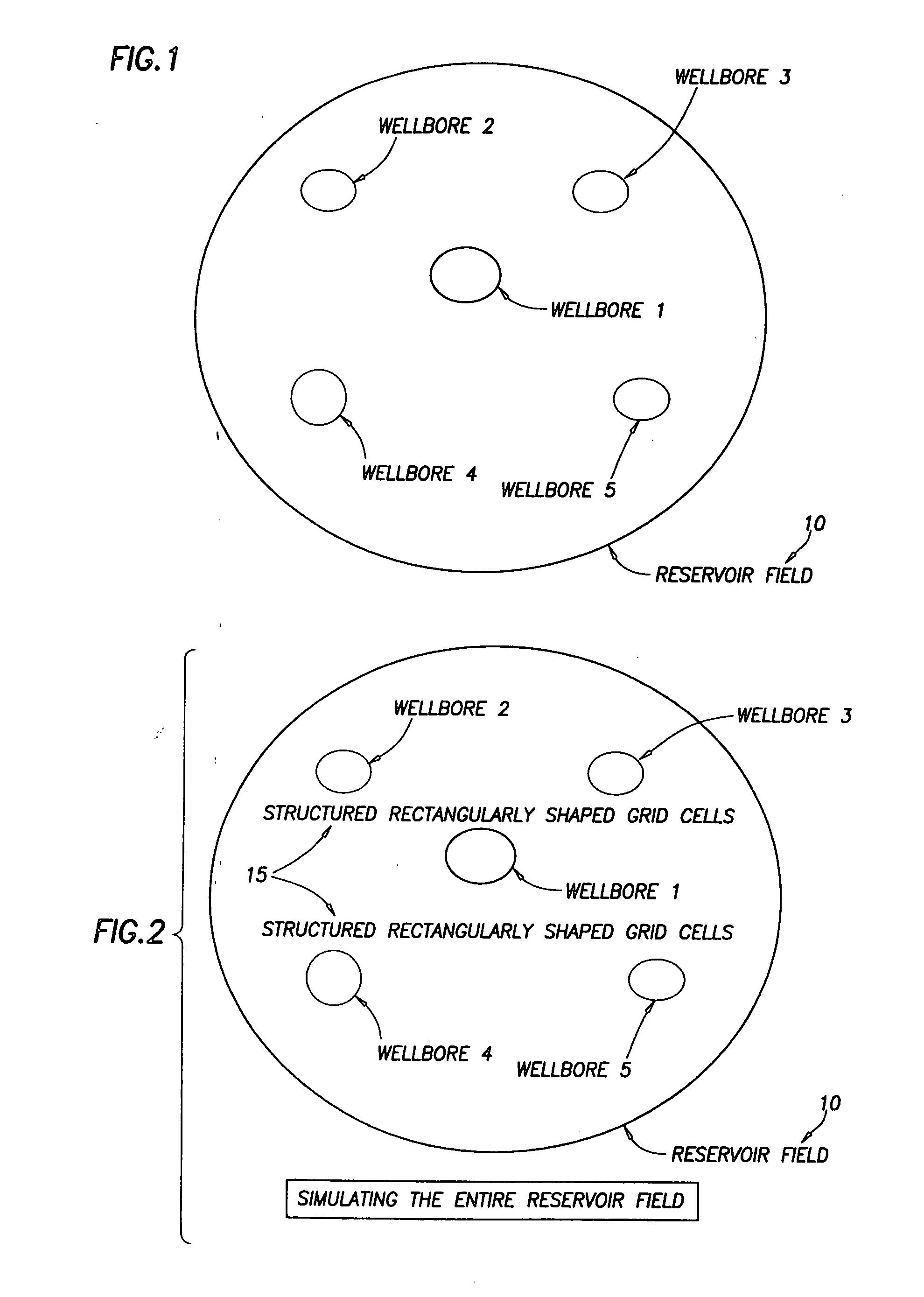
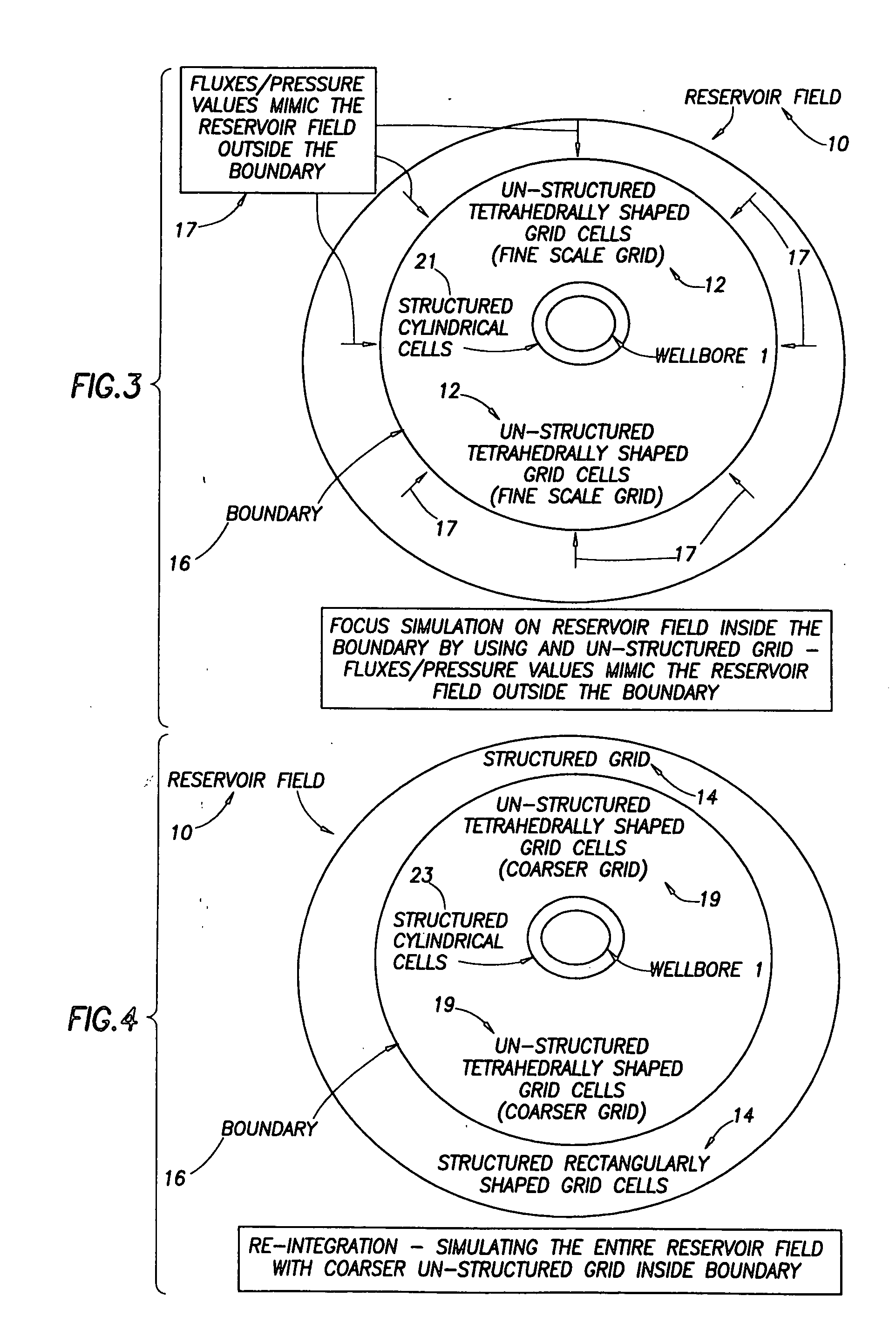
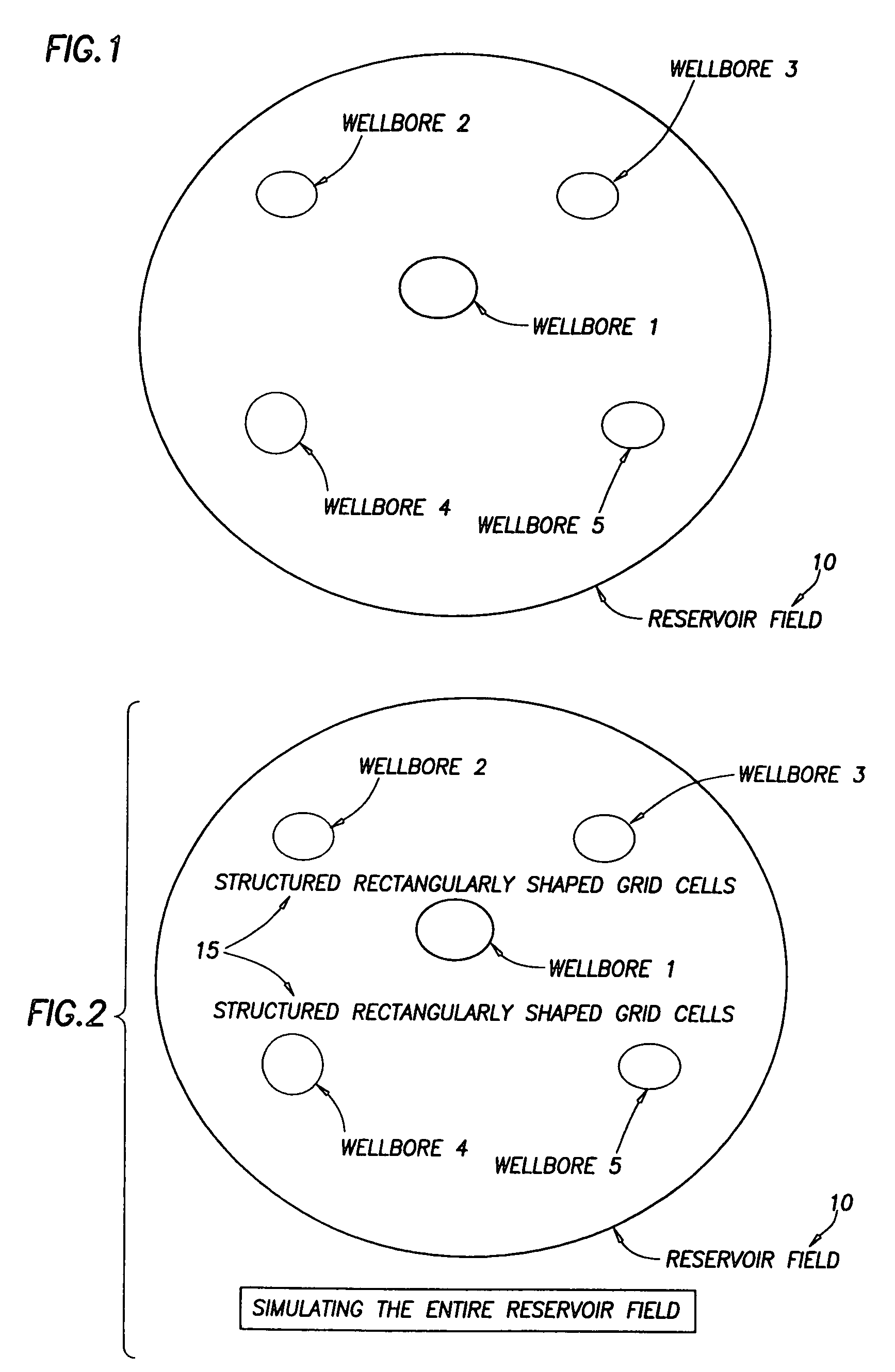
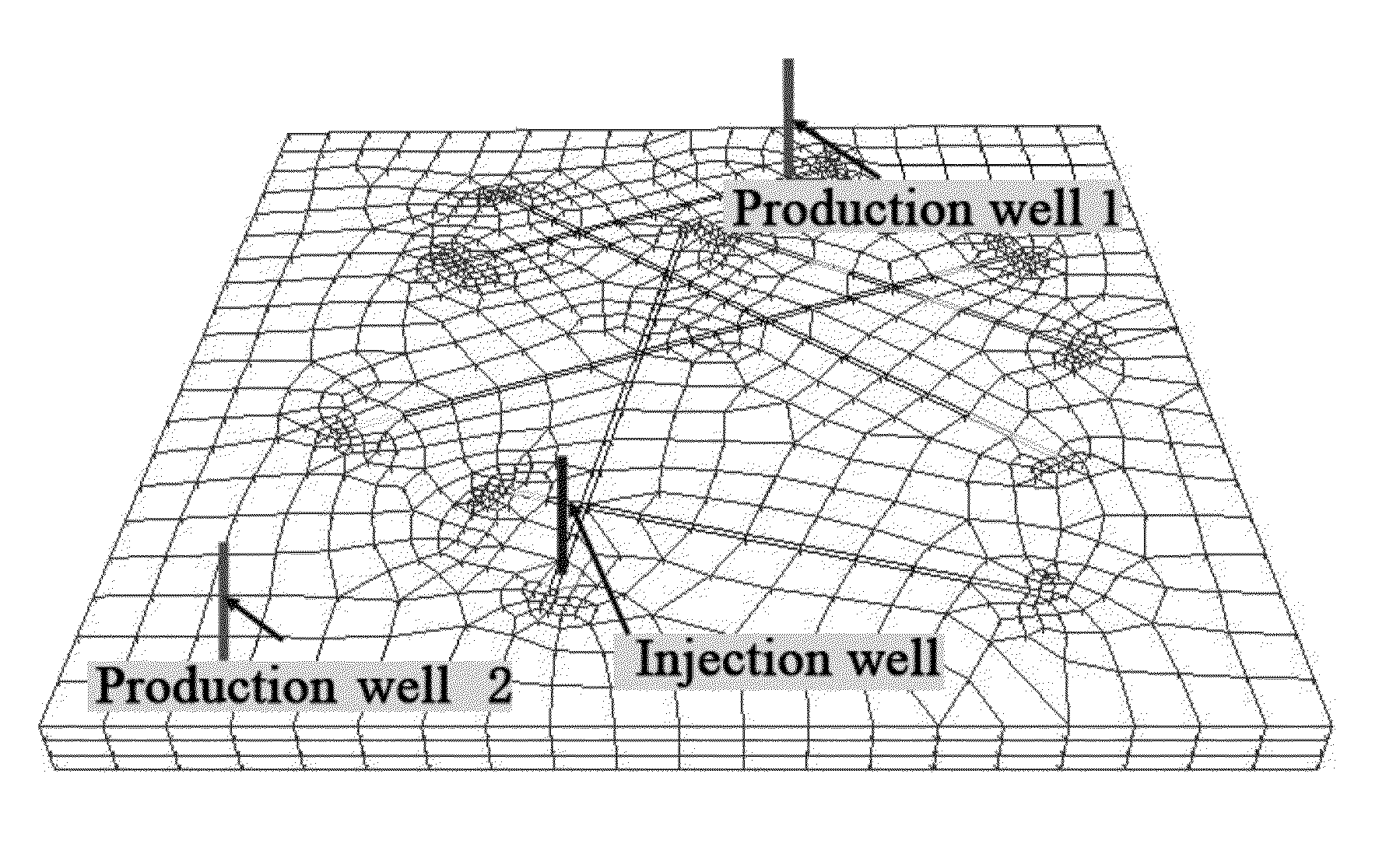
Near wellbore modeling method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050015231A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationModel methodScale structure
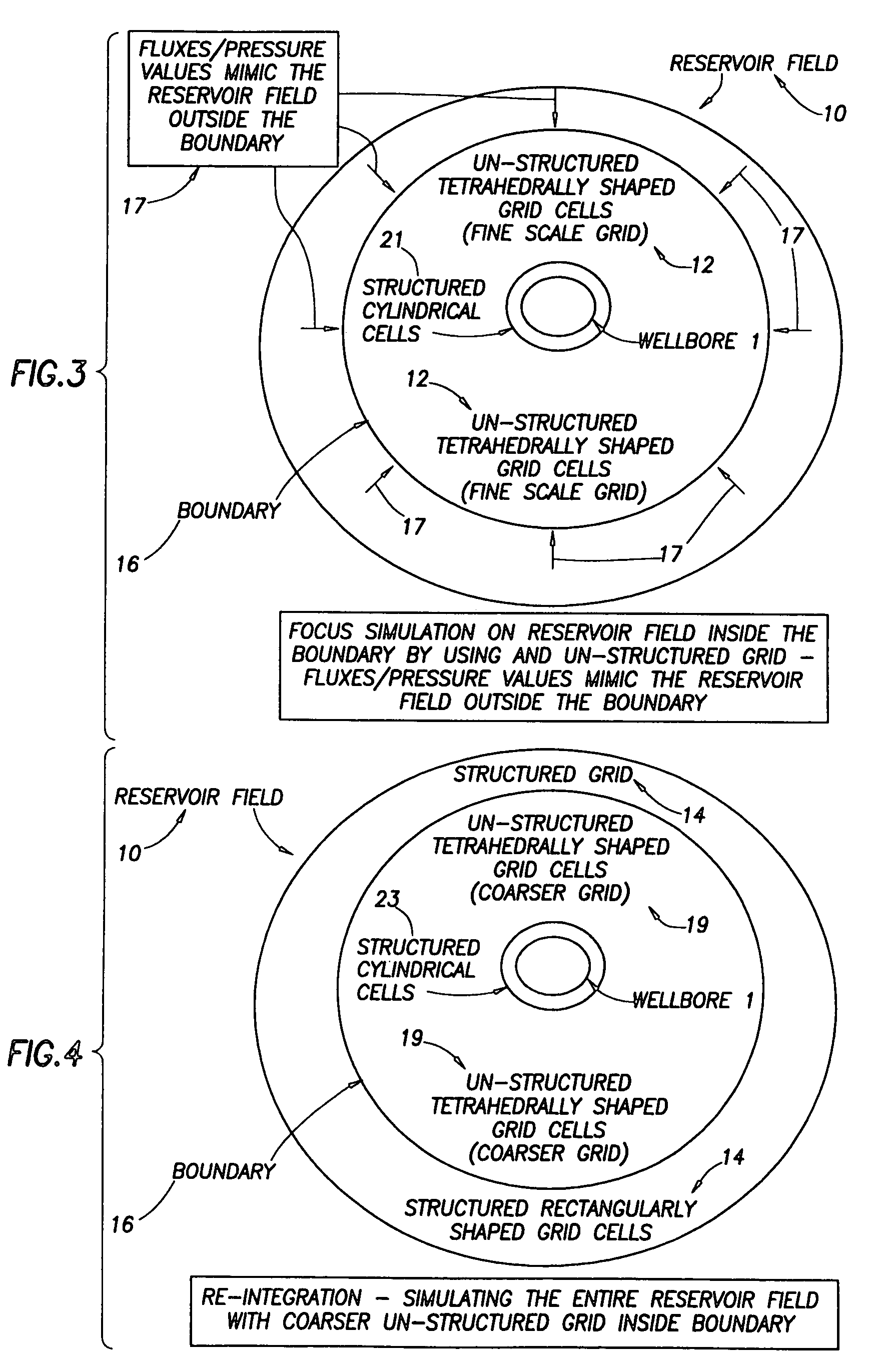
A “near wellbore modeling” software will, when executed by a processor of a computer, model a localized area of a reservoir field which surrounds and is located near a specific wellbore in the reservoir field by performing the following functions: (1) receive input data representative of a reservoir field containing a plurality of wellbores, (2) establish a boundary around one specific wellbore in the reservoir field which will be individually modeled and simulated, (3) impose an “fine scale” unstructured grid inside the boundary consisting of a plurality of tetrahedrally shaped grid cells and further impose a fine scale structured grid about the perforated sections of the specific wellbore, (4) determine a plurality of fluxes / pressure values at the boundary, the fluxes / pressure values representing characteristics of the reservoir field located outside the boundary, (5) establish one or more properties for each tetrahedral cell of the unstructured grid and each cylindrical grid cell of the structured grid, (6) run a simulation, using the fluxes / pressure values at the boundary to mimic the reservoir field outside the boundary and using the fine scale grid inside the boundary, to thereby determine a plurality of simulation results corresponding, respectively, to the plurality of grid cells located inside the boundary, the plurality of simulation results being representative of a set of characteristics of the reservoir field located inside the boundary, (7) display the plurality of simulation results which characterize the reservoir field located inside the boundary, and (8) reintegrate by coarsening the grid inside the boundary, imposing a structured grid outside the boundary, and re-running a simulation of the entire reservoir field.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Near wellbore modeling method and apparatus
ActiveUS7451066B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal receiversModel methodScale structure
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
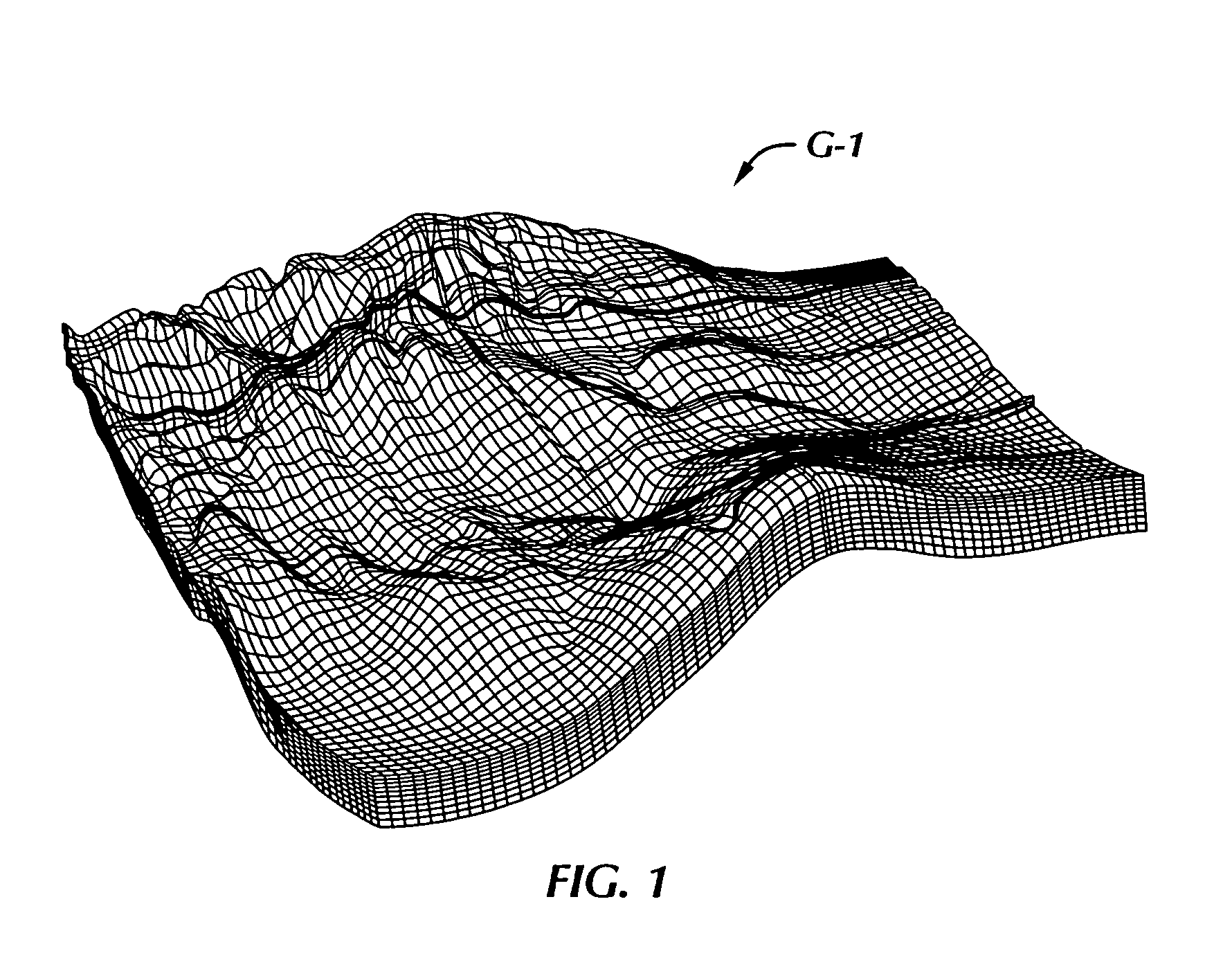
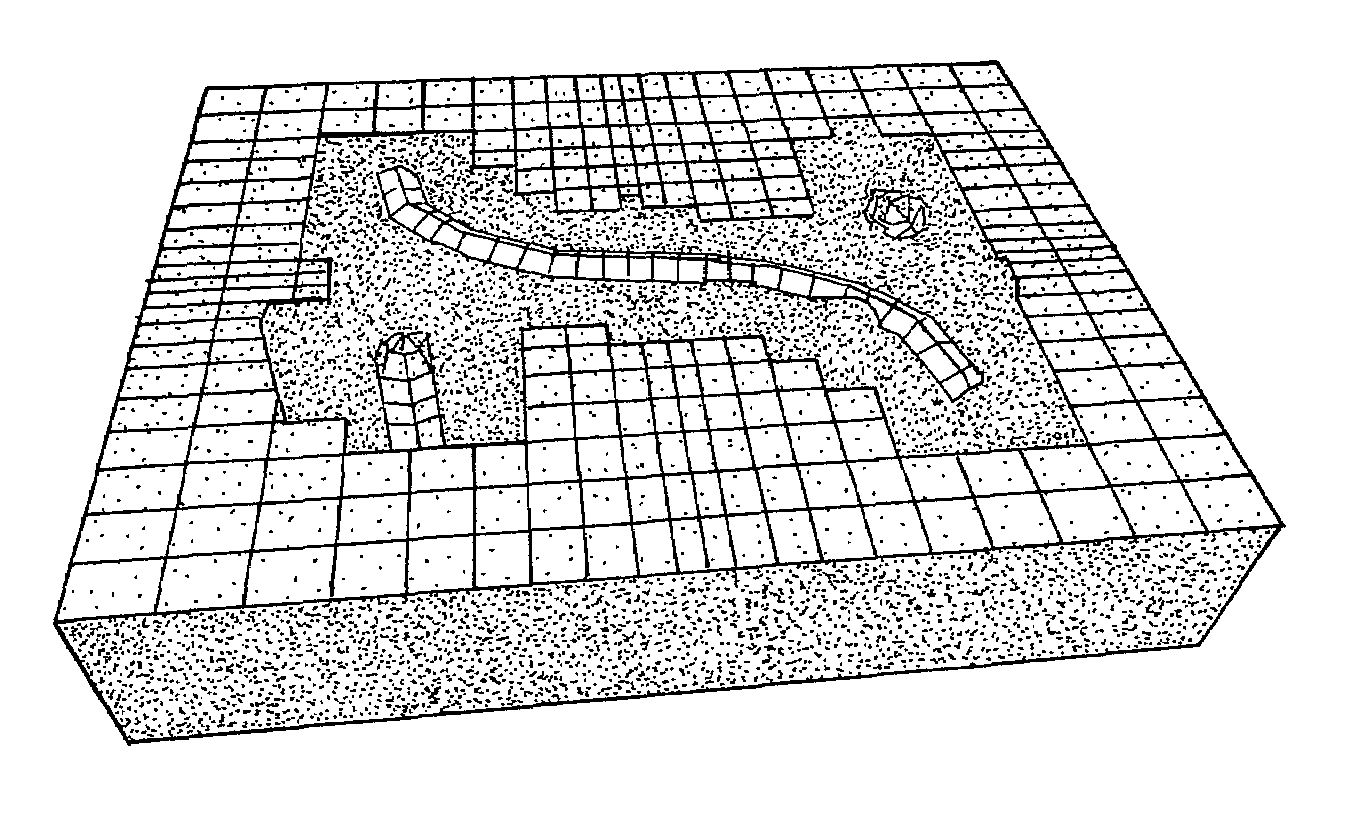
Method of generating a hybrid grid allowing modelling of a heterogeneous formation crossed by one or more wells
InactiveUS6907392B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingImage data processing detailsHybrid meshHydrocarbon
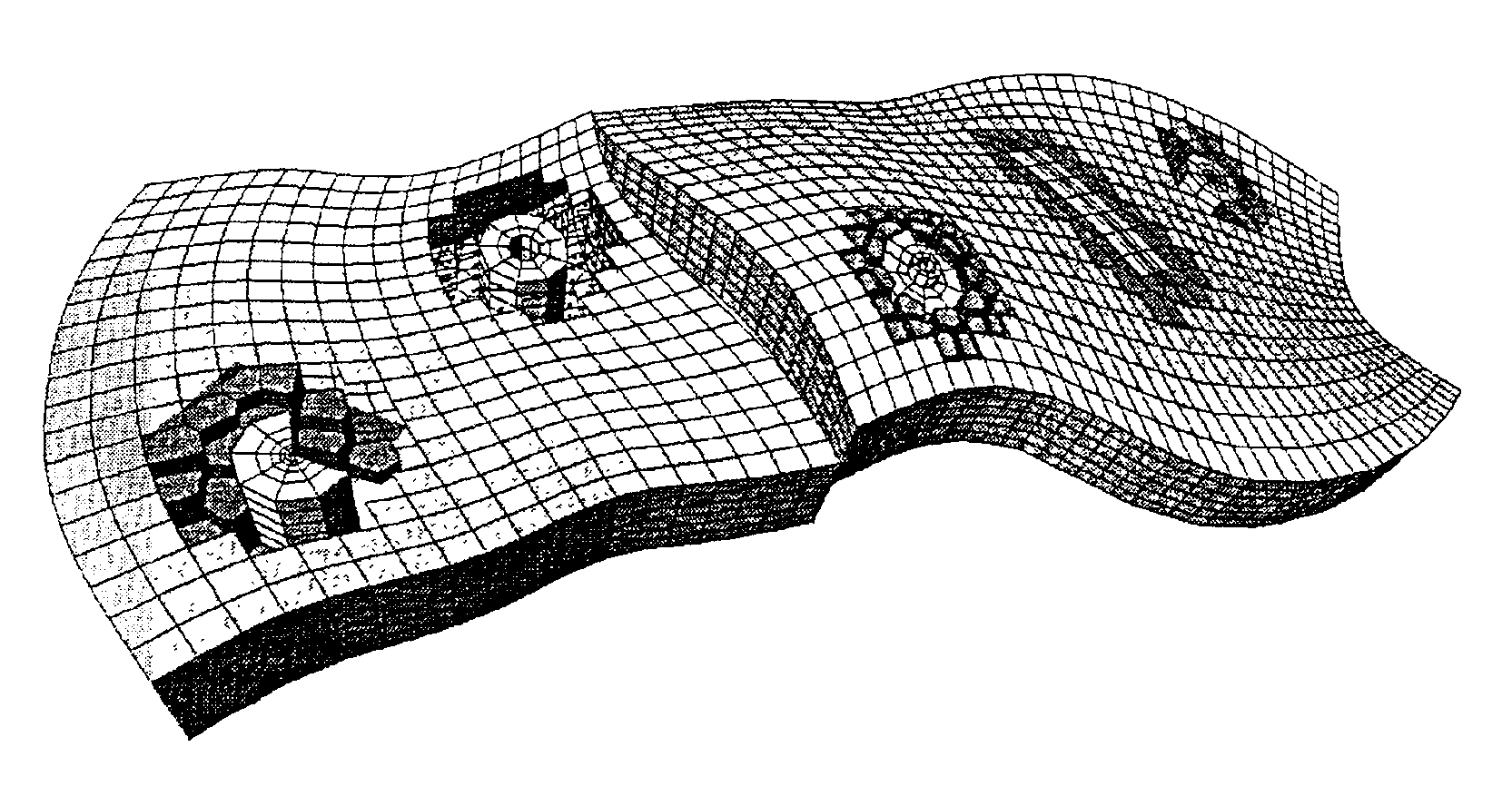
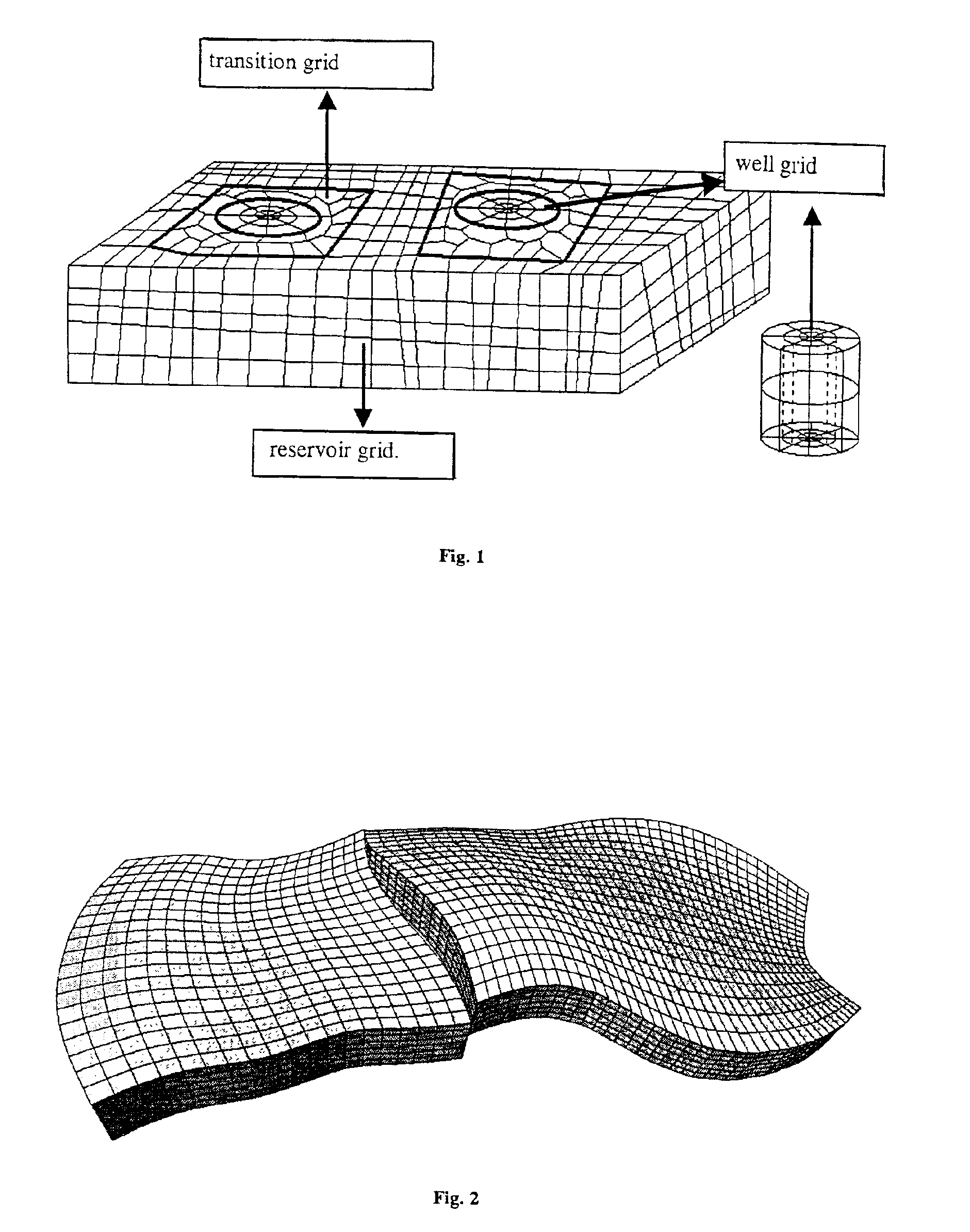
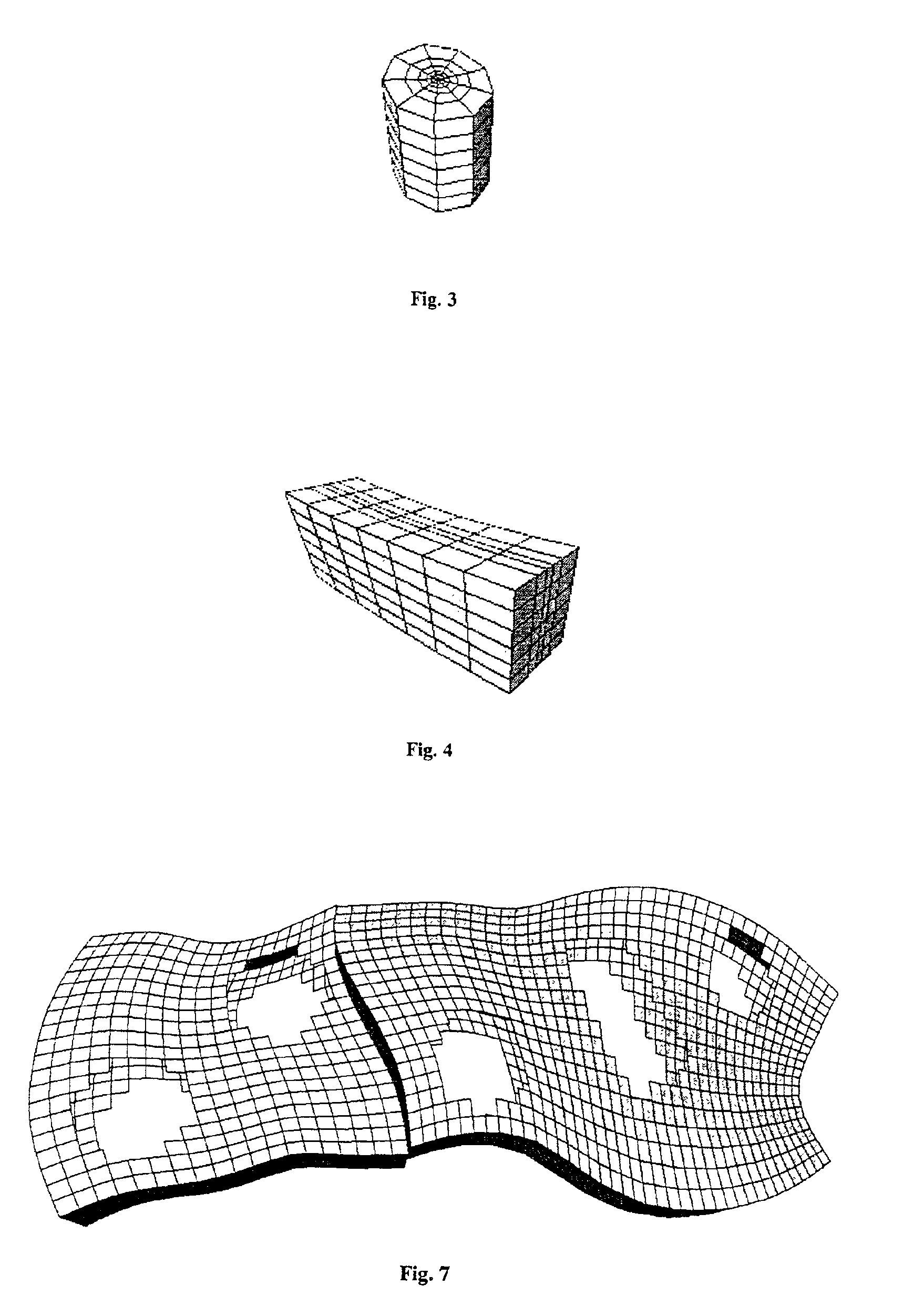
A method of generating a hybrid grid allowing modelling of a heterogeneous formation crossed by one or more pipes such as, for example, an underground formation where one or more wells have been drilled, in order to form a representative model, for example of fluid flows in the formation in accordance with a defined numerical pattern is disclosed. The method comprises associating a first structured grid for gridding of the heterogeneous medium regarding discontinuities thereof with a second structured, radial type grid for gridding of a zone around each pipe or well, which allows better constraints linked with flows in the zone, and transition of non-structured grids that are interposed between the first grid and each second well grid. Various grids are combined, each with its own formation, representation and exploration methods, structured grids which are advantageous in facilitating control and comprehension of the reservoir images formed and more flexible non-structured grids for gridding of complex zones. An application is simulation of hydrocarbon reservoirs.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
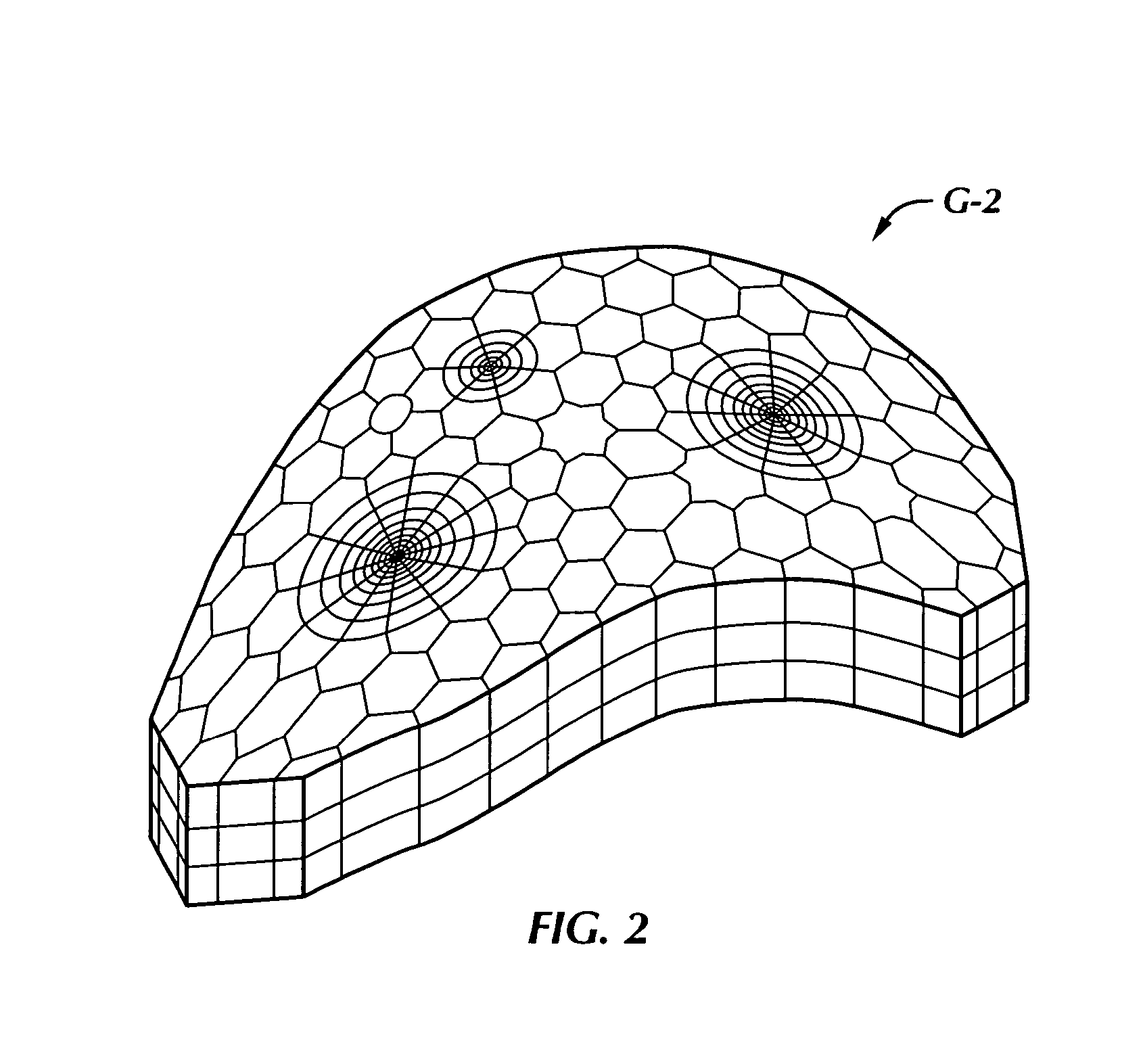
Method of generating a grid on a heterogenous formation crossed by one or more geometric discontinuities in order to carry out simulations
InactiveUS7047165B2GeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationPower diagramEngineering
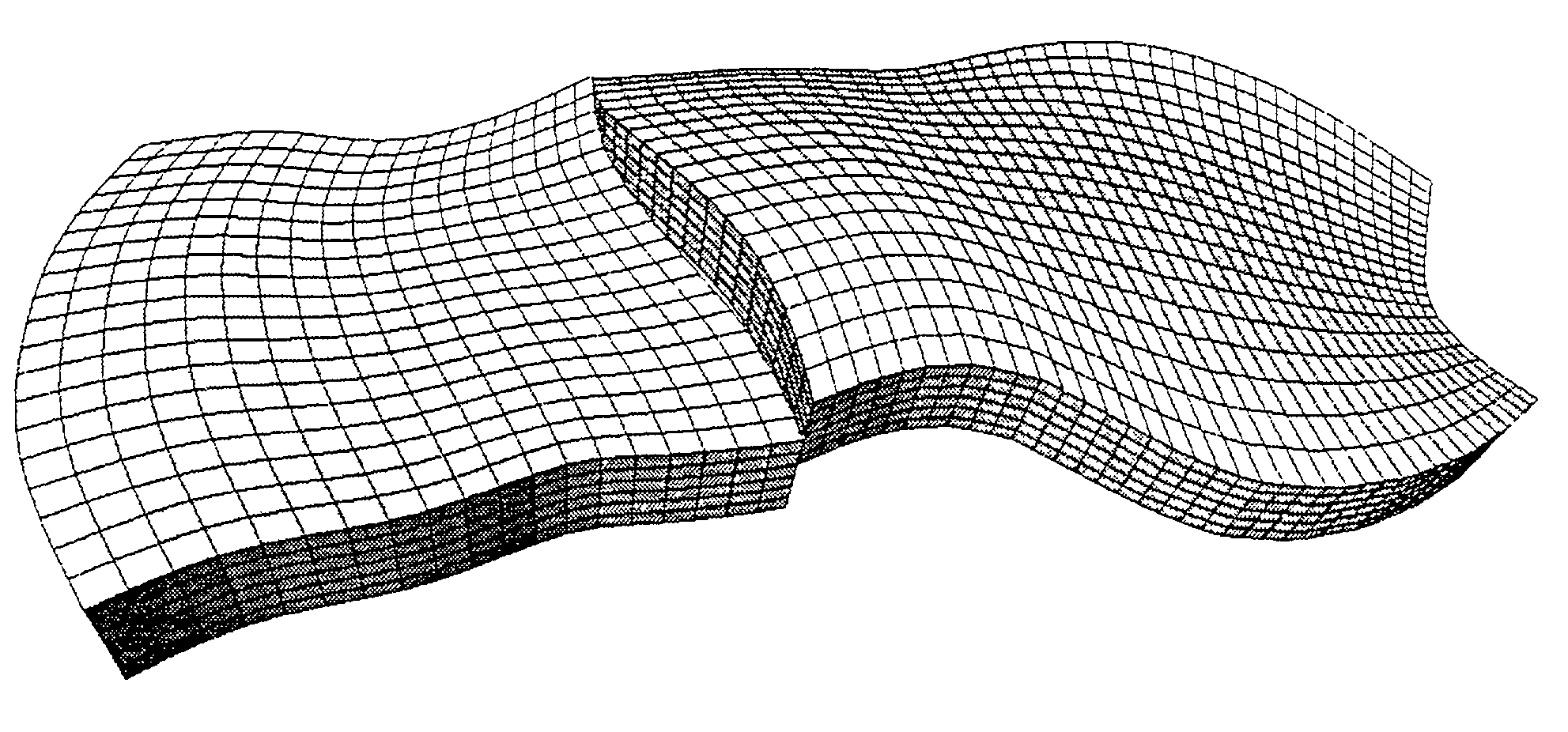
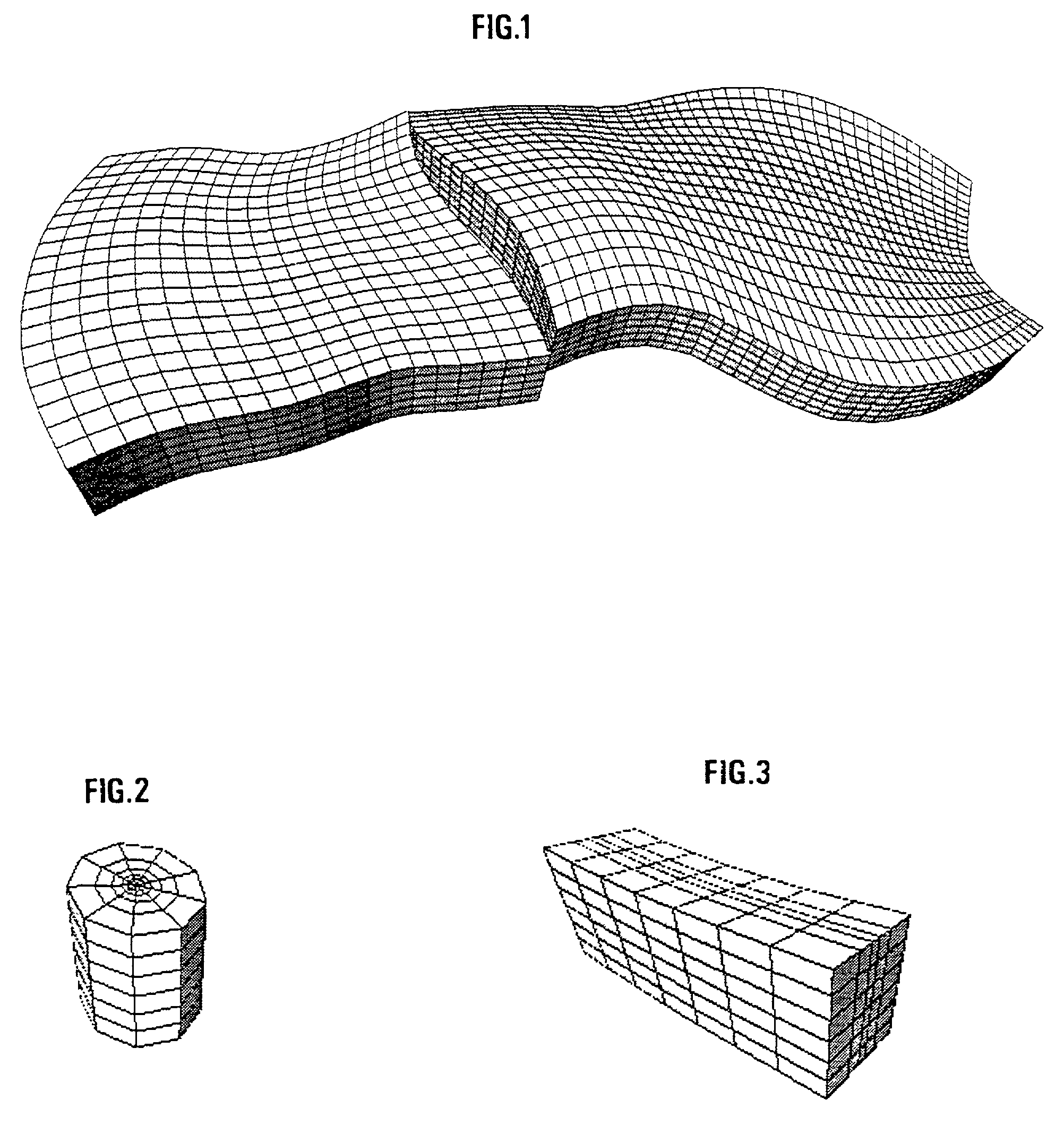
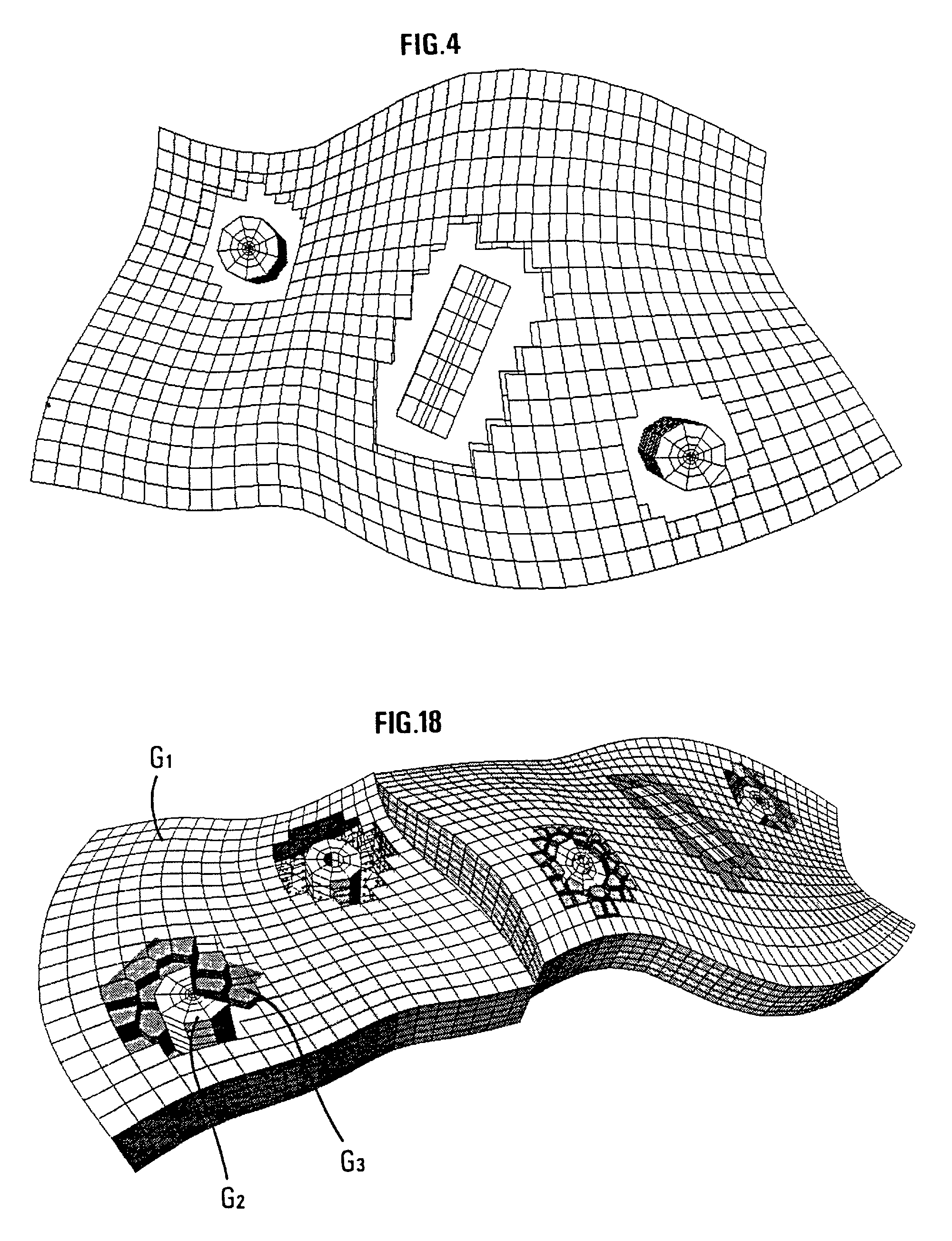
A method of generating a hybrid grid of a heterogeneous formation crossed by one or more geometric discontinuities such as, for example, an underground formation where one or more wells have been drilled, or a fractured formation, by combining structured grids and non-structured grids in order to carry out simulations in accordance with a defined numerical pattern is disclosed. Hybrid gridding is performed by associating a first structured grid (G1) for gridding of the heterogeneous medium considering discontinuities thereof with second structured, radial type grids (G2) for gridding of a zone around each pipe or well, which allows better consideration of constraints linked with flows in the zone. In order to connect the first grid of the medium and the second well grids, non-structured transition grids (G3) are interposed there between. A power diagram technique is used, which is particularly advantageous in that it allows appropriate connection of non-regular structured grids. An application is hydrocarbon reservoir simulation.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
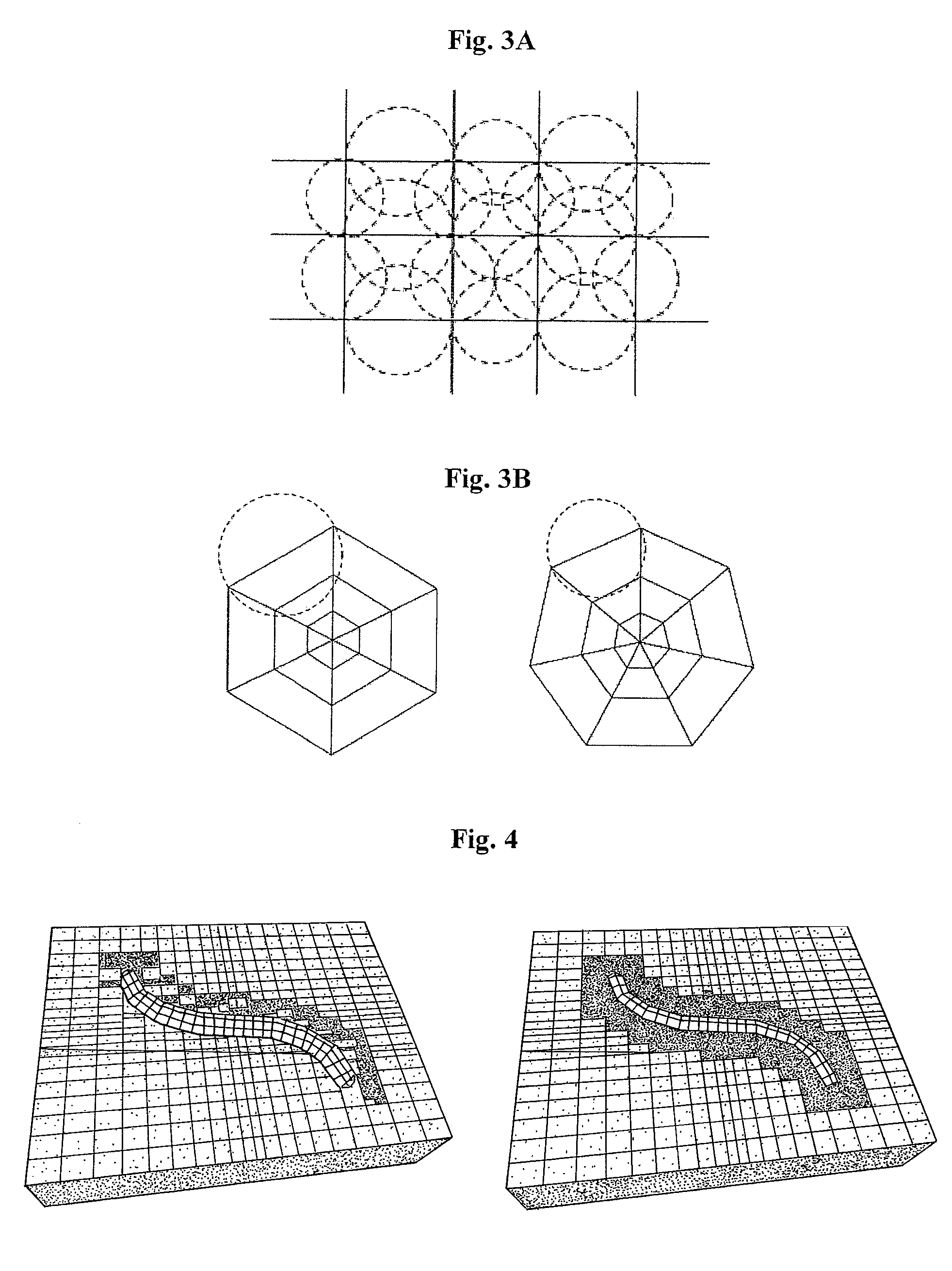
Method of generating a conforming hybrid grid in three dimensions of a heterogeneous formation crossed by one or more geometric discontinuities in order to carry out simulations
ActiveUS20050273303A1Long distanceImprove regularityFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationQuality controlComputer science
Method of generating a hybrid grid, in order to carry out simulations in accordance with a defined numerical scheme, in three dimensions and admissible in the numerical scheme sense, of a heterogeneous formation crossed by one or more geometric discontinuities such as, for example, an underground formation where one or more wells have been drilled, or a fractured formation, by combining structured grids and unstructured grids. The hybrid grid is achieved by associating a first structured grid for gridding the heterogeneous medium with second structured grids for gridding a zone around each discontinuity. A cavity of minimum size, allowing the cells of the transition grid to have an intermediate size between the size of the cells of the first grid and the size of the cells of the second grids, is first generated, entirely automatically. A transition grid meeting the constraints of the numerical scheme used for simulation is then constructed. Finally, the quality of the transition grid is improved by optimizing it under quality controls in the numerical scheme sense, in order to define a perfectly admissible transition grid in the sense of the numerical scheme selected. Applications: hydrocarbon reservoir simulators for example.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Solution method and apparatus for large-scale simulation of layered formations
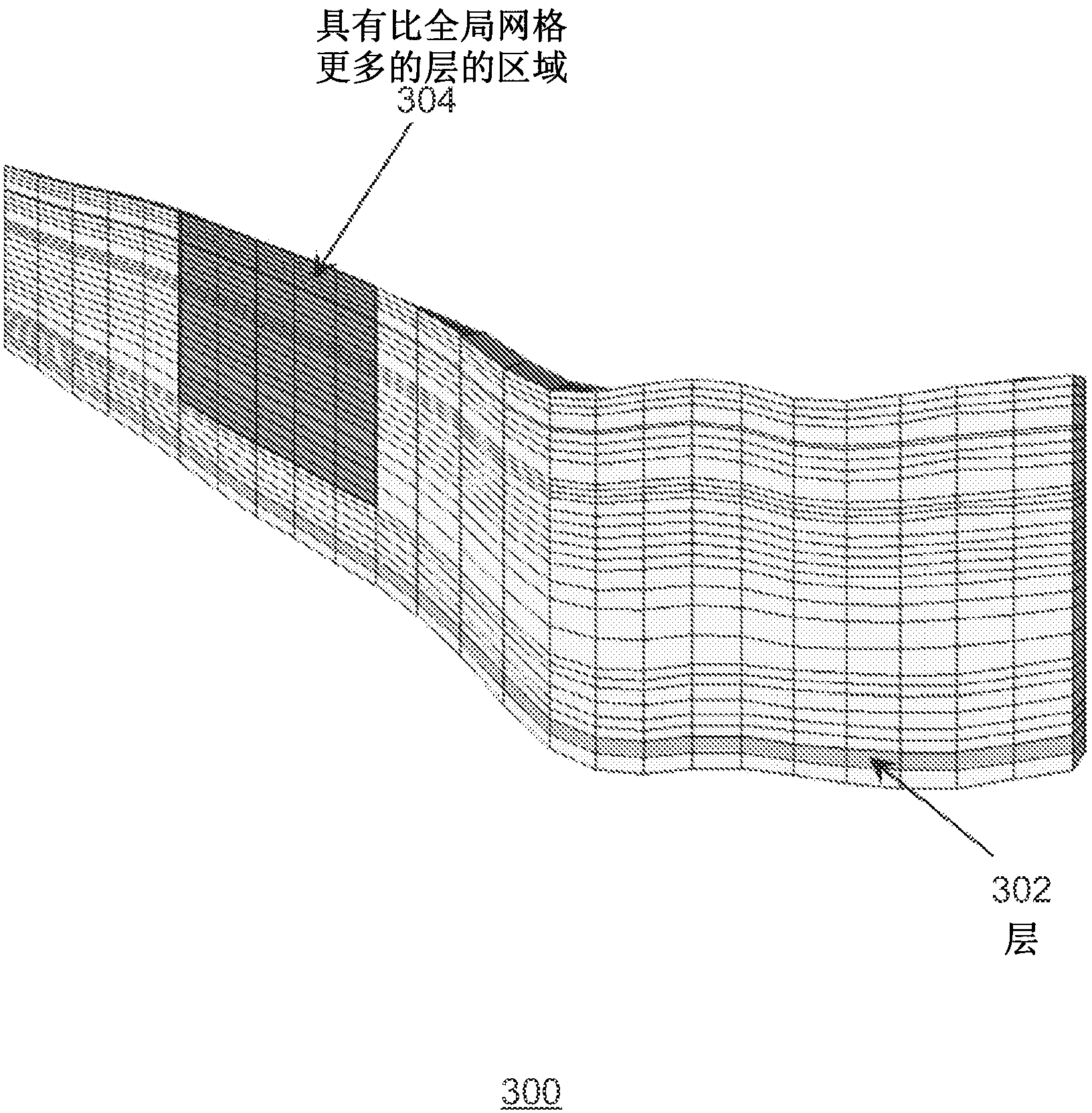
ActiveUS7596480B2Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSupercomputerTypes of mesh
A targeted heterogeneous medium in the form of an underground layered formation is gridded into a layered structured grid or a layered semi-unstructured grid. The structured grid can be of the irregular corner-point-geometry grid type or the simple Cartesian grid type. The semi-unstructured grid is really unstructured, formed by arbitrarily connected control-volumes derived from the dual grid of a suitable triangulation; but the connectivity pattern does not change from layer to layer. Problems with determining fluid movement and other state changes in the formation are solved by exploiting the layered structure of the medium. The techniques are particularly suited for large-scale simulation by parallel processing on a supercomputer with multiple central processing units (CPU's).
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Method of generating a conforming hybrid grid in three dimensions of a heterogeneous formation crossed by one or more geometric discontinuities in order to carry out simulations
ActiveUS7634395B2Improve shape regularityFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationHydrocarbonMesh grid
A method, having application for hydrocarbon reservoir simulation, generates a hybrid grid, in order to carry out simulations in accordance with a defined numerical scheme, in three dimensions in a numerical scheme, of a heterogeneous formation crossed by at least one geometric discontinuity such as, an underground formation where at least one well has been drilled, or a fractured formation, by combining structured grids and unstructured grids. The hybrid grid includes a first structured grid for gridding the heterogeneous medium with second structured grids for gridding a zone around each discontinuity. A cavity of minimum size is automatically generated, with cells of the transition grid being an intermediate size between the size of the cells of the first grid and the size of the cells of the second grids.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
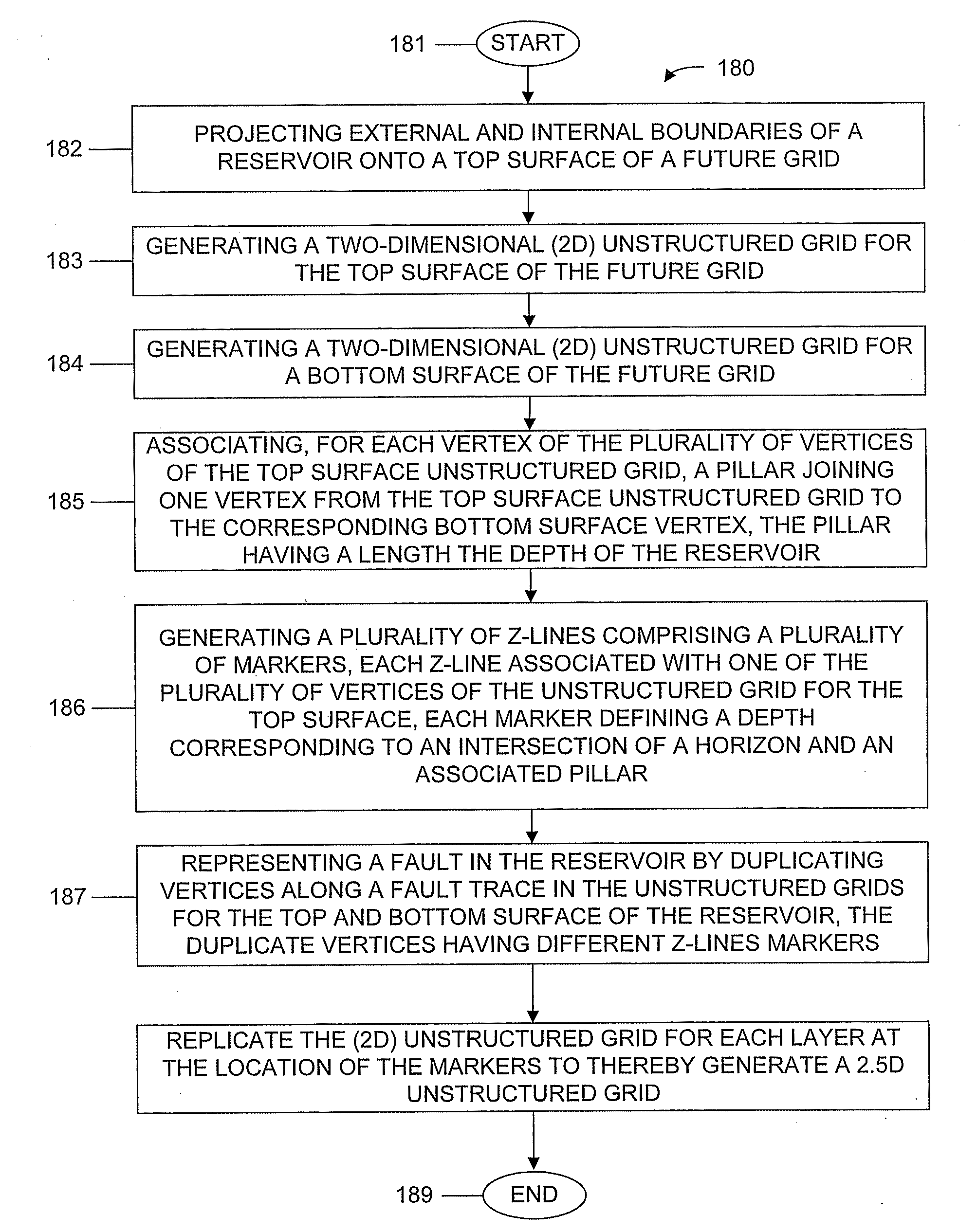
Machine, Program Product, and Computer-Implemented Method to Simulate Reservoirs as 2.5D Unstructured Grids
ActiveUS20110313745A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPrinted circuit aspectsComputational scienceData set
Example embodiments utilize machines to model reservoir geometry having geological layers as 2.5D unstructured grids. Example embodiments include program products to simulate a reservoir by generating a reservoir data system, performing a numerical fluid flow simulation, and visualizing the simulation. Data system embodiments include data structures to model a reservoir geometry as laterally unstructured two-dimensional (2D) grids and associated layer depths defining z-lines to thereby define a 2.5D unstructured grid, including datasets for: vertices of the grid cells for the future grid top and bottom surfaces, a number and listing of vertices for each grid cell, cell center coordinates, and vertex adjacency information using a compressed sparse row format. Computer-implemented methods include projecting external and internal boundaries onto a future grid surface; generating 2D unstructured, e.g., Voronoi, grids, for the top and bottom surfaces; and generating z-lines of depths corresponding to reservoir layers to thereby generate 2.5D unstructured grids.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
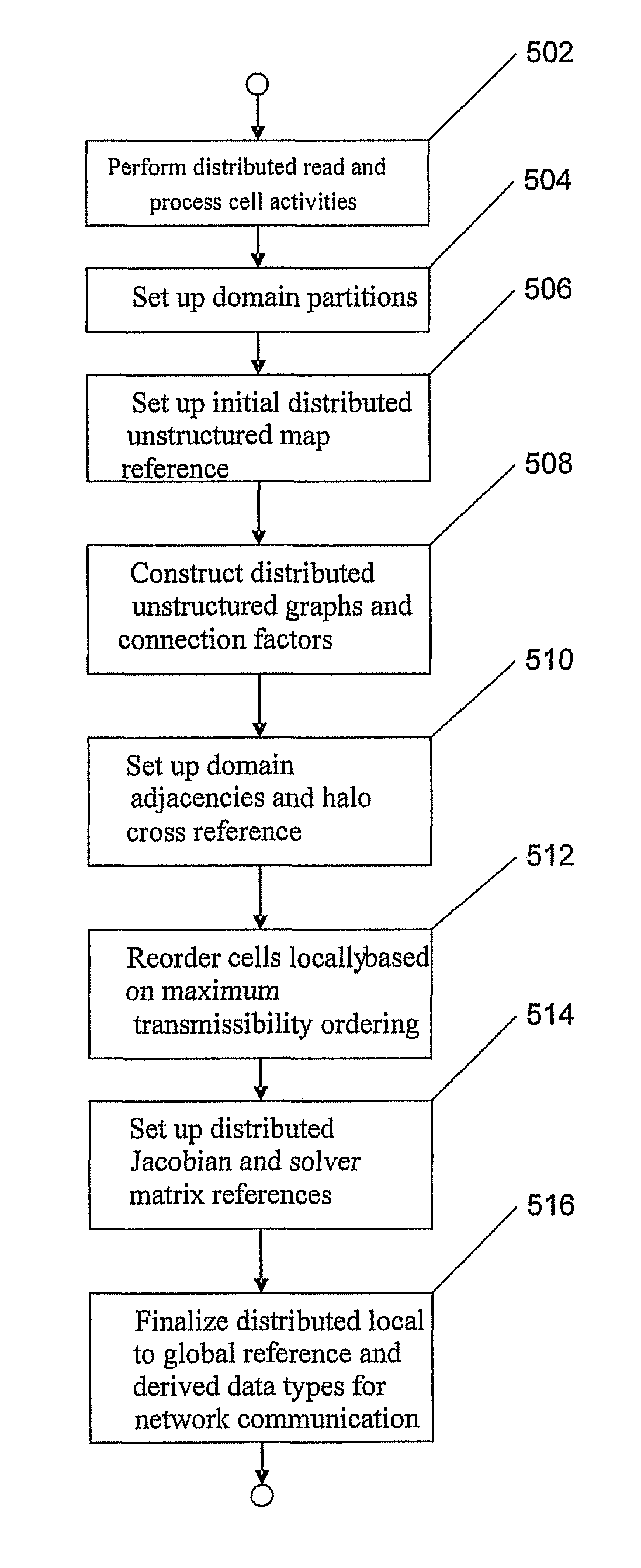
Machine, computer program product and method to generate unstructured grids and carry out parallel reservoir simulation
ActiveUS8386227B2Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCell indexParallel processing
A machine, computer program product, and method to enable scalable parallel reservoir simulations for a variety of simulation model sizes are described herein. Some embodiments of the disclosed invention include a machine, methods, and implemented software for performing parallel processing of a grid defining a reservoir or oil / gas field using a plurality of sub-domains for the reservoir simulation, a parallel process of re-ordering a local cell index for each of the plurality of cells using characteristics of the cell and location within the at least one sub-domain and a parallel process of simulating at least one production characteristic of the reservoir.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
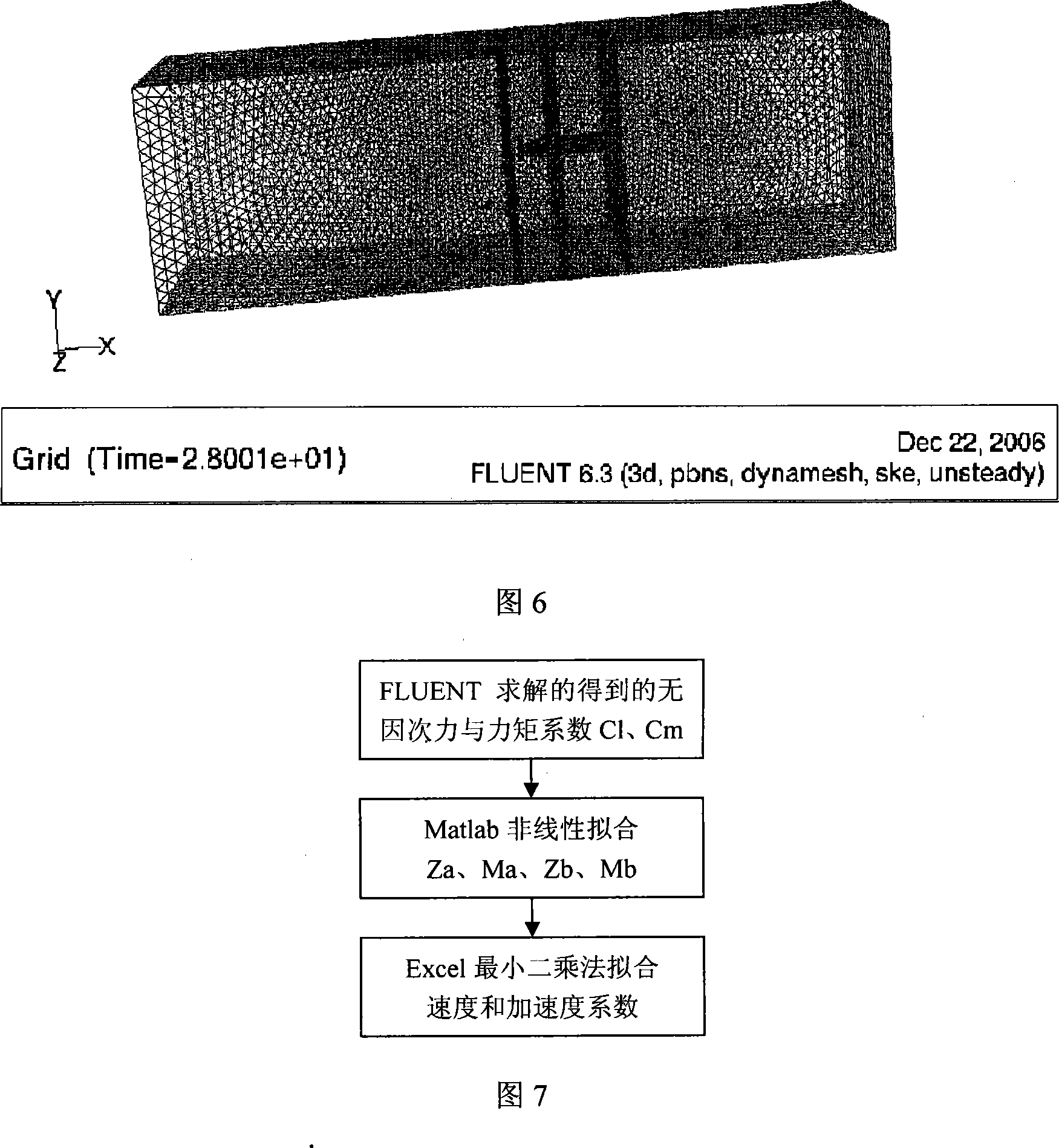
Digital ship model planar motion mechanism experimental method based on CFD software
InactiveCN101246515AAchieve pure swaying motionAccurate settingSustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsVertical planeResearch Object
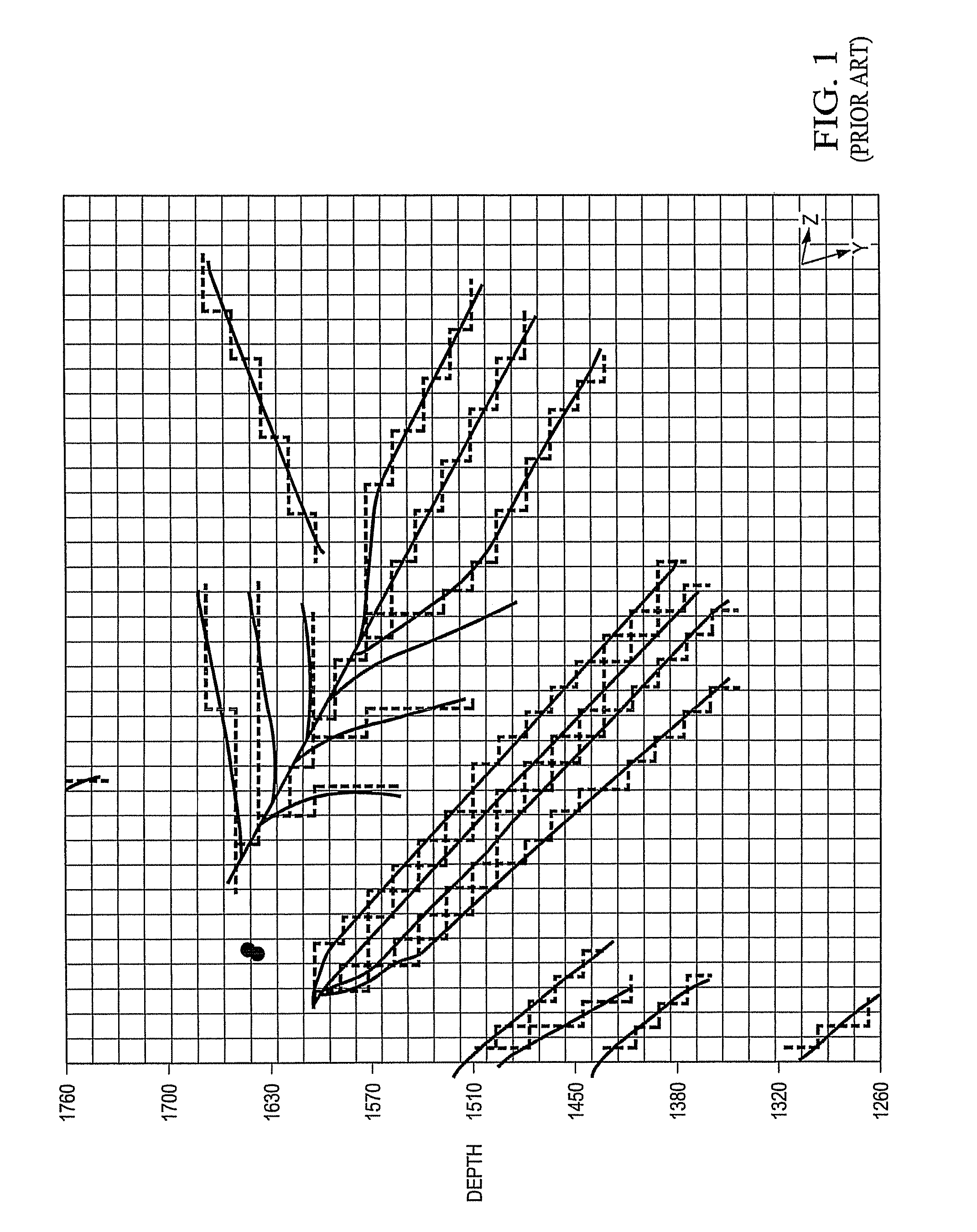
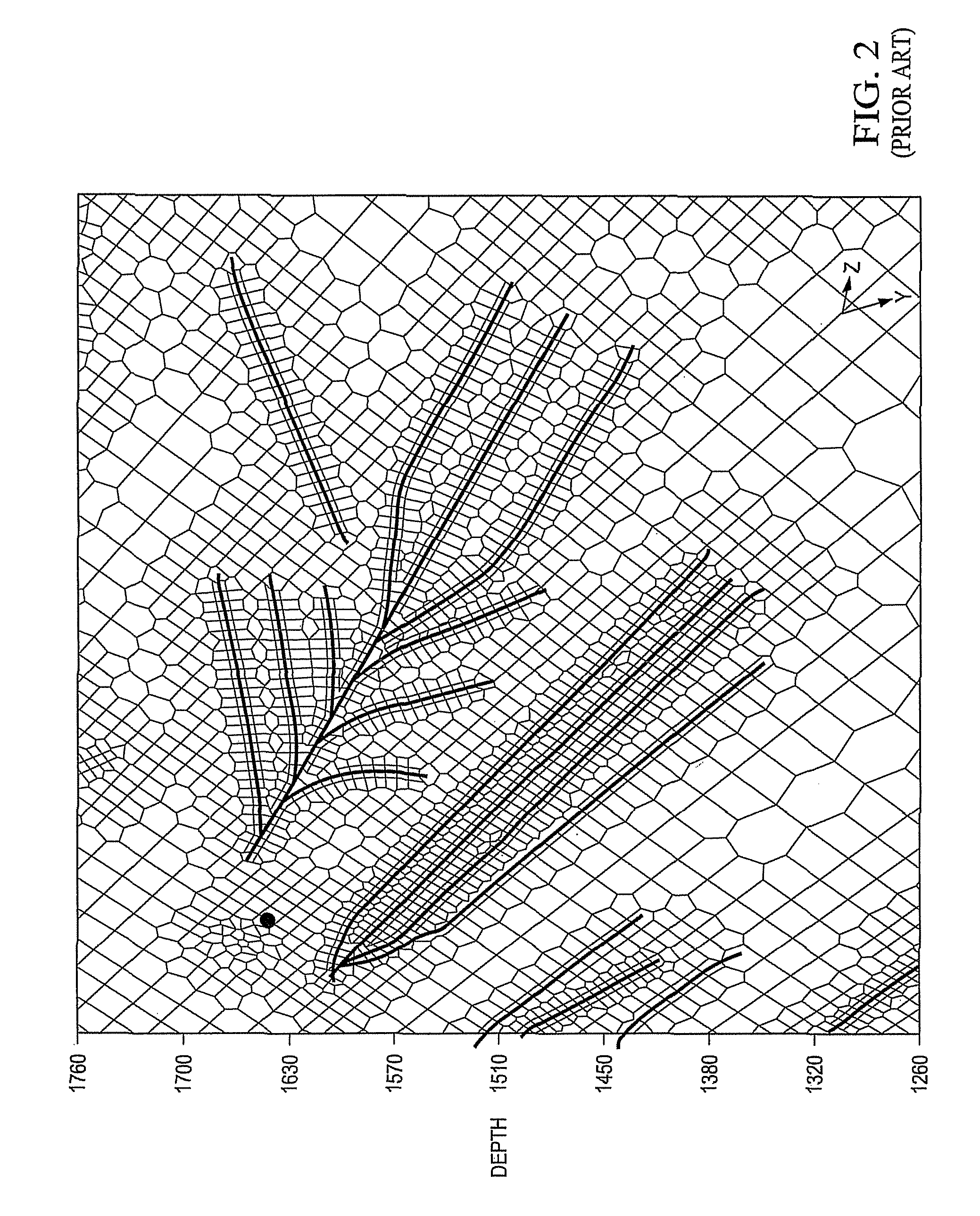
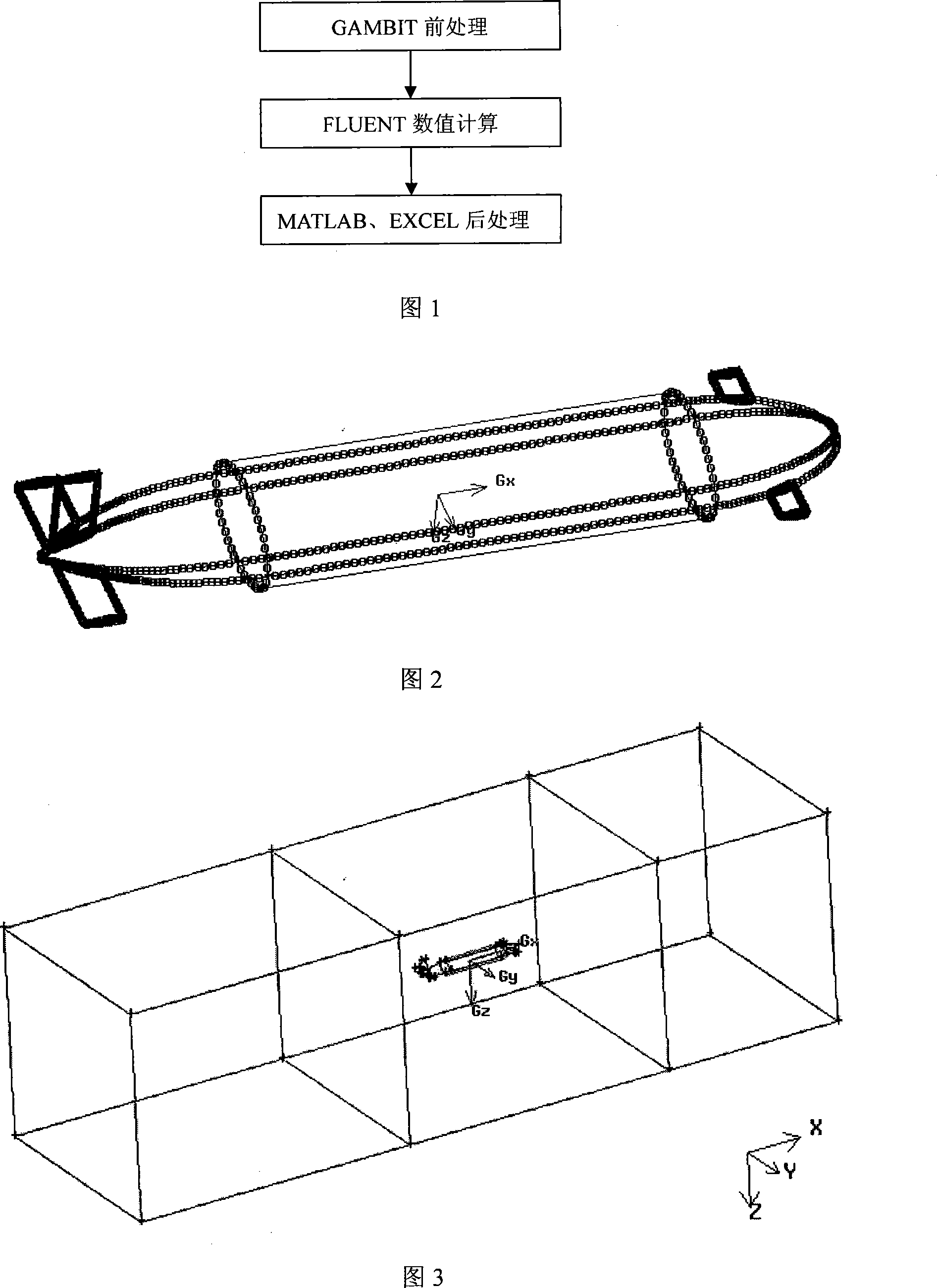
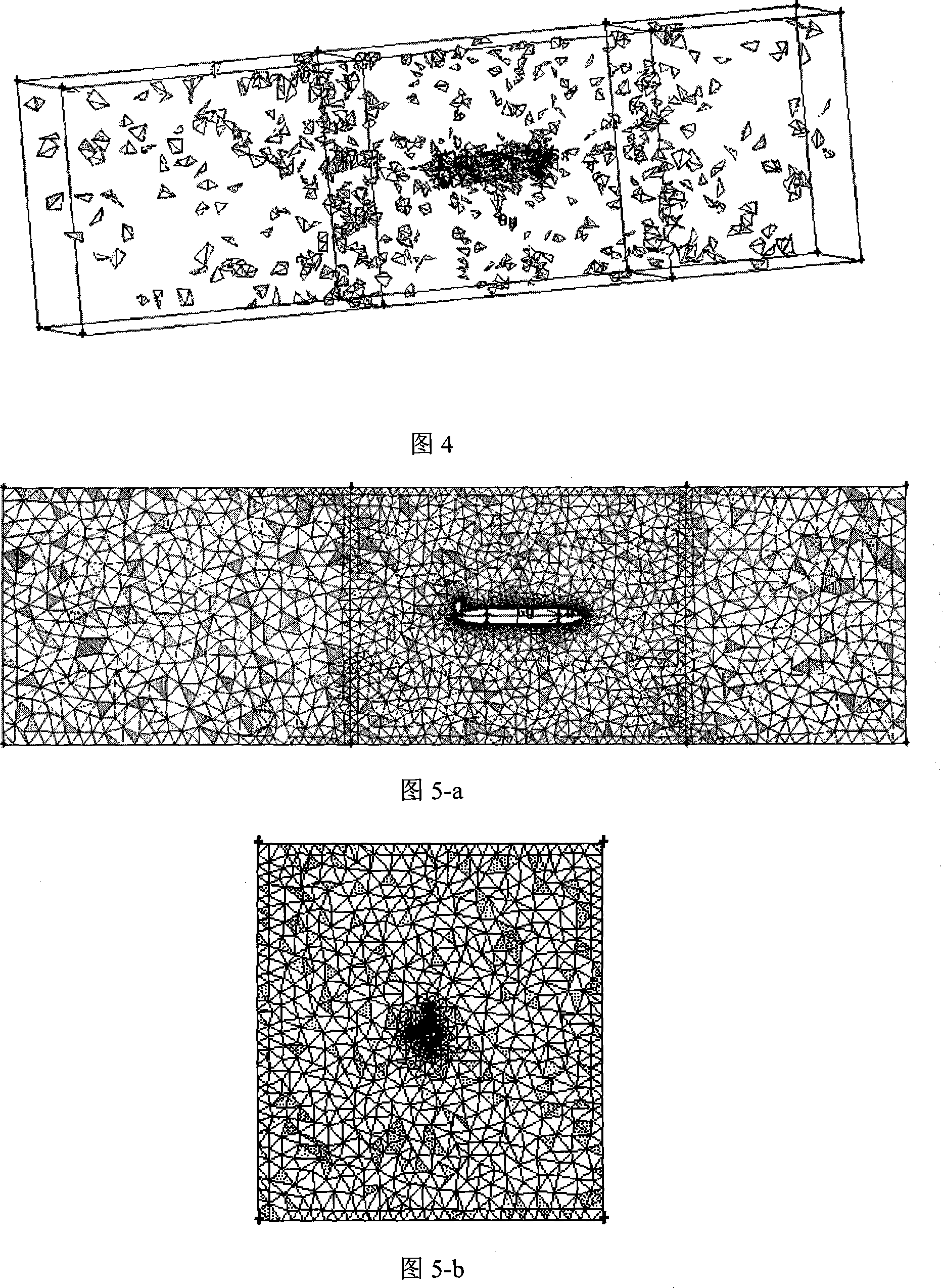
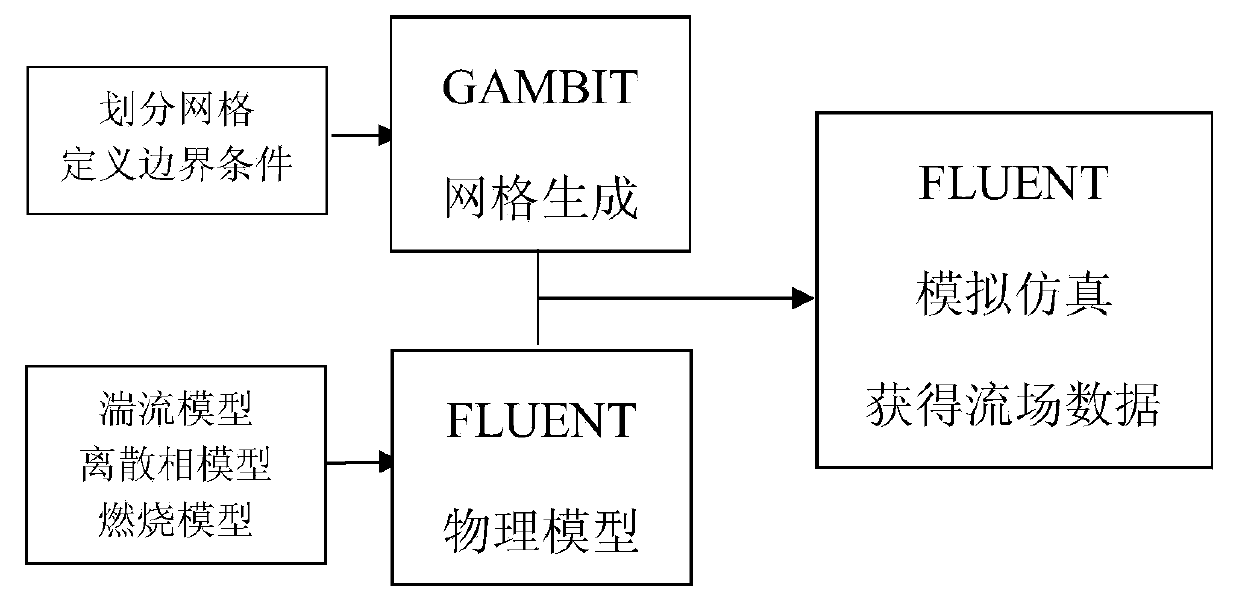
The invention provides a digital ship model plane motion organization experimental method based on computation fluid dynamics CFD software FLUENT. The method includes applying a FLUENT pre-process software GAMBIT to establish a research object model and a control domain; arranging a triangle grid on the model surface, then arranging a unstructured grid in the control domain; setting the boundary condition, joining an user-defined function UDF document, introducing dynamic grid technology, using a finite volume method based on the complete unstructured grid, realizing a pure swaying movement, a pure rising and falling movement, a pure oscillatory movement, a pure pitching movement and a pure rolling movement carried on by a plane motion organization experiment; applying a science computation software MATLAB to do Fourier expansion of a force and a moment coefficient obtained by the FLUENT, being fitted by EXCEL least squares method, obtaining a hydrodynamic force coefficient of a vertical plane and a horizontal plane as well as the related hydrodynamics analysis by dimensionless. The invention carries on the digit plane motion organization experiment using the CFD software, can satisfy the request of hydrodynamic force data in the design initial period of a submersible.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
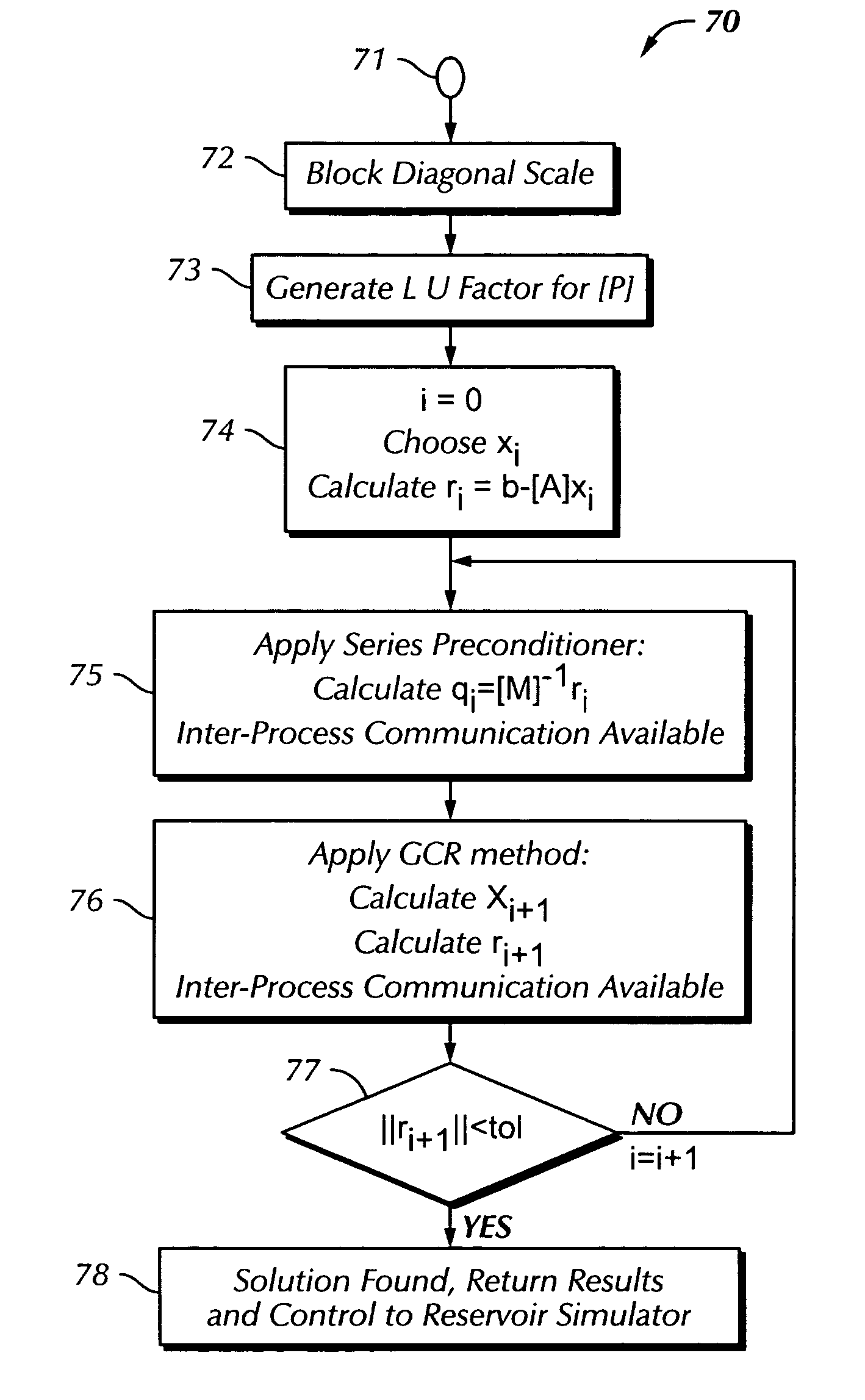
Giga-cell linear solver method and apparatus for massive parallel reservoir simulation
ActiveUS20130211800A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputational scienceImage resolution
A linear solver methodology is applied to reservoir data to solve for large system of equations arising from high-resolution reservoir simulation of giant oil fields with minimal upscaling using either structured grids or unstructured grids. Full geologic complexity and discontinuities at the resolution desired for accurate simulation results may be taken into account. A general unstructured method is provided, so that very complex flow geometry near multi-lateral wells can be modeled.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Machine, program product, and computer-implemented method to simulate reservoirs as 2.5D unstructured grids
ActiveUS8463586B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPrinted circuit aspectsComputational scienceData set
Example embodiments utilize machines to model reservoir geometry having geological layers as 2.5D unstructured grids. Example embodiments include program products to simulate a reservoir by generating a reservoir data system, performing a numerical fluid flow simulation, and visualizing the simulation. Data system embodiments include data structures to model a reservoir geometry as laterally unstructured two-dimensional (2D) grids and associated layer depths defining z-lines to thereby define a 2.5D unstructured grid, including datasets for: vertices of the grid cells for the future grid top and bottom surfaces, a number and listing of vertices for each grid cell, cell center coordinates, and vertex adjacency information using a compressed sparse row format. Computer-implemented methods include projecting external and internal boundaries onto a future grid surface; generating 2D unstructured, e.g., Voronoi, grids, for the top and bottom surfaces; and generating z-lines of depths corresponding to reservoir layers to thereby generate 2.5D unstructured grids.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Modeling Subsurface Processes On Unstructured Grid
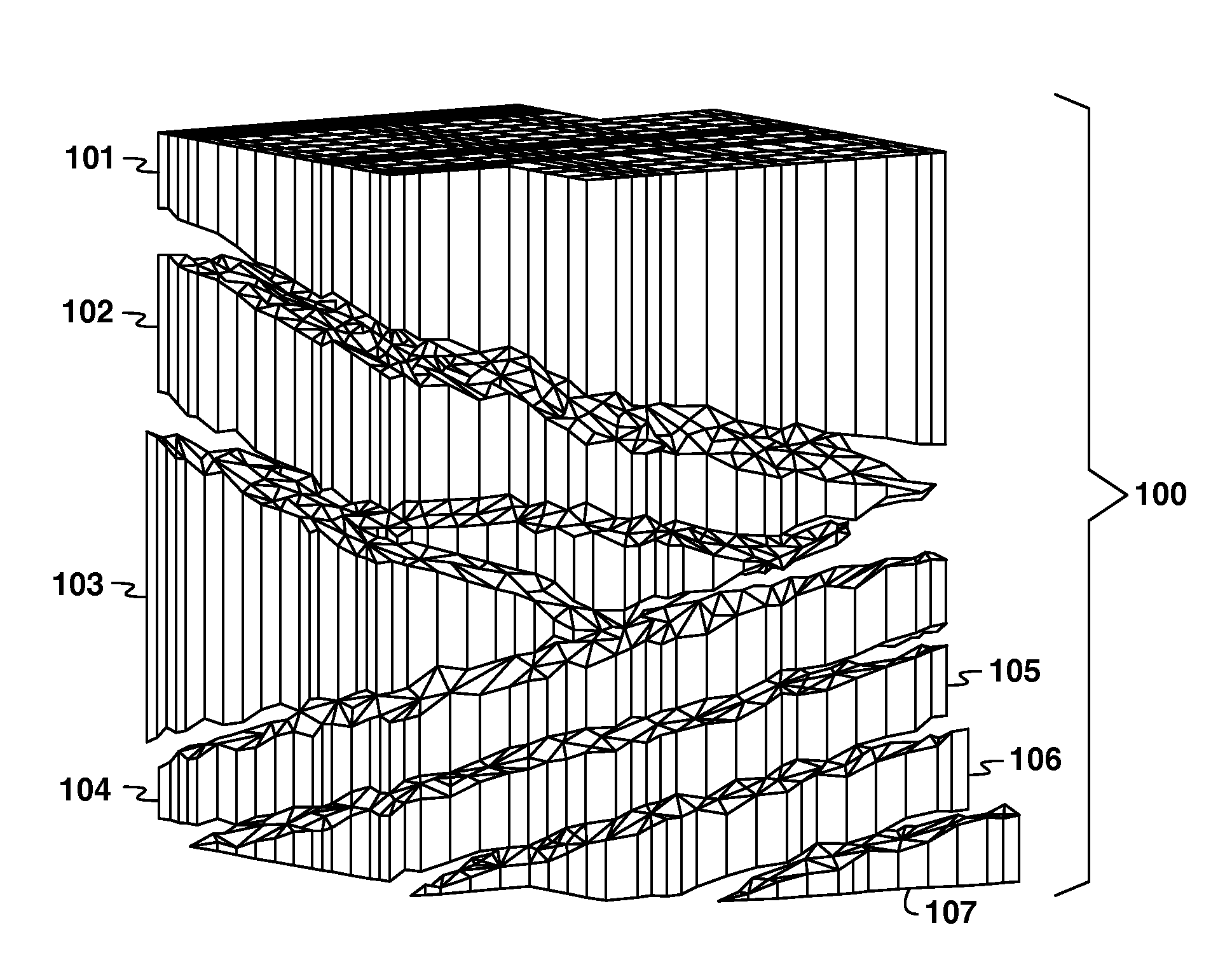
ActiveUS20100211370A1Increase the number ofAccurate modelingSeismologyGeomodellingDiffusionElement analysis
Embodiments of the invention involve forming a prismatic grid and solving a convection-diffusion problem using the prismatic grid and mixed finite element analysis. The prismatic grid may be formed by providing a triangular mesh on a plane of a model. The mesh is then coarsened to make cells that are less desirable larger. The coarsened grid is then projected to form the prismatic grid. Each cell of the grid is then assigned a plurality of degrees of freedom. Mixed finite element analysis of the grid produces a matrix, which is then solved to yield a solution to the convention-diffusion problem.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Numerical simulation method for characterizing fluid channelling along large-aperture fractures of reservoirs
InactiveUS20120173220A1Rapid fluid channelingEffective simulationSeismologyDesign optimisation/simulationOil fieldPetroleum reservoir
A numerical simulation method for characterizing fluid channeling along large-aperture fractures of reservoirs relates to the field of petroleum reservoir development research and computational fluid dynamics. The conventional method can not effectively represent the rapid fluid channeling along large-aperture fractures. Aiming at solving the above technical problem, an advanced method is provided in the present invention. In the invented method, the geometric similarity and hydraulic similarity treatments of large-aperture fractures can be made simultaneously, moreover, the traditional numerical simulation software was improved to be an unstructured grid simulator. Therefore, the method of the present invention can effectively simulate the rapid fluid channeling along large-aperture fractures, consequently it can ensure the reliability of the simulation results and provide reasonable reference for the adjustment and optimization of oil field development plans. The present invention is simple in principle and easy to use, thus it has a great value of application and popularization.
Owner:GEO SCI RES INST OF SHENGLI OIL FIELD OF SINOPEC
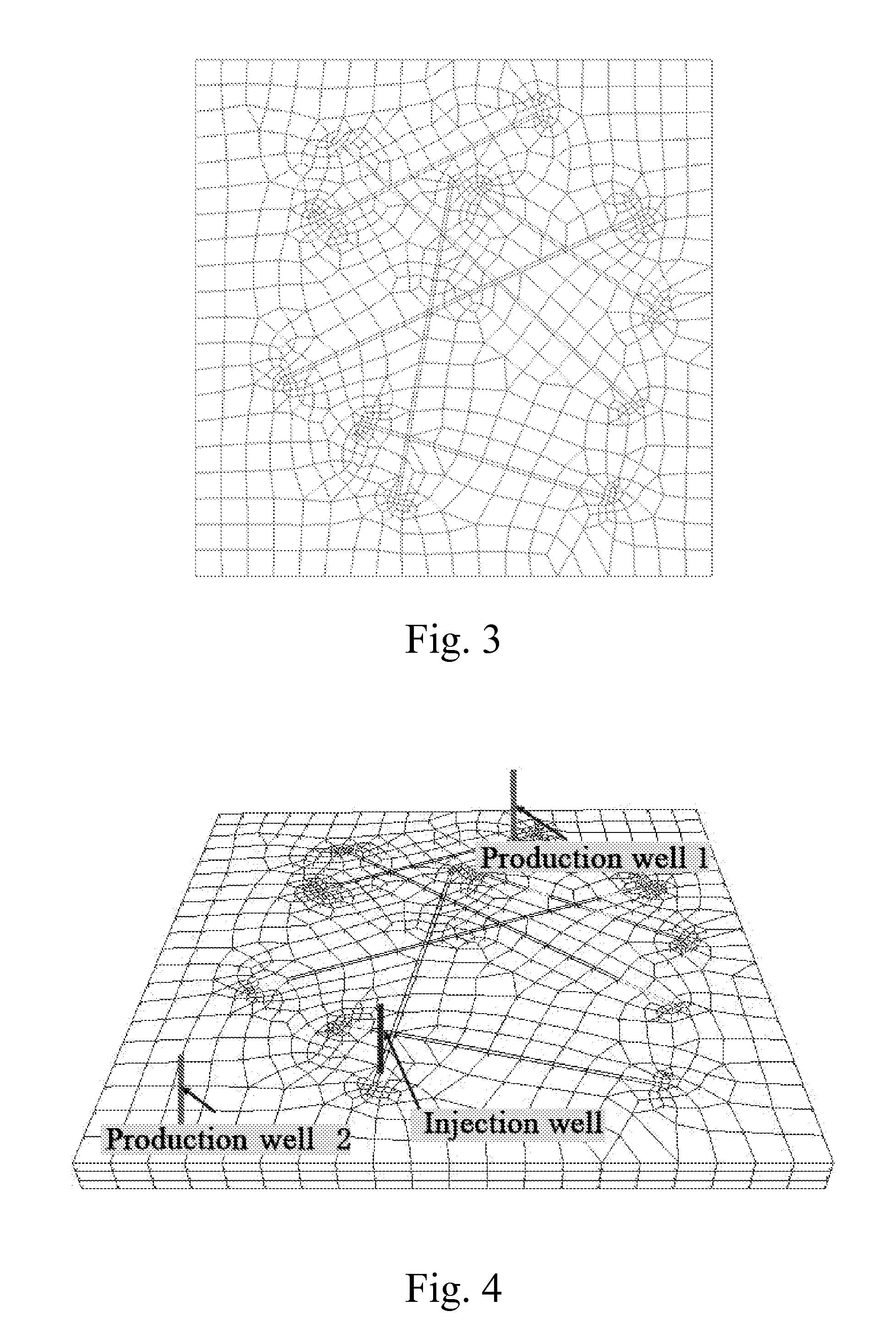
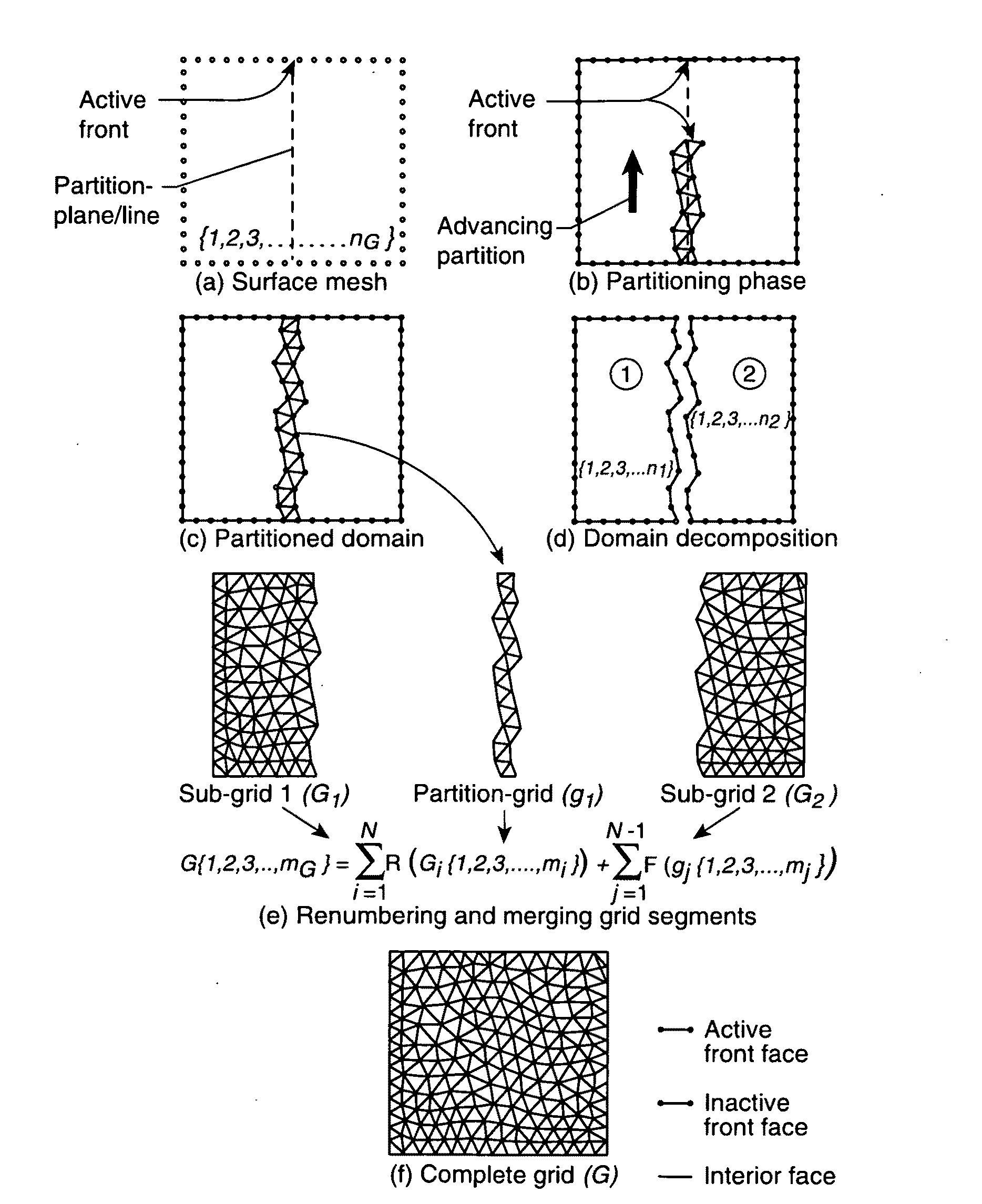
Domain Decomposition By the Advancing-Partition Method for Parallel Unstructured Grid Generation
InactiveUS20100134498A1Drawing from basic elements3D-image renderingDecompositionDomain decomposition methods
In a method for domain decomposition for generating unstructured grids, a surface mesh is generated for a spatial domain. A location of a partition plane dividing the domain into two sections is determined. Triangular faces on the surface mesh that intersect the partition plane are identified. A partition grid of tetrahedral cells, dividing the domain into two sub-domains, is generated using a marching process in which a front comprises only faces of new cells which intersect the partition plane. The partition grid is generated until no active faces remain on the front. Triangular faces on each side of the partition plane are collected into two separate subsets. Each subset of triangular faces is renumbered locally and a local / global mapping is created for each sub-domain. A volume grid is generated for each sub-domain. The partition grid and volume grids are then merged using the local-global mapping.
Owner:NASA
Generating unconstrained voronoi grids in a domain containing complex internal boundaries
Unstructured grids are automatically constructed in a domain containing complex internal boundaries. Simulation grids are constructed for reservoirs or fields which contain complex fault planes. Reconciling among generated fault grid-points and other reservoir / field grid-points is performed, enabling the use of unconstrained Delaunay triangulation. High-quality orthogonal unstructured grids are provided with good convergence properties for reservoir simulation.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Numerical simulation method for characterizing fluid channelling along large-aperture fractures of reservoirs
InactiveUS8532969B2Rapid fluid channelingEffective simulationSeismologyDesign optimisation/simulationDependabilityGeometric similarity
Owner:GEO SCI RES INST OF SHENGLI OIL FIELD OF SINOPEC
Method for assessing tide energy resource through numerical simulation of sea model
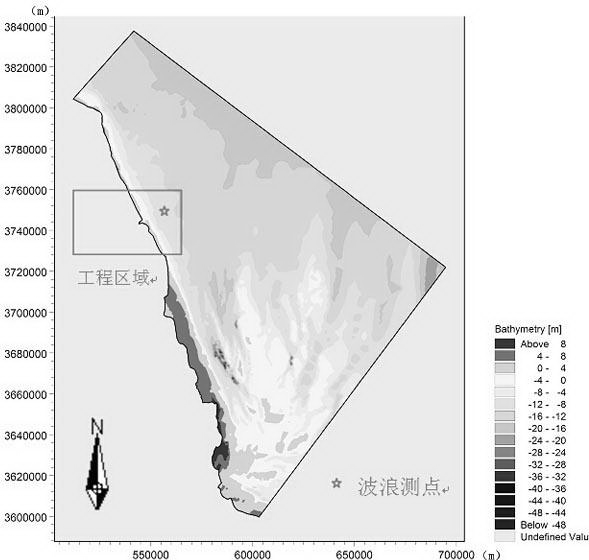
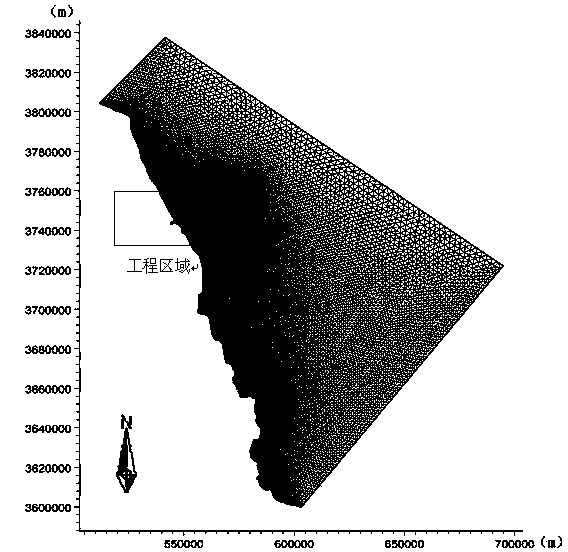
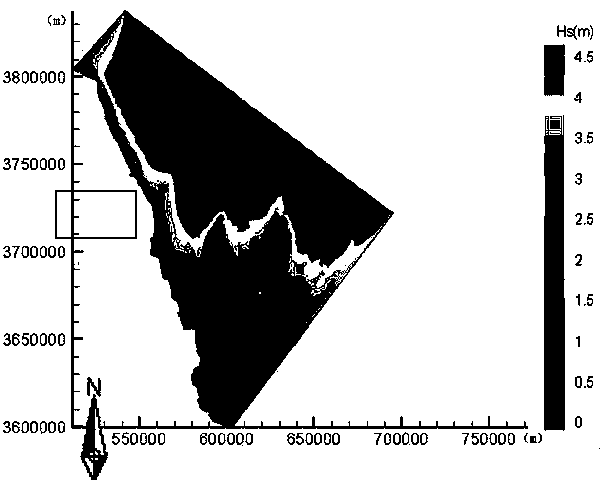
InactiveCN103390248ASolve the shortageAccurate estimateData processing applicationsTerrainSurface ocean
The invention relates to a method for assessing a tide energy resource through a numerical simulation of sea model. The technological steps are as follows: a target sea area is selected; sea chart splicing work of the target sea area is completed, and a high-precision terrain data product of the target sea area is manufactured; water depth terrain data measured through a field investigation are combined with satellite data, so that water depth terrain data of the target sea area are obtained; non- structural grid is performed on a calculation area of the target sea area, and the sea model is constructed; number value simulation calculation is performed with the sea model; a simulation calculation result and actually measured data are compared and verified; the energy flow density is calculated; the standing stock is calculated by selecting a section with a larger energy flow density; the developable tide energy power and the resource category are acquired according to the obtained standing stock; and an assessment result is displayed through a visualization technology. The method provides an important way for accurately assessing the tide energy level of the target sea area and solving the problem that the energy in coastal and sea island areas of our country is short.
Owner:牟林 +6
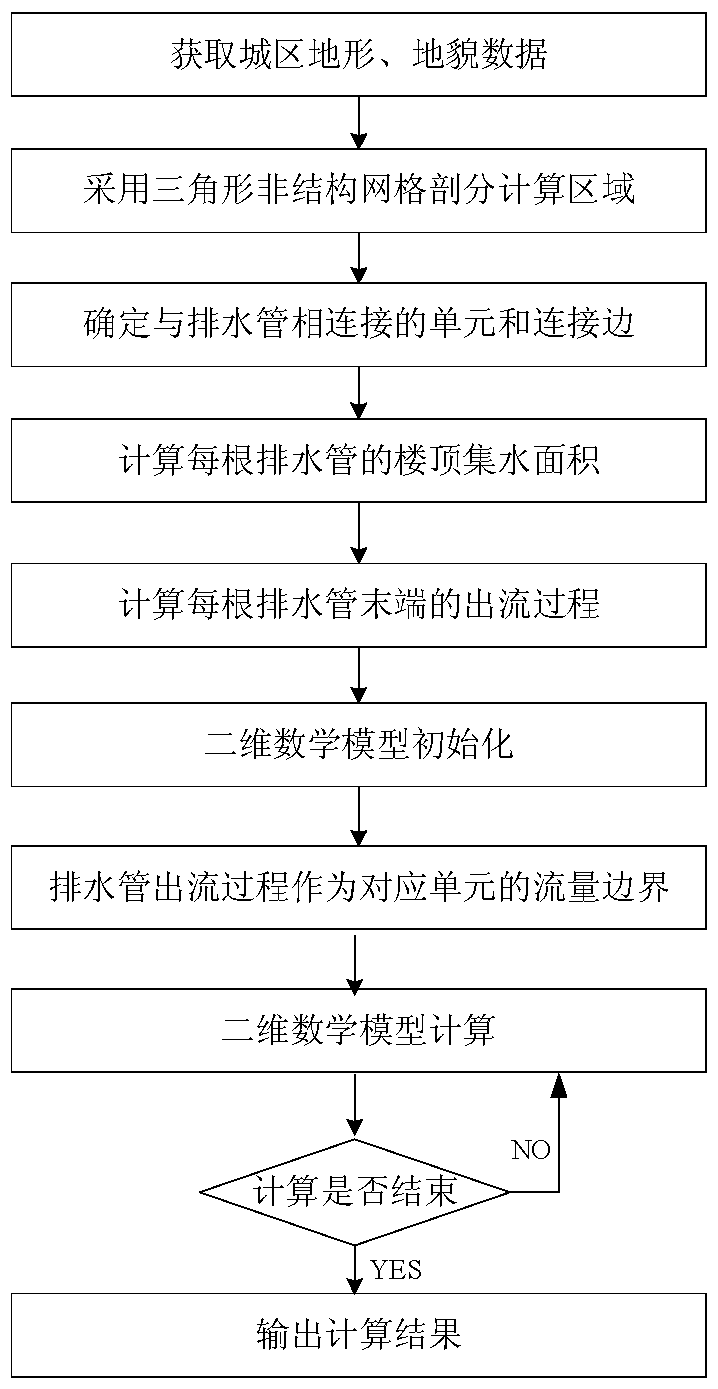
Two-dimensional numerical simulation method of urban surface runoff
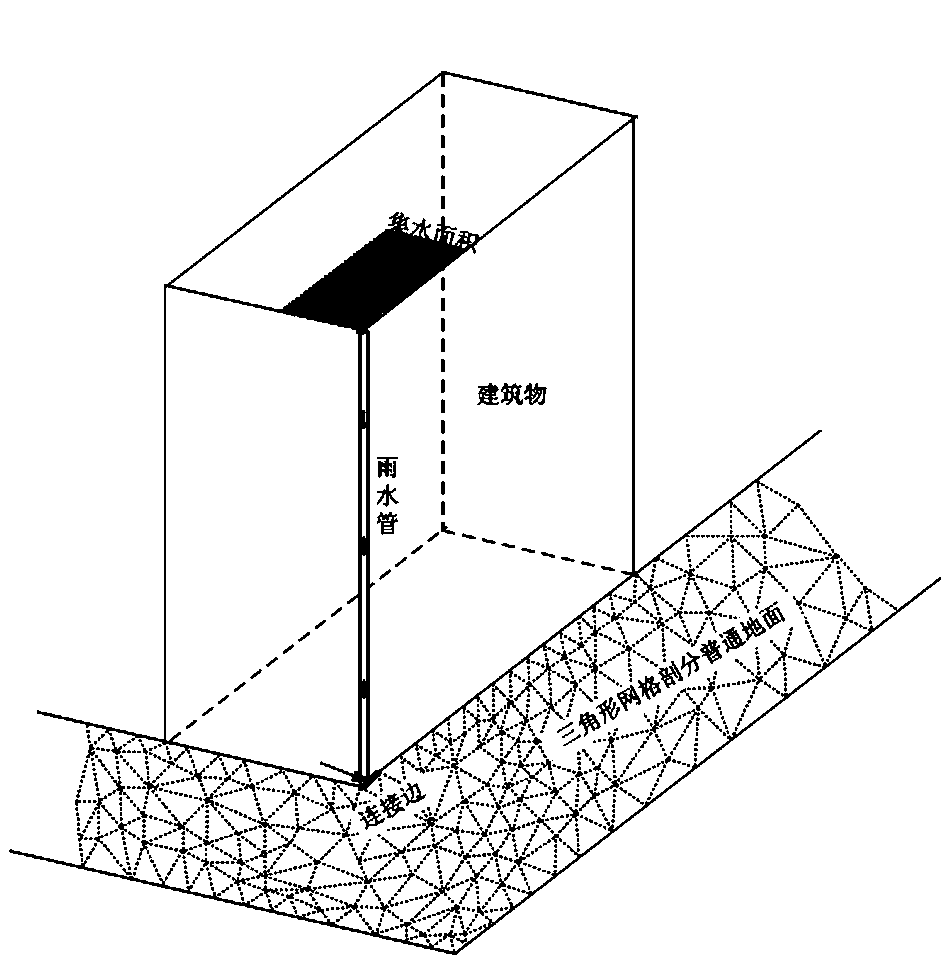
ActiveCN109543275AGuaranteed runoff mass conservation characteristicsHigh simulationGeometric CADClimate change adaptationControl lineLandform
The invention provides a two-dimensional numerical simulation method of urban surface runoff. After obtaining urban topography and geomorphology data, the triangular unstructured mesh is used to discrete the computational area of the urban area. The area where the building is located does not participate in dissection, and its contour line is used as the control line of mesh dissection. Each rainwater pipe of the building is connected with the ground through the confluence connecting edge. Firstly the method calculates the confluence area of each rainwater pipe, and then calculates the discharge process of each rainwater pipe. Two-dimensional Godunov model is used to simulate the rainwater outflow process. The rainfall in the surface grid element is treated as the source term in the model,and the rainwater outflow process is regarded as the flow boundary condition of the element corresponding to the connecting edge. The invention fully considers the characteristics of building confluence in the urban area, which can not only ensure the mass conservation characteristic of the whole urban area during flood calculation, but also consider the influence of the water flow momentum at the outlet of the rain pipe on the surface runoff, thus overcoming the shortcoming that the existing urban flood and waterlogging model can not consider the building confluence process, and improving the calculation accuracy.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Modeling subsurface processes on unstructured grid
ActiveUS8396699B2Increase the number ofAccurate modelingSeismologyGeomodellingDiffusionElement analysis
Embodiments of the invention involve forming a prismatic grid and solving a convection-diffusion problem using the prismatic grid and mixed finite element analysis. The prismatic grid may be formed by providing a triangular mesh on a plane of a model. The mesh is then coarsened to make cells that are less desirable larger. The coarsened grid is then projected to form the prismatic grid. Each cell of the grid is then assigned a plurality of degrees of freedom. Mixed finite element analysis of the grid produces a matrix, which is then solved to yield a solution to the convention-diffusion problem.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
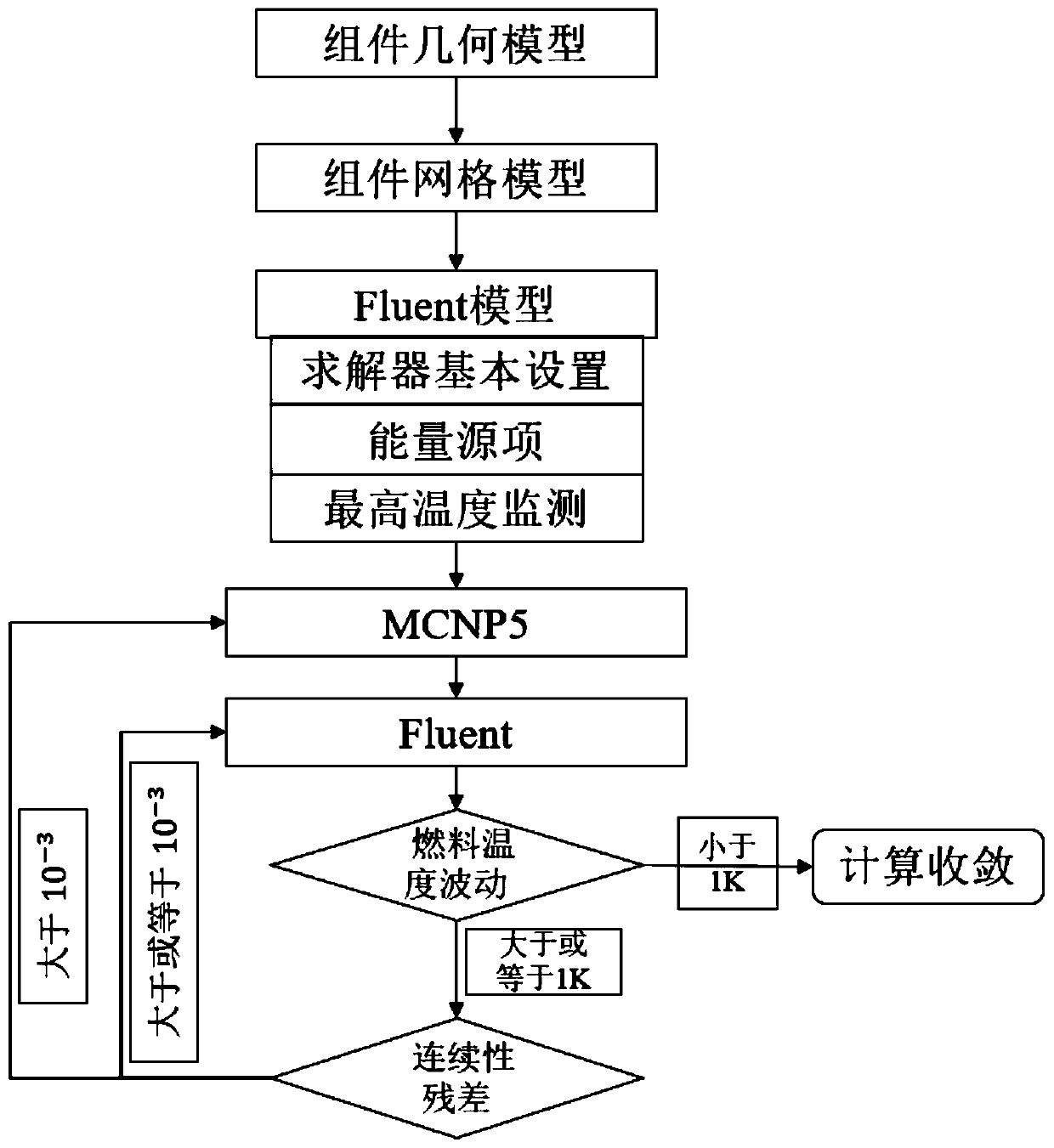
Nuclear reactor core physical and thermal coupling simulation method
ActiveCN111414722AHigh precisionReduce workloadMathematical modelsDesign optimisation/simulationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention discloses a nuclear reactor core physical and thermal coupling simulation method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, establishing a computational domain unstructured grid model by adopting Fluent pretreatment software, and then importing the grid model into Fluent to establish an example; extracting grid information and flow field data in a Fluent example by adopting auser-defined function function of Fluent software, and automatically generating an input file required by MCNP5 calculation; controlling MCNP5 to complete calculation of a neutron physical field by means of a user-defined function function of Fluent, analyzing the output file of the MCNP5, and extracting fission power data of a nuclear fuel region; transmitting the fission power into Fluent software and executing calculation; after initial convergence of Fluent calculation, regenerating an MCNP5 input file by using the user-defined function of the Fluent, calling the MCNP5 again to calculate fission power data, and transmitting the fission power data to the Fluent; and repeating the above steps until Fluent is finally converged. According to the invention, physical and thermal coupling canbe conveniently realized, and a foundation is laid for research of a numerical reactor.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for simulating fluid flow
ActiveCN101329700ASolve the problem of not being able to deal effectively with irregular boundariesImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsPhysical spaceComputational problem
The invention discloses a method used for simulating fluid flow, and the scope of the fluid flow comprises obstacles represented by irregular boundaries; the method is characterized in that: a structured grid of initial physical space is built, and evolved into a complex structured grid by applying treatment to the irregular boundaries one by one, and every irregular boundary is inserted into the complex structured grid as a zero iso-surface to obtain a complex invisible structured grid (CISgrid for short); a unit vertex of the CISgrid is used as a computational node, a finite difference method is adopted to carry out fluid flow numerical simulation according to node connected regulation. According to effective regulation inside the CISgrid, post-treatment of the fluid flow numerical simulation is carried out. The method solves the problem that the irregular boundaries can not be effectively treated when the fluid flow simulation is directly carried out with the structured grid and the finite difference method, avoids the problem of the introduction of the complex structured grid by the adaptation of an unstructured grid and the complex numerical computation based on the unstructured grid, and effectively improves the efficiency of the fluid flow simulation.
Owner:北京网格天地软件技术股份有限公司
Marine controlled source electromagnetic method finite element forward method of anisotropic media
InactiveCN106980736AAvoid the effects of singularityEasy constructionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsScalar potentialMaxwell's equations
The present invention is a marine controlled source electromagnetic method finite element forward method of anisotropic media. The method comprises: firstly, setting a reference electrical conductivity, wherein three non-zero diagonal elements of the reference electrical conductivity are electrical conductivities in the direction of three main axes: x, y, z; next, setting three Euler rotation angles, and after three times of Euler rotation, obtaining an electrical conductivity tensor model in any direction; then starting from Maxwell equations, obtaining a finite element equation that is satisfied by magnetic vector potential and scalar potential under Coulomb regulations on a condition that the electrical conductivity presents anisotropy; then, performing discrete segmentation on a research region by using a non-structural grid, so that a complicated geoelectric model can be constructed; combining an incomplete LU discomposition pre-condition factor with an IDR(s) algorithm, so as to realize efficient and precise solution of a large sparse linear equation; and finally, deriving vector potential and scalar potential of a secondary field by using weighted moving least squares solution, to obtain each component of an electromagnetic field. The method provided by the present invention has excellent universality and can be promoted for electromagnetic method numerical value simulation with complicated electrical conductivity distribution and high precision.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Unstructured grid nesting wave numerical simulation method
InactiveCN104331599AReduce in quantityImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsComputational scienceTerrain
The invention discloses an unstructured grid nesting wave numerical simulation method, which includes the following main steps: an unstructured grid is adopted to create a mathematical model of waves in a large area; an unstructured grid is adopted to create a mathematical model of waves in a shallow-water engineering sea area; according to computational domains of different sizes, the numerical simulation of the waves is carried out. The unstructured grid nesting wave numerical simulation method achieves the following advantages: on the basis of bringing the unstructured grid wave mathematical models into full play, by applying the grid nesting technology, the unstructured grid nesting wave numerical simulation method greatly reduces the number of the grids in the computational domains, and increases the speed of computation; by applying the grid nesting technology, the unstructured grid nesting wave numerical simulation method can deploy finer computational grids in order to adapt to complex terrains and irregular coast boundaries, so that the accuracy of computed results can be increased.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL COMM PLANNING & DESIGN INST
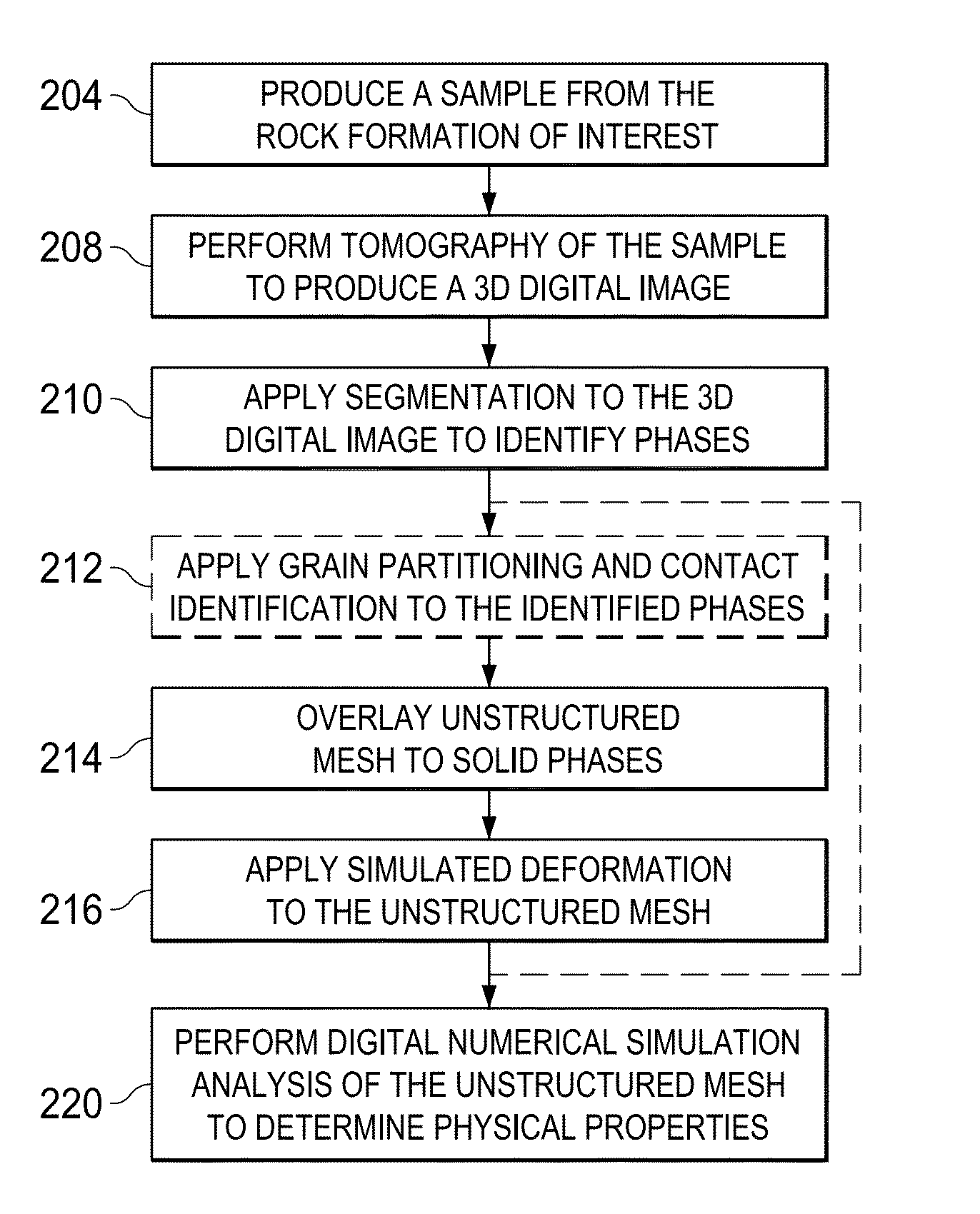
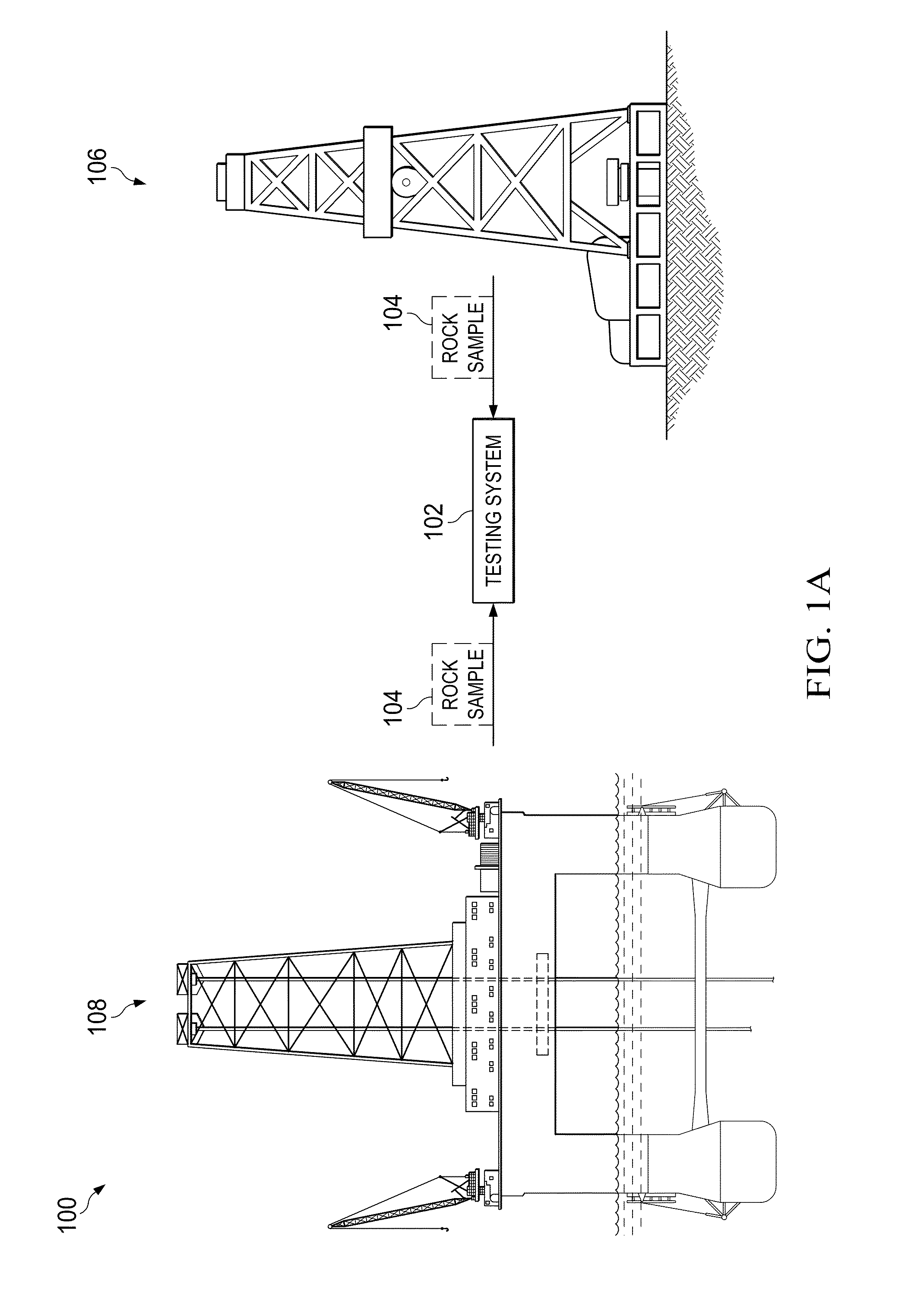
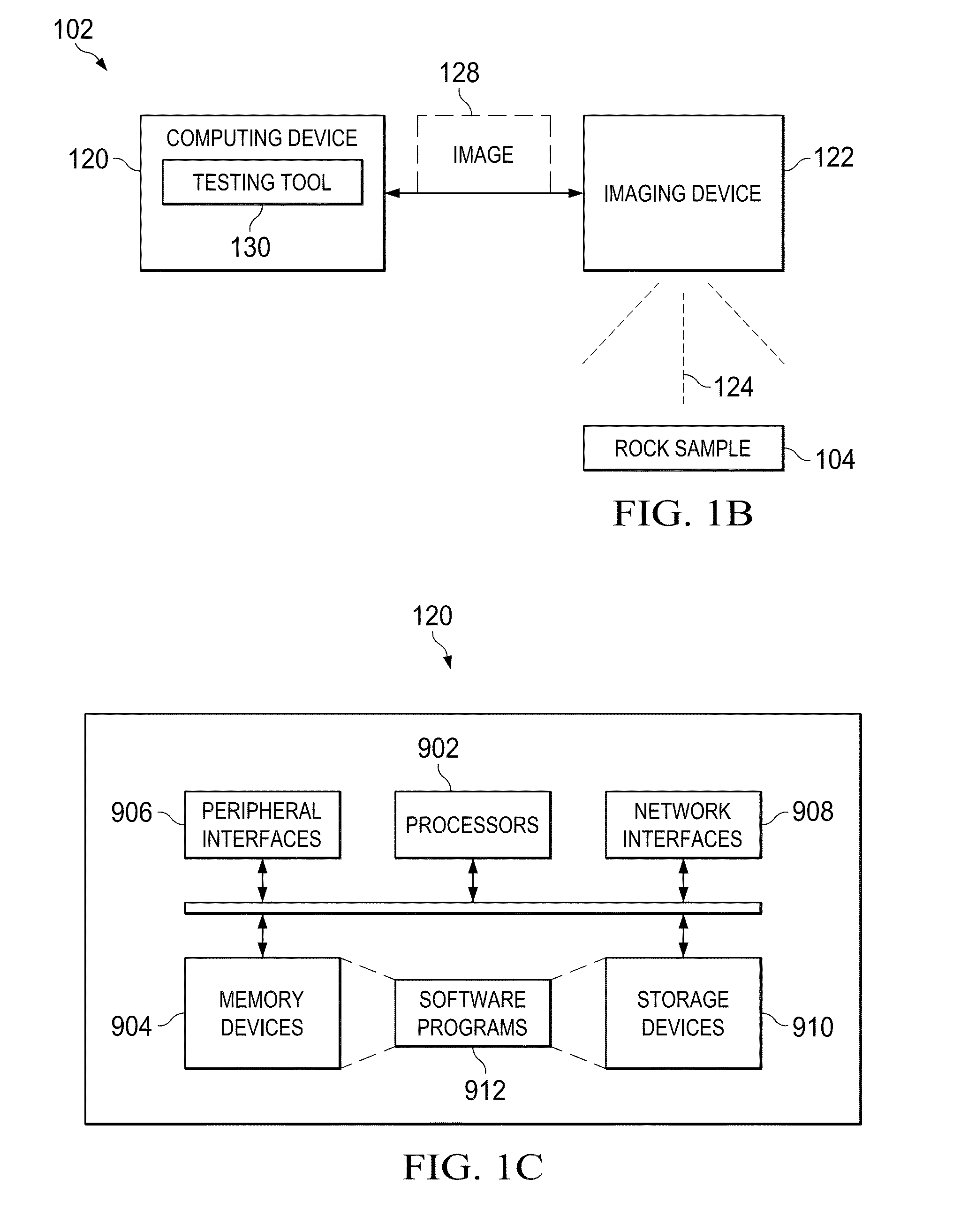
Image-based direct numerical simulation of petrophysical properties under simulated stress and strain conditions
A testing system for performing image based direct numerical simulation to characterize petrophysical properties of a rock sample under the simulated deformation condition, for example as representative of subsurface conditions. A digital image volume corresponding to x-ray tomographic images of a rock sample is segmented into its significant elastic phases, such as pore space, clay fraction, grain contacts and mineral type, and overlaid with an unstructured finite element mesh. A simulated deformation is applied to the segmented image volume, and the resulting deformed unstructured mesh is numerically analyzed, for example by way of direct numerical simulation, to determine the desired petrophysical properties.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
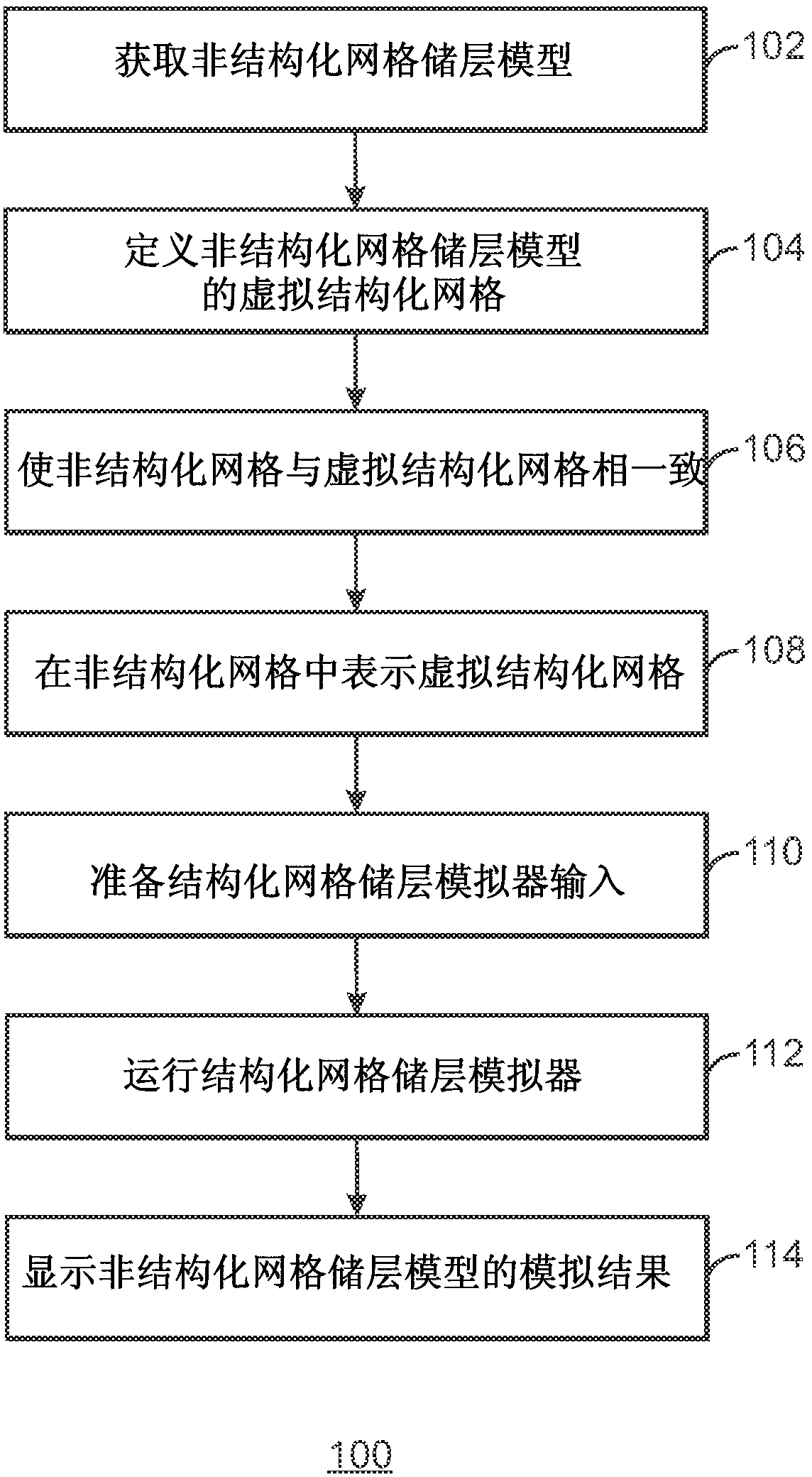
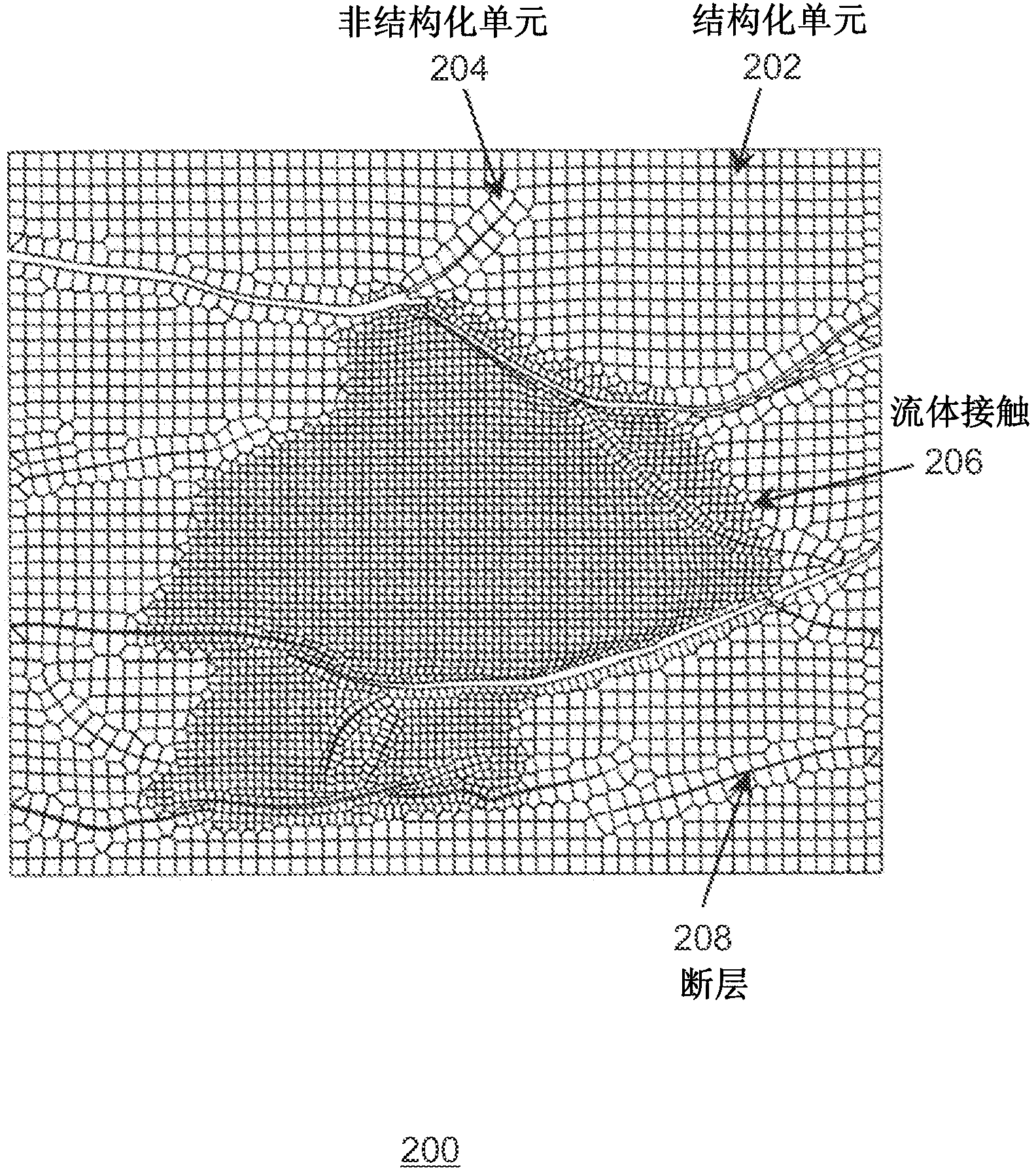
Systems and methods for subsurface reservoir simulation
InactiveCN103282915ADesign optimisation/simulationGeological measurementsComputational scienceDiscretization
Systems and methods for providing a reservoir simulation are based on data from an unstructured grid using a structured grid reservoir simulator. Exemplary methods comprise obtaining an unstructured grid reservoir model comprising a reservoir model discretized on an unstructured grid. A virtual structured grid is defined for the unstructured grid reservoir model. The unstructured grid is aligned with the virtual structured grid by adding cells to the unstructured grid to make the unstructured grid and virtual structured grid have the same number of cells. The virtual structured grid may be represented in the unstructured grid. Structured grid reservoir simulator input data comprising reservoir model data assigned to the virtual structured grid is prepared based on reservoir model data in the unstructured grid model. A structured grid reservoir simulation is performed using the structured grid reservoir simulator input data to produce a reservoir simulation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Rocket plume simulation method
ActiveCN104050334AImprove computing efficiencyEasy to observe field data distributionSpecial data processing applicationsCombustion chamberChemical reaction
The invention discloses a rocket plume simulation method which includes the following steps that an unstructured grid is generated by means of Gambit software and a boundary condition is set; the grid is led into Fluent, and plume flow field physical models are solved by means of Fluent software, wherein the plume flow field physical models include a turbulence model, a dispersed phase model and a combustion model; a boundary condition and an iteration initial value are set in the Fluent according to model requirements or actual situations, and flow field data are obtained through analog simulation. a parameter model for plume flow field compute is built based on the mechanism study of a rocket plume flow field and according to the combustion theory, hydromechanics and gas dynamics and with the consideration of combustion chemical reactions in a combustion chamber, main features of the plume flow field can be objectively described, flow field data on specific conditions are quickly obtained through simulation, input parameters are provided for compute of infrared features of rocket plumes, plume computer precision is improved, and plume simulation time is saved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Embedded discrete fracture model-based fractured well modeling and simulation method
ActiveCN105653746AAccurate descriptionAccurate portrayalSpecial data processing applicationsGeneration processCoarse mesh
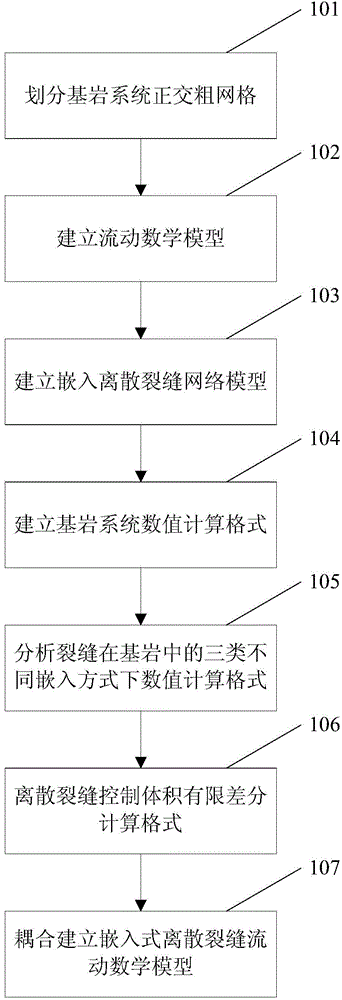
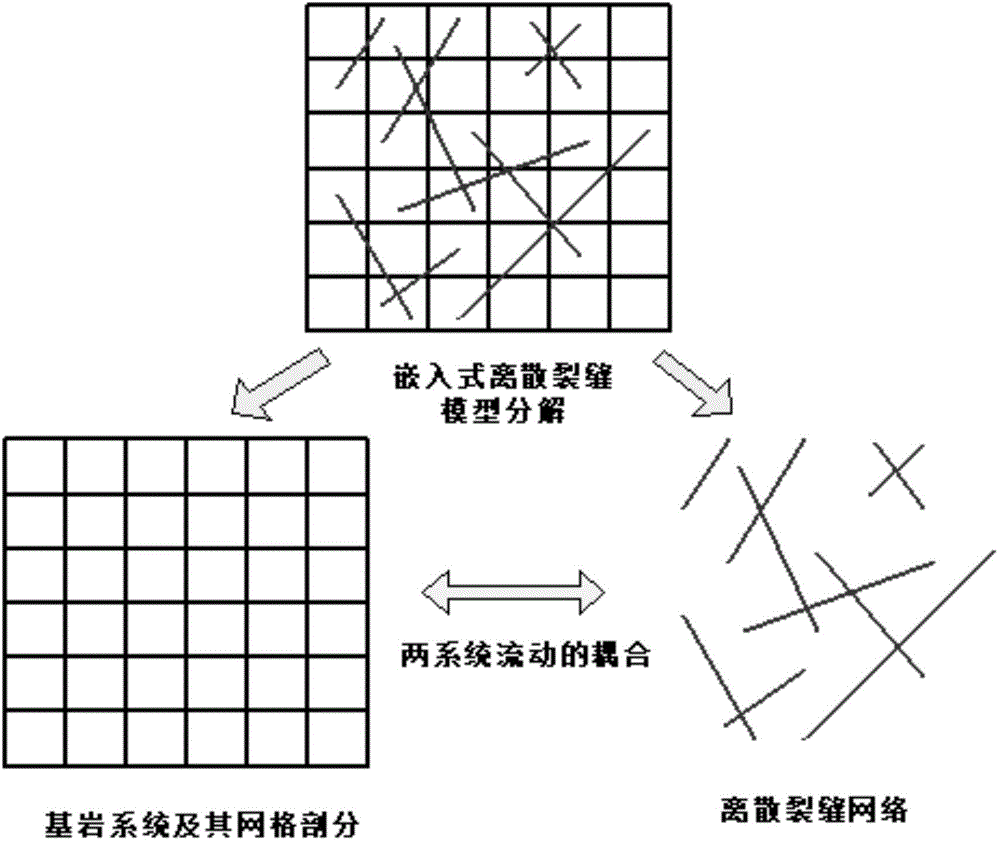
The invention provides an embedded discrete fracture model-based fractured well modeling and simulation method. The method includes: dividing a bed rock system orthogonal coarse meshes, and extracting coarse mesh nodes and fracture information; dividing the system into a bed rock system and a fracture system, and establishing a flow mathematical model for the bed rock system and the fracture system each; establishing a corresponding embedded discrete fracture net model; establishing a bed rock system numerical calculation format based on a simulation finite difference method; analyzing the numerical calculation format of fractures in bed rocks in three different embedded manners; establishing a numerical calculation format of an embedded discrete fracture net system based on a control volume finite difference method; and serving the fracture system as a source term of the bed rock system, and establishing an embedded discrete fracture flow mathematical model by coupling the fracture system and the bed rock system. The embedded discrete fracture model-based fractured well modeling and simulation method can avoid a complicated unstructured mesh generation process, and improve the accuracy and the high efficiency of a fractured well fracture description and simulation method.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for architectural design by utilizing simplified models and unstructured grids
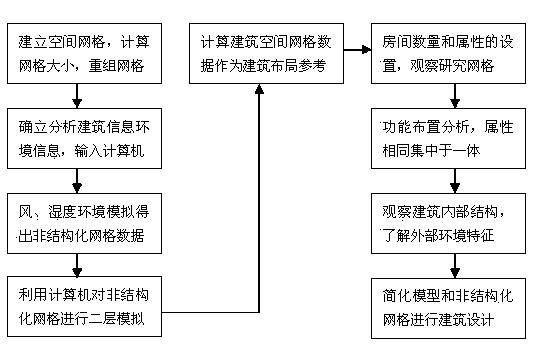
ActiveCN103823931AReasonable designSimple designSpecial data processing applicationsBuilding designBuilding model
The invention relates to a method for architectural design by utilizing simplified models and unstructured grids. The method includes: necessarily simplifying cumbersome steps during the architectural design; making the simplified building models through software inside a building and taking the detected building as a large space grid; inputting building information and environment information into a computer for simulation of the building environment and the humidity environment to acquire data of the unstructured grids of the whole building; calculating each space building grid according to the acquired data; analyzing functional arrangement of the building as required and integrally concentrating functional zones identical in attribute as far as possible to enable the building to be standard and vertical. By the method, convenience in observation of an internal structure of the building facilitates knowledge of external environment characteristics, so that a designer can observe, study and work out good works conveniently and rapidly.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com