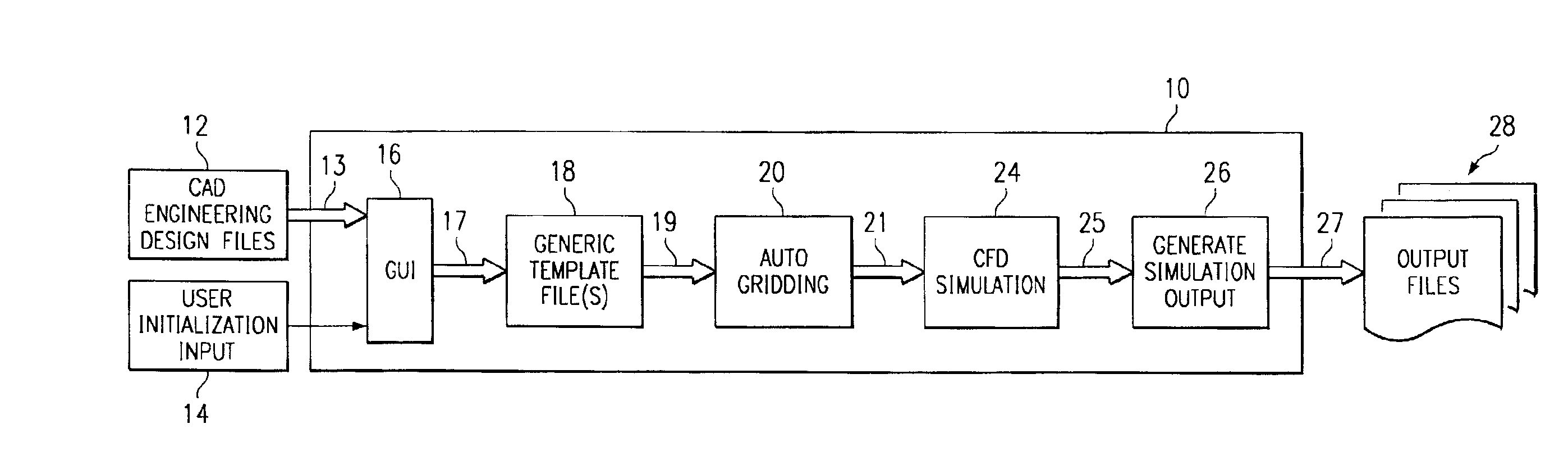
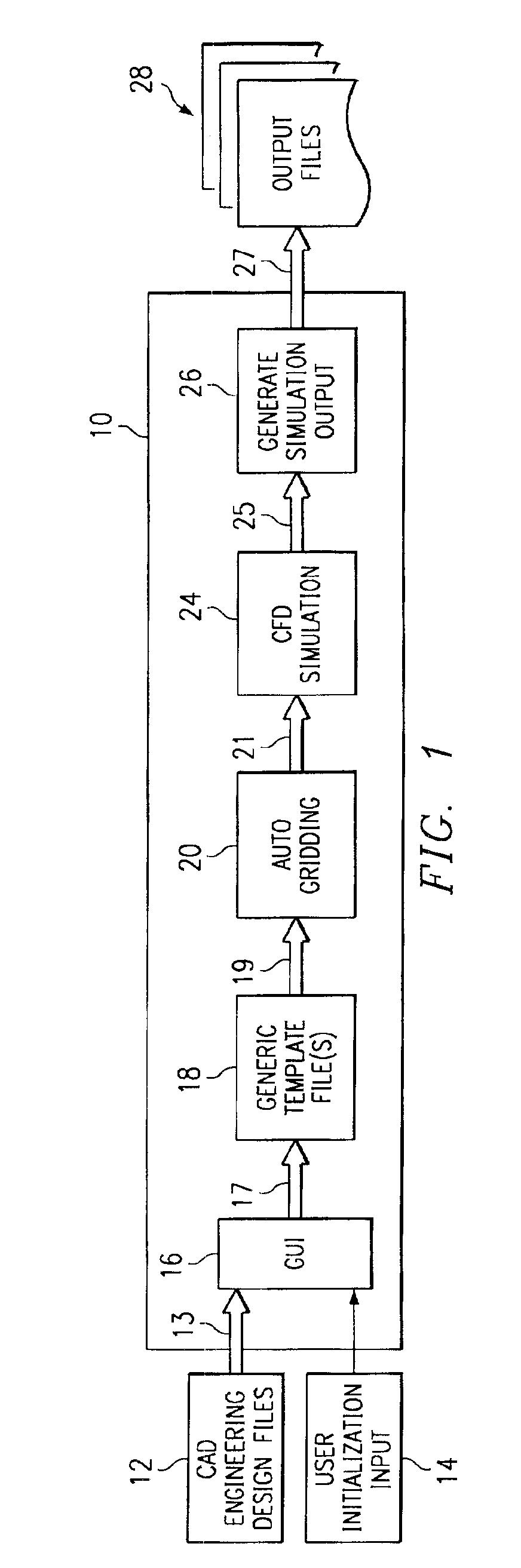
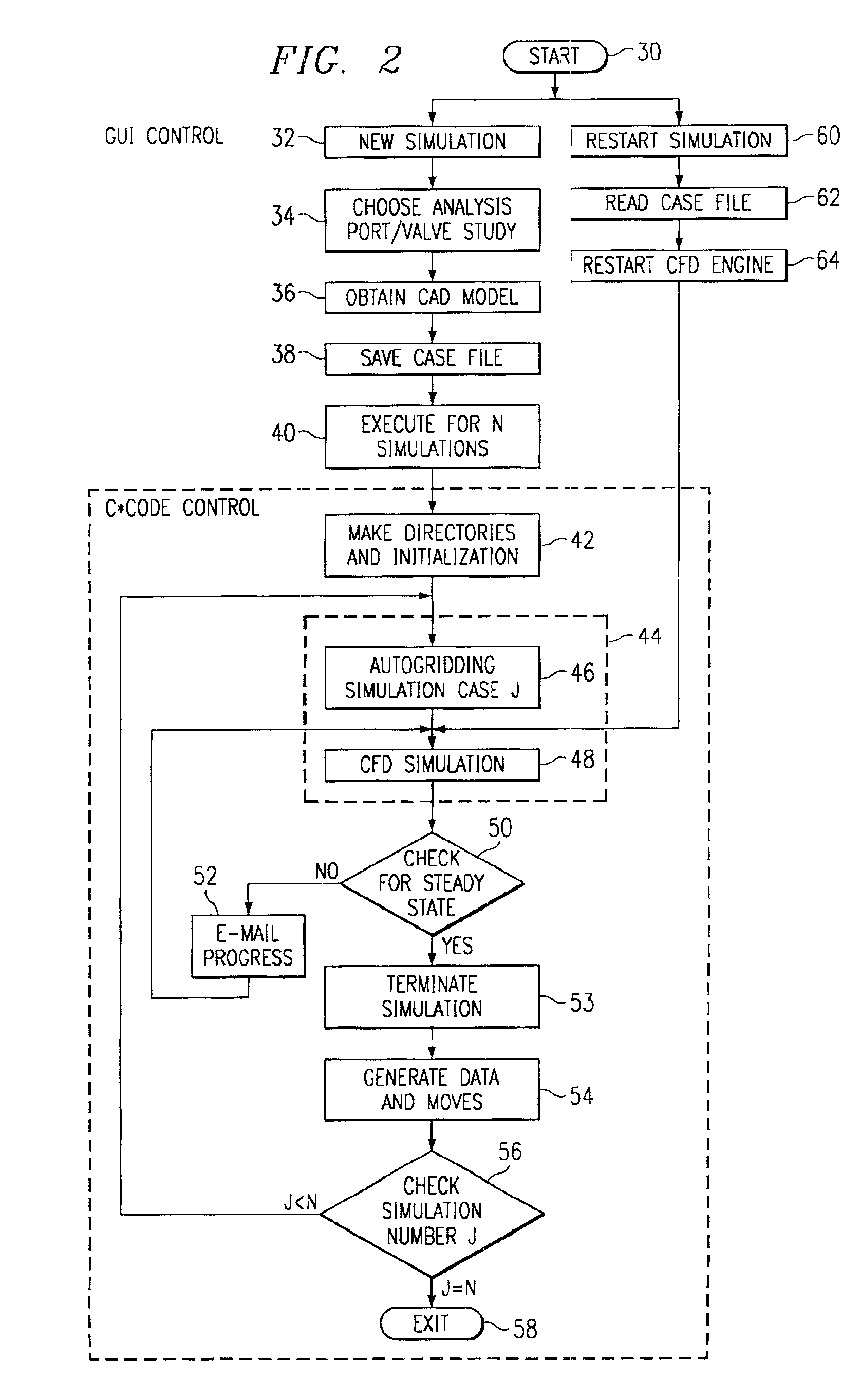
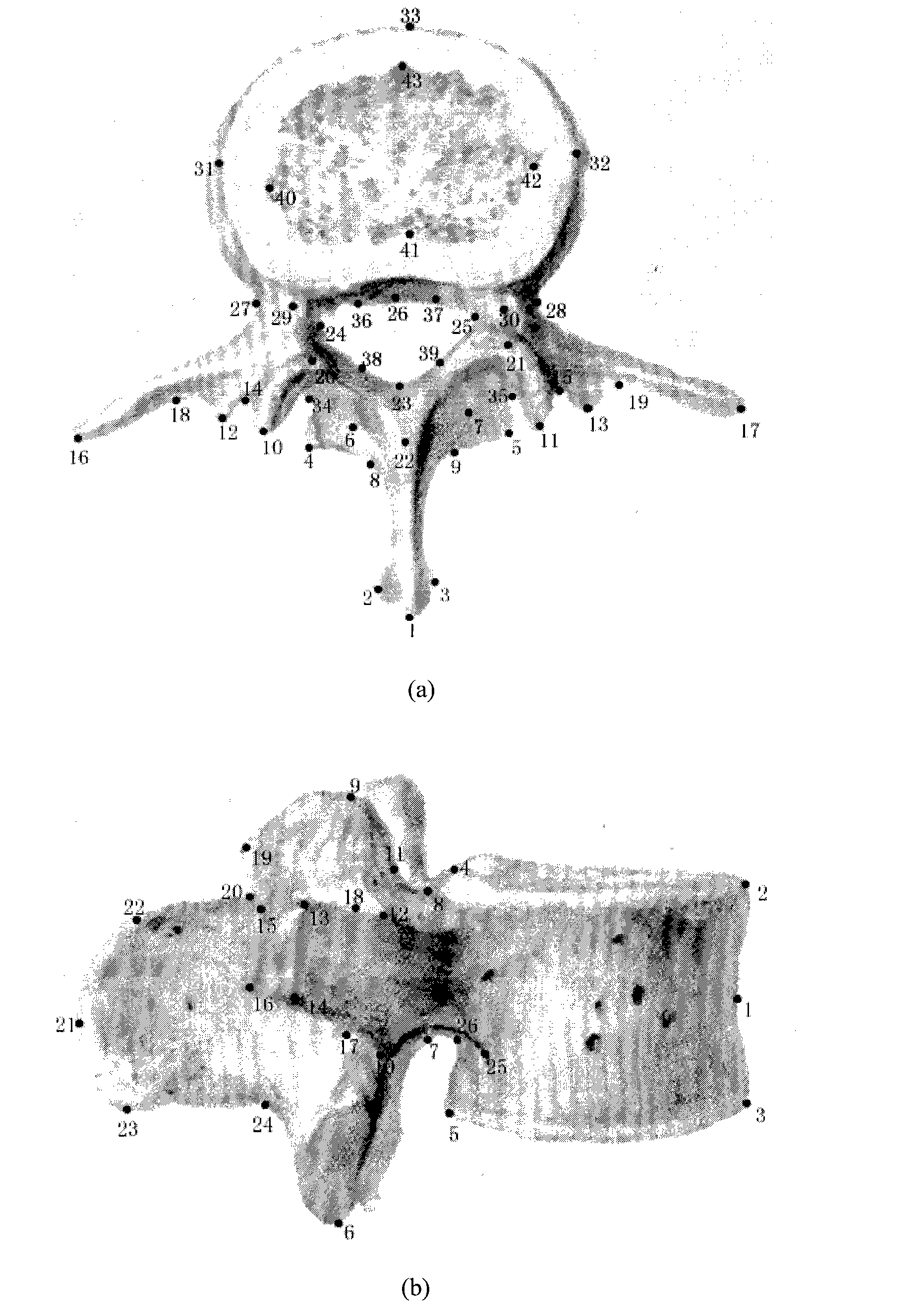Patents
Literature
72 results about "Volume mesh" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Volumetric meshes are a polygonal representation of the interior volume of an object. Unlike polygon meshes, which represent only the surface as polygons, volumetric meshes also discretize the interior structure of the object.
Finite element preprocessing method for reconstructing three-dimensional entity model
InactiveCN104282040AShorten the timeReduce preparation timeSpecial data processing applications3D modellingPoint cloudFinite element analyse
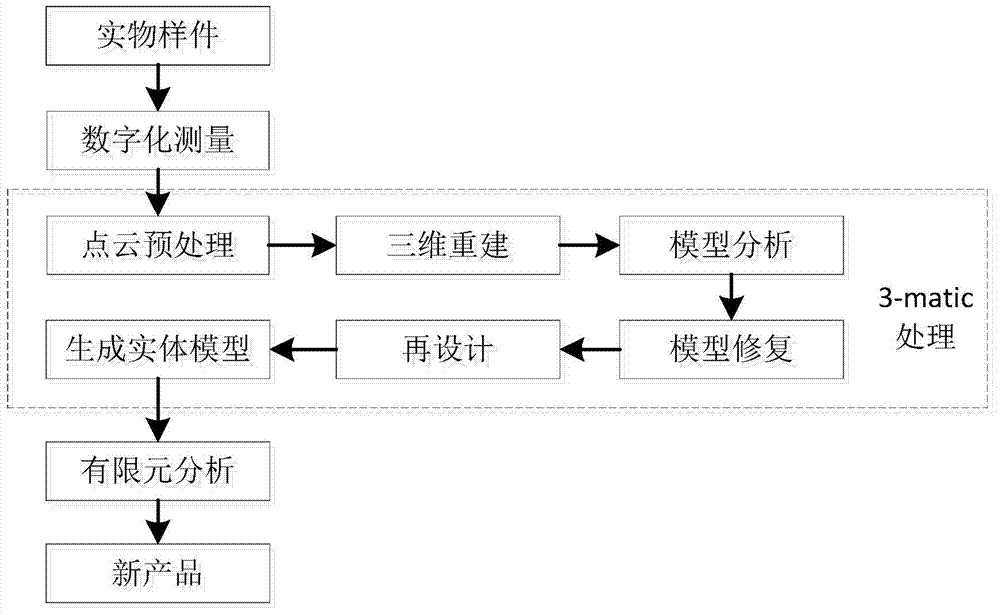
A finite element pre processing method for reconstructing a three-dimensional entity model comprises the steps that first, a material object is scanned so that point cloud data can be acquired; second, the point cloud data are imported to 3-matic software, and the position of the model is adjusted; third, the point cloud data are de-noised and sampled; fourth, three-dimensional reconstructing of the point cloud data is performed through a computer, wherein the point cloud data are packaged so that a surface mesh model can be generated; fifth, thin wall characteristic analysis is performed on the model so that a basic model structure can be known; sixth, three-dimensional repair is performed on model meshes, so that the edges of the model are matched with the defect contour of the material object; seventh, the model is redesigned as required, and thus the structure of the model can be more reasonable and meet the design requirement; eighth, the meshes of the redesigned model are partitioned again; ninth, a volume mesh is generated, material attributes are added, and the new model is saved in the format through which finite elements can be directly analyzed; tenth, finite elements are analyzed. Through the method, the scanned data processing time is shortened and FEA / CFD pre processing time are shortened, and optimal design of the model can be conveniently performed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
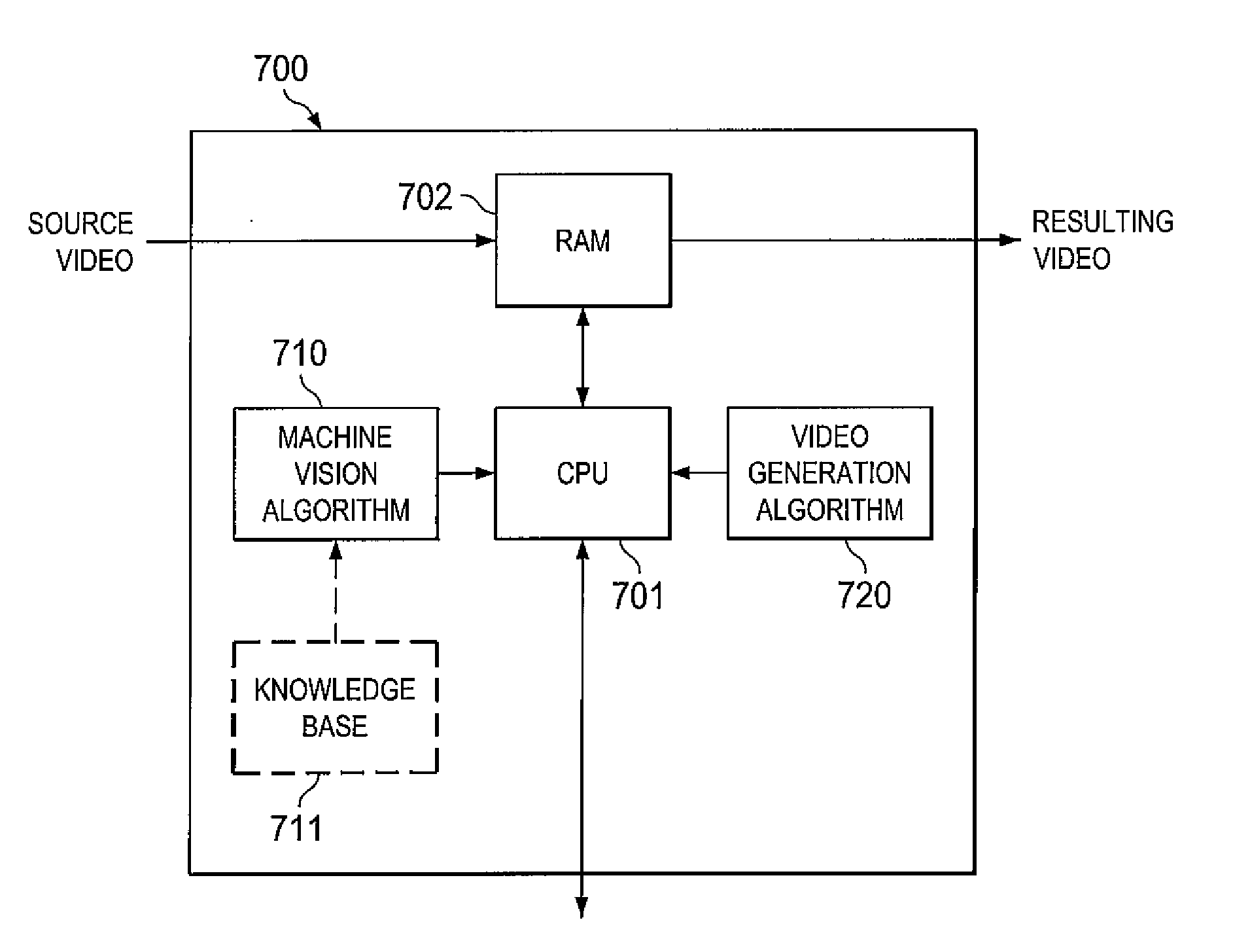
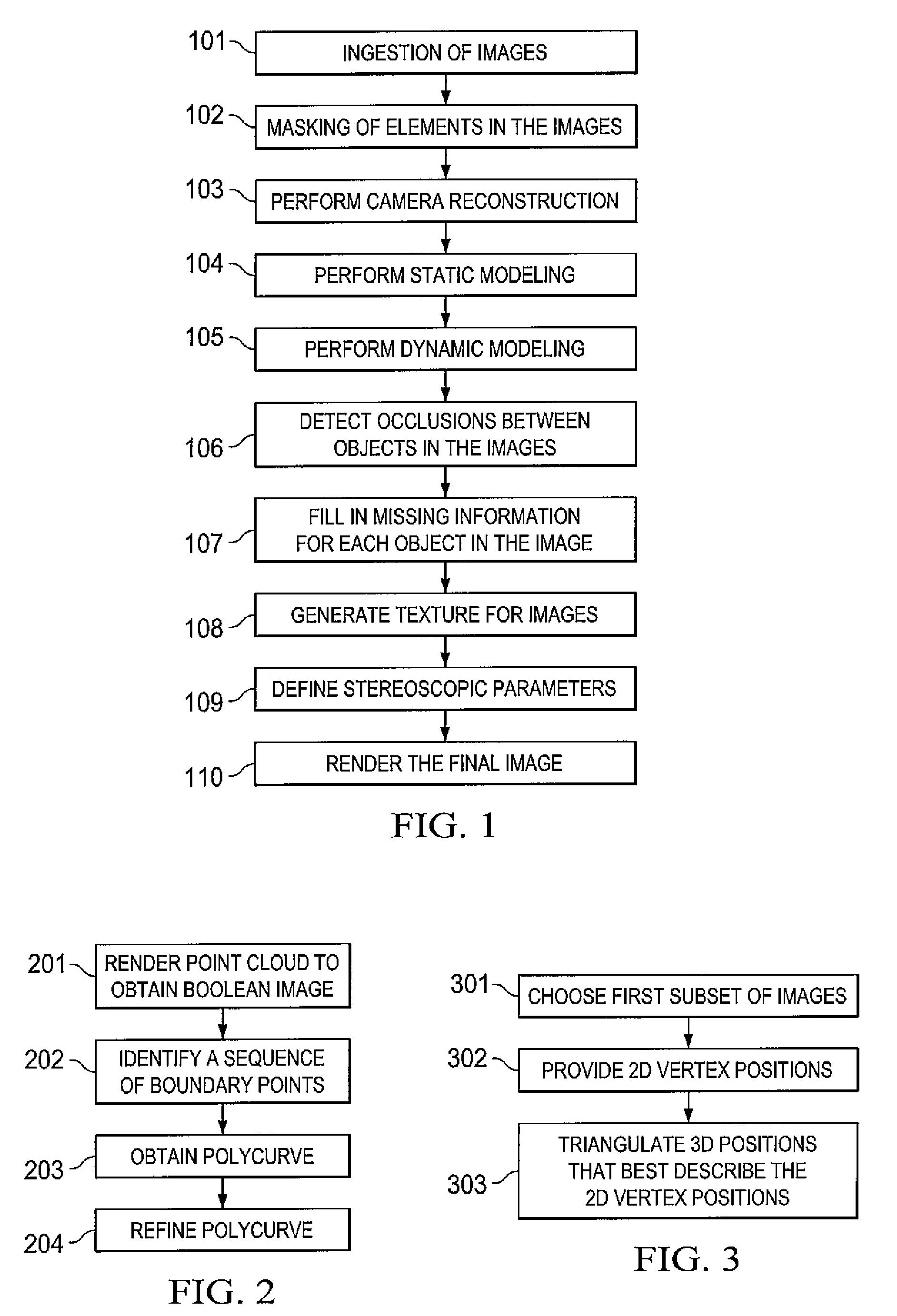
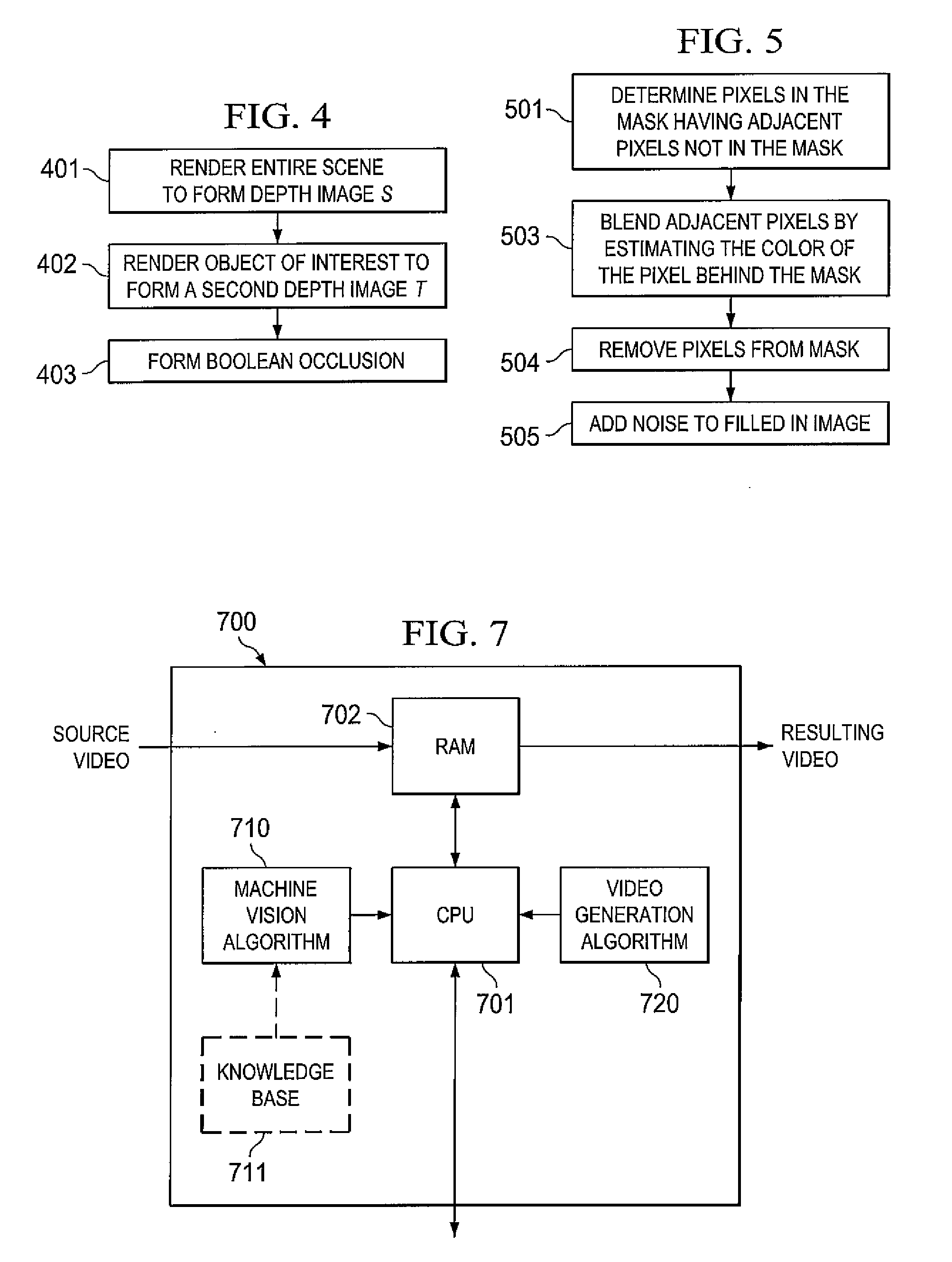
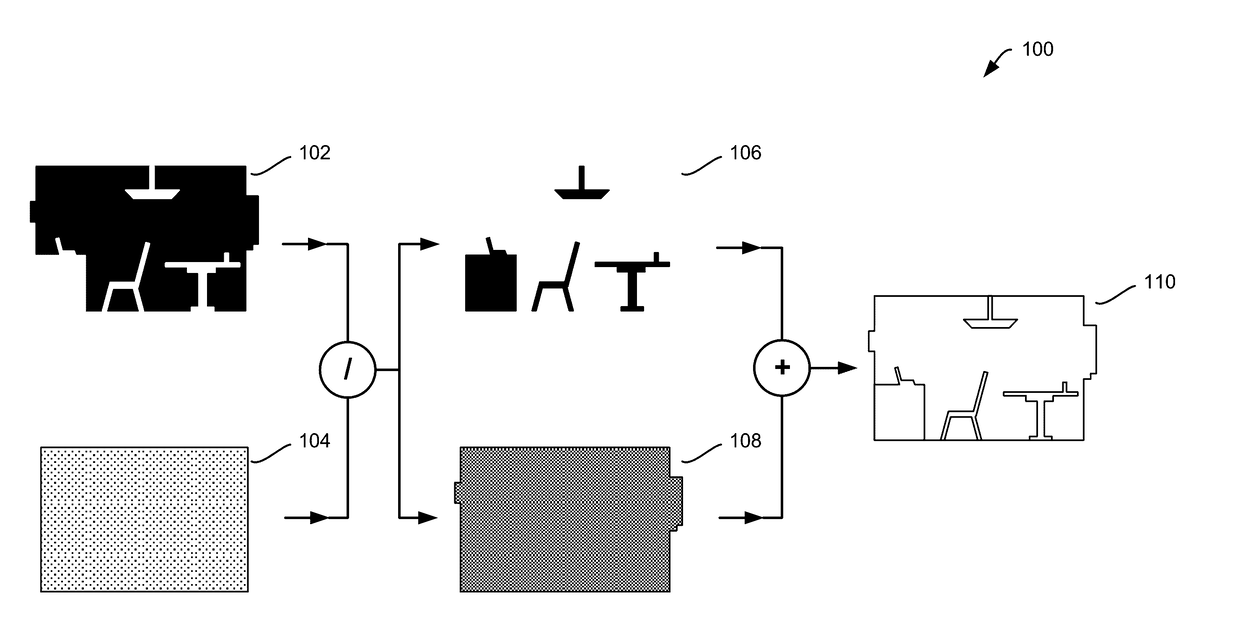
Systems and methods for 2-d to 3-d image conversion using mask to model, or model to mask, conversion
InactiveUS20080225045A1Details involving processing stepsImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Image conversion
The present invention is directed to systems and methods for controlling 2-D to 3-D image conversion. In one embodiment, a mask is generated from an object model of the image. The mask is then used to from a 2-D mesh which is then converted to a 3-D volume mesh. The 3-D volume mesh is then used to produce 3-D image conversion.
Owner:CONVERSION WORKS
Method for constructing vertebral three-dimensional geometry and finite element mixture model
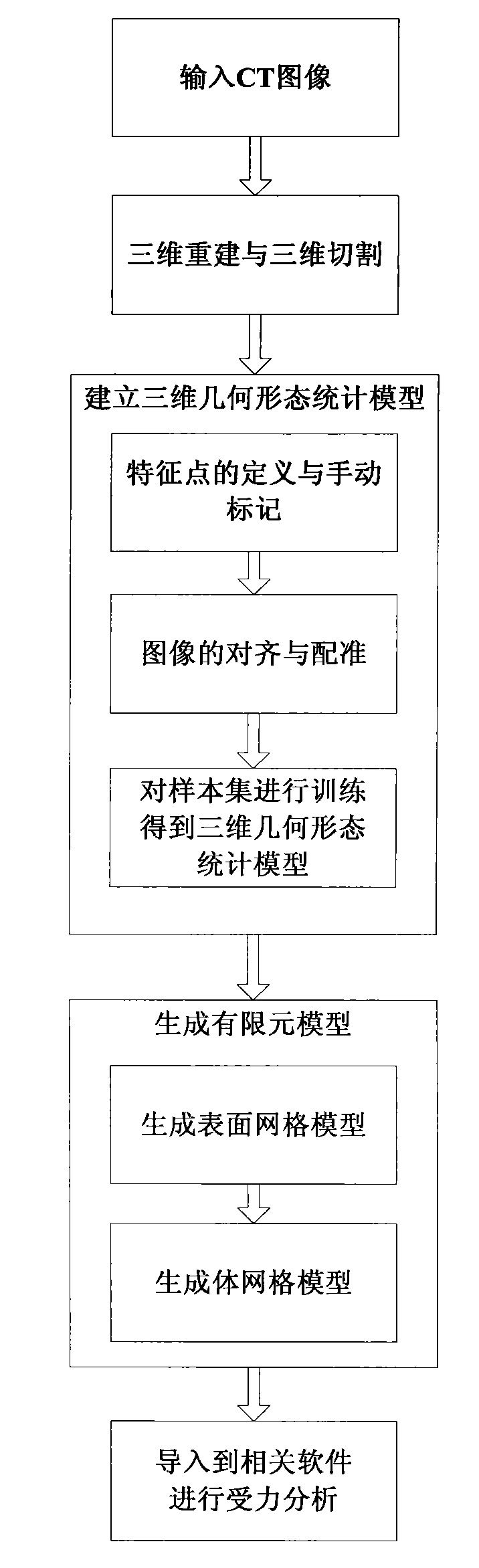
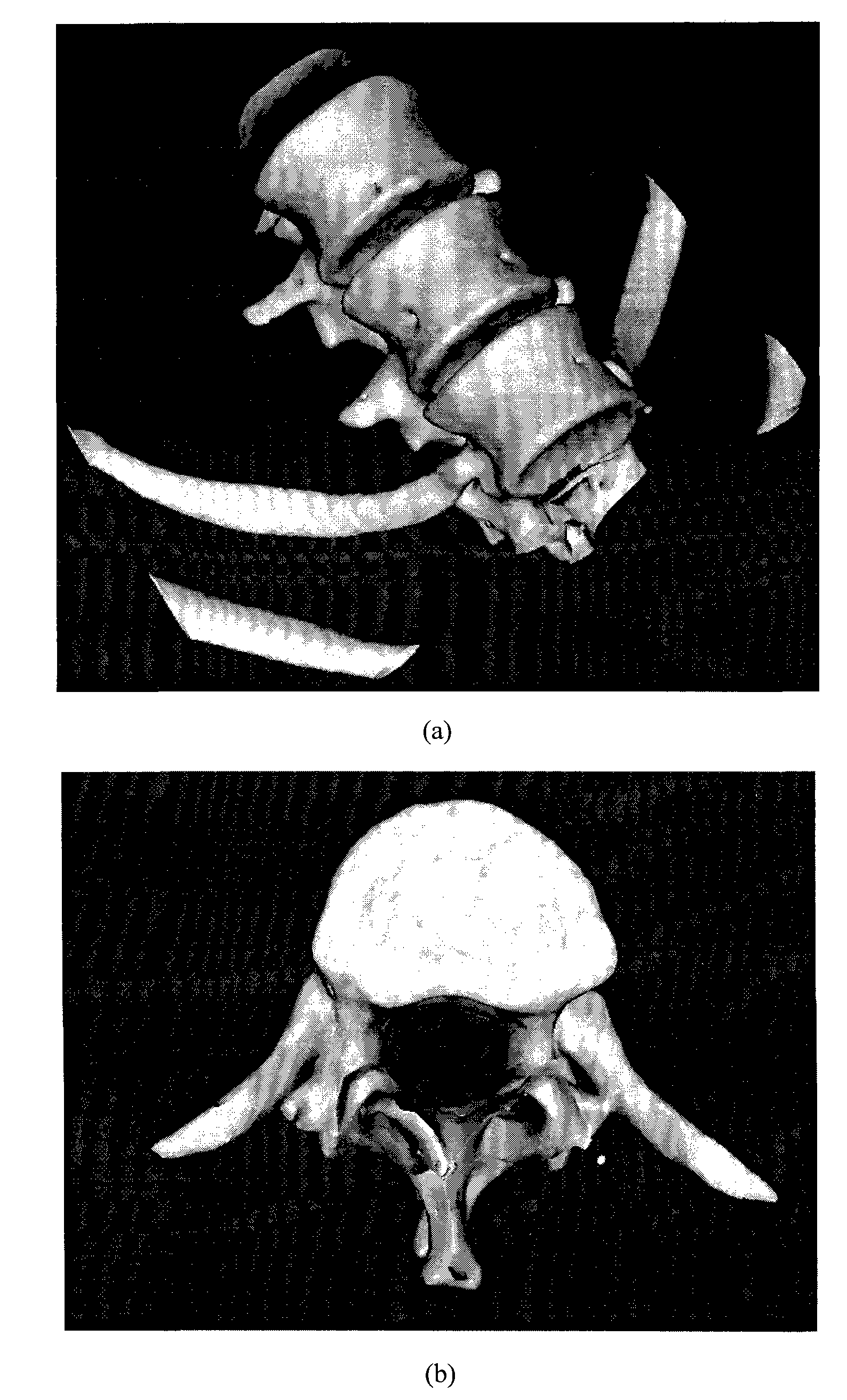
The invention provides a method for constructing a vertebral three-dimensional geometry and finite element mixture model, which belongs to the technical field of processing of medical images. The method comprises the following construction processes of: inputting a vertebral computer tomography (CT) image; performing three-dimensional reconstruction and three-dimensional cutting on the CT image to acquire a vertebral three-dimensional image set; establishing a three-dimensional geometric statistical model, namely defining and manually calibrating vertebral characteristic points, aligning and registering vertebral images, and training a sample set to acquire the statistical model; and generating a finite element model, importing the statistical model, generating a surface mesh model, and generating a volume mesh model, wherein the model can be directly imported into finite element analysis software for biomechanics analysis. By the method, a vertebral geometrical shape can be precisely described, the accuracy of finite element analysis results can be ensured, and the precision of vertebral models can be improved. The method is convenient to use, facilitates the scientific measurement of the shapes and the stress of vertebras and can be used for researches related to vertebral columns and the vertebras in the field of surgical medicine.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-scale finite-volume method for use in subsurface flow simulation
InactiveUS7546229B2Precision therapyComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationScale heterogeneityPorous medium
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC +1
Automatic localization geometry detection
ActiveUS20180058861A1Lower the volumeInstruments for road network navigationImage analysisGeographic sitePoint cloud
Embodiments include apparatus and methods for generating a localization geometry or occupancy grid for a geographic location. Point cloud that describes a vicinity of a pathway is collected by a distance sensor and describing a vicinity of the pathway. The point cloud data is reduced or filtered to a predetermined volume with respect to the roadway. The remaining point cloud data is projected onto a two-dimensional plane including at least one pixel formation. A volumetric grid is defined according to the at least one pixel formation, and a voxel occupancy for each of a voxels forming the volumetric grid is determined. The arrangement of the voxel occupancies or a sequence of data describing the voxel occupancies is a localization geometry that describes the geographic location of the pathway.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
Automatic geometrical and mechanical analyzing method and system for tubular structures
InactiveUS20100290679A1Effective applicationQuality improvementDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementVascular bodyData set
A method and system for analyzing tubular structures, such as vascular bodies, with respect to their geometrical properties and mechanical loading conditions is disclosed. To this end, geometrical and structural models of vascular bodies are generated from standard sets of image data. The method or system works automatically and the tubular structure is analyzed within clinical relevant times by users without engineering background. Most critical in that sense is the integration of novel volume meshing and 3D segmentation techniques. The derived geometrical and structural models distinguish between structural relevant types of tissue, e.g., for abdominal aortic aneurysms the vessel wall and the intra-luminal thrombus are considered separately. The structural investigation of the vascular body is based on a detailed nonlinear Finite Element analysis. Here, the derived geometrical model, in-vivo boundary / loading conditions and finite deformation constitutive descriptions of the vascular tissues render the structural biomechanical problem. Different visualization concepts are provided and allow an efficient and detailed investigation of the derived geometrical and mechanical data. In addition, this information is pooled and statistical properties, derived from it, can be used to analyze vascular bodies of interest.
Owner:VASCOPS
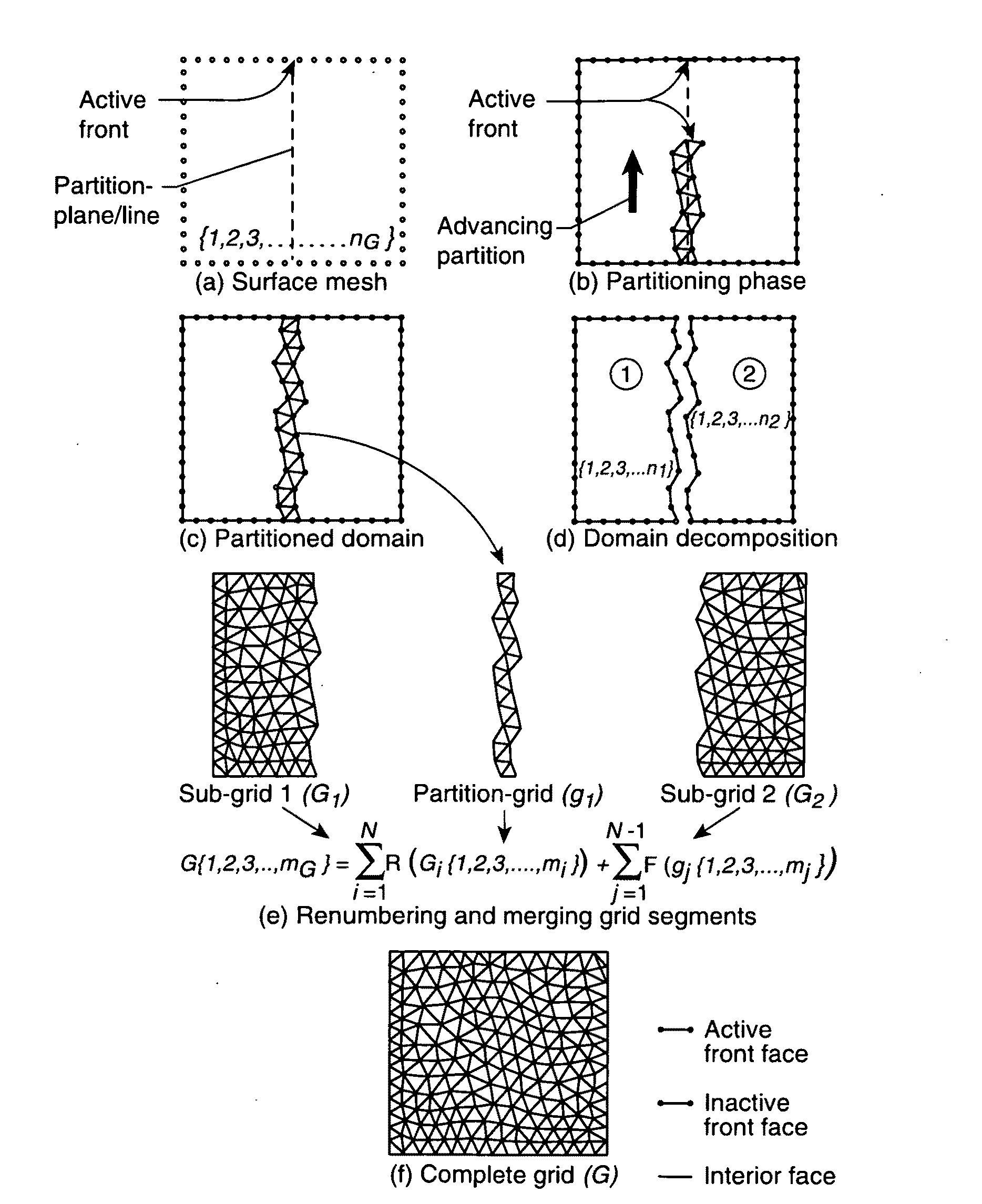
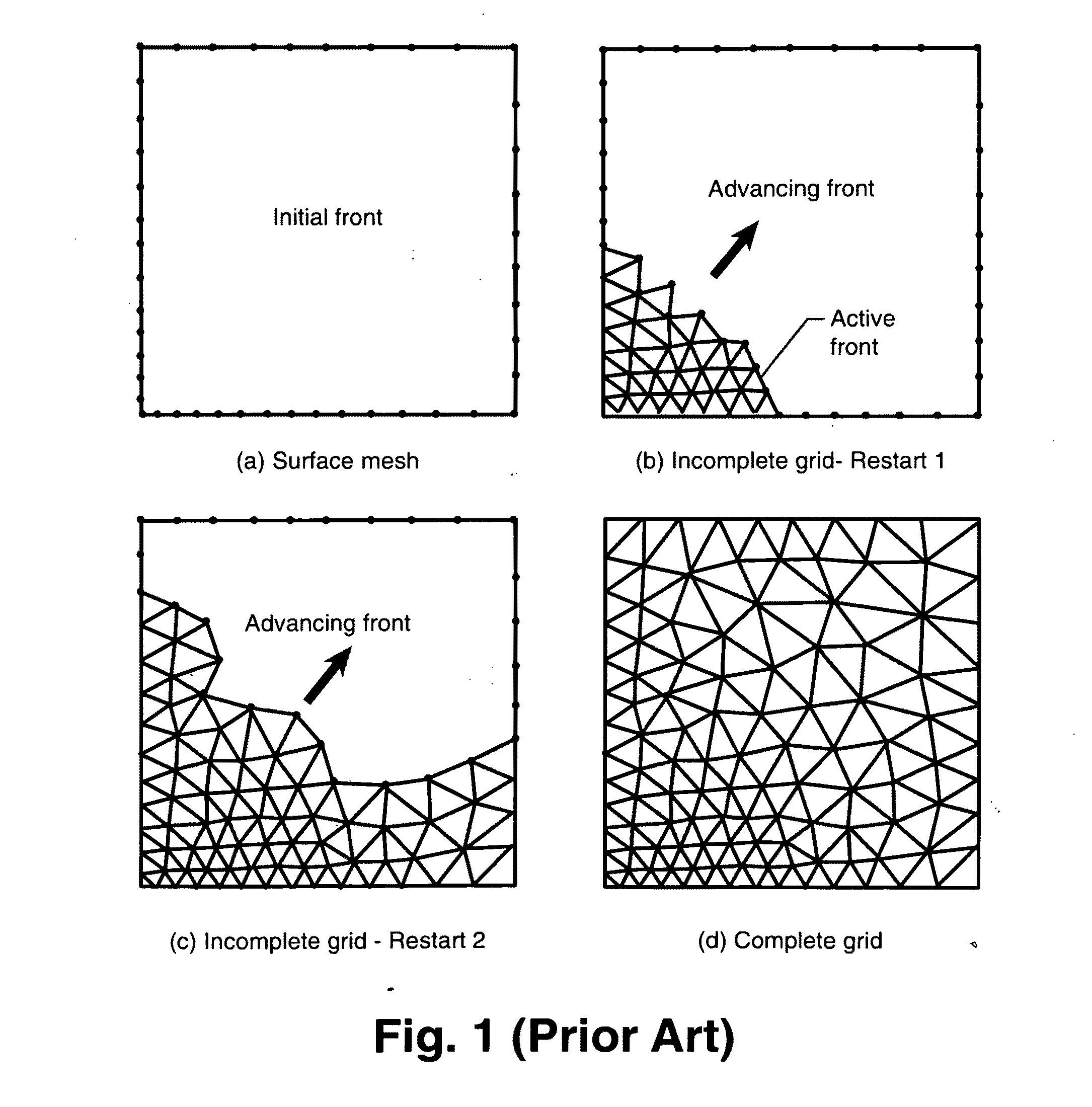
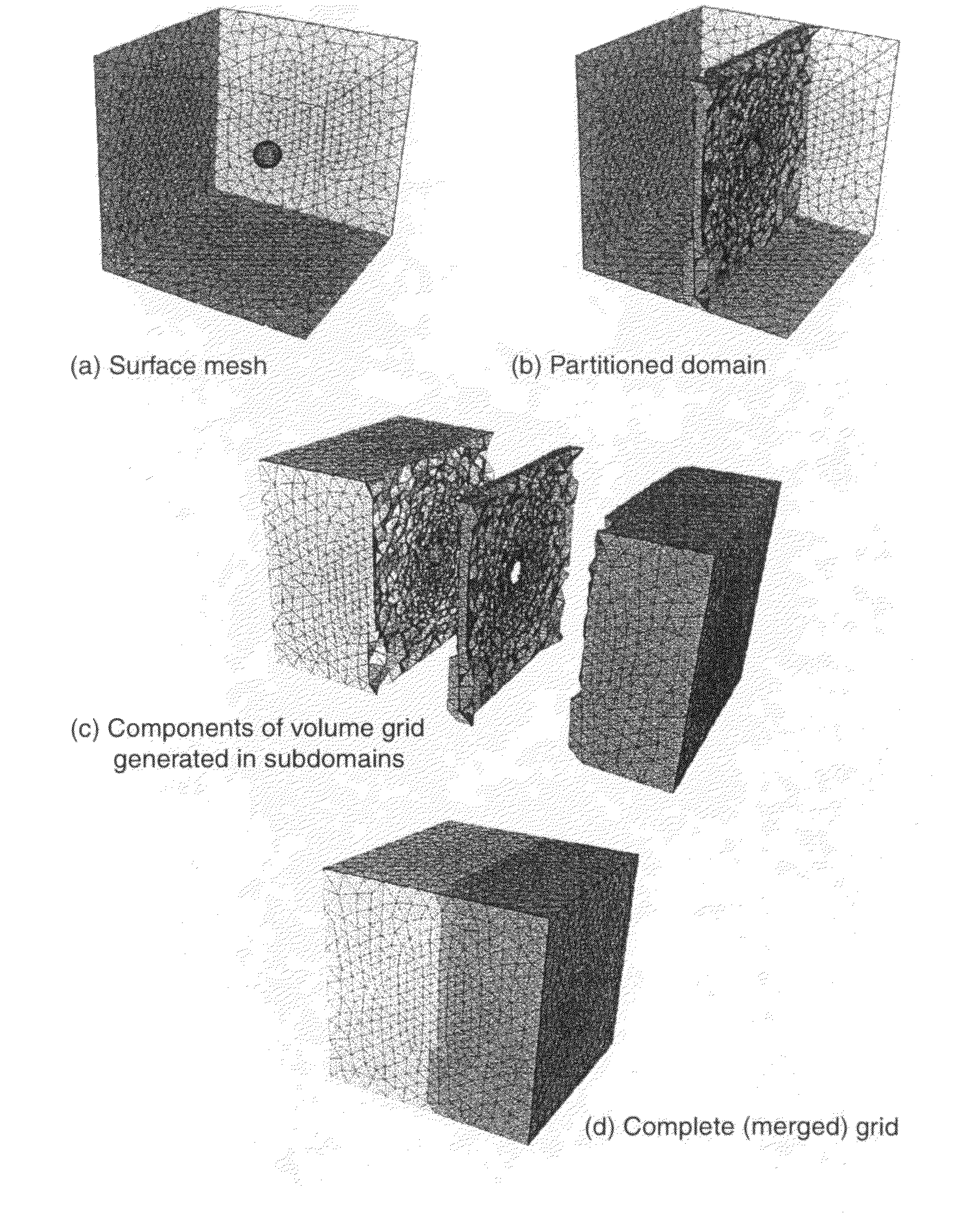
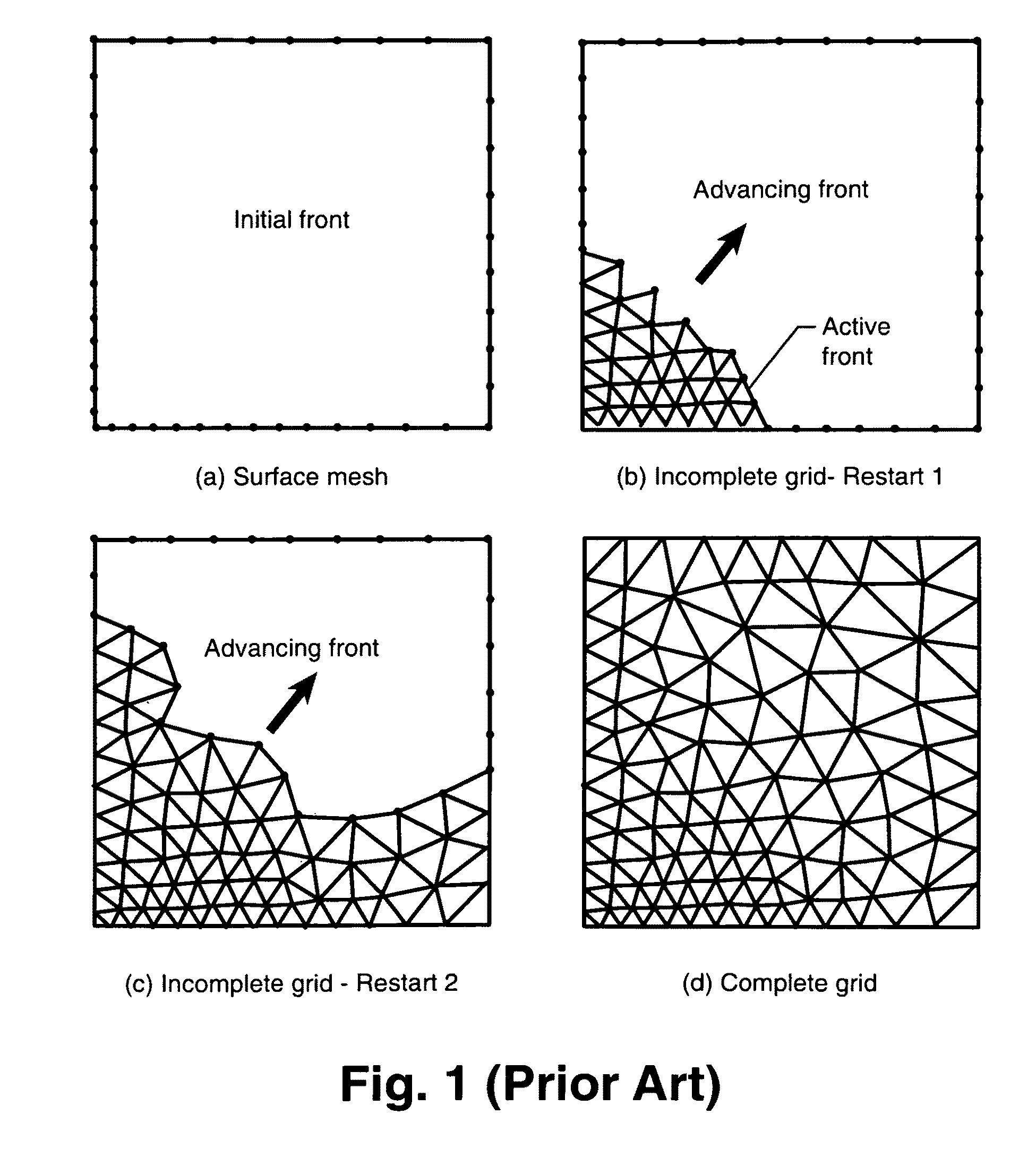
Domain Decomposition By the Advancing-Partition Method for Parallel Unstructured Grid Generation
InactiveUS20100134498A1Drawing from basic elements3D-image renderingDecompositionDomain decomposition methods
In a method for domain decomposition for generating unstructured grids, a surface mesh is generated for a spatial domain. A location of a partition plane dividing the domain into two sections is determined. Triangular faces on the surface mesh that intersect the partition plane are identified. A partition grid of tetrahedral cells, dividing the domain into two sub-domains, is generated using a marching process in which a front comprises only faces of new cells which intersect the partition plane. The partition grid is generated until no active faces remain on the front. Triangular faces on each side of the partition plane are collected into two separate subsets. Each subset of triangular faces is renumbered locally and a local / global mapping is created for each sub-domain. A volume grid is generated for each sub-domain. The partition grid and volume grids are then merged using the local-global mapping.
Owner:NASA
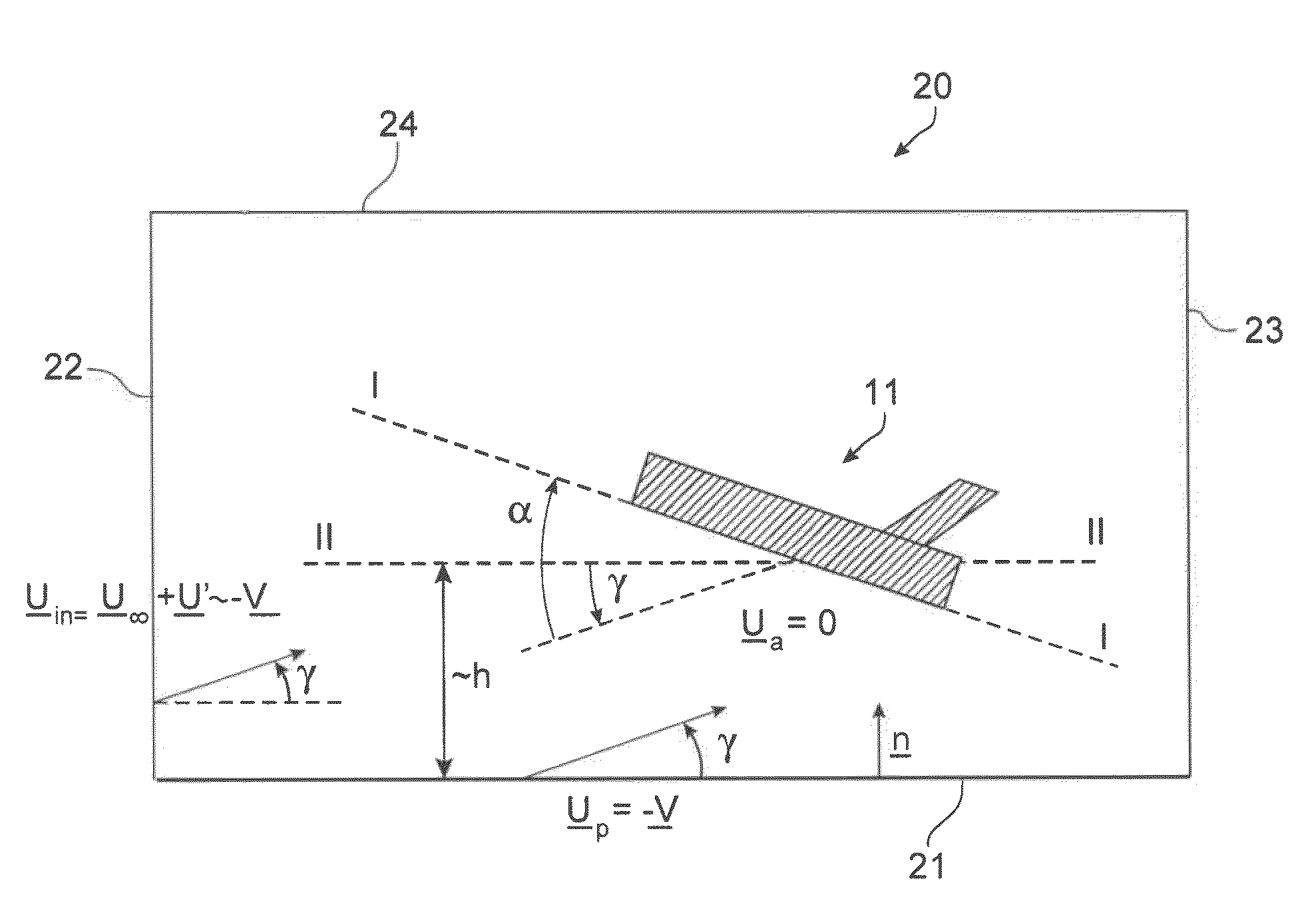
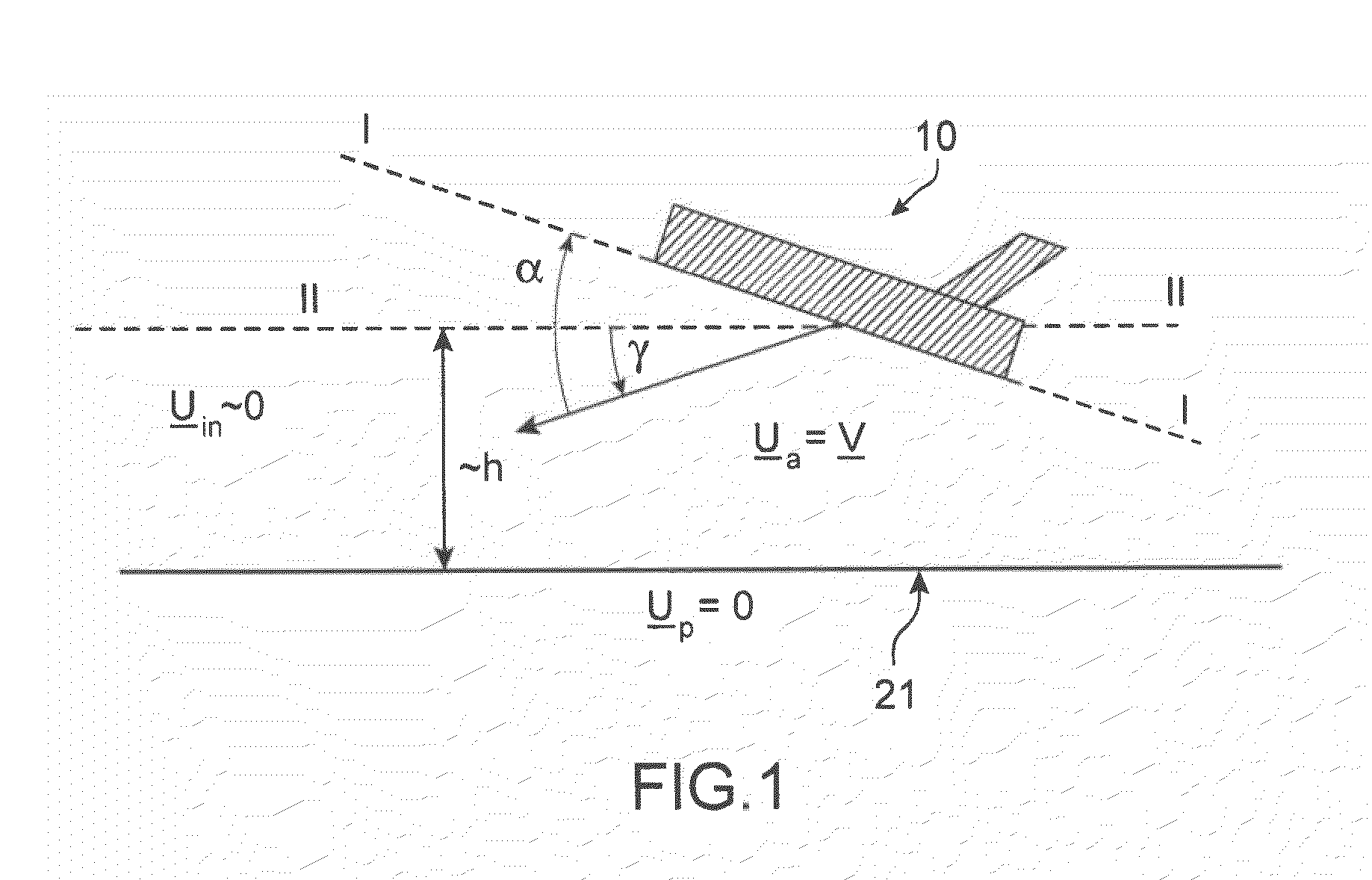
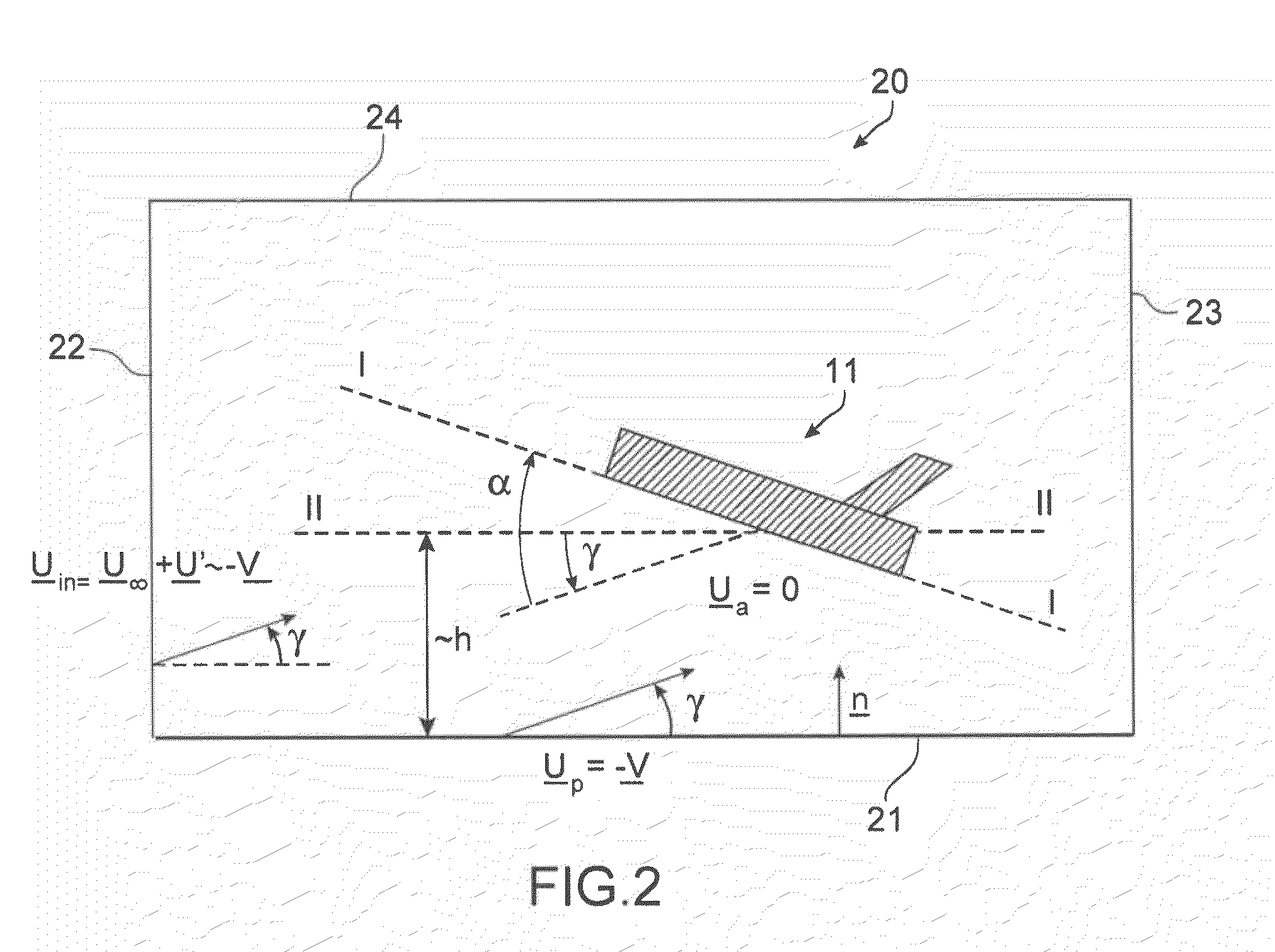
Method and tool for simulation of the aerodynamic behaviour of an aircraft in flight close to the ground
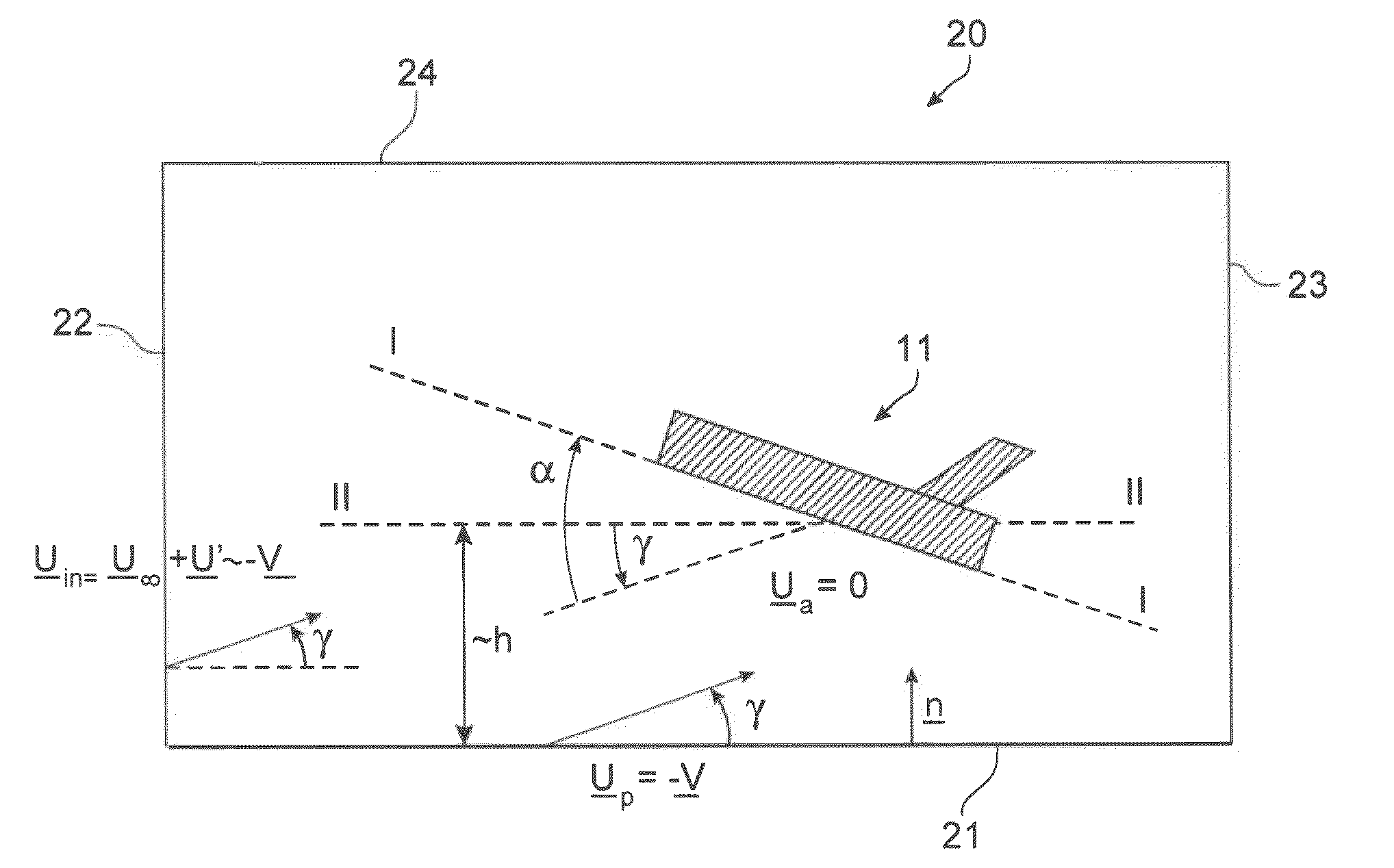
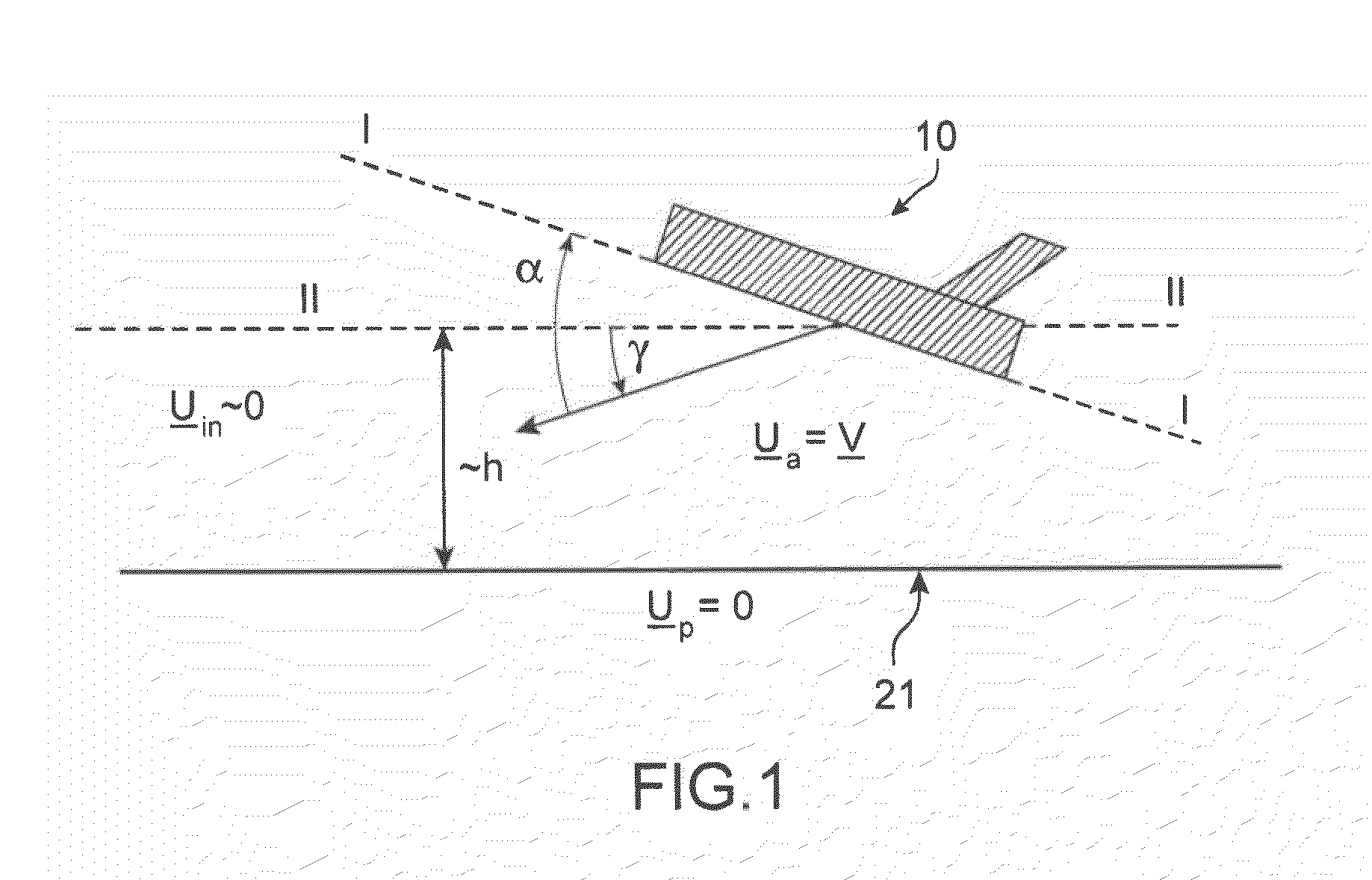
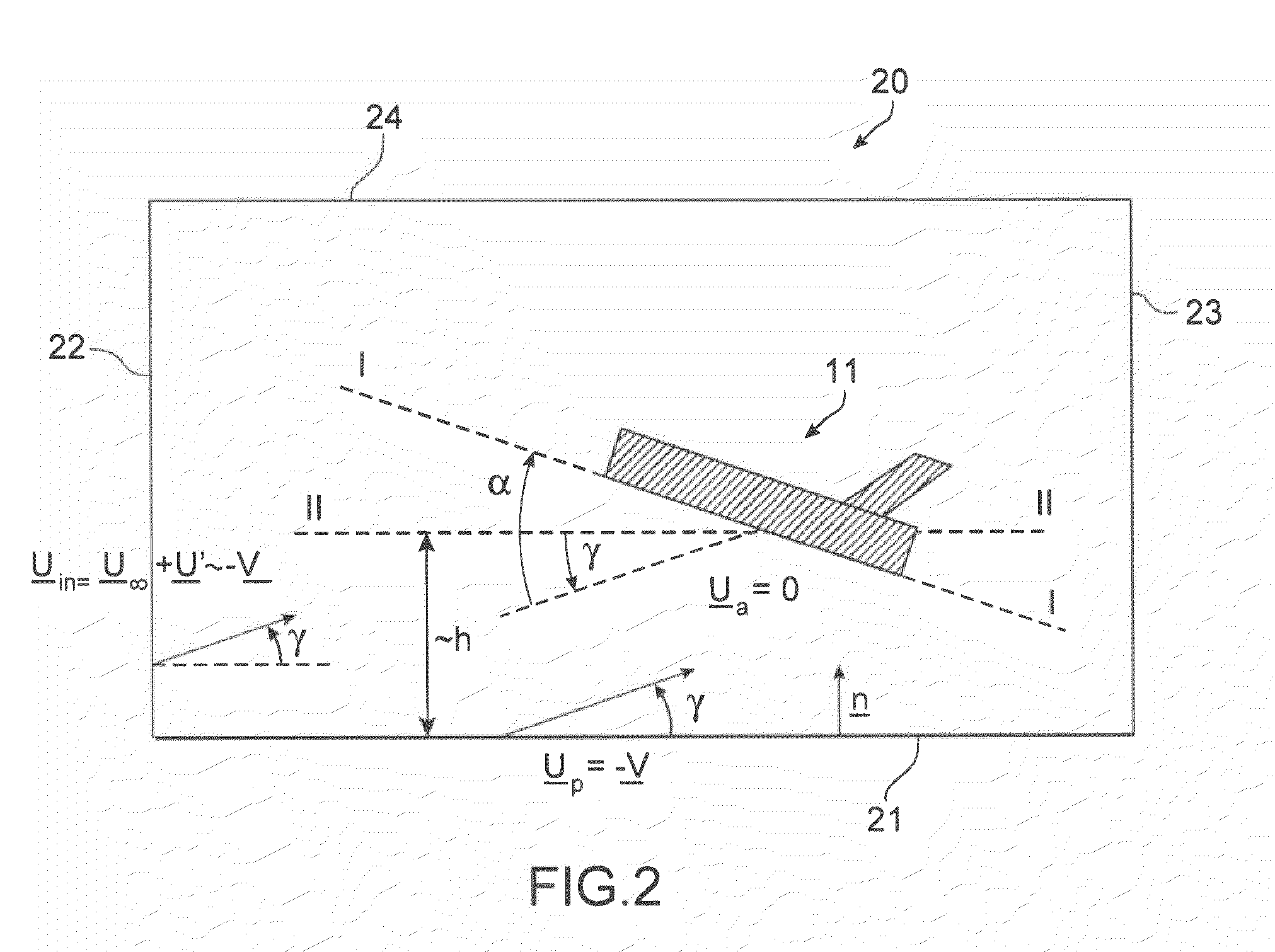
The invention relates to a method of computer simulation of the aerodynamic behaviour of an aircraft (10) in flight close to the ground. This method is used to identify the slope effect relative to the ground effect.To achieve this, a uniform boundary condition comprising a predetermined speed (UP) with a non-zero tangential component and a non-zero normal component is imposed on a plane (21) modelling the ground; and a discrete numerical model of the Navier-Stokes equations is solved by computer on a volume mesh with said boundary condition imposed on said plane (21), so as to obtain a numerical solution for a fluid flow inside a computational domain defined by said mesh.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
System and method of virtual flowbench simulation
InactiveUS6941249B1Eliminates and reduces disadvantageSimulator controlDesign optimisation/simulationComputational scienceStable state
A computerized method of virtual flowbench simulation of fluid flow interaction with an object described in at least one design file includes receiving user-defined input via a user interface, the user-defined input including a specification of the at least one design file, accessing the at least one design file, and accessing a generic template describing basic geometries of the object, and modifying the basic geometries of the object with the at least one design file. Automatically, surface and volume mesh are generated in the object, and fluid flow interaction with the object is simulated. Predetermined data parameters are measured and stored during simulation. The method automatically checks the predetermined data parameter measurements to determine whether steady state has been reached and whether a predetermined maximum number of time steps has been reached. The method then automatically terminates the simulation in response to the steady state being reached or the predetermined maximum number of time steps being reached. An output of predetermined data parameter measurements is then generated.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
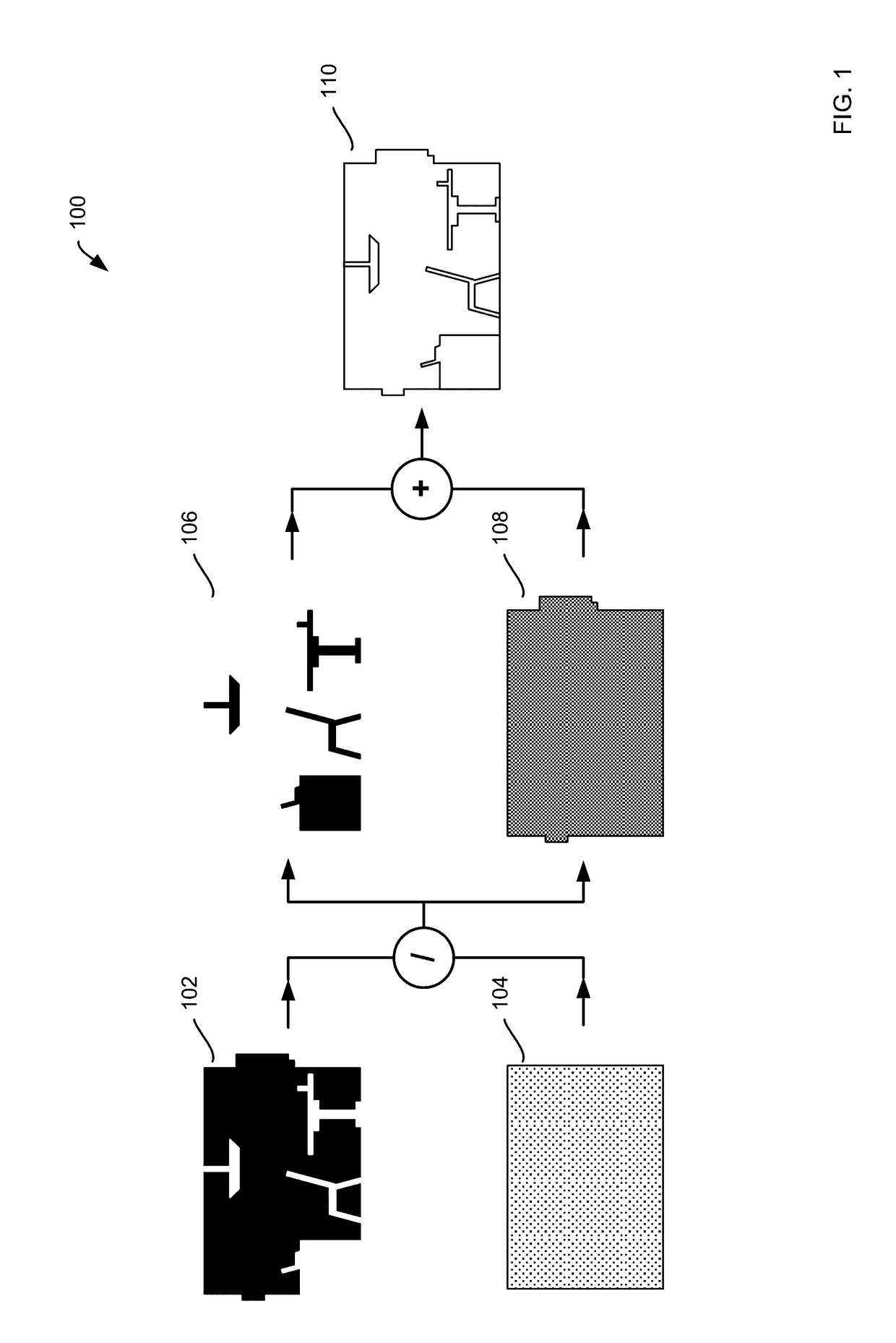
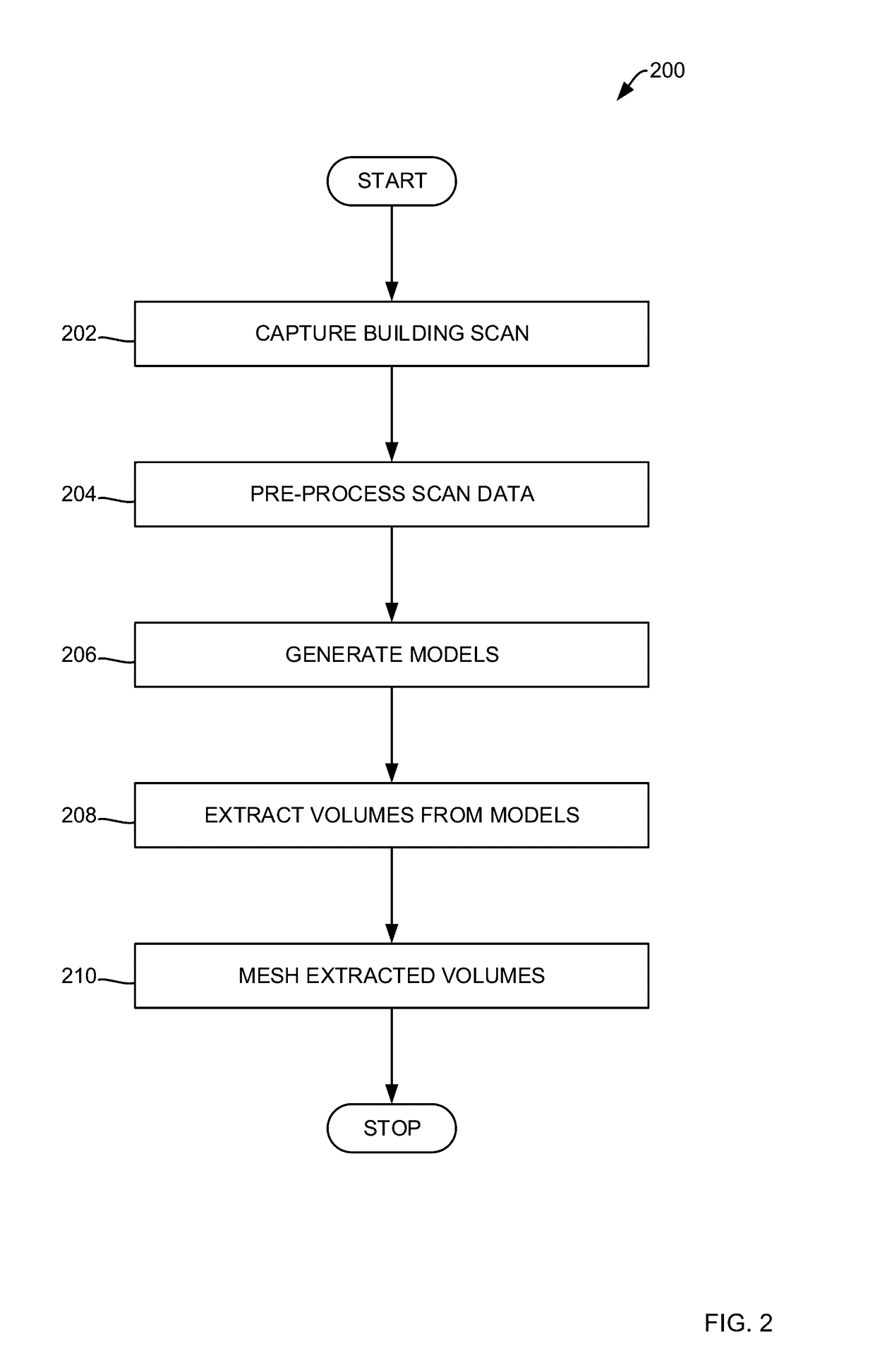
Methods for indoor 3D surface reconstruction and 2d floor plan recovery utilizing segmentation of building and object elements
ActiveUS20170148211A1Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionFloor plan3d surfaces
Methods for indoor 3D surface reconstruction and 2D floor plan recovery by segmenting a number of objects and building structure elements from a building scan using an electronic computing device are presented, the methods including: causing the electronic computing device to capture the building scan, where the building scan includes a number of scan points; pre-processing scan data from the building scan; generating an octree and a 2.5D model from the pre-processed scan data; extracting interior and exterior volumes from the octree model and the 2.5D model; and meshing the extracted volumes to generate a 3D object geometry and a 3D building geometry, where the 3D object geometry corresponds with the number of objects and the 3D building geometry corresponds with the indoor 3D surface reconstruction of building structure elements.
Owner:HILTI AG
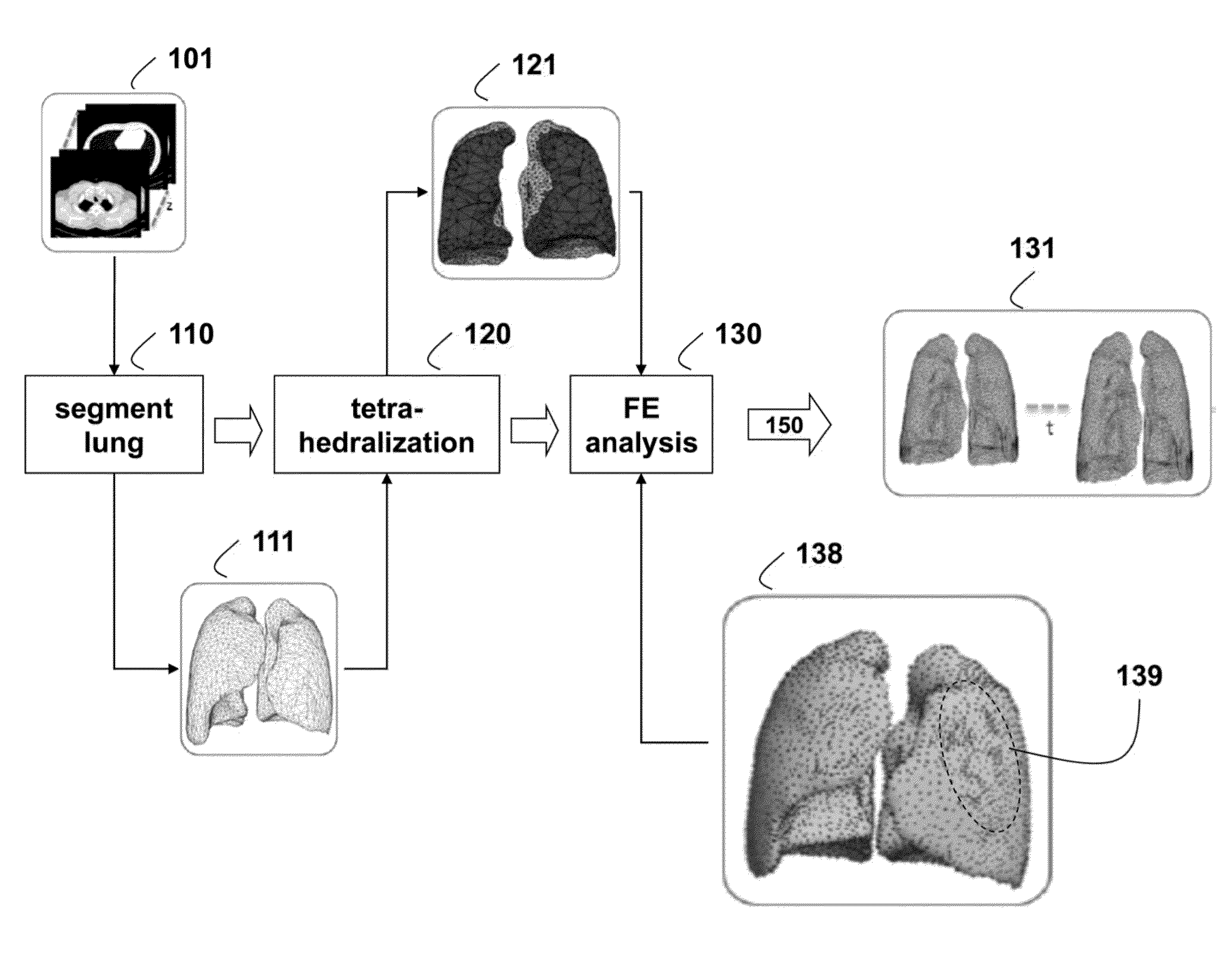
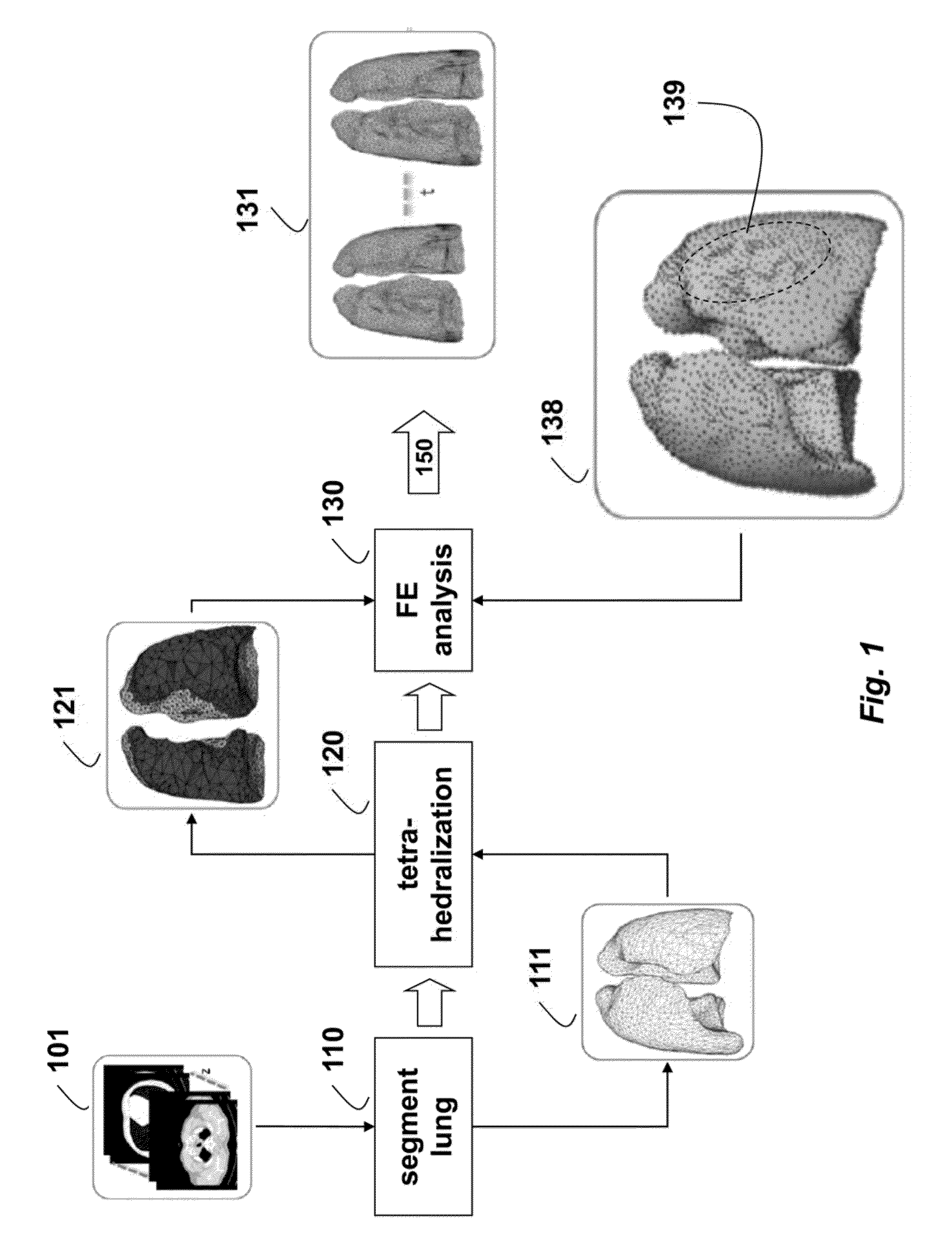
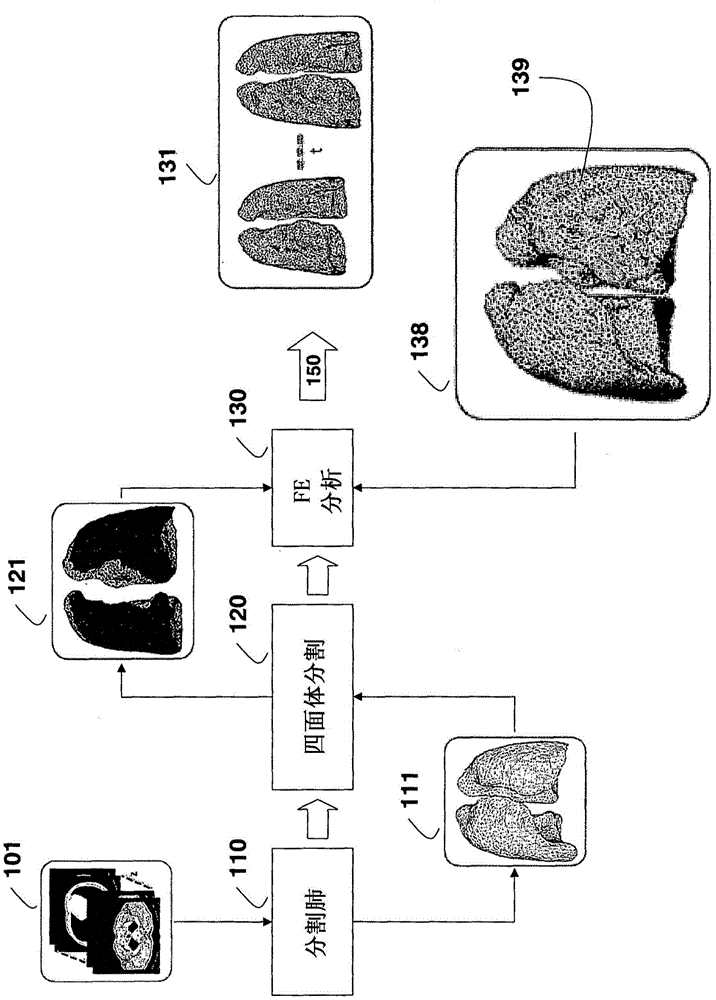
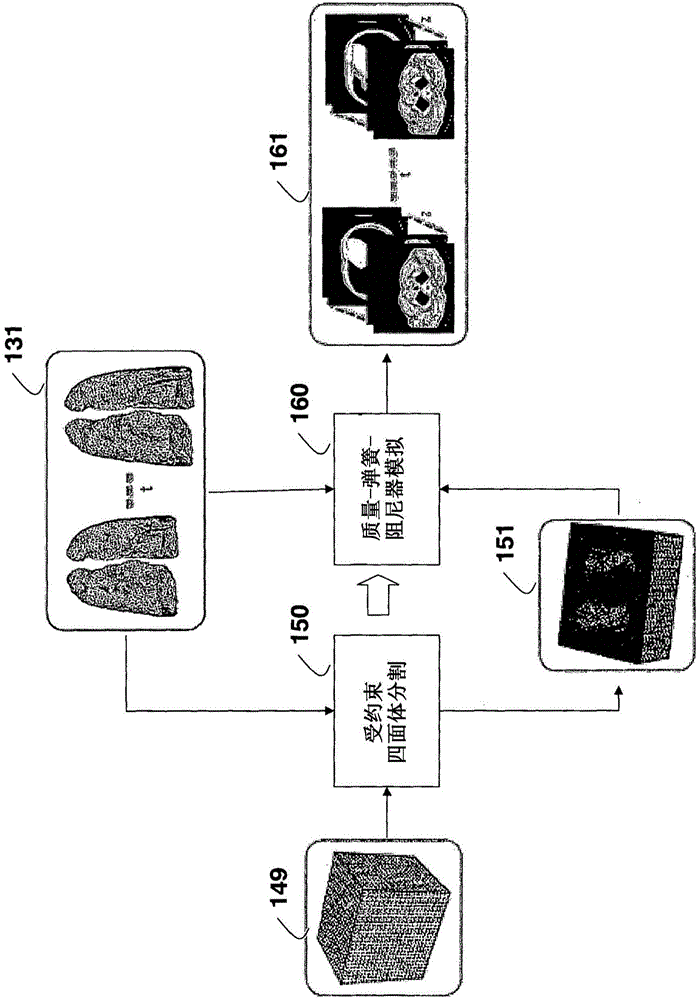
Method for Simulating Thoracic 4DCT
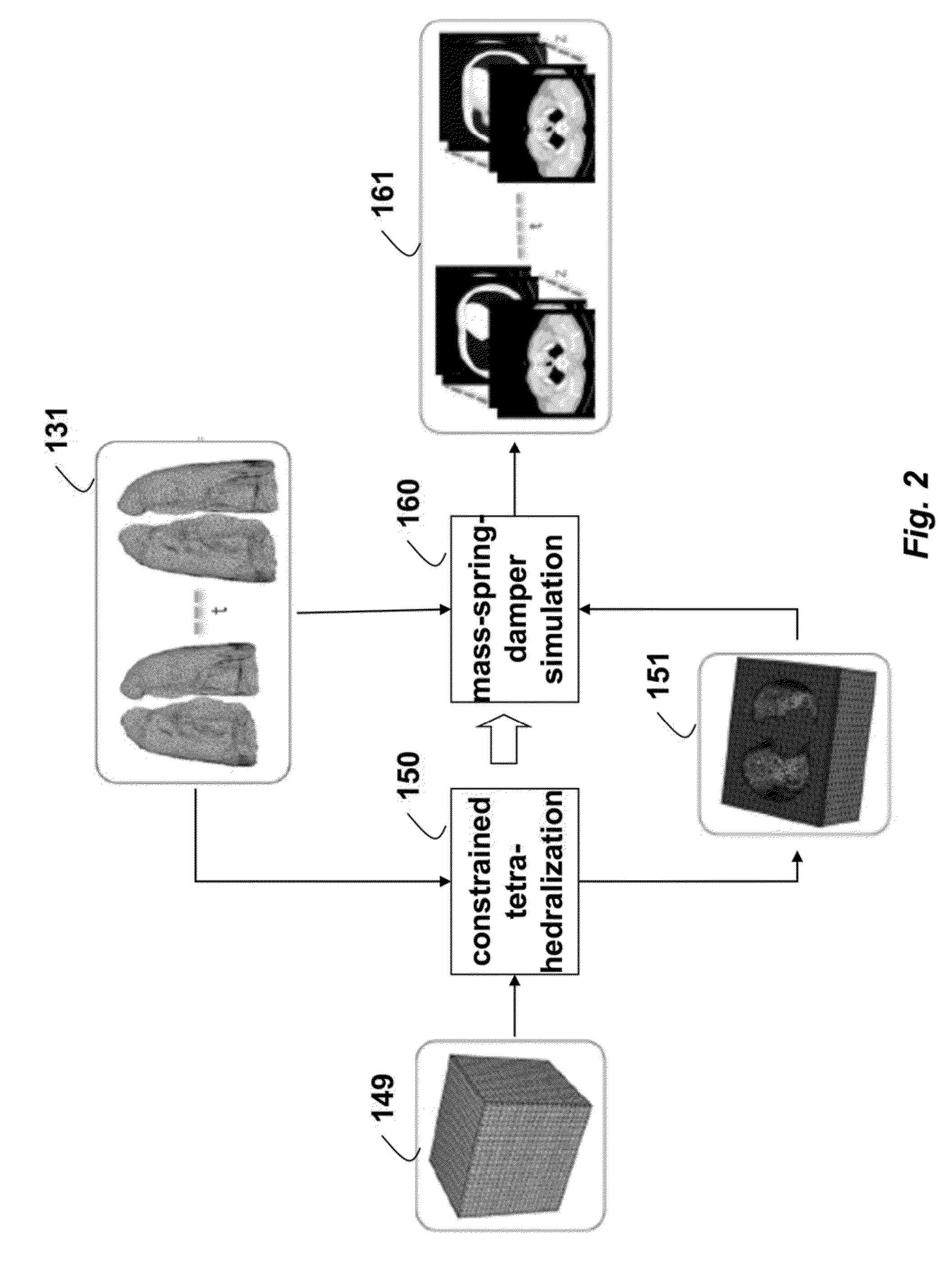
InactiveUS20140226884A1Deformations of other organs can also be simulatedConstraining deformationMedical simulationDetails involving processing stepsMass spring damperElement analysis
Four-dimensional (4D) computed tomography (CT) is simulated by first generating a surface mesh from a single thoracic CT scan. Tetrahedralization is applied to the surface mesh to obtain a first volume mesh. Finite element analysis, using boundary constraints and load definitions, is applied to the first volume mesh to obtain a lung deformation according to an Ogden model. Constrained tetrahedralization, using control points, is applied to the lung deformation to obtain a second volume mesh, which is then deformed using mass-spring-damper simulation to produces the 4DCT.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
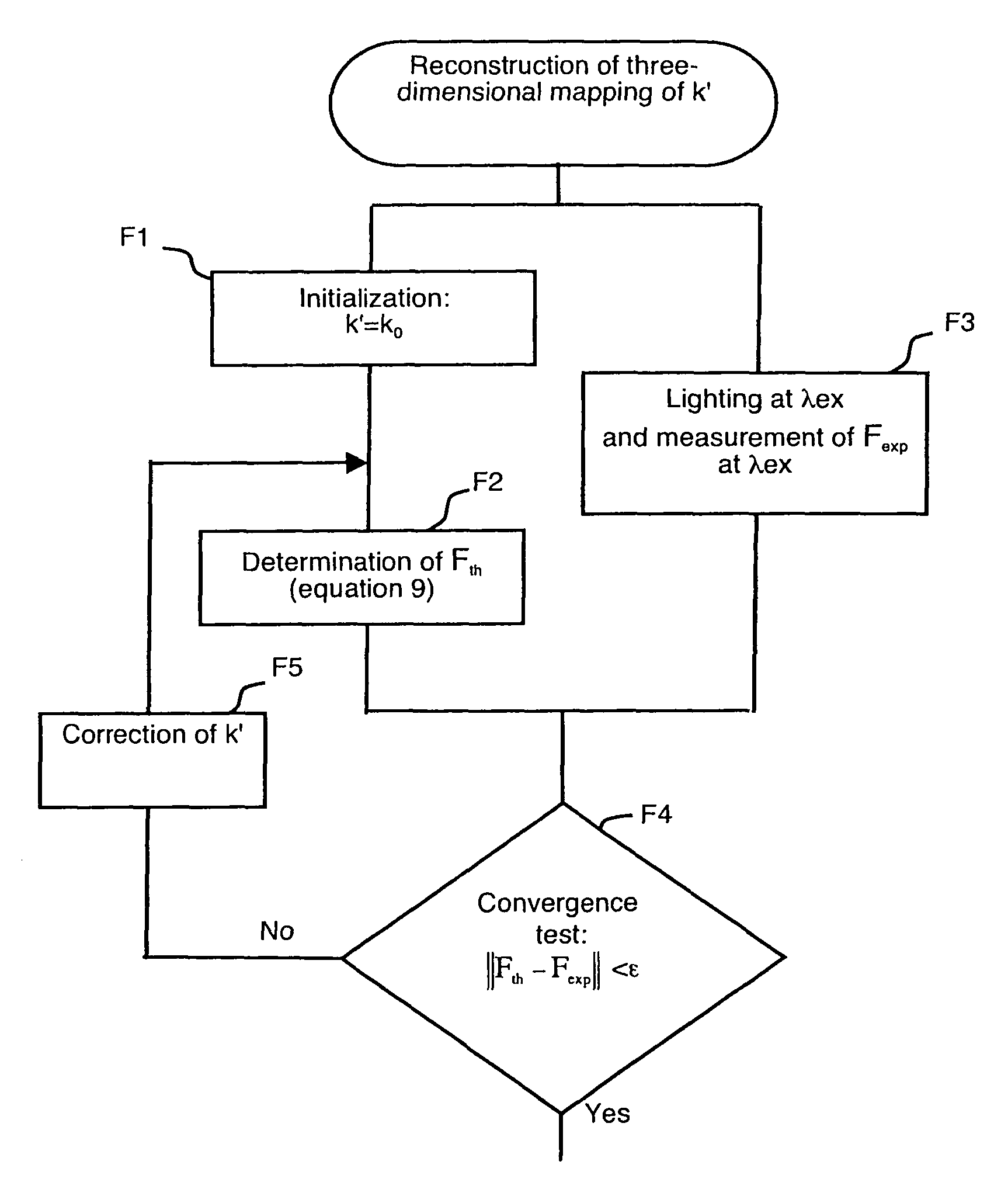
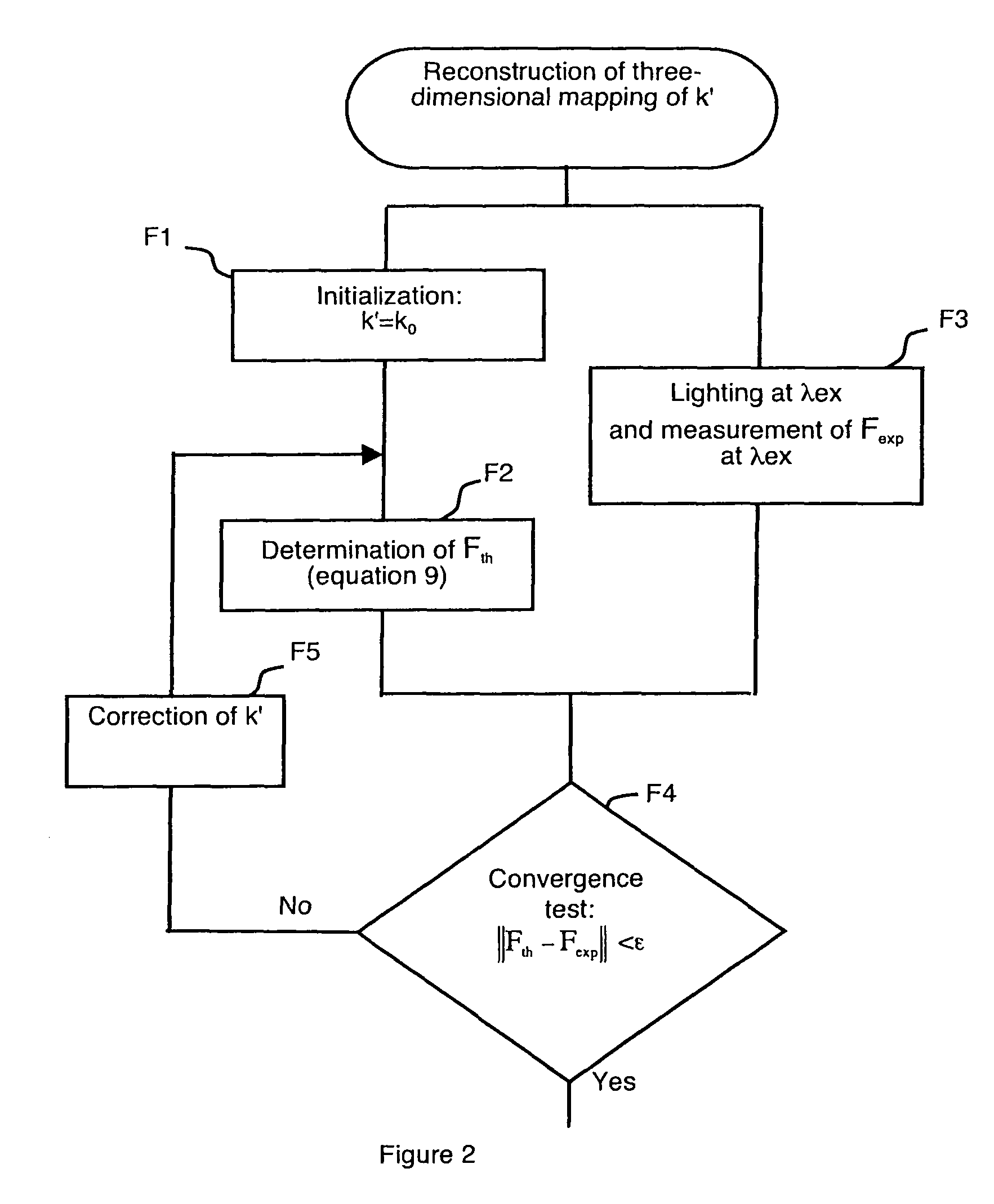
Method for reconstructing the distribution of fluorophores in a non-homogeneous medium by optical tomography in continuous mode
ActiveUS7965389B2Reconstruction from projectionRadiation pyrometryContinuous lightUltrasound attenuation
The method enables a non-homogeneous diffusing object to be examined by illuminating the object with a continuous light by means of a light source. It previously comprises reconstruction of the three-dimensional spatial mapping of an attenuation variable representative of the diffusion and absorption non-homogeneities of the object, by resolving a diffusion equation∇2F({right arrow over (r)}S, {right arrow over (r)})−k′2({right arrow over (r)})F({right arrow over (r)}S, {right arrow over (r)})=ASδ({right arrow over (r)}−{right arrow over (r)}S).In the diffusion equation, AS is a constant, {right arrow over (r)} the spatial coordinate of any point of the mesh of a volume at least partially containing the object, and {right arrow over (r)}S the spatial coordinate of the light source. The transfer functions of an equation used for reconstructing the distribution of fluorophores integrate the attenuation variable reconstituted in this way.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
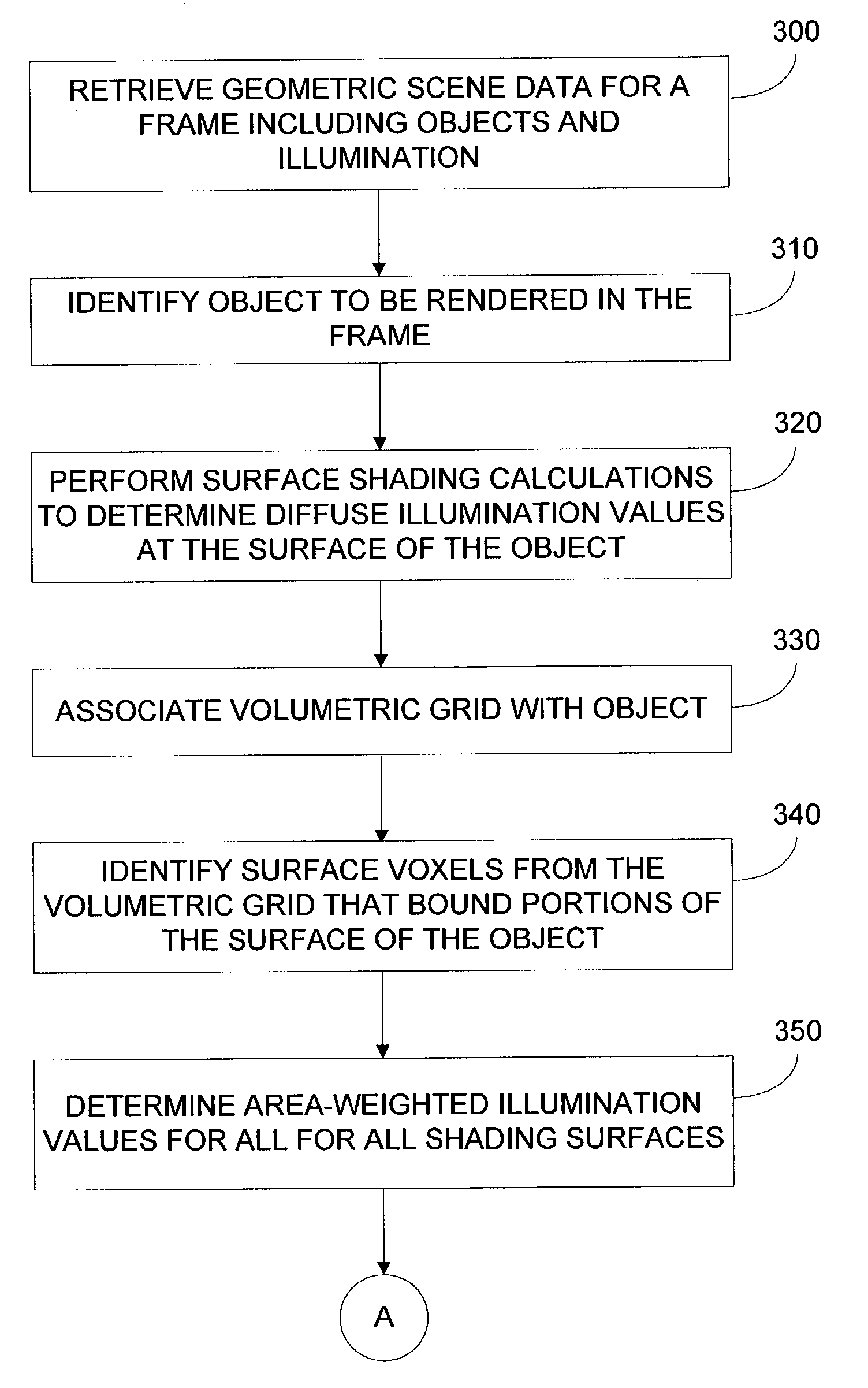
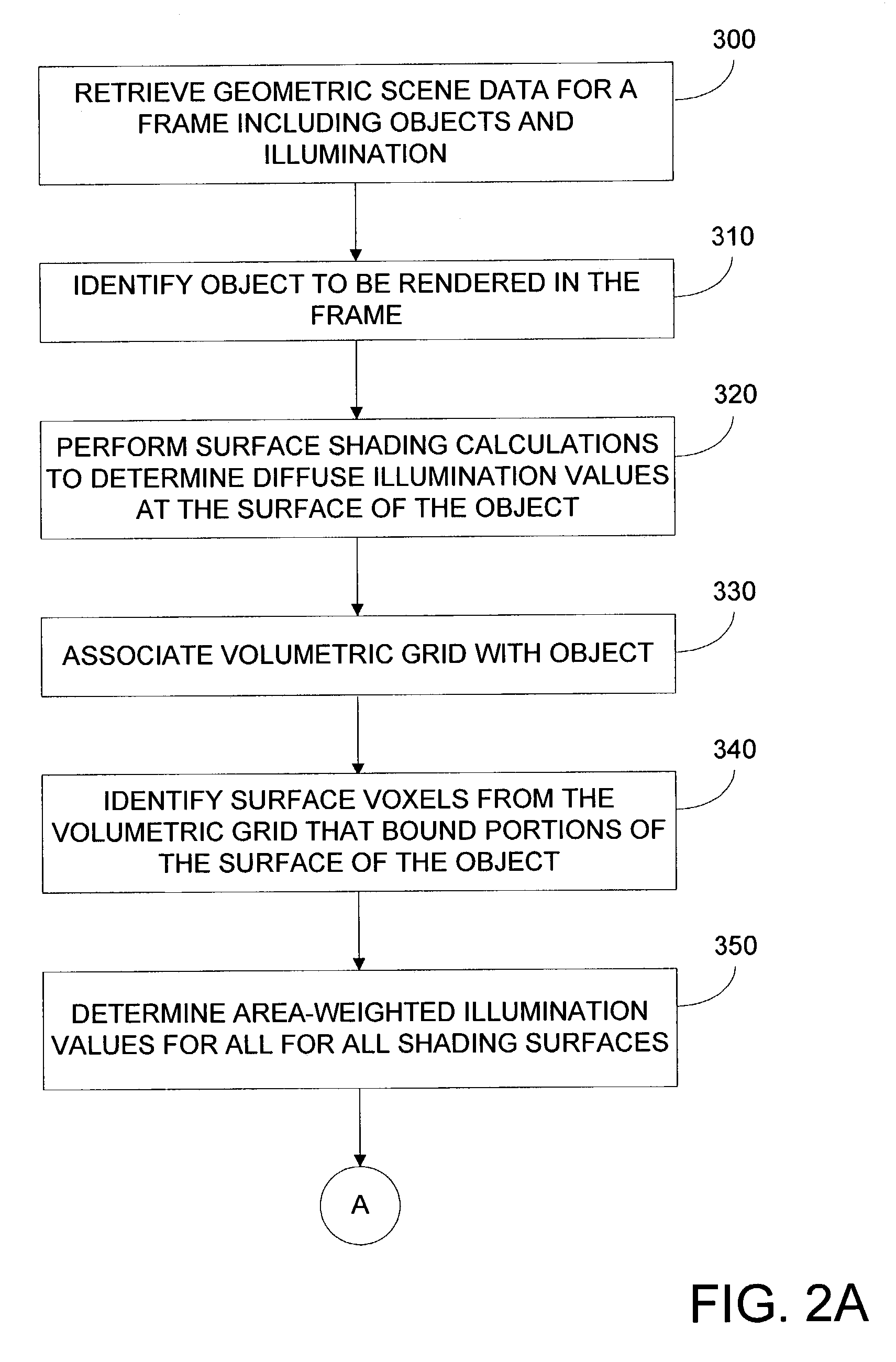
Method and apparatus for rendering of translucent objects using volumetric grids
ActiveUS7019744B2Smoothness across multiple geometry elementQuickly solve transport3D-image rendering3D modellingVoxelLow-pass filter
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
Multi-scale finite-volume method for use in subsurface flow simulation
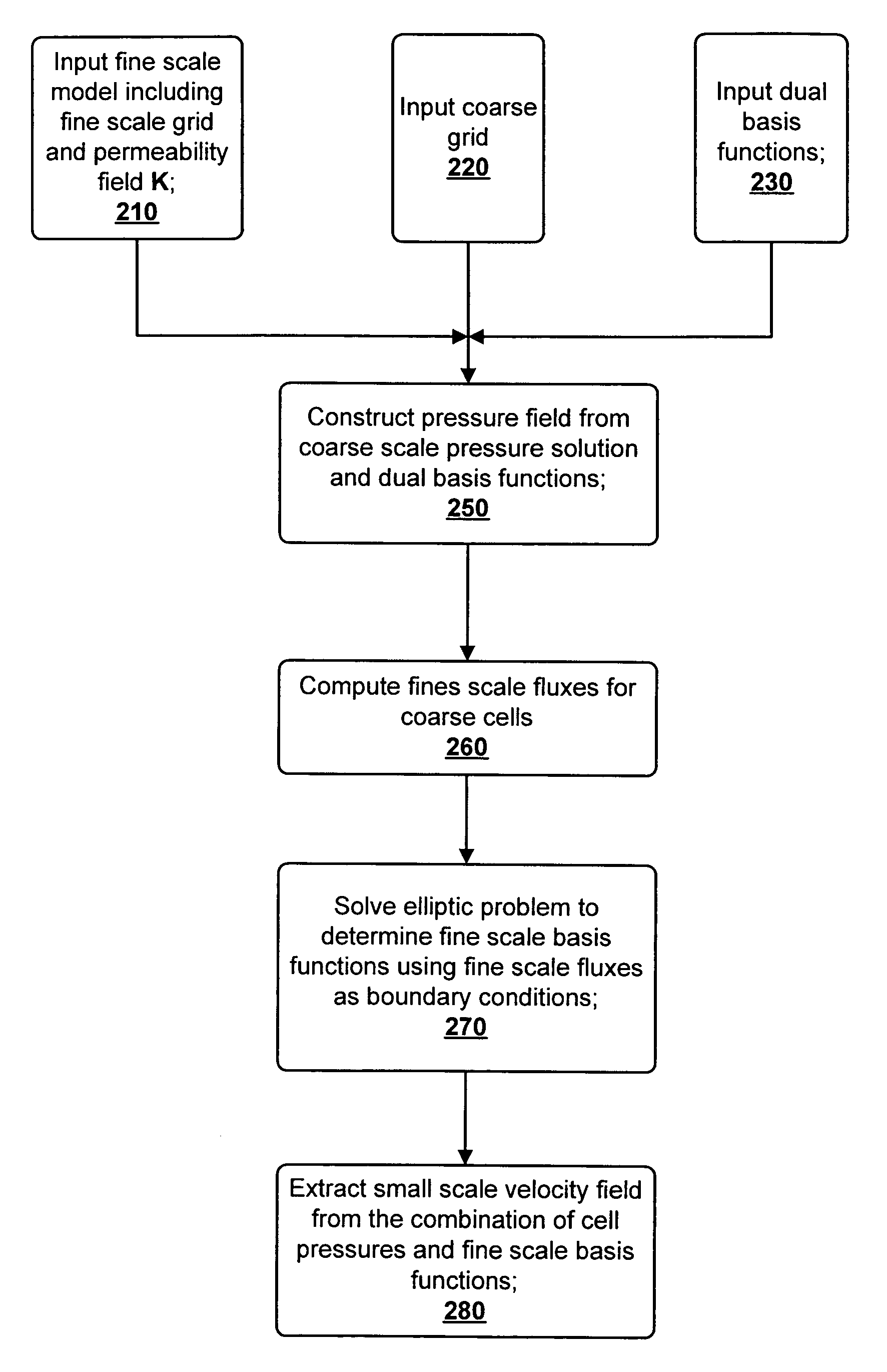
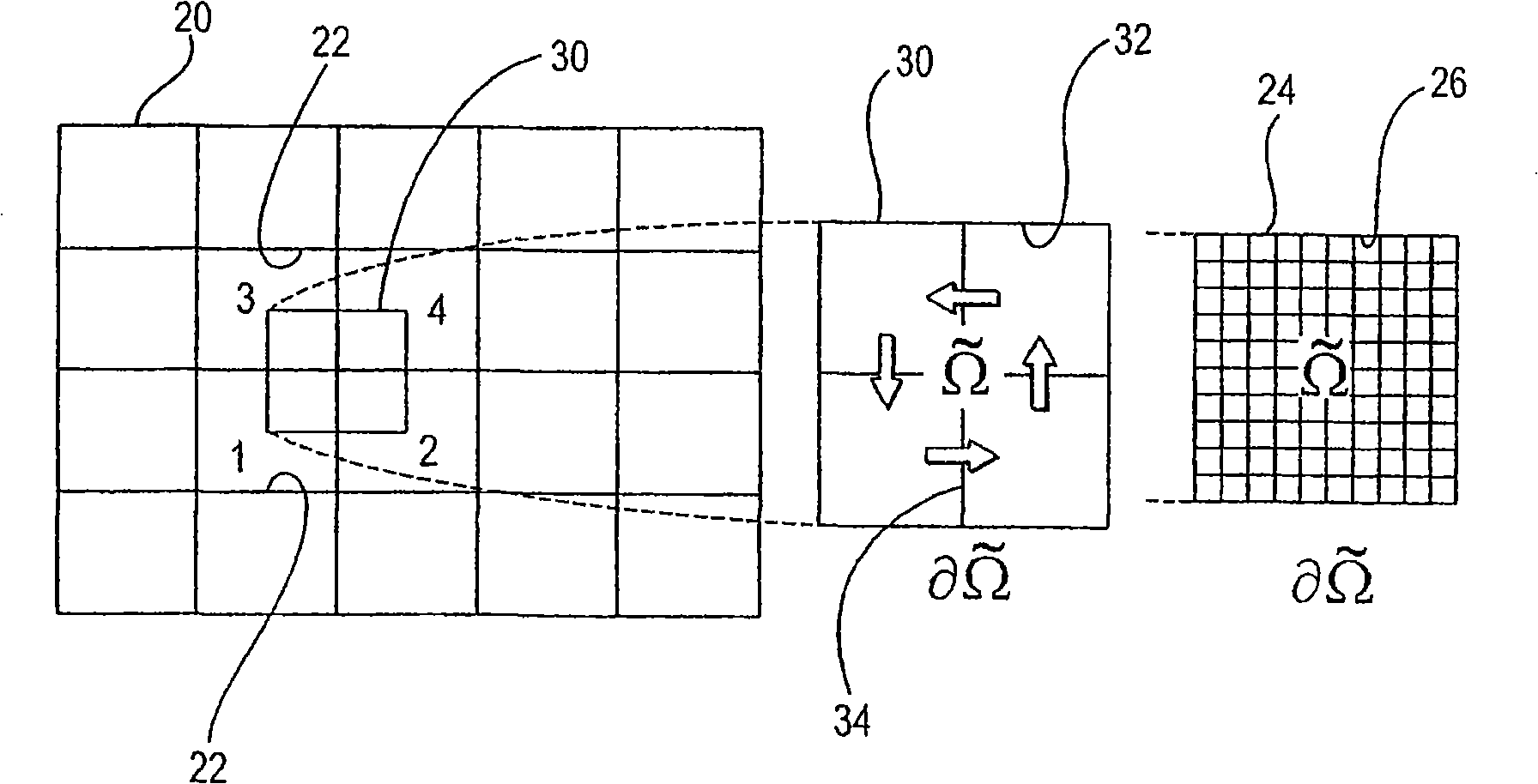
The invention discloses a multi-scale finite-volume (MSFV) method to solve elliptic problems with a plurality of spatial scales arising from single or multi-phase flows in porous media. The method uses an orthogonal 2D grid (20) of a coarse grid unit (22). The bottom layer of fine grid (24) of a fine grid unit (26) comprises fine scale seepage rate information. The method efficiently captures the effects of small scales on the coarse grid, is conservative, and treats tensor seepage rate correctly. The underlying idea is to construct transmission rate that captures the local properties of a differential operator. The method leads to a multi-point discretization scheme for a finite-volume solution algorithm.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC +2
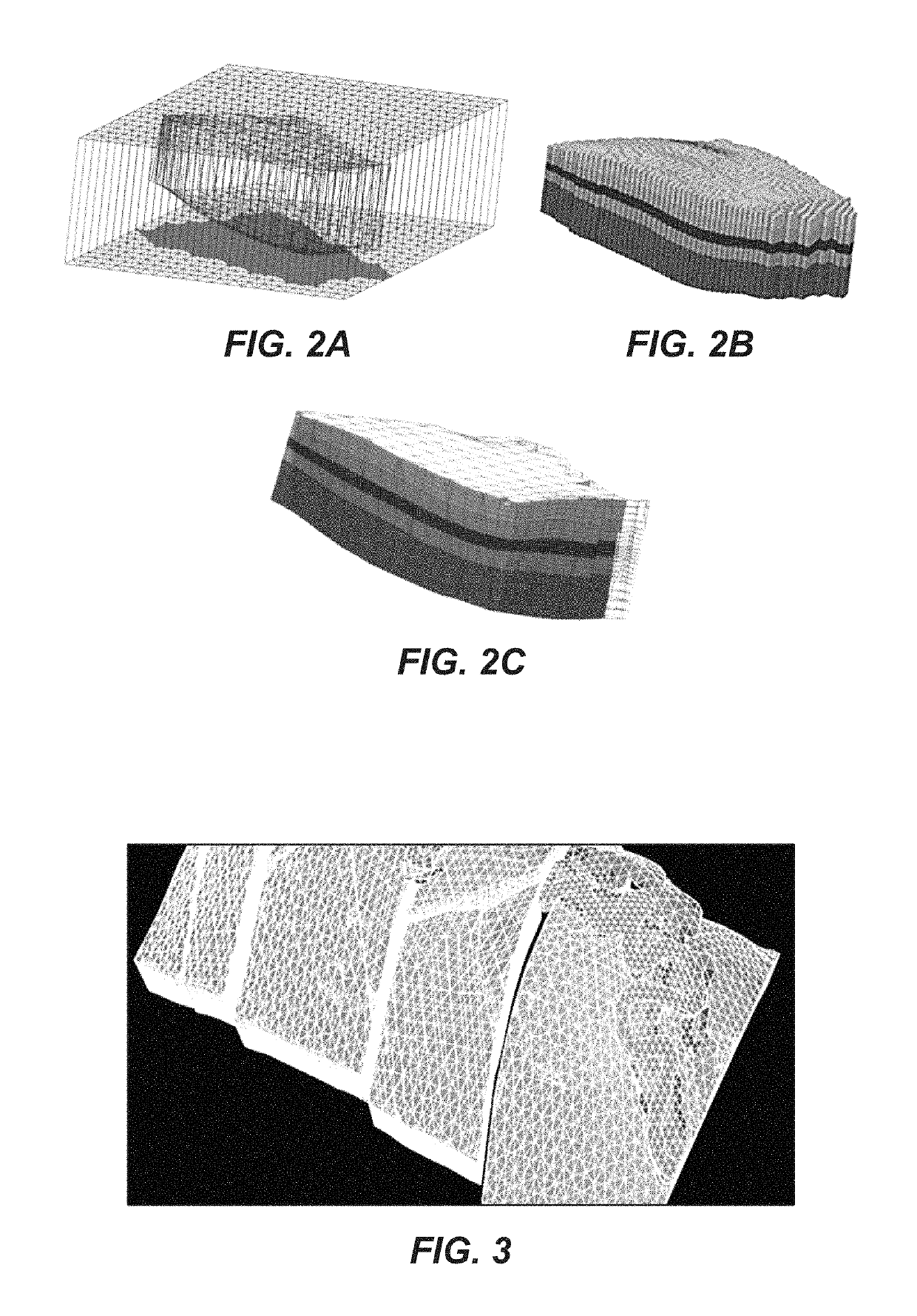
Volumetric Grid Generation in a Domain with Heterogeneous Material Properties
Method for generating a 3D grid, and for defining a material property model on the grid, to use, for example, in a reservoir simulator. A mapping is defined (61,71) to a design space in which the material property is described as a piecewise smooth implicit or explicit function in three dimensions. Grid geometry is constructed only in the physical space of the model (62-65,73-76), and no grid is required in the design space. The material property, for example permeability, is sampled in the design space (66,77) to populate the cells in the grid constructed in the physical domain. Prismatic grid cells may be truncated based on faults and horizons (65), or maybe conformed to fault surfaces using a 3D parameterization of the model (76). Only forward mapping, i.e. from the physical domain to the design space, is required.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method for simulating thoracic 4DCT
InactiveCN104956405AImprove accuracyMedical simulationDetails involving processing stepsMass spring damperElement analysis
Four-dimensional (4D) computed tomography (CT) is simulated by first generating a surface mesh from a single thoracic CT scan. Tetrahedralization is applied to the surface mesh to obtain a first volume mesh. Finite element analysis, using boundary constraints and load definitions, is applied to the first volume mesh to obtain a lung deformation according to an Ogden model. Constrained tetrahedralization, using control points, is applied to the lung deformation to obtain a second volume mesh, which is then deformed using mass-spring-damper simulation to produces the 4DCT.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
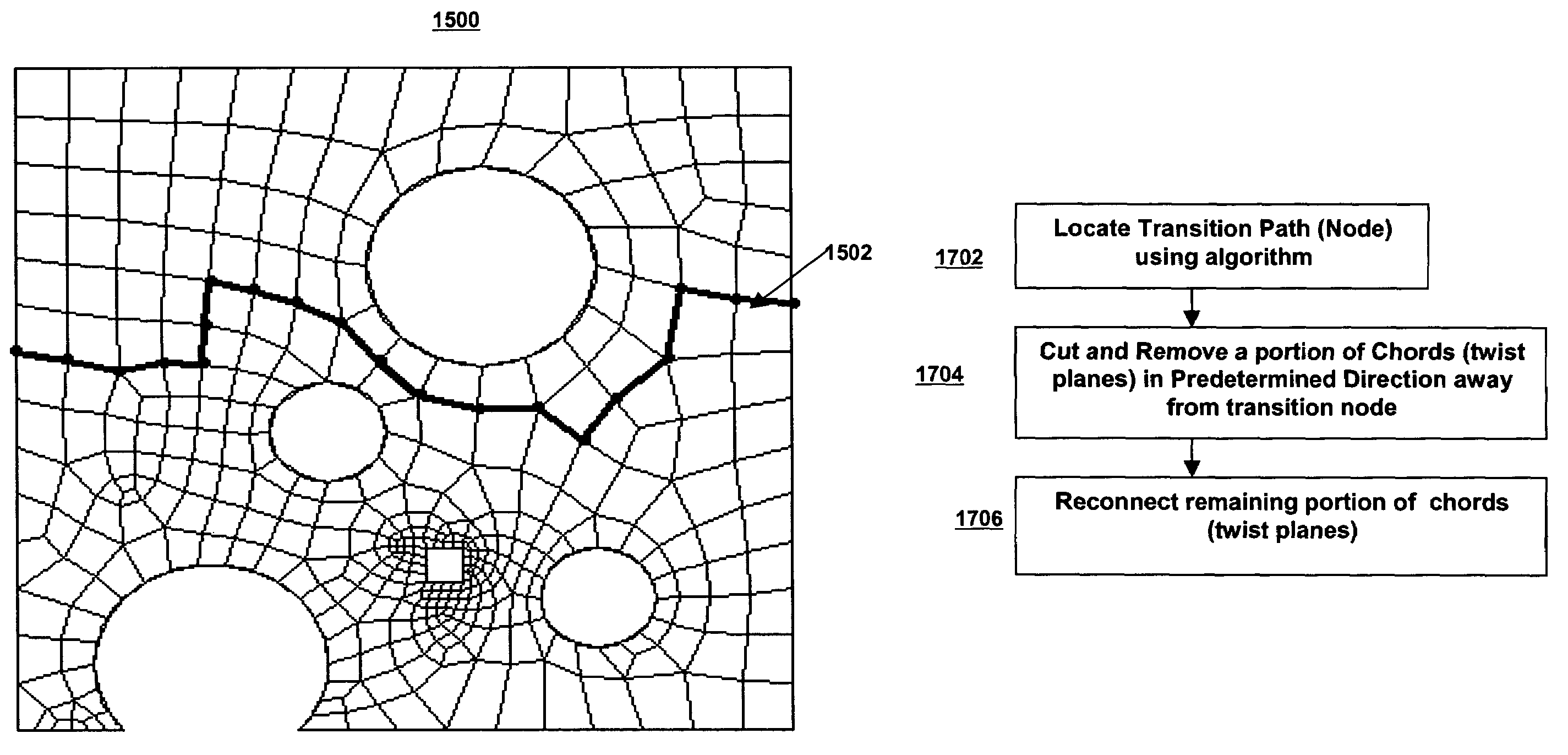
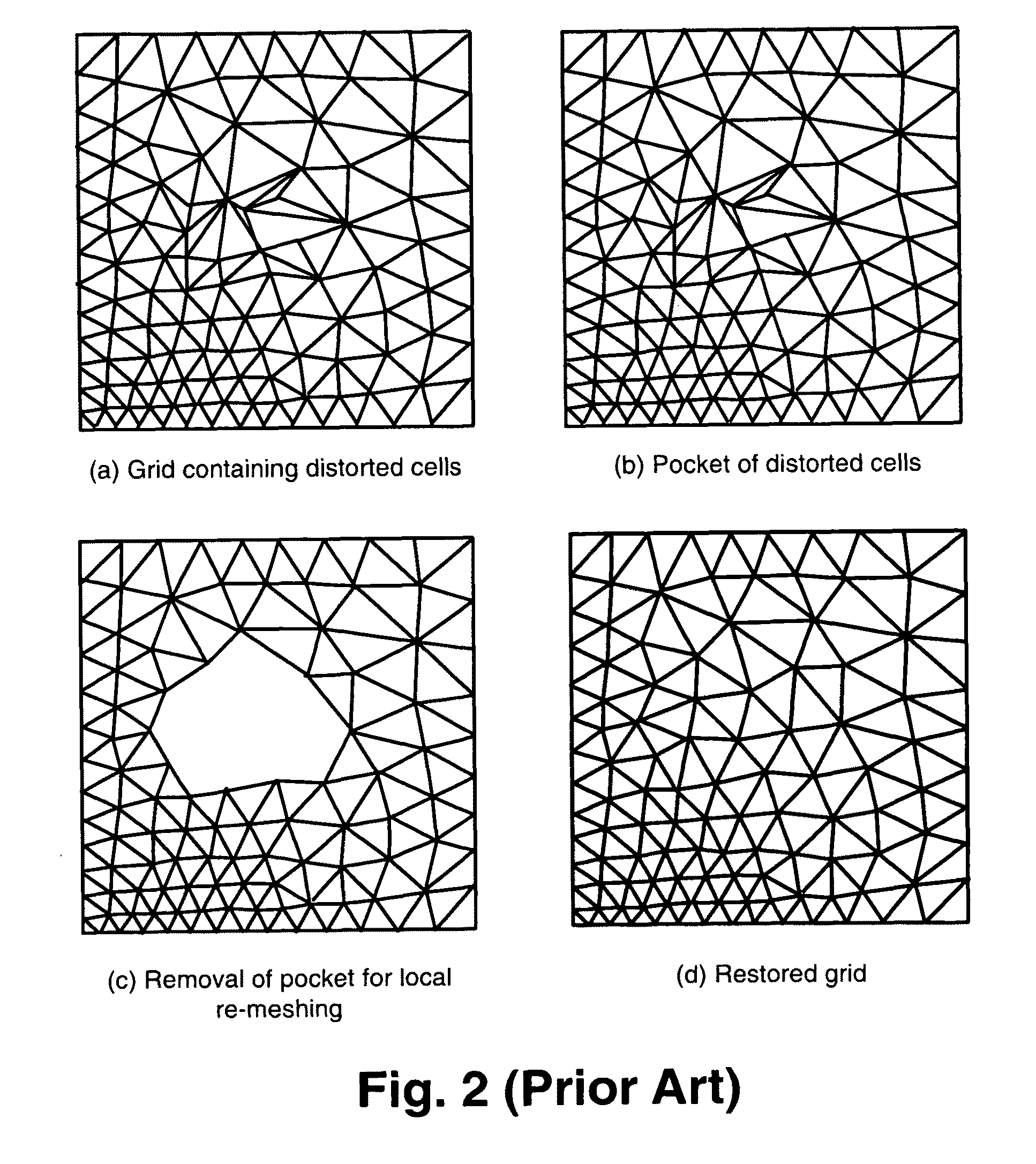
Method of modifying a volume mesh using sheet extraction
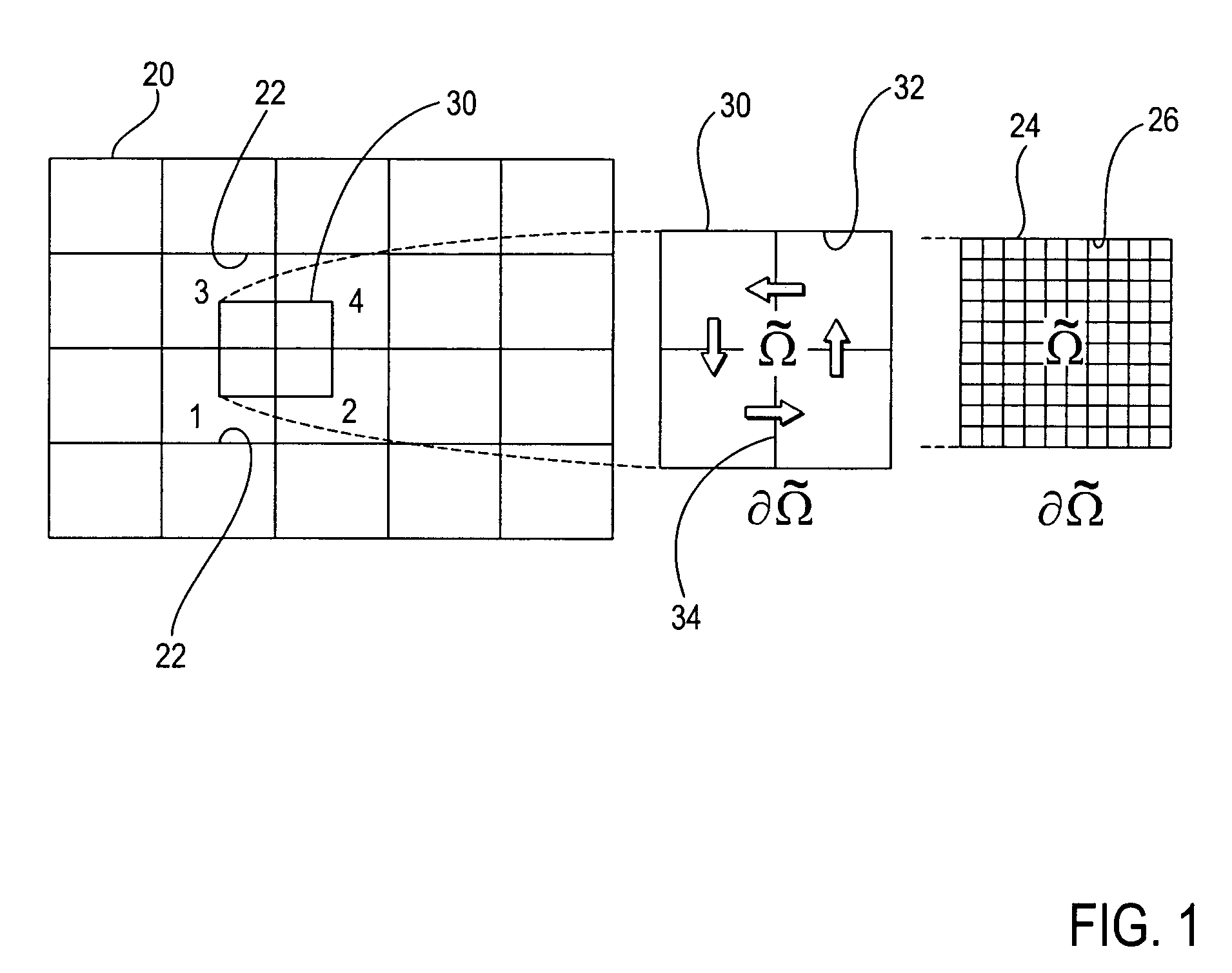
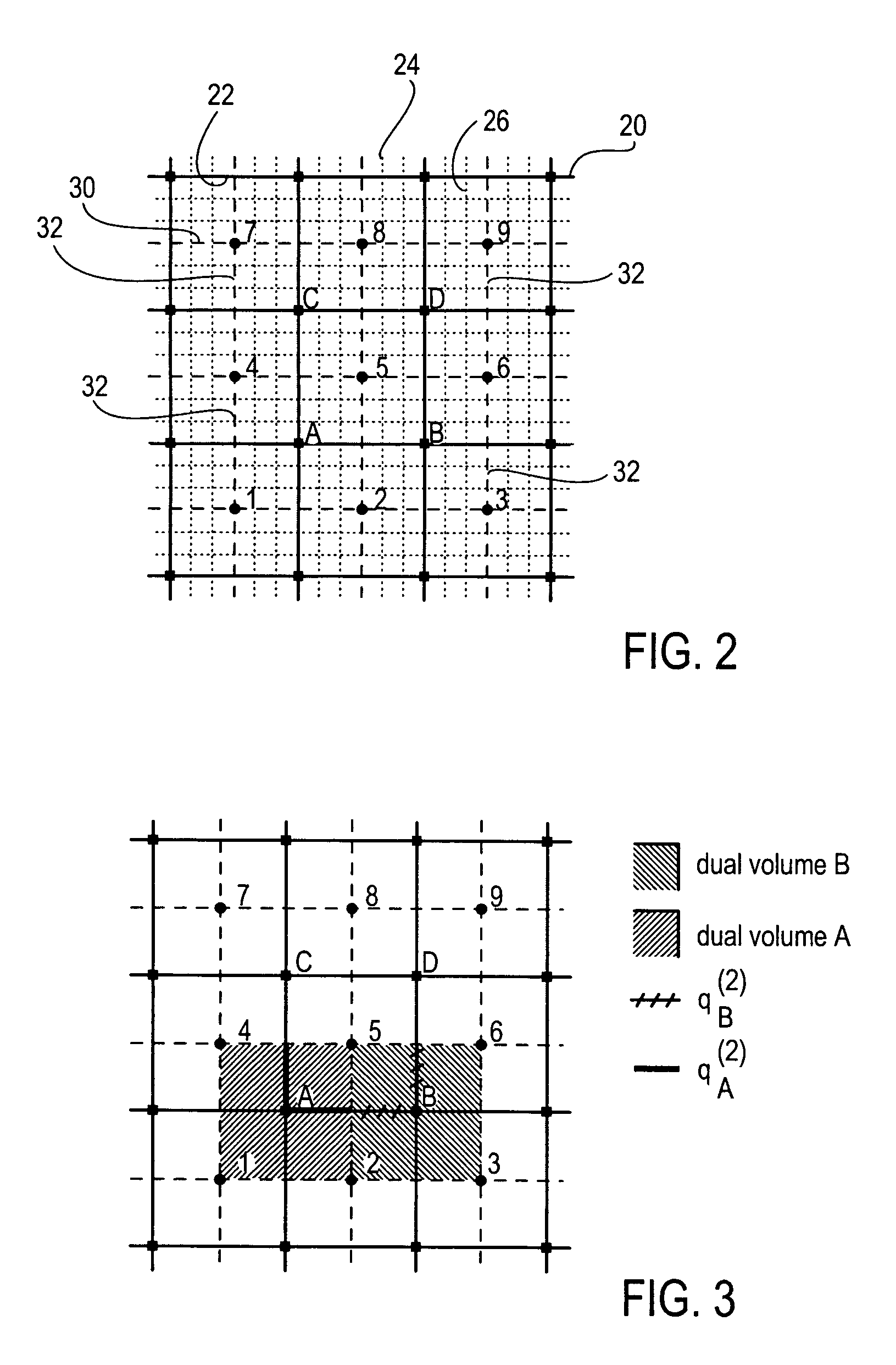
InactiveUS7181377B1Computation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsComputer graphics (images)Mesh grid
A method and machine-readable medium provide a technique to modify a hexahedral finite element volume mesh using dual generation and sheet extraction. After generating a dual of a volume stack (mesh), a predetermined algorithm may be followed to modify the volume mesh of hexahedral elements. The predetermined algorithm may include the steps of determining a sheet of hexahedral mesh elements, generating nodes for merging, and merging the nodes to delete the sheet of hexahedral mesh elements and modify the volume mesh.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
System and method for editing geological models by switching between volume-based models and surface-based structural models augmented with stratigraphic fiber bundles
Owner:ASPEN PARADIGM HLDG LLC
Non-convex hull surfaces
ActiveUS20150120260A1Computation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsData setPolygon mesh
The invention is a computer implemented method, device, system, or article for reconstructing a surface of an object. In particular, the invention comprises estimating a non-convex hull signed distance function parameters from a data set of an object and evaluating the non-convex hull signed distance function on vertices of a volumetric mesh. The invention further comprises approximating the zero level set of the non-convex hull signed distance function by a polygonal mesh using an isosurface algorithm to provide surface reconstruction of an object.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
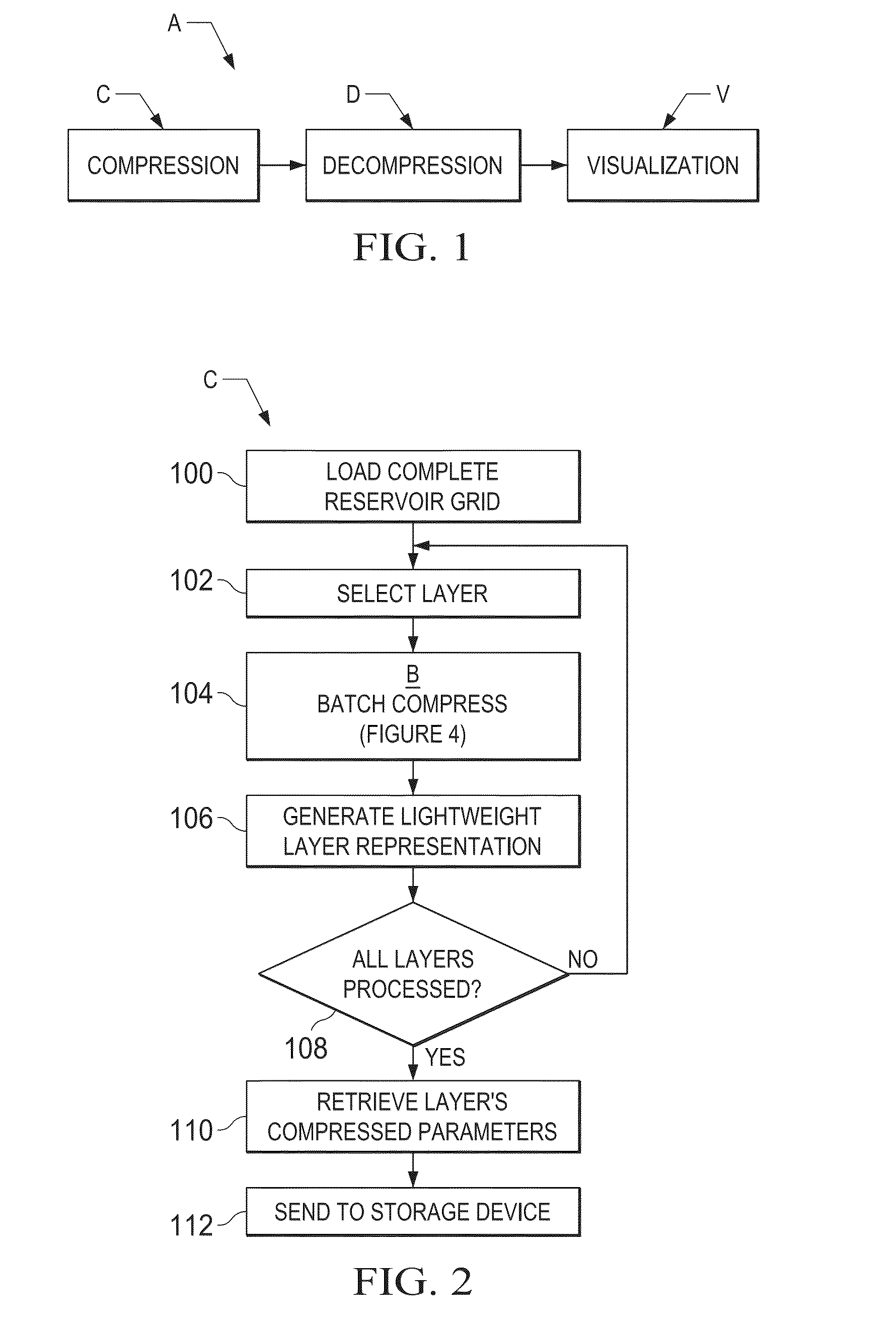
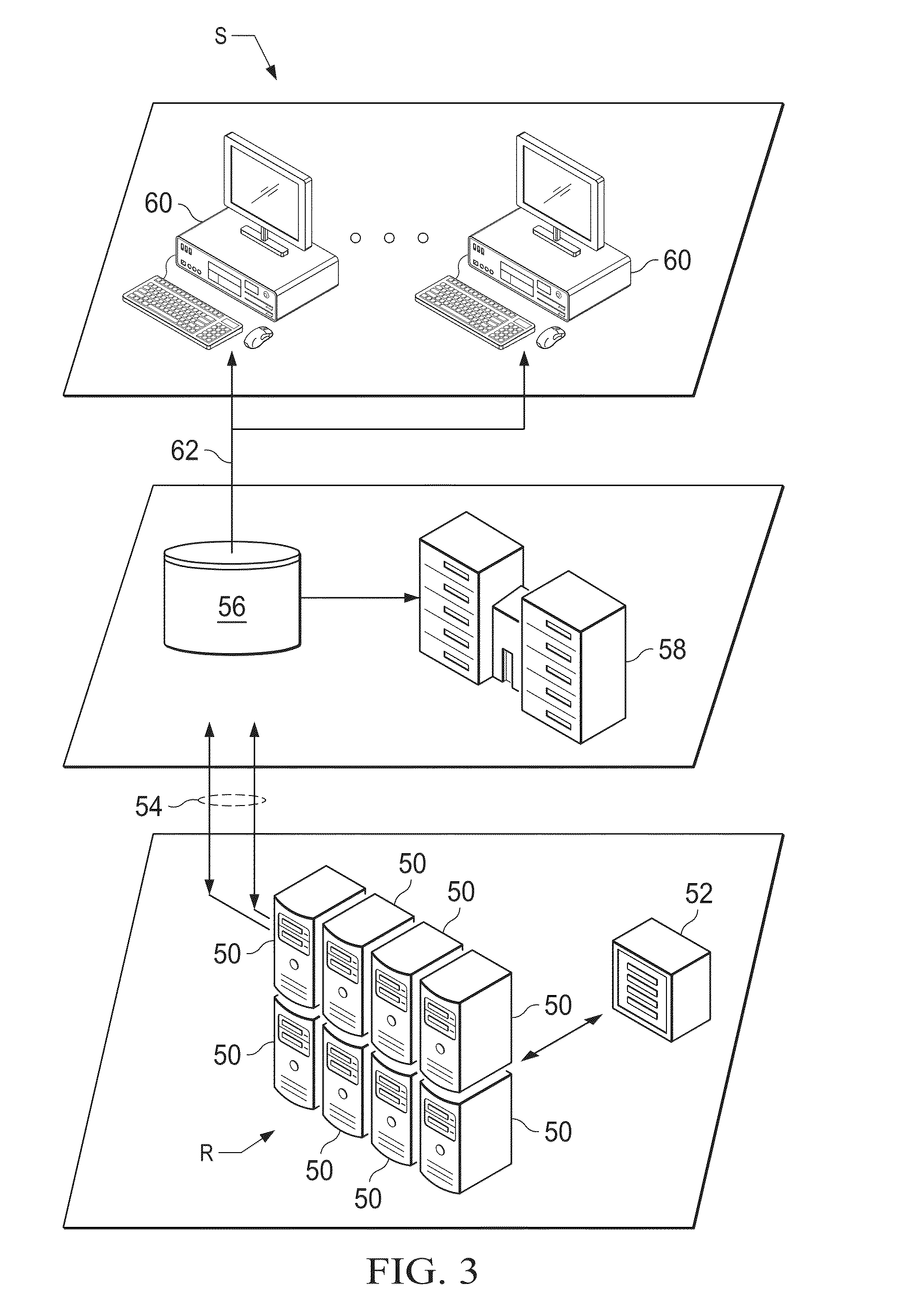
Data Compression of Hydrocarbon Reservoir Simulation Grids
ActiveUS20150149139A1Reduced representationCode conversionFluid removalData compressionColor mapping
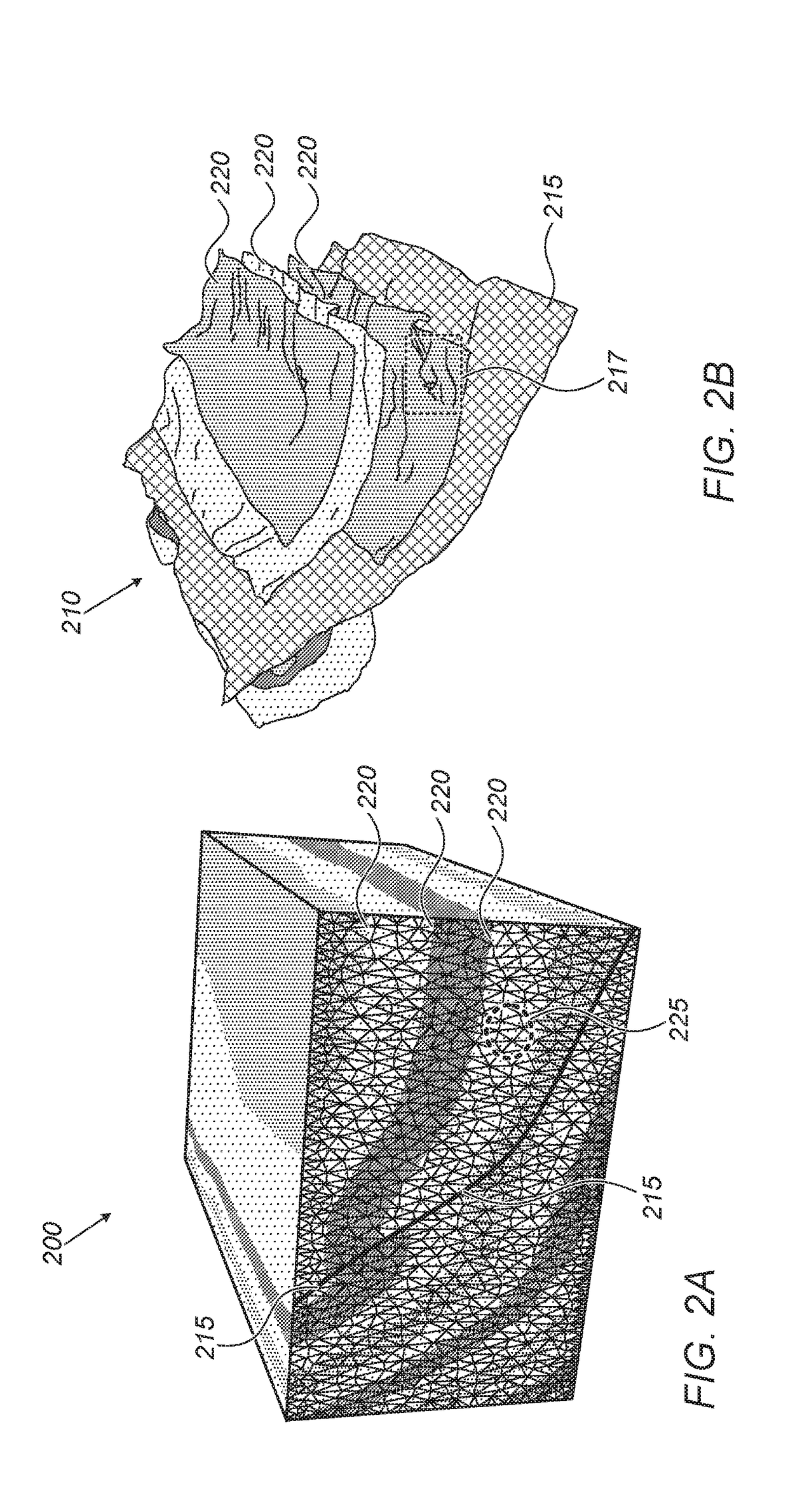
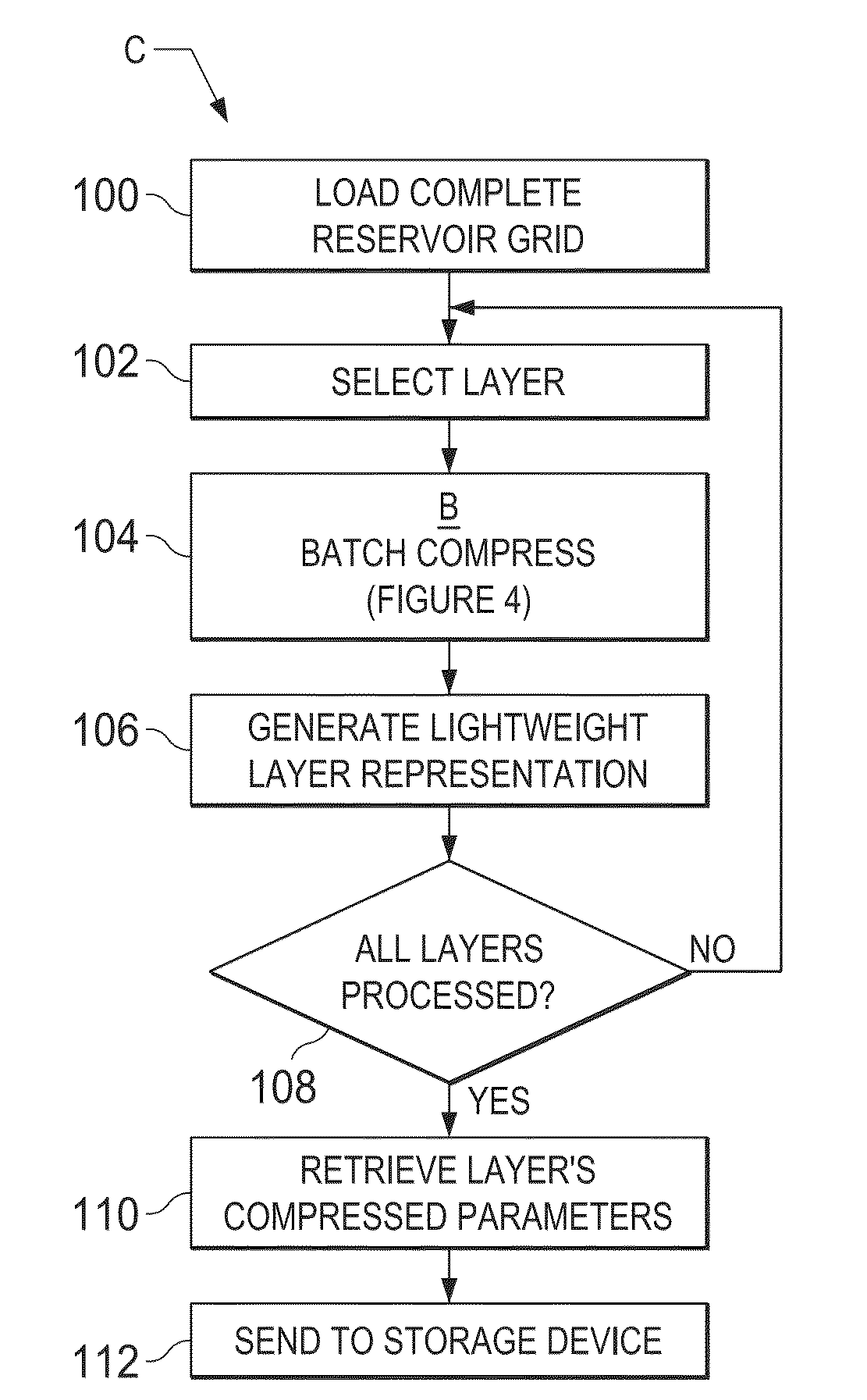
A dense volumetric grid coming from an oil / gas reservoir simulation output is translated into a compact representation that supports desired features such as interactive visualization, geometric continuity, color mapping and quad representation. A set of four control curves per layer results from processing the grid data, and a complete set of these 3-dimensional surfaces represents the complete volume data and can map reservoir properties of interest to analysts. The processing results yield a representation of reservoir simulation results which has reduced data storage requirements and permits quick performance interaction between reservoir analysts and the simulation data. The degree of reservoir grid compression can be selected according to the quality required, by adjusting for different thresholds, such as approximation error and level of detail. The processions results are of potential benefit in applications such as interactive rendering, data compression, and in-situ visualization of large-scale oil / gas reservoir simulations.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO +1
Simulation method of aerodynamic parameters of canard configuration aircraft and terminal equipment
ActiveCN107451354ALow costShort cycleGeometric CADSustainable transportationTerminal equipmentSimulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of aircrafts, and provides a simulation method of aerodynamic parameters of a canard configuration aircraft and terminal equipment. The method includes the steps that a three-dimensional model of the canard configuration aircraft is established; meshing is conducted on the surface of the three-dimensional model of the canard configuration aircraft and a flow field domain corresponding to the three-dimensional model of the canard configuration aircraft, and the volume mesh of the flow field domain is obtained according to the mesh of the surface of the three-dimensional model and the mesh of the outer surface of the flow field domain; a k-epsilon turbulent mathematic model for simulating air flow in the volume mesh is established; simulation solving is conducted on the aerodynamic parameters of the canard configuration aircraft through the k-epsilon turbulent mathematic model. According to the scheme, the three-dimensional model of the canard configuration aircraft is established, then the volume mesh of the corresponding flow field domain is obtained according to the three-dimensional model of the aircraft, and air in the volume mesh around the aircraft is simulated through the turbulent mathematic model to obtain the aerodynamic parameters of the aircraft. The simulation method is short in cycle, low in cost and precise.
Owner:PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY ORDNANCE ENG COLLEGE
Method of modifying a volume mesh using sheet insertion
InactiveUS7098912B1Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringMesh grid
A method and machine-readable medium provide a technique to modify a hexahedral finite element volume mesh using dual generation and sheet insertion. After generating a dual of a volume stack (mesh), a predetermined algorithm may be followed to modify (refine) the volume mesh of hexahedral elements. The predetermined algorithm may include the steps of locating a sheet of hexahedral mesh elements, determining a plurality of hexahedral elements within the sheet to refine, shrinking the plurality of elements, and inserting a new sheet of hexahedral elements adjacently to modify the volume mesh. Additionally, another predetermined algorithm using mesh cutting may be followed to modify a volume mesh.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
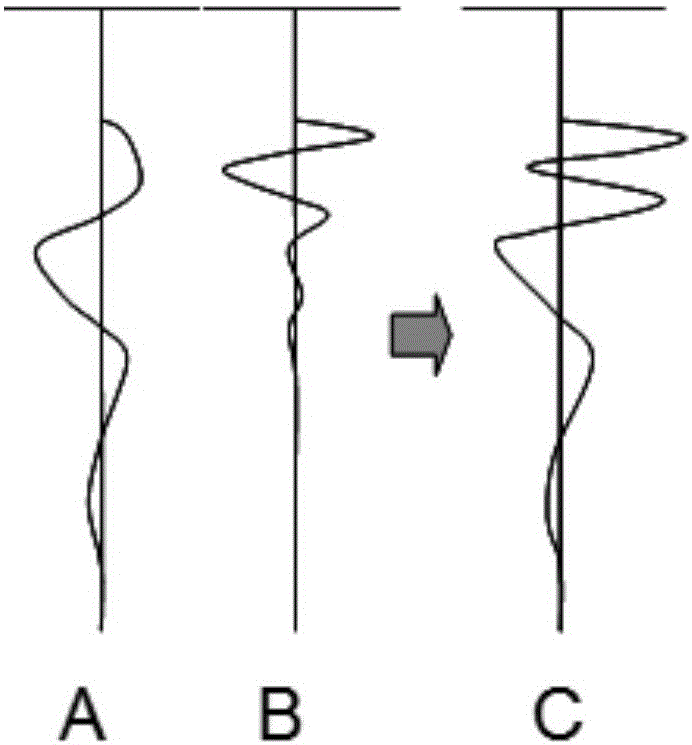
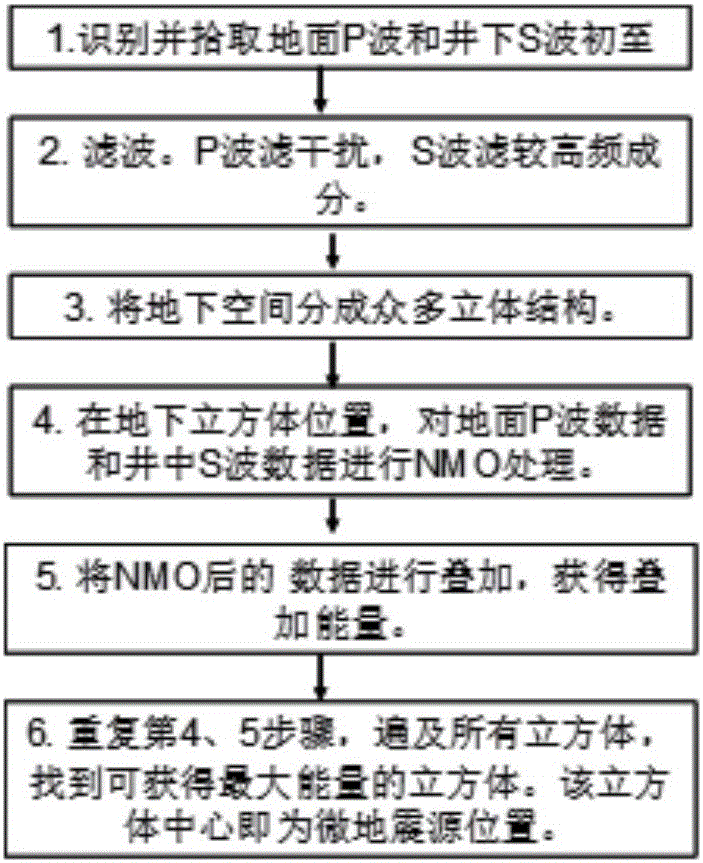
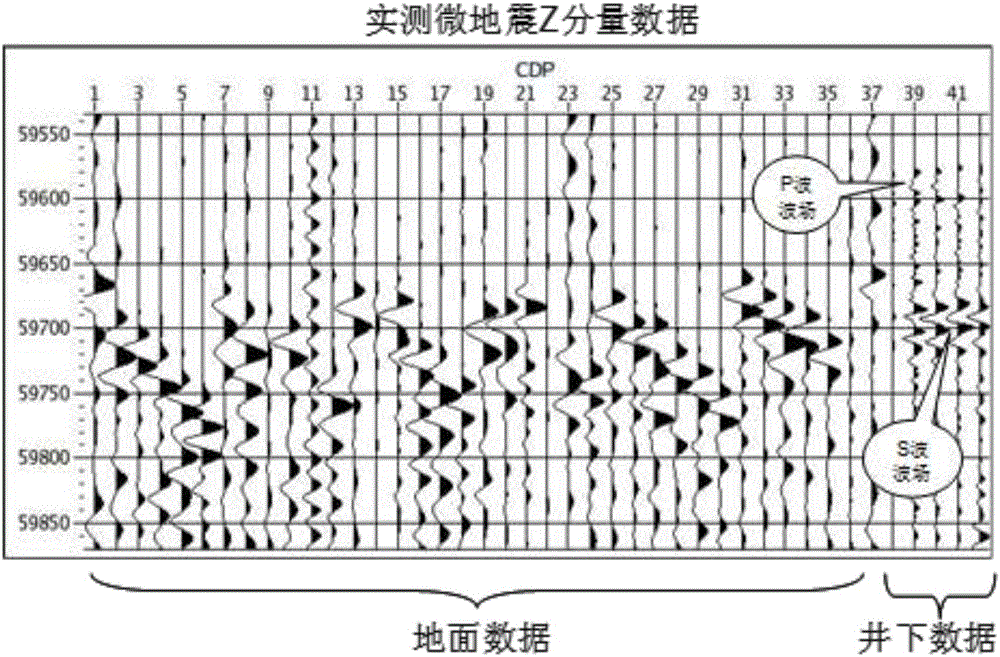
Method for measuring and determining micro-seismic focus
The invention relates to the disaster, resources and environment field, particularly to a method for measuring and determining a micro-seismic focus. The method comprises the steps of collection, pretreatment, first-motion picking up, division of to-be-measured underground space into fine volume meshes, NMO working, signal superposition, and coordinate point determination and the like. With the method, a defect that a maximum energy method can not be applied to down-hole micro-seismic data and ground micro-seismic data to determine a micro-seismic position can be overcome. According to the method, hydraulic fracturing micro-seismic data collected on the ground and data collected under the well are combined and the down-hole micro-seismic position is obtained based on joint inversion. The practical data inversion result demonstrates that the method provides a new way for obtaining a seismic focus position based on inversion by means of a maximum energy superposition method by using the combined ground and down-hole micro-seismic data.
Owner:CHINA UNITED COALBED METHANE +1
Domain decomposition by the advancing-partition method for parallel unstructured grid generation
In a method for domain decomposition for generating unstructured grids, a surface mesh is generated for a spatial domain. A location of a partition plane dividing the domain into two sections is determined. Triangular faces on the surface mesh that intersect the partition plane are identified. A partition grid of tetrahedral cells, dividing the domain into two sub-domains, is generated using a marching process in which a front comprises only faces of new cells which intersect the partition plane. The partition grid is generated until no active faces remain on the front. Triangular faces on each side of the partition plane are collected into two separate subsets. Each subset of triangular faces is renumbered locally and a local / global mapping is created for each sub-domain. A volume grid is generated for each sub-domain. The partition grid and volume grids are then merged using the local-global mapping.
Owner:NASA
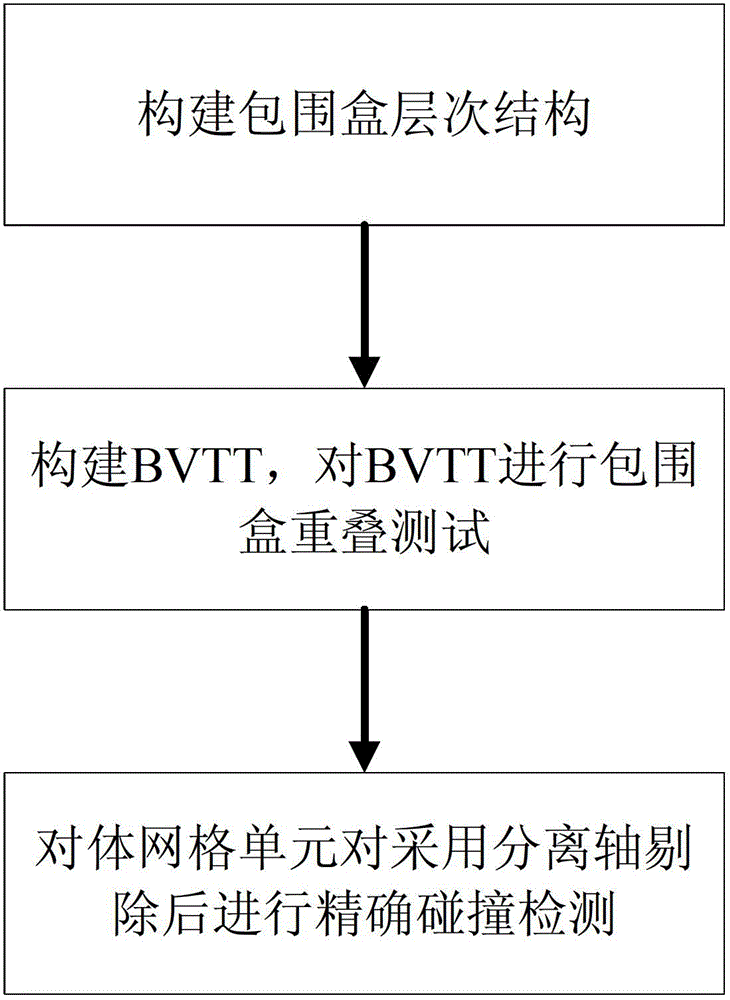
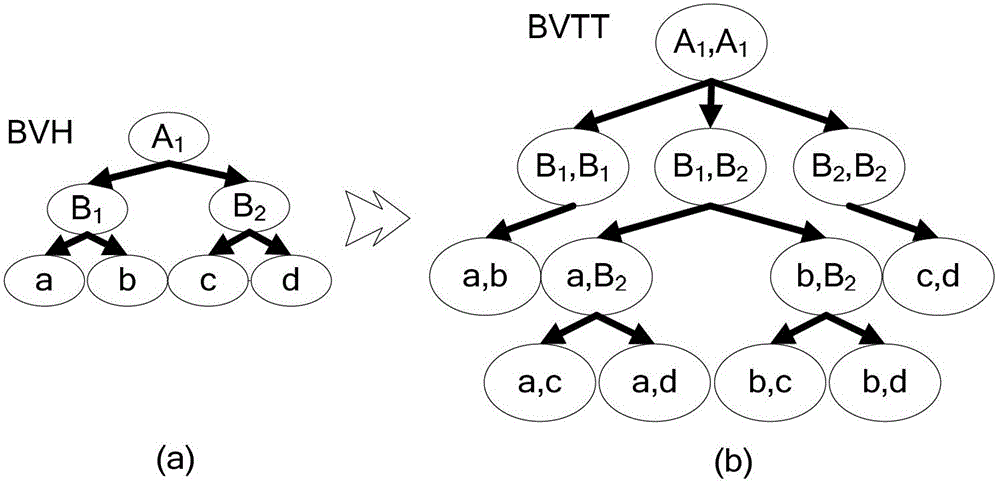
Volume mesh scene continuous collision detection method based on separation axis removal
ActiveCN102722910ARejection detection Rejection efficiency is highImprove culling efficiency3D modellingCollision detectionCollision test
The invention discloses a volume mesh scene continuous collision detection method based on separation axis removal, comprising the steps that: (1) a bounding box hierarchical structure is built; (2) BVTT is built and a bounding box overlapping test is carried out on the BVTT; and (3) a precise collision test is carried out on a volume mesh unit after the separation axis removal. During the stage of the precise collision test, the separation axis is used to remove correspondent collision cases. As the separation axis has a high test and removal efficiency, and a quick test speed, the continuous collision detection efficiency is improved, the number of the precise collision test is greatly reduced, the overall speed of the continuous collision test is greatly accelerated and a good compatibility is ensured.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Human body 3D modeling method based on mobile phone scanning
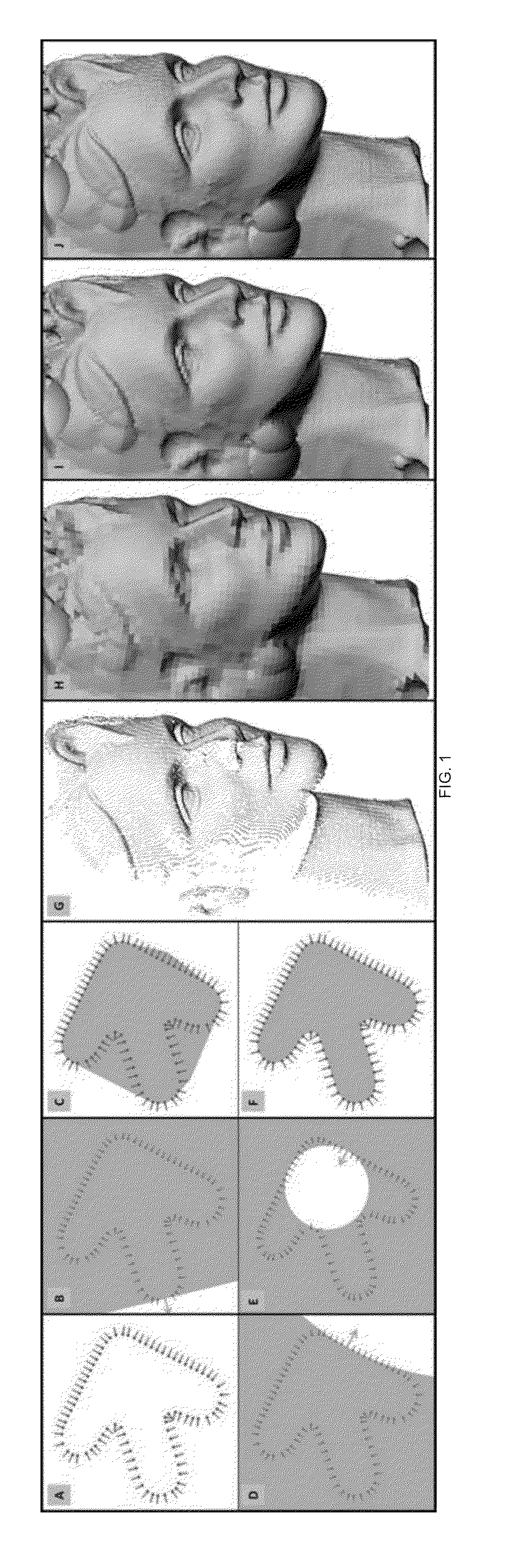
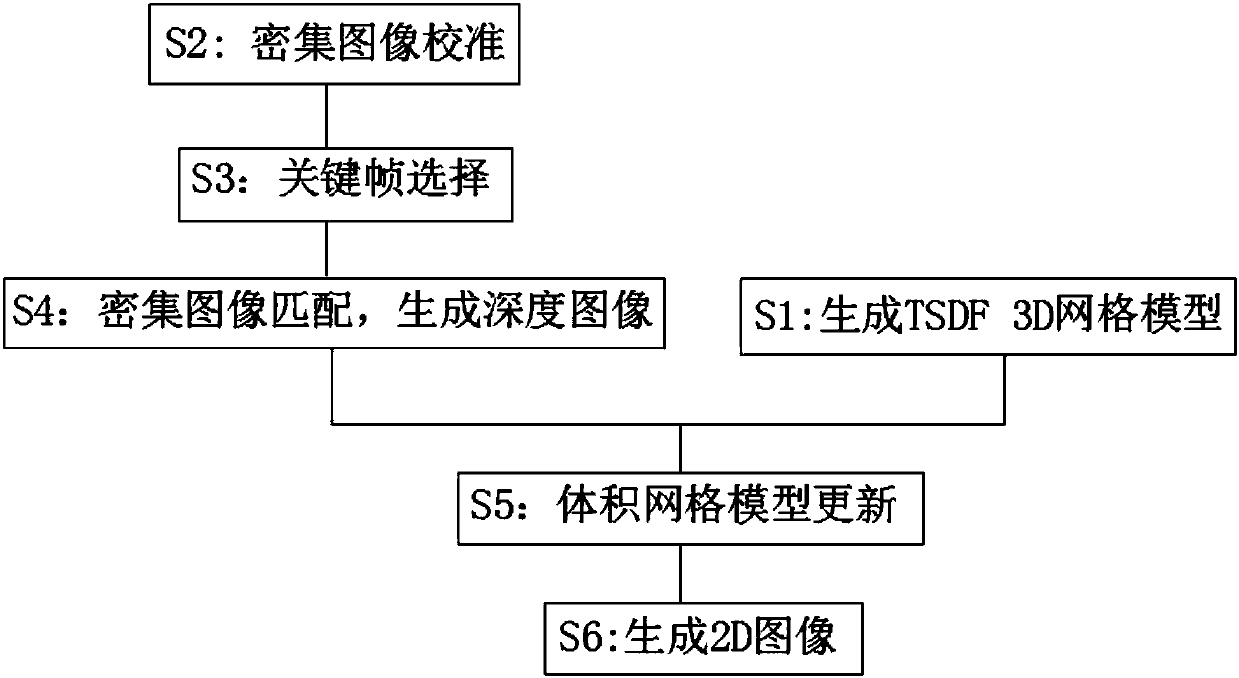
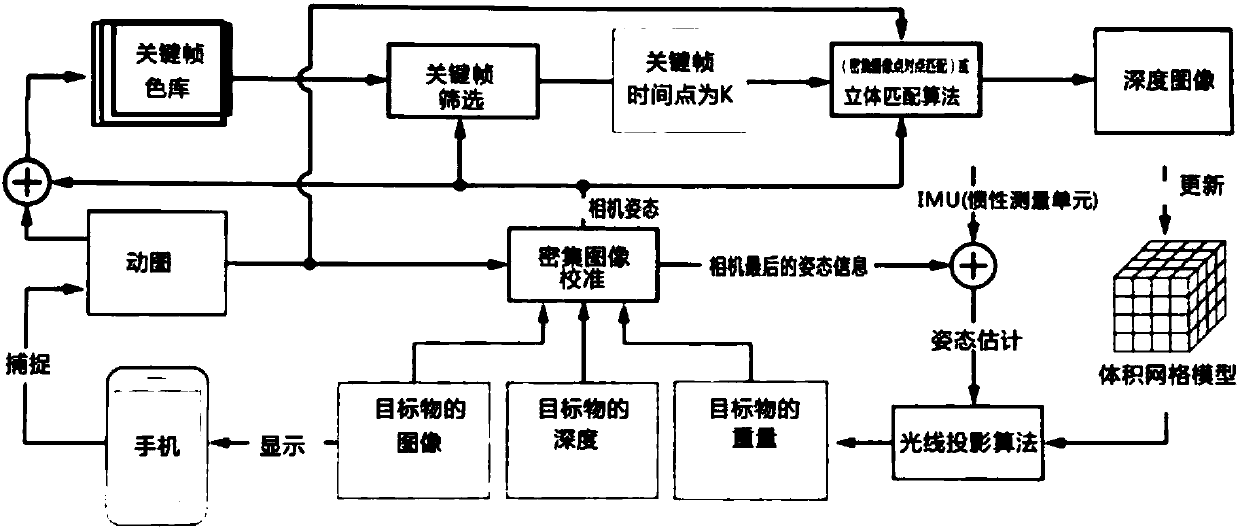
InactiveCN108053482AReduce scan timeEasy to operateDetails involving processing stepsSubstation equipmentHuman bodyImage calibration
The invention discloses a human body 3D modeling method based on mobile phone scanning. The method is applied to a mobile phone. The method includes the following steps: S1: generating a TSDF 3D meshmodel; S2: performing intensive image calibration; S3: performing key frame selection; S4: performing intensive image matching to generate a depth image; S5: performing volumetric mesh model updating;and S6: generating a human body 2D image on a mobile phone screen. The method uses the camera of the mobile phone to carry out three-dimensional modeling of the human body, does not require any accompanying equipment, and uses the mobile phone's own computing power to complete the three-dimensional modeling and calculation of the human body. By using the principle of human symmetry, as long as the half body is scanned, the system will perform 3D automatic generation of the entire human body; the user's scanning time is greatly saved, and when the user holds a mobile phone in one hand, 3D modeling cannot be influenced if scanning is inconvenient; and any data about the consumer is not required, the operation is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:喻强
Volumetric grid generation in a domain with heterogeneous material properties
Method for generating a 3D grid, and for defining a material property model on the grid, to use, for example, in a reservoir simulator. A mapping is defined (61,71) to a design space in which the material property is described as a piecewise smooth implicit or explicit function in three dimensions. Grid geometry is constructed only in the physical space of the model (62-65,73-76), and no grid is required in the design space. The material property, for example permeability, is sampled in the design space (66,77) to populate the cells in the grid constructed in the physical domain. Prismatic grid cells may be truncated based on faults and horizons (65), or maybe conformed to fault surfaces using a 3D parameterization of the model (76). Only forward mapping, i.e. from the physical domain to the design space, is required.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method and tool for simulation of the aerodynamic behaviour of an aircraft in flight close to the ground
A method of computer simulation of an aerodynamic behavior of an aircraft in flight close to the ground includes generating a volume mesh of a three-dimensional geometric domain. The volume mesh is at least partly delimited by a three-dimensional geometric model of the aircraft and by a plane modelling the ground. The volume mesh defines a computational domain. The method also includes imposing a uniform boundary condition on the plane comprising a predetermined speed vector with a non-zero tangential component and a non-zero normal component, and solving a discrete numerical model of the Navier-Stokes equations by computer on the volume mesh with the uniform boundary condition imposed on the plane to obtain a numerical solution of a fluid flow inside said computational domain.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
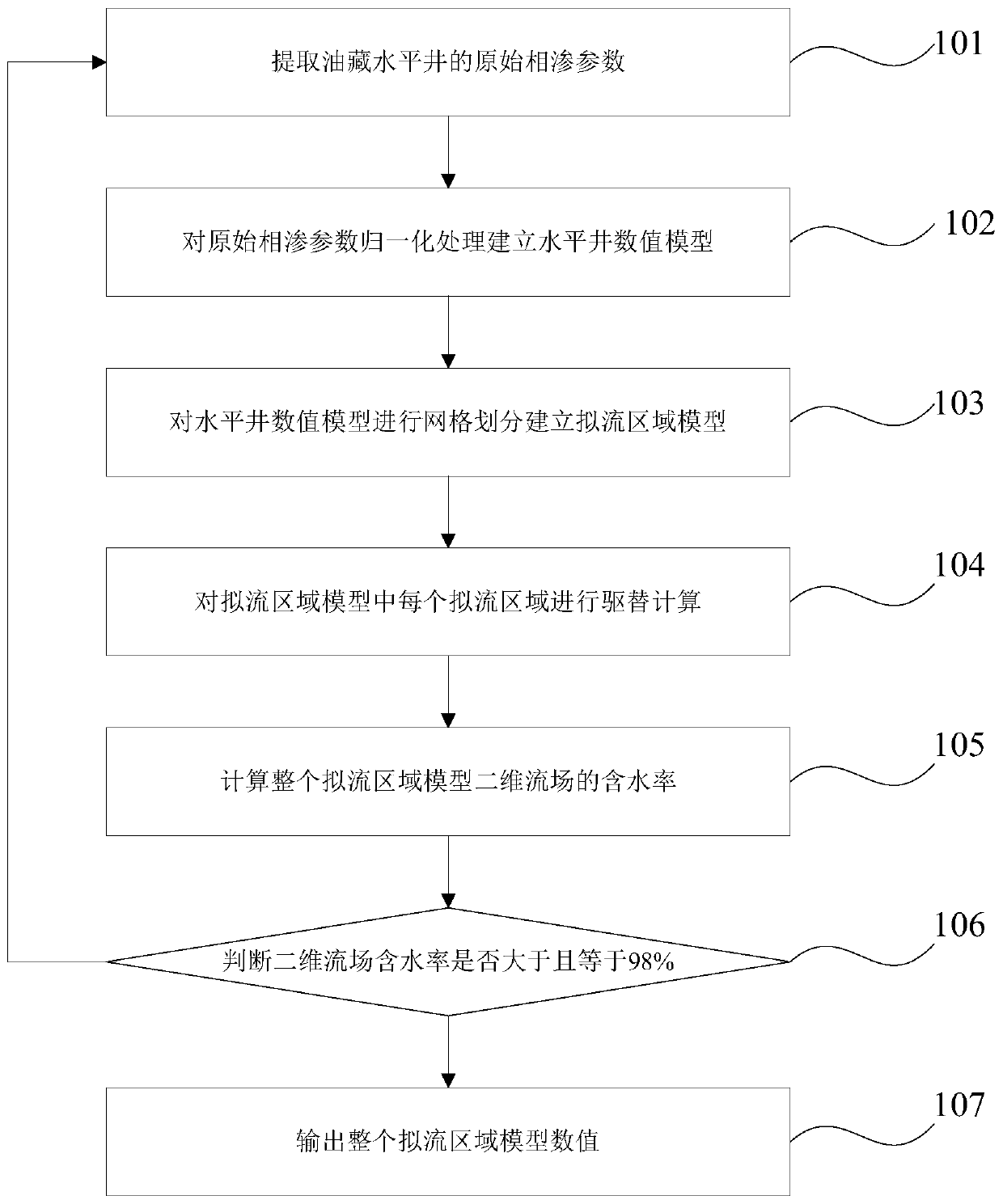
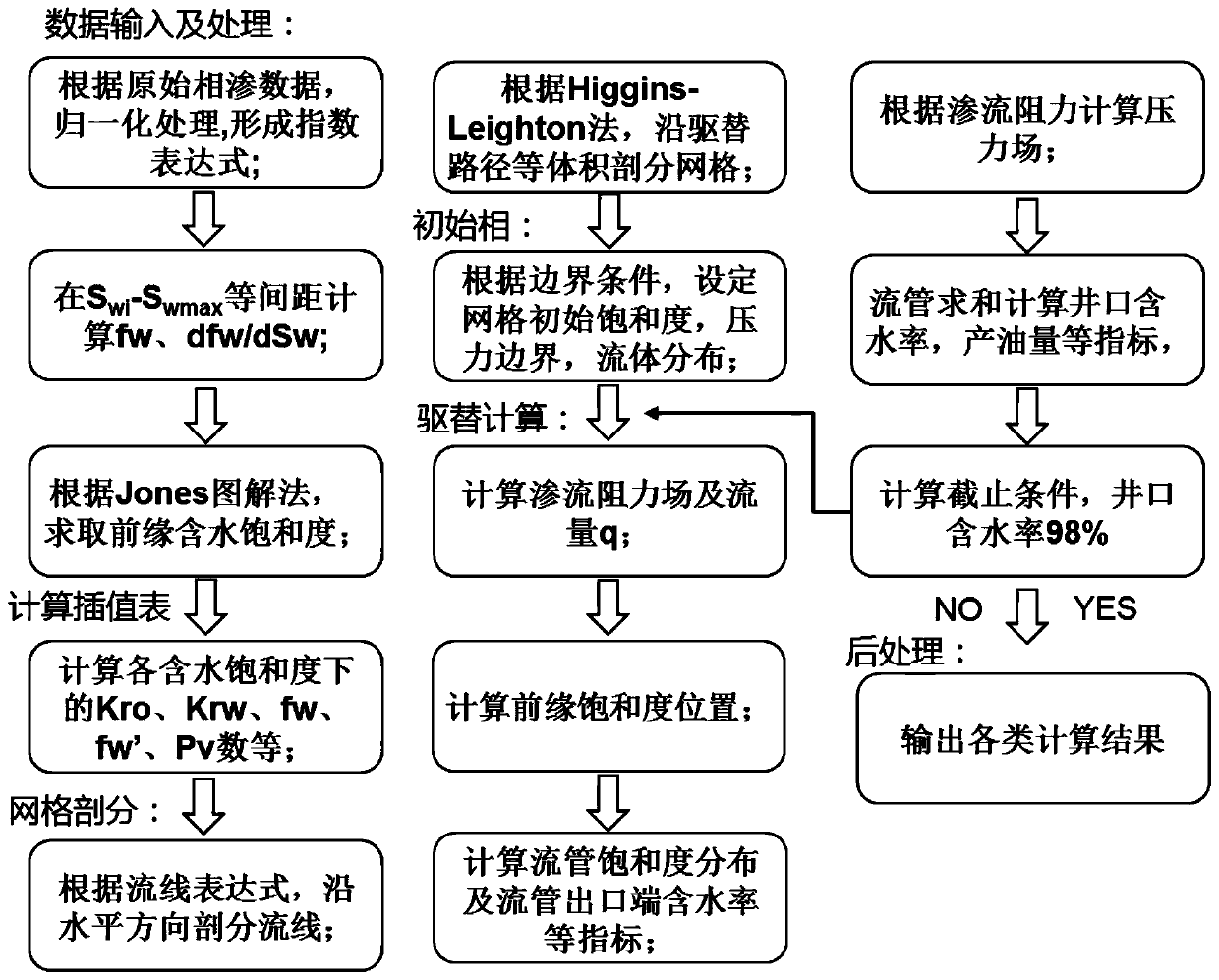
Bottom water reservoir horizontal well water flooding numerical simulation method based on quasi-streamline method
ActiveCN109858177ASolving problems with numerical scatterNumerical simulation method is simpleClimate change adaptationSpecial data processing applicationsLeading edgeWater flooding
The invention provides a bottom water reservoir horizontal well water flooding numerical simulation method based on a quasi-streamline method, which comprises the following steps: step 1, collecting basic static and dynamic information of a reservoir, and providing parameters for numerical simulation calculation; step 2, calculating parameter tables such as Kro, Krw, fw, fw 'and PV under each water saturation according to the relative permeability experiment data; 3, determining quasi-streamline distribution according to the form of the bottom water ridge, and performing isovolumetric mesh generation along the streamline; 4, initializing a model, and setting initial saturation, a pressure boundary and the like of a grid according to the actual condition of an oil reservoir; step 5, calculating simulation parameters such as saturation field distribution, seepage resistance and the like according to a water drive leading edge displacement theory. Aiming at the understanding problem of the water displacement rule of the bottom water reservoir, a bottom water displacement theoretical model is established by adopting a quasi-streamline method, the development dynamics of a horizontal well of the bottom water reservoir are simulated, and theoretical and technical support is provided for making a bottom water reservoir development technical policy.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
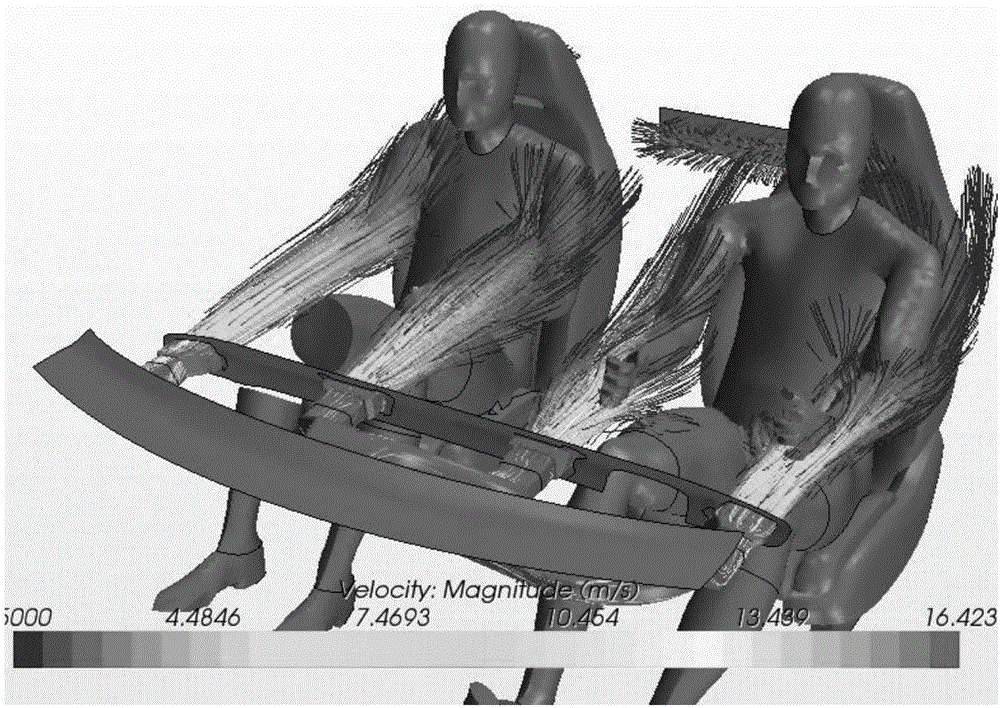
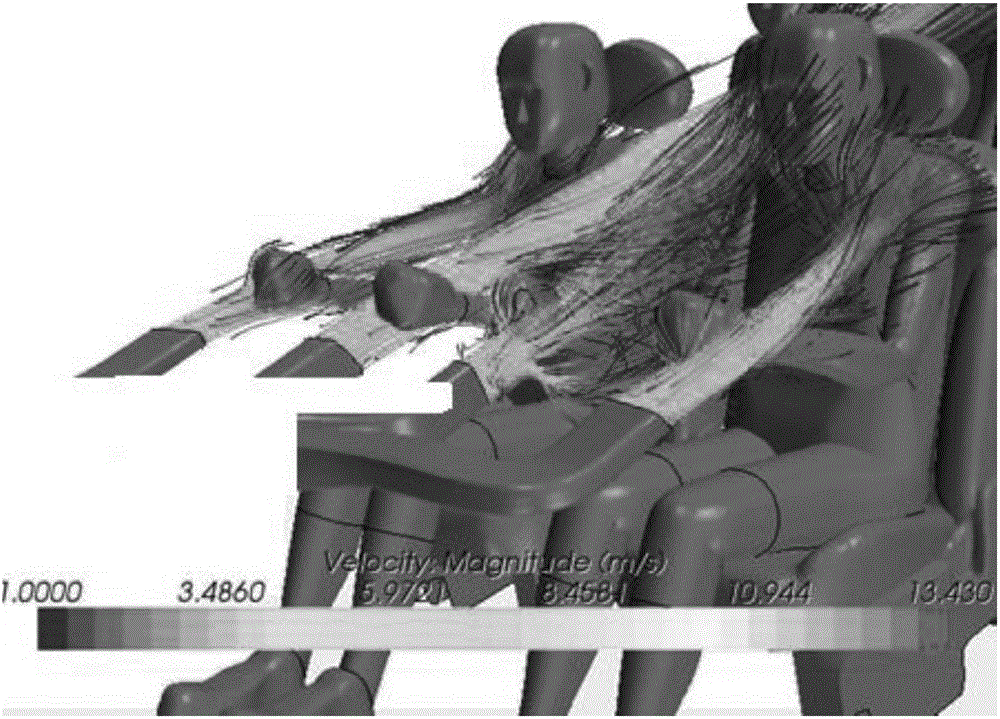
Simulation method and device of passenger compartment refrigeration effect
ActiveCN106326571AShort analysis timeReduce workloadDesign optimisation/simulationConstraint-based CADHuman bodyPhysical model
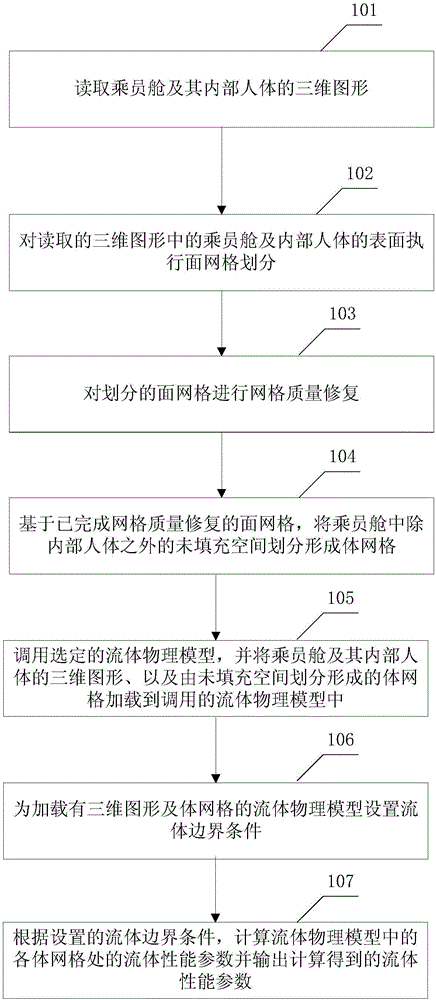
The invention provides and discloses a simulation method and a simulation device of a passenger compartment refrigeration effect. The method comprises the following steps: reading the three-dimensional graph of a passenger compartment and the three-dimensional graph of a human body in the passenger compartment; executing surface mesh division on the passenger compartment and the surface of the human body; repeatedly repairing the mesh quality of surface meshes; on the basis of the repaired surface mesh, dividing space in the passenger compartment into volume meshes; calling a fluid physical model, and loading the three-dimensional graph of the passenger compartment, the three-dimensional graph of the human body in the passenger compartment, and the volume meshes formed by the division of unfilled space into the fluid physical model; setting a fluid boundary condition, and calculating and outputting fluid performance parameters of volume meshes according to the fluid boundary condition. According to the simulation method, an airflow movement direction in the passenger compartment, the airflow speed of the human body surface, the distribution situation of airflow on the human body surface and the like can be obtained for evaluating whether the refrigeration effect of the passenger compartment conforms to the standard of the comfort level of the passenger compartment. Time is saved, manpower and financial resource consumption can be reduced, and cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:CH AUTO TECH CORP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com