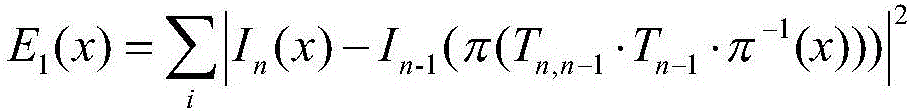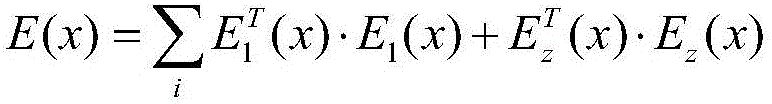Patents
Literature
50 results about "Signed distance function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
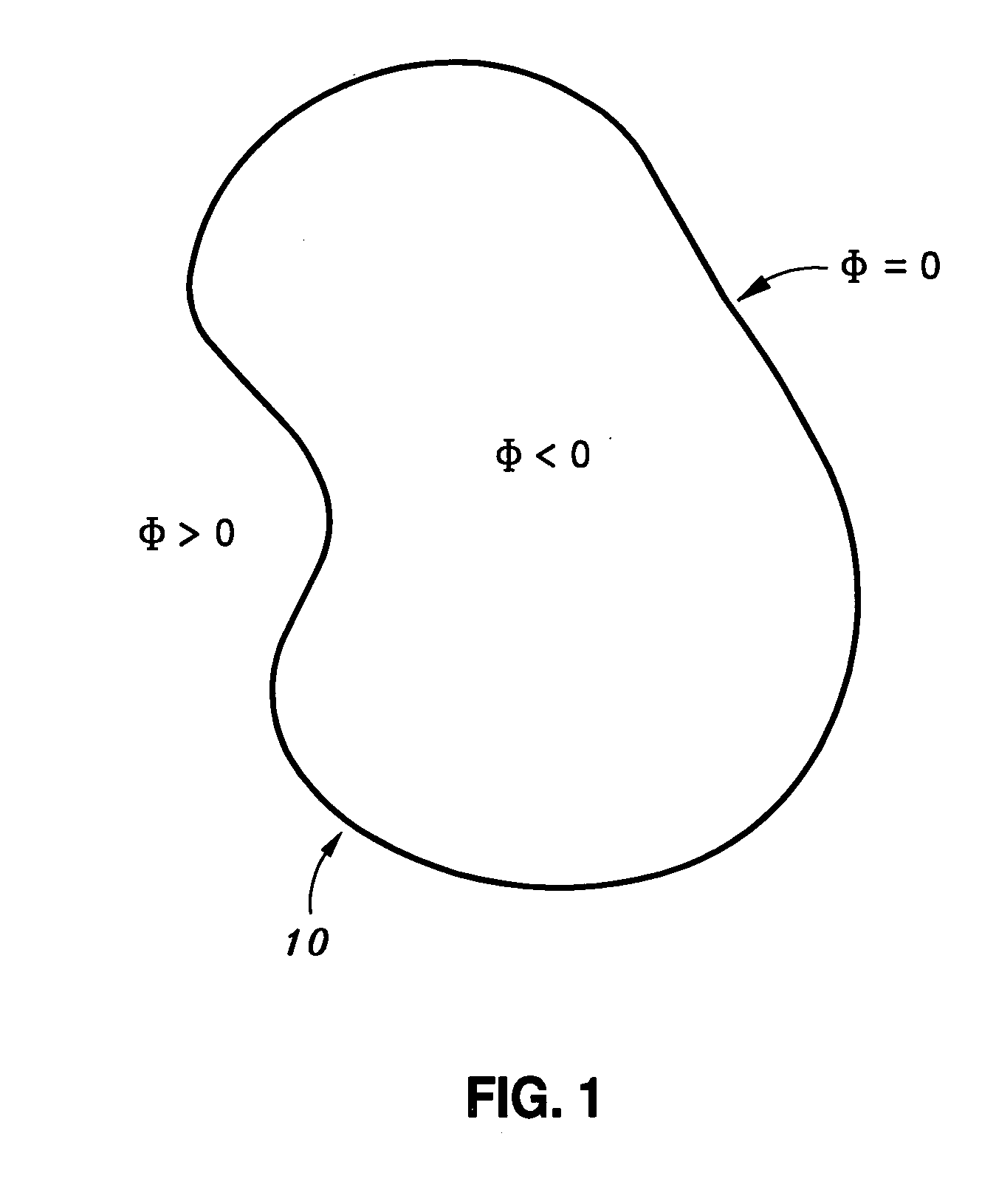
In mathematics and its applications, the signed distance function (or oriented distance function) of a set Ω in a metric space determines the distance of a given point x from the boundary of Ω, with the sign determined by whether x is in Ω. The function has positive values at points x inside Ω, it decreases in value as x approaches the boundary of Ω where the signed distance function is zero, and it takes negative values outside of Ω. However, the alternative convention is also sometimes taken instead (i.e., negative inside Ω and positive outside).
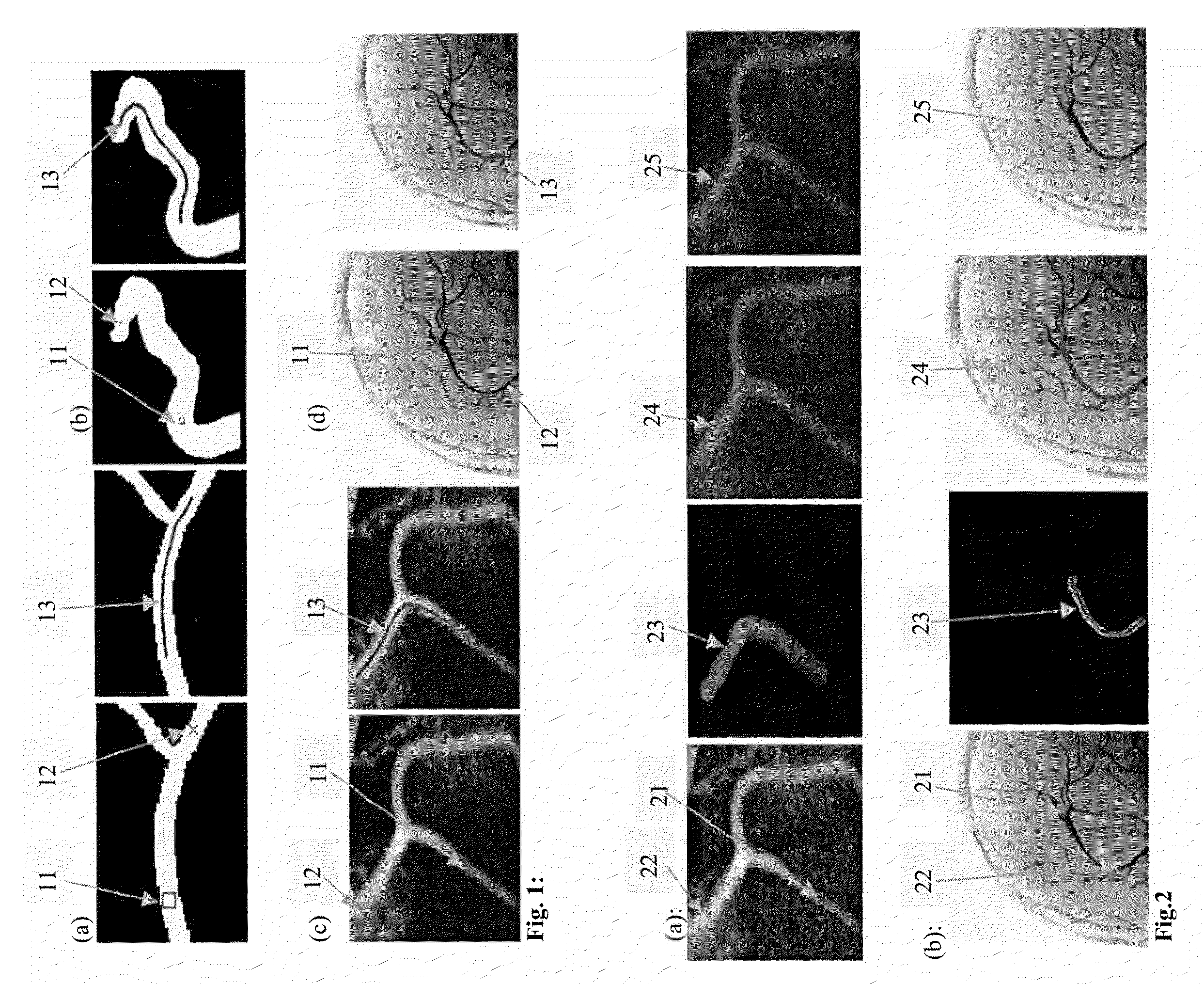
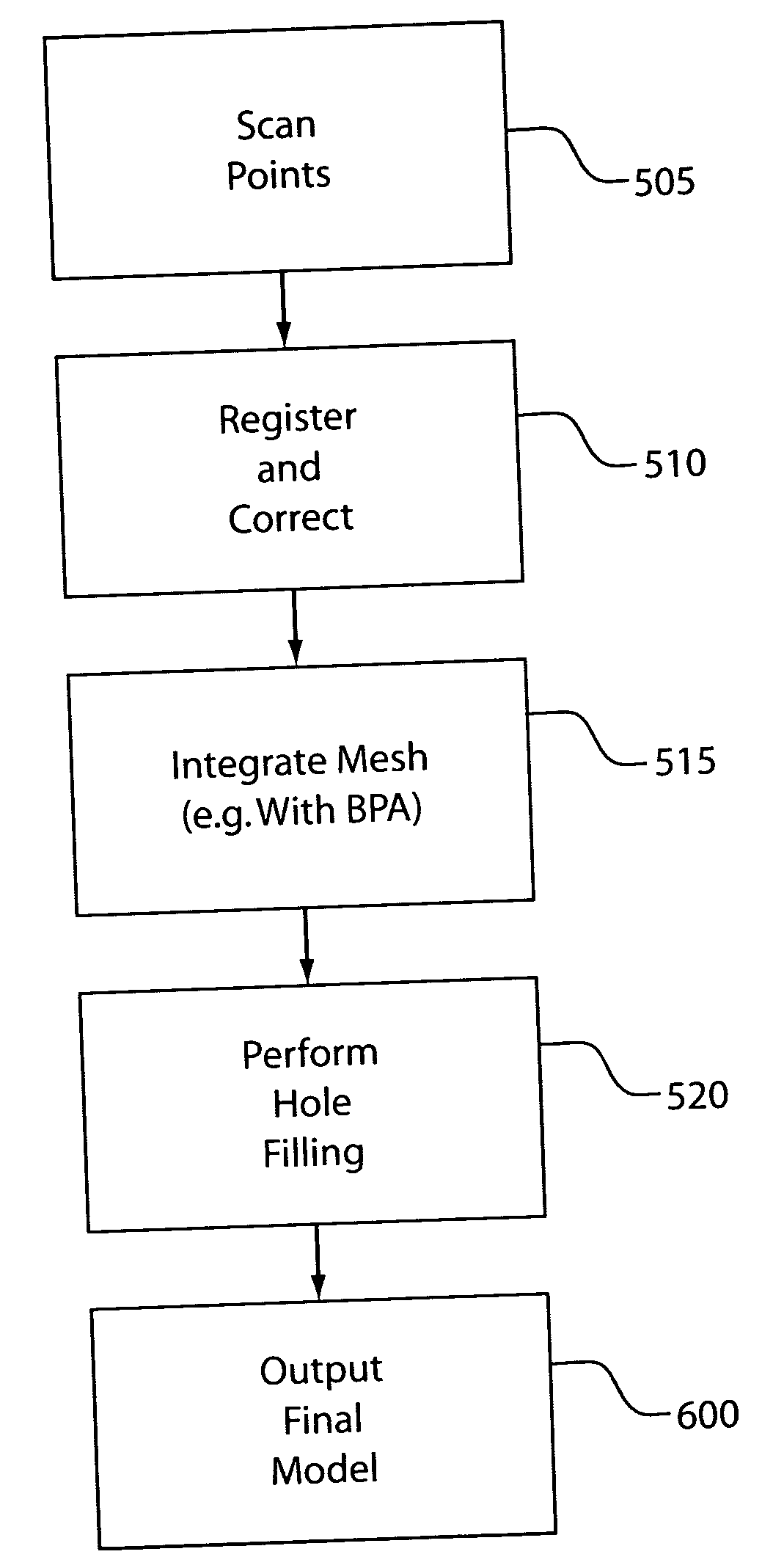
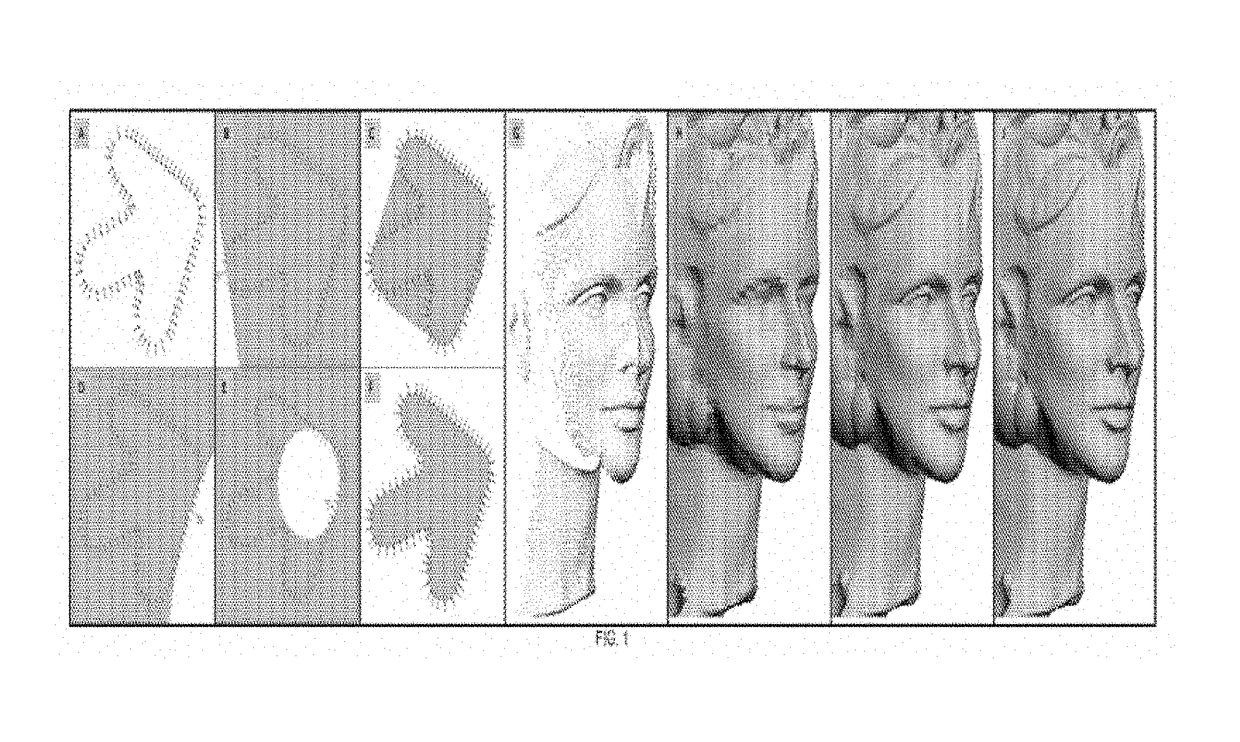
System and method for hole filling in 3D models
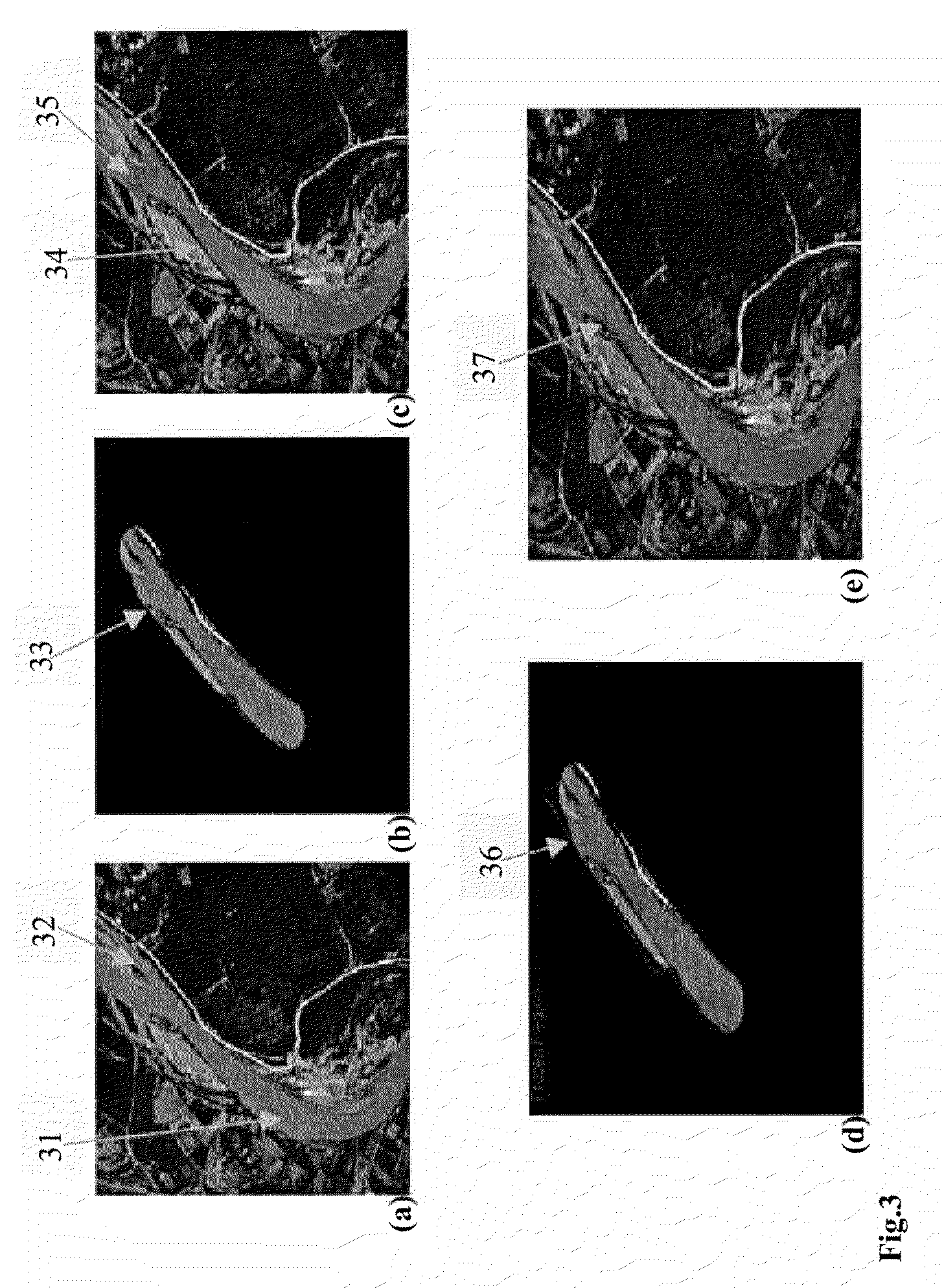
InactiveUS20050057561A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Digital image
A method for hole-filling in 3D models includes identifying vertices adjacent to hole boundaries in a mesh of points on a digital image and constructing a signed distance function based on vertices adjacent to hole boundaries. A Radial Basis Function is fit based on the constructed signed distance function and evaluated on a grid, which include the hole. The points on the hole surface are extracted and meshed to fill the hole.
Owner:IBM CORP
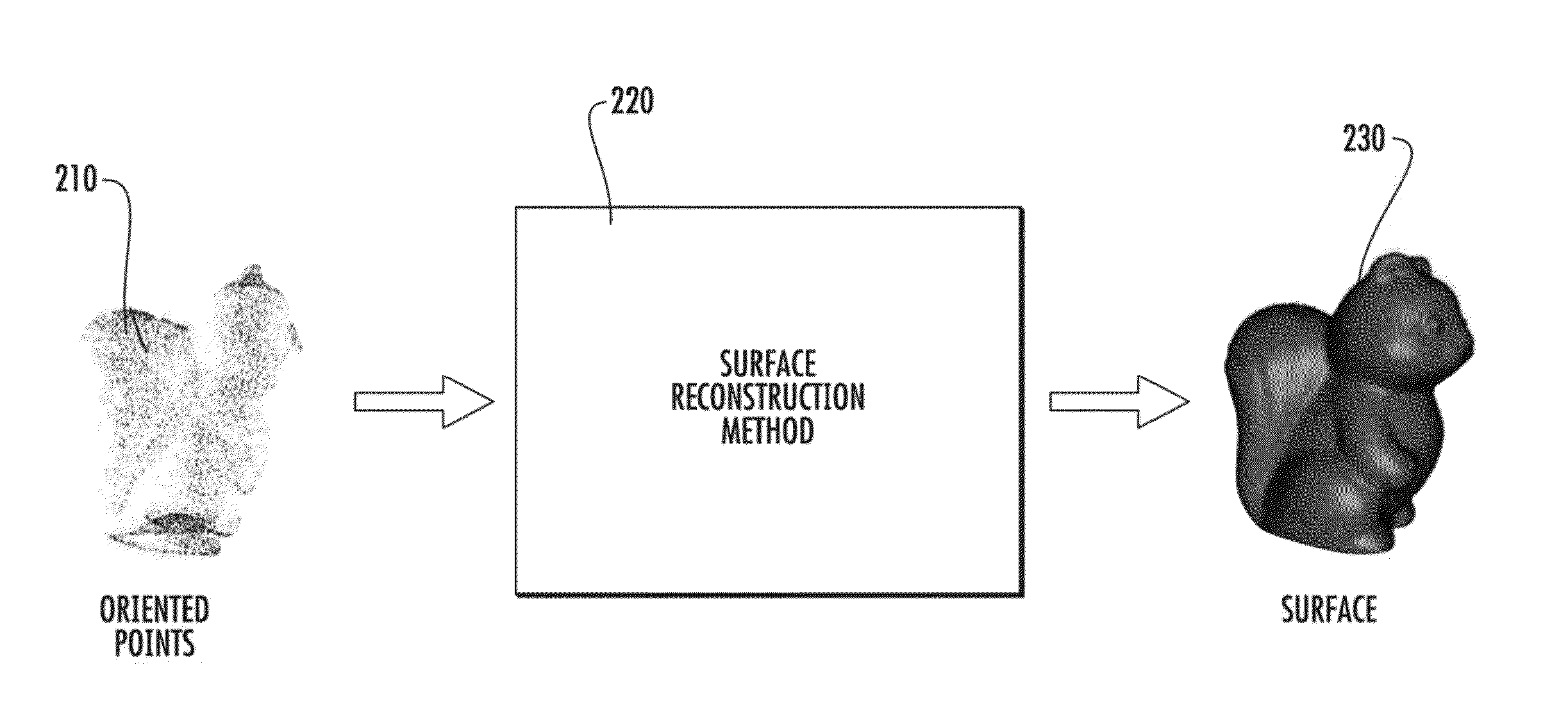
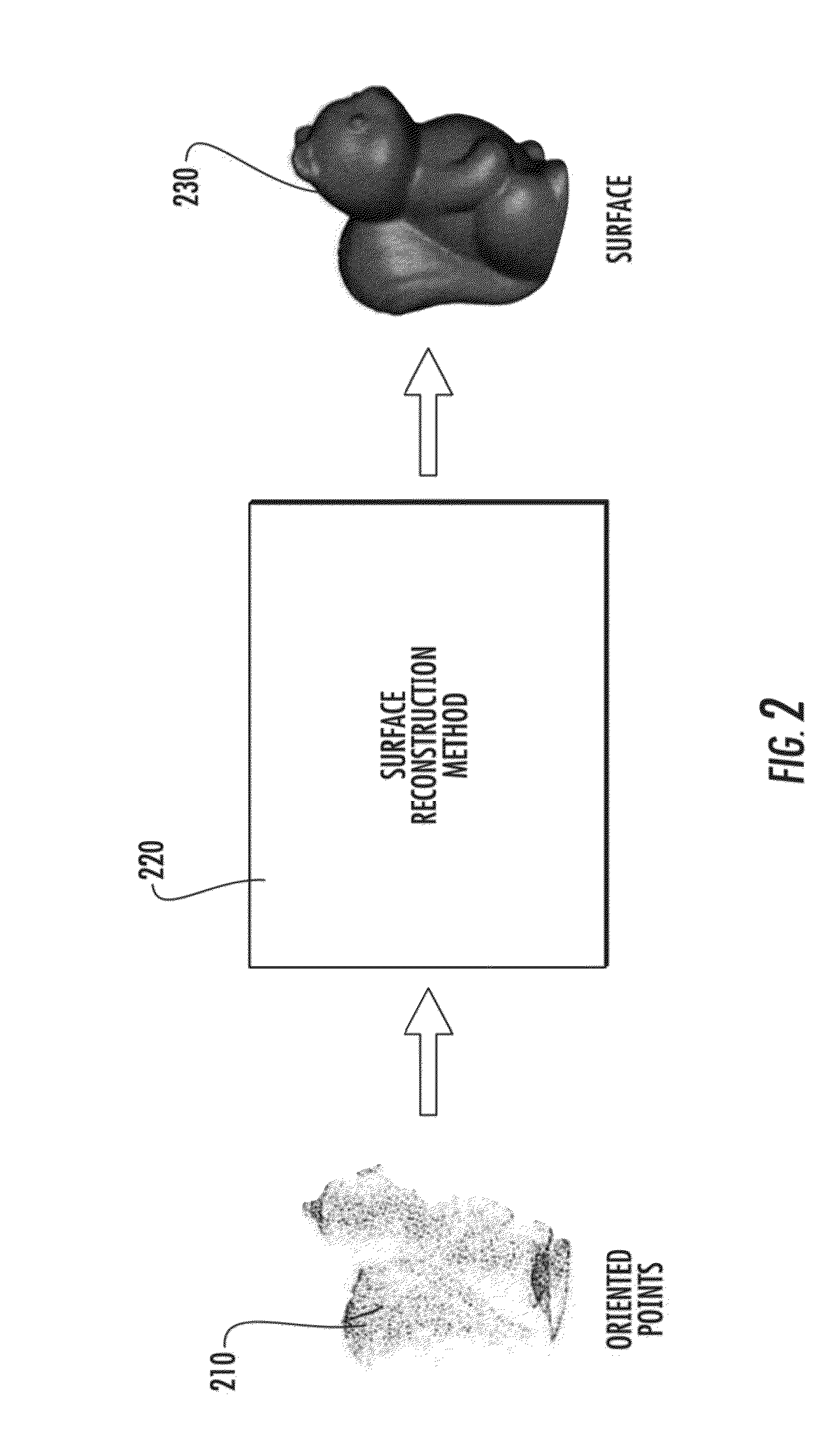
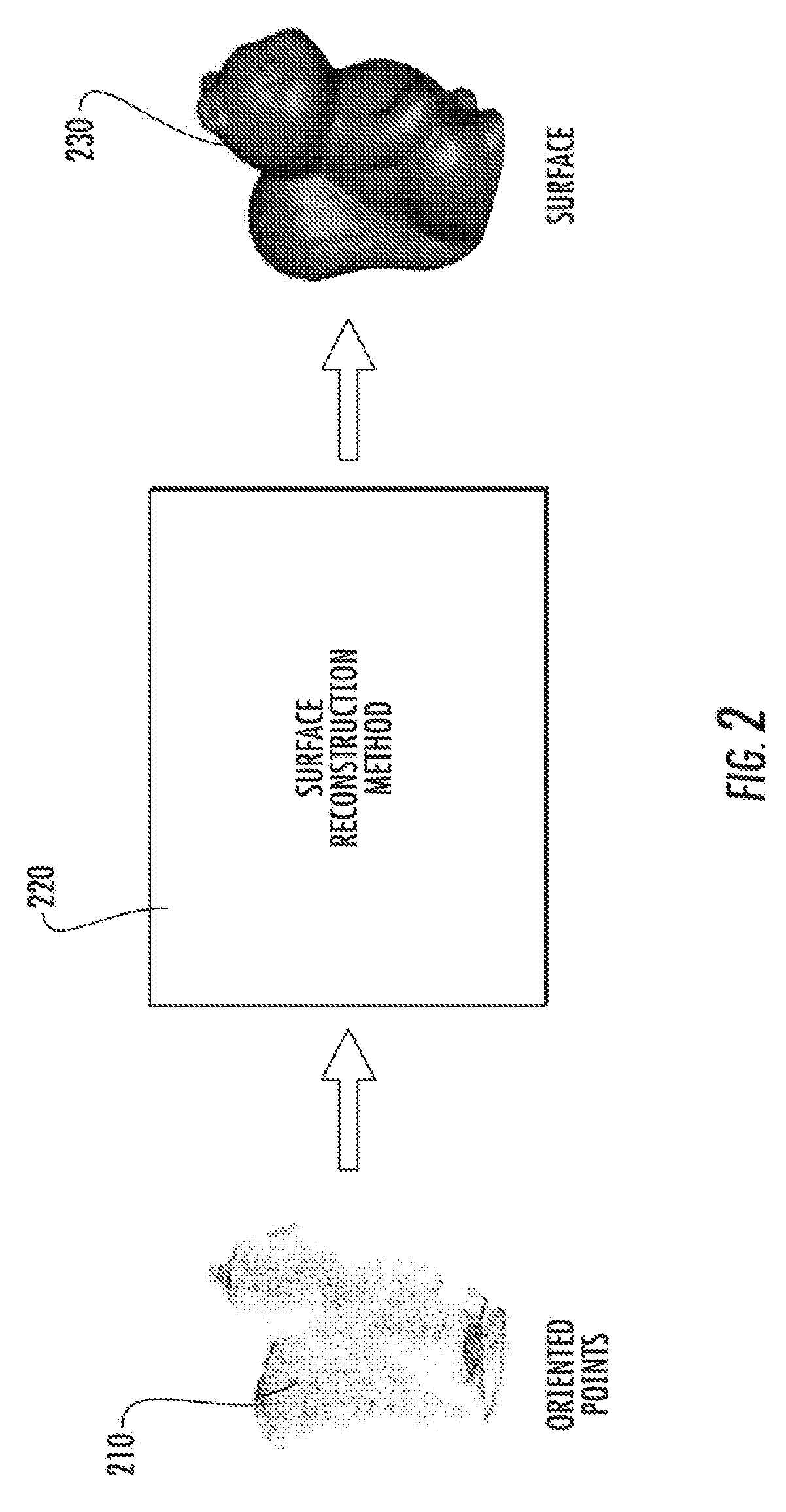
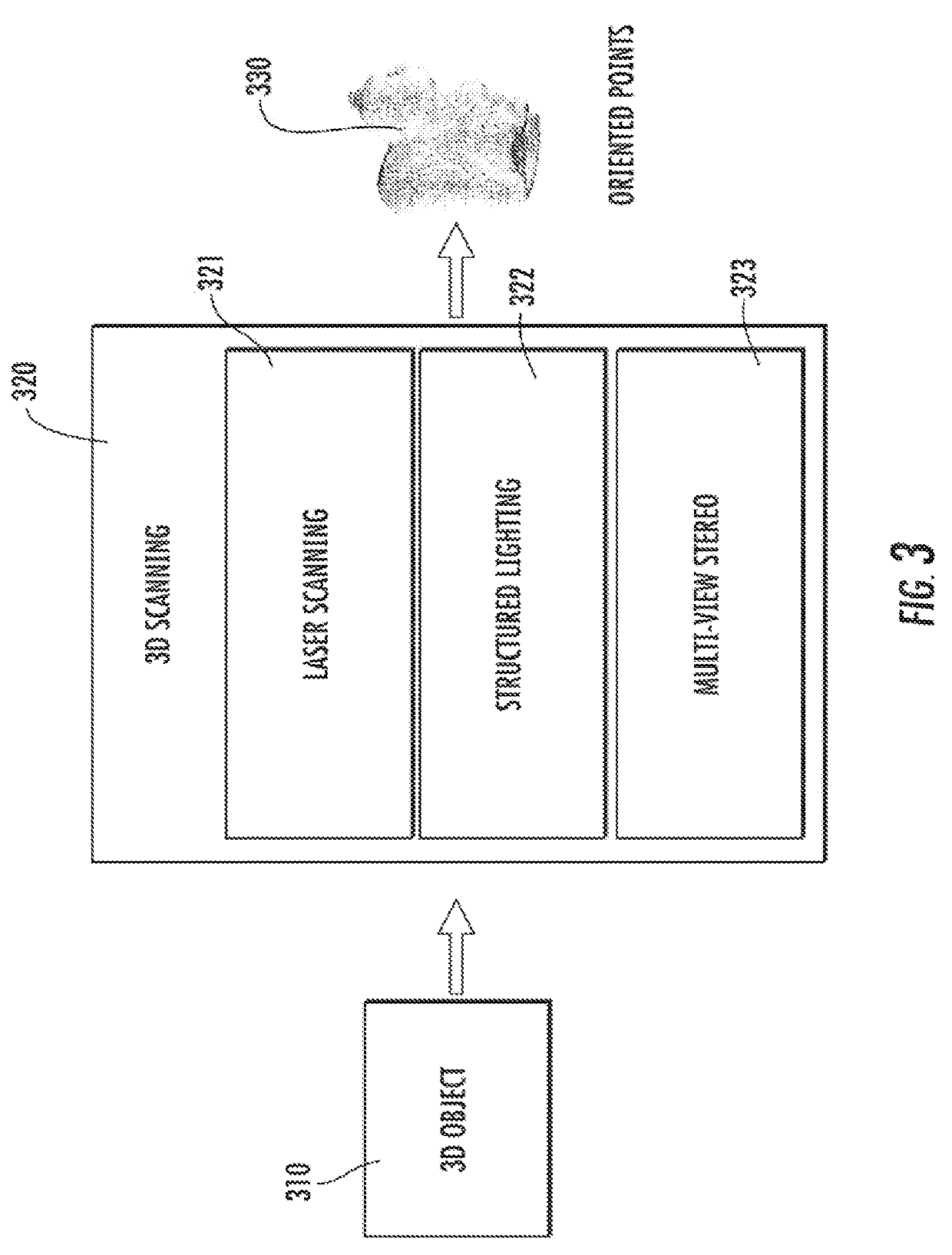
Method to reconstruct a surface from oriented 3-d points
InactiveUS20140172377A1Easy to implementQuality improvementSpecial data processing applicationsImage generationDiscretizationSymbol of a differential operator
A method for the problem of reconstructing a watertight surface defined by an implicit equation from a finite set of oriented points. As in other surface reconstruction approaches disctretizations of this continuous formulation reduce to the solution of sparse least-squares problems. Rather than forcing the implicit function to approximate the indicator function of the volume bounded by the surface, in the present formulation the implicit function is a smooth approximation of the signed distance function to the surface. Then solution thus introduced is a very simple hybrid FE / FD discretization, which together with an octree partitioning of space, and the Dual Marching Cubes algorithm produces accurate and adaptive meshes.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Method for segmenting image with non-uniform gray scale based on level set function
InactiveCN102354396AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyImage enhancementEnergy functionalComputer vision
The invention provides a method for segmenting an image with non-uniform gray scale based on a level set function. The method comprises the following steps: constructing the level set function; constructing image segmentation energy functional; and carrying out level set function evolution so that the energy functional is minimized so as to obtain an image segmentation boundary, wherein, the energy functional comprises a global energy statistical item, a local energy statistical item and an energy penalty item. In the invention, on the basis of a C-V (Chan-Vese) model, a Gaussian kernel function is introduced and the local statistical information for the image with the non-uniform gray scale is fully utilized so as to optimize the 'energy' functional for a minimized closed curve; and by adding the energy penalty item, convergence of a signed distance function (SDF) is ensured and the time-consuming reinitialization process is avoided. Experiments prove that by adopting the method for segmenting the image with the non-uniform gray scale, clear and accurate segmentation results can be obtained and the segmentation accuracy and efficiency for the image with the non-uniform gray scale can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
An object segmentation method based on prior shape and cv model
The invention relates to an object segmentation method based on a priori shape and a CV (Computer Vision) model. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a signed distance function by selecting the priori shape; carrying out affine transformation on the signed distance function of the priori shape according to vectors of affine transformation parameters, wherein the affine transformation parameters are changed and finally tend to stabilize in the process of iterating a level set function; and finally, obtaining various affine transformation parameters of the next time according to a level set iteration formula evolution movable outline curved line and various affine parameter iteration formulae. According to the method disclosed by the invention, on the basis of keeping rotary, zoom and translation invariance of a priori shape model, stretching in X and Y directions and shear unchanged constraint energy item can be increased; and a space object with larger posture transformation under a complex background can be well segmented by expanding the self-adaptive transformation of the priori shape.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
New path planning method based on regular grid DEM data
ActiveCN107228668AImprove efficiencyImprove effectivenessNavigational calculation instrumentsEvaluation resultRegular grid
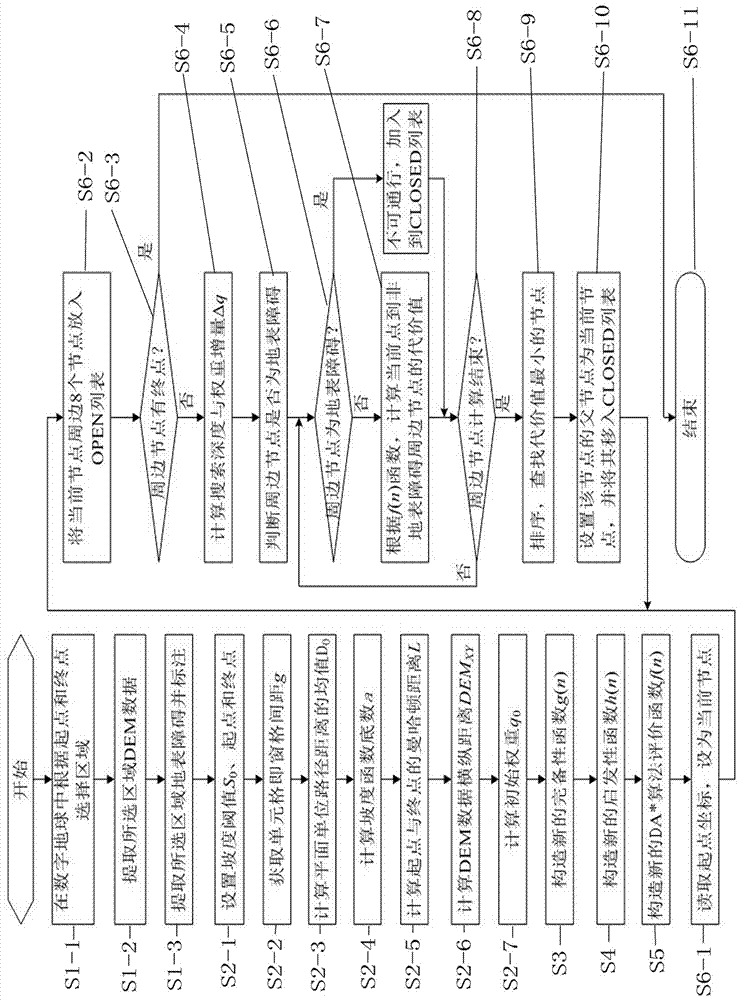
The present invention discloses a new path planning method based on regular grid DEM data. According to the new path planning method, the distance and the slope are used as the evaluation indexes of the path search; in order to balance the interaction between the distance and the slope, the complete function g(n) of a DA* algorithm is designed based on the distance function of the space path and the slope function constructed with the exponential function; the parameter in the function is calculated with the DEM data, and the new complete function g(n) is optimized so as to be adapted to the change of different resolutions of the DEM data; based on the same strategy and the function construction method, the new heuristic function h(n) of the DA* algorithm is constructed; and in order to improve the search efficiency of the algorithm, by setting the initial weight and dynamically adjusting the weight in the search process, the influence of the complete function and the heuristic function on the evaluation result is changed, such that the new constructed DA* path finding algorithm can efficiently search the appropriate path. According to the preset invention, the new path planning method can self-adapt to the DEM data resolution, and can be used in different application environments.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
System and method for hole filling in 3D models
InactiveUS7272264B2Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Digital image
A method for hole-filling in 3D models includes identifying vertices adjacent to hole boundaries in a mesh of points on a digital image and constructing a signed distance function based on vertices adjacent to hole boundaries. A Radial Basis Function is fit based on the constructed signed distance function and evaluated on a grid, which include the hole. The points on the hole surface are extracted and meshed to fill the hole.
Owner:IBM CORP
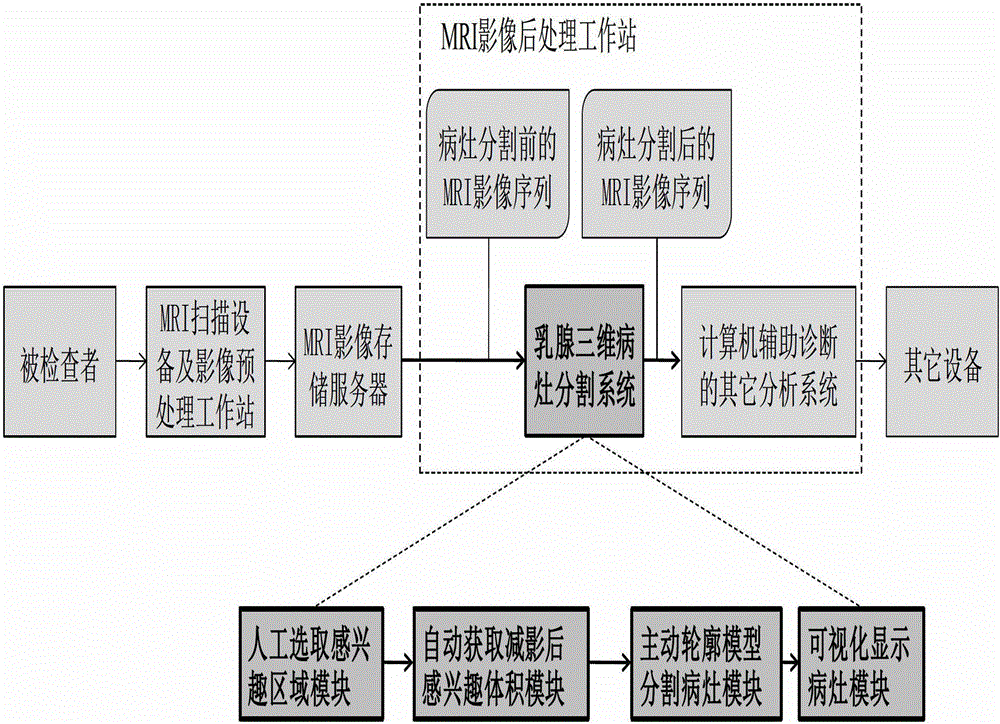
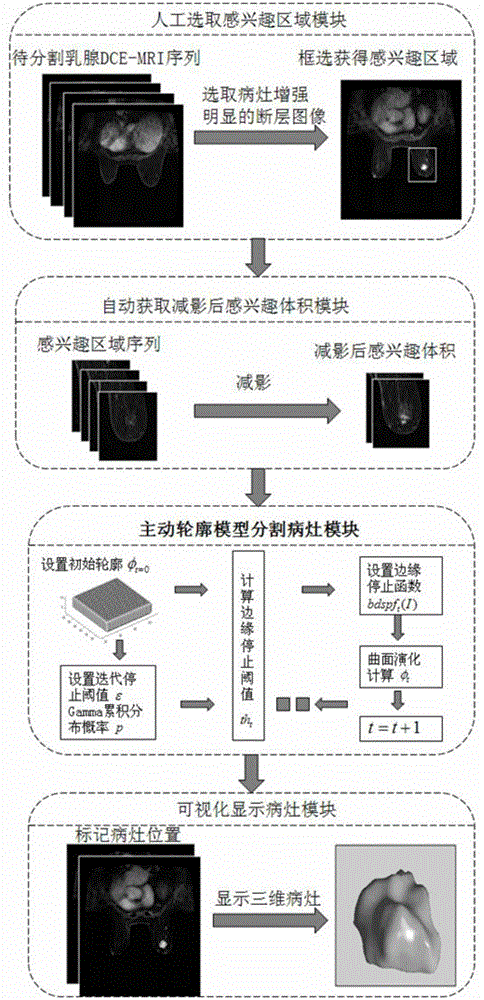
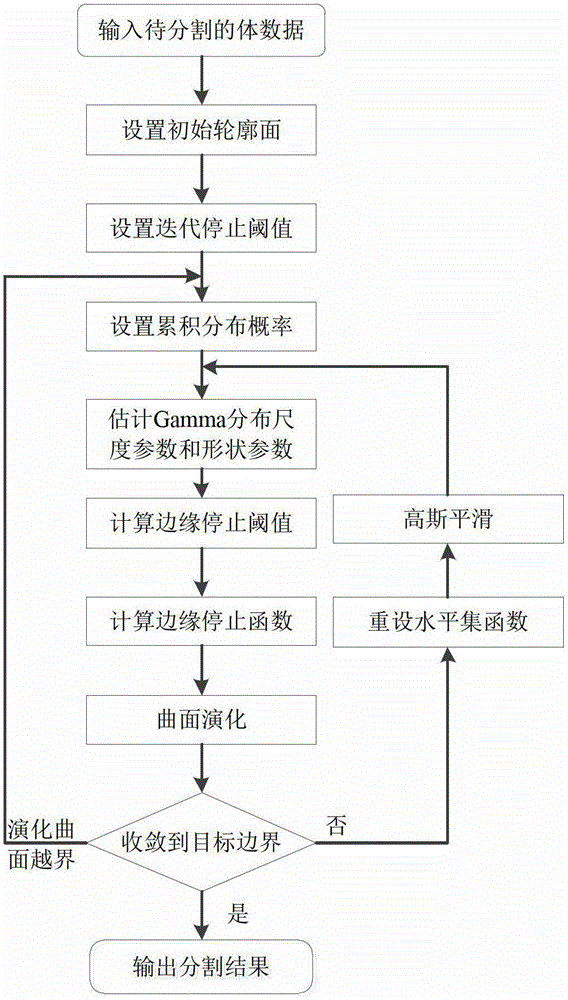
Active contour model based method for segmenting mammary gland DCE-MRI focus
ActiveCN103337074AReduce complexityAccurately identify fuzzy boundariesImage analysisContour segmentationSpeed of processing
An active contour model based method for segmenting mammary gland DCE-MRI focus belongs to the field of medical image segmentation and comprises the following steps: obtaining mammary gland DCE-MRI image sequence data by MRI scanning equipment; manually selecting a region of interest; automatically obtaining subtracted size of interest, active contour segmenting focus and visually display focus. According to the invention, based on the features that statistical distributions of mammary gland DCE-MRI image backgrounds are consistent and internal distributions in the focus are different, an edge stopping function of the active contour model is designed, thereby realizing reliable segmentation of the focus and effectively avoiding edge outleakage phenomenon; during the model evolutionary process, re-initialization of a signed distance function is not required, so that the real-time performance of the system is higher. The method has a lower requirement on manual operation in implementation, is high in intelligent degree, low in data storage space requirement, and quick in processing speed, and can effectively obtain comprehensive and steric space information of the focus through three-dimensional angle segmentation, which facilitates the multi-angle observation and analysis of the focus by a doctor.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
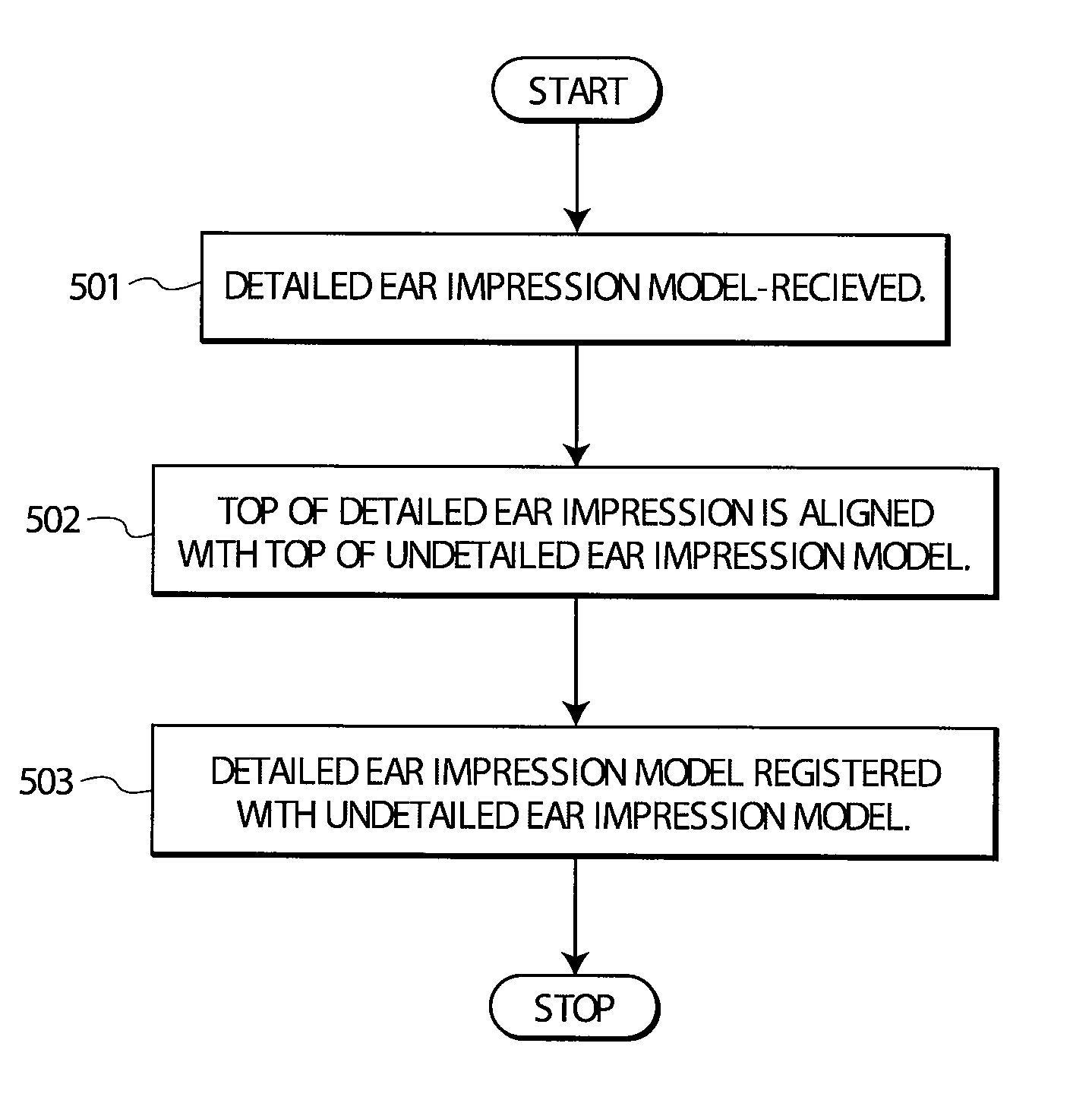
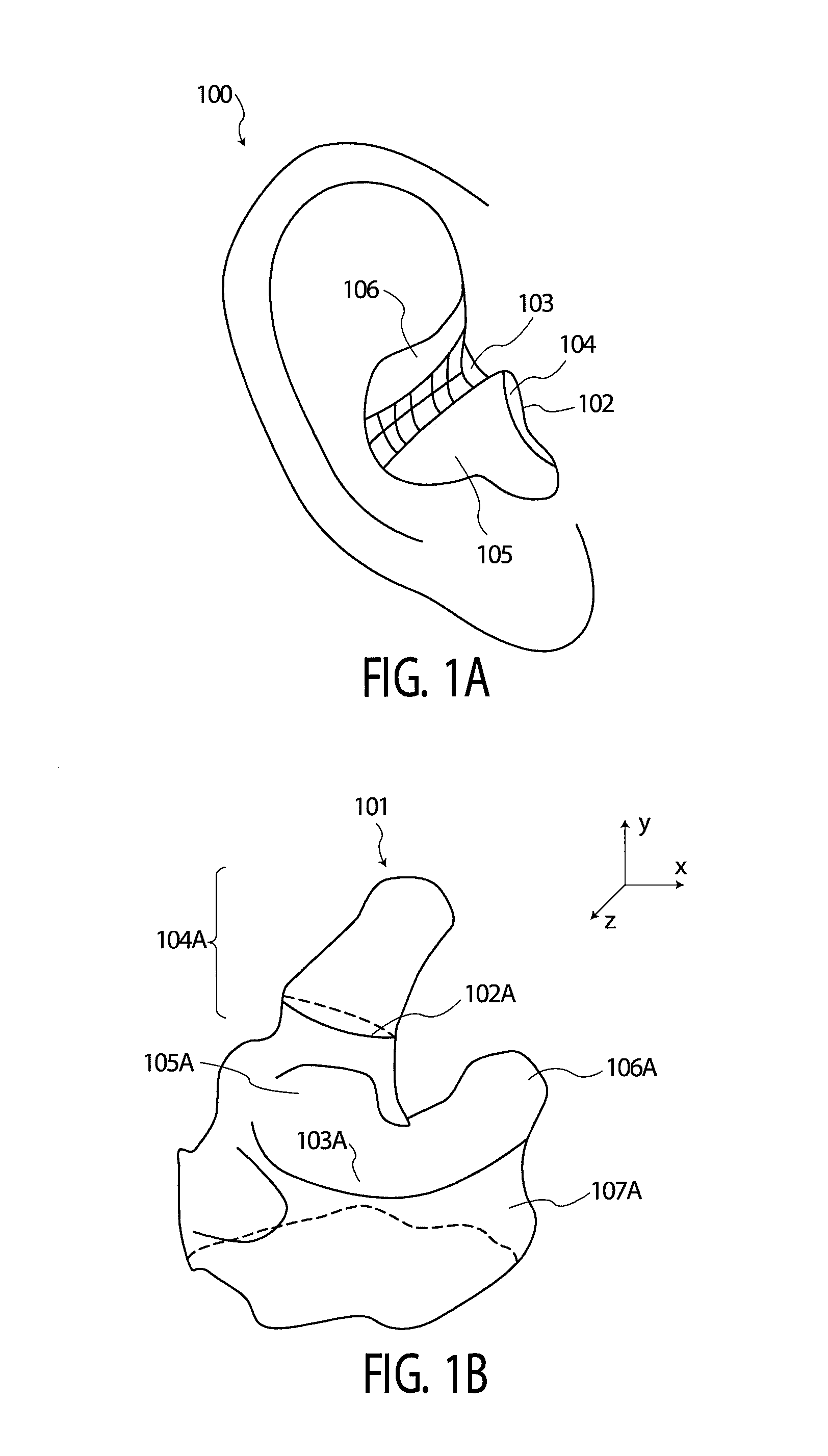
Method and apparatus for the rigid and non-rigid registration of 3D shapes
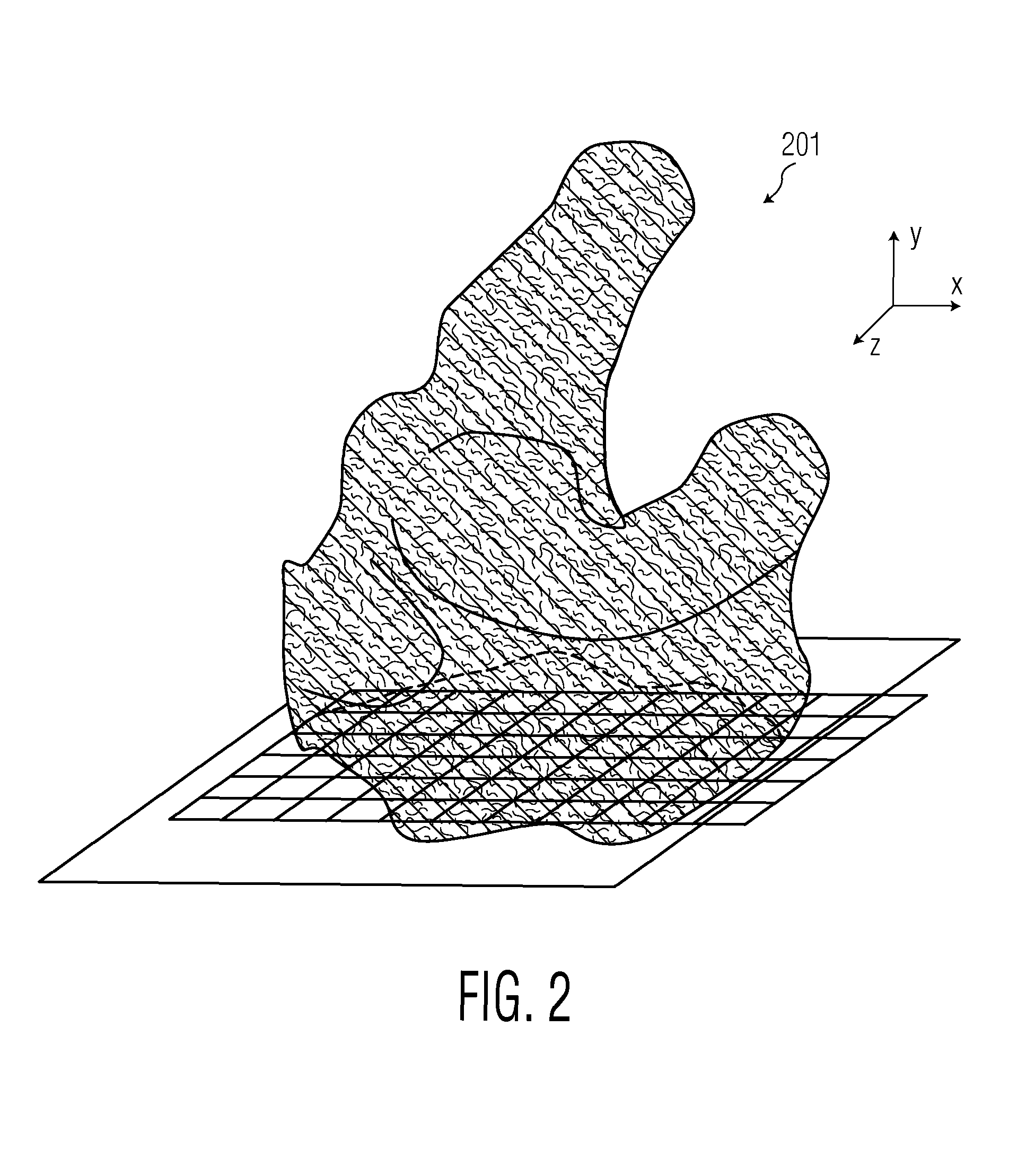
InactiveUS7801708B2Minimizing energyFully automatedImage enhancementImage analysis3d shapesThree dimensional shape
A method for registering two three-dimensional shapes is disclosed whereby the two shapes are represented as zero level set of signed distance functions and the energy between these two functions is minimized. In a first embodiment, two undetailed ear impression models are rigidly registered with each other. In another embodiment, a detailed ear impression is initially aligned with an undetailed ear impression model and, then, the detailed ear impression model is rigidly registered with the undetailed ear impression model as a function of the signed distance functions. In accordance with another embodiment, an undetailed ear impression model is non-rigidly registered with a template ear impression model as a function of the signed distance functions.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and Apparatus for the Rigid and Non-Rigid Registration of 3D Shapes
InactiveUS20070058829A1Simple methodMinimizing energyImage enhancementImage analysis3d shapesThree dimensional shape
A method for registering two three-dimensional shapes is disclosed whereby the two shapes are represented as zero level set of signed distance functions and the energy between these two functions is minimized. In a first embodiment two undetailed ear impression models are rigidly registered with each other. In another embodiment, a detailed ear impression is initially aligned with an undetailed ear impression model and, then, the detailed ear impression model is rigidly registered with the undetailed ear impression model as a function of said signed distance functions. In accordance with another embodiment, an undetailed ear impression model is non-rigidly registered with a template ear impression model as a function of said signed distance functions.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Mould cavity numerical control machining spiral curve track planning method
InactiveCN101452284AControl residual heightImprove processing efficiencyProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlVelocity function
The invention relates to a method for programming a spiral curve track through die cavity numerical control machining .The boundary of a die cavity is embedded into a level set function of a high one-dimensional space; a zero level set of the level set function is the boundary of the die cavity; and the level set function is initialized to a sign distance function. Bias of the boundary of the die cavity is obtained through the solution of a level set equation; and a speed function of the level set equation is corrected so that a high-curvature region can be smooth in generating a bias line. The distance between the bias lines is controlled through the control of time for boosting the boundary; in the process of boosting the boundary of the die cavity, the complex topological change is naturally treated; and the spiral curve track is programmed in different regions respectively. The method is suitable for programming a cutter track of a numerical control machining system with a common die cavity and a complex die cavity; the cutter track is continuous and smooth; and for the complex die cavity with island, the method can realize automatic division in regions and carry out spiral curve track programming in different regions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Dual range vehicle remote
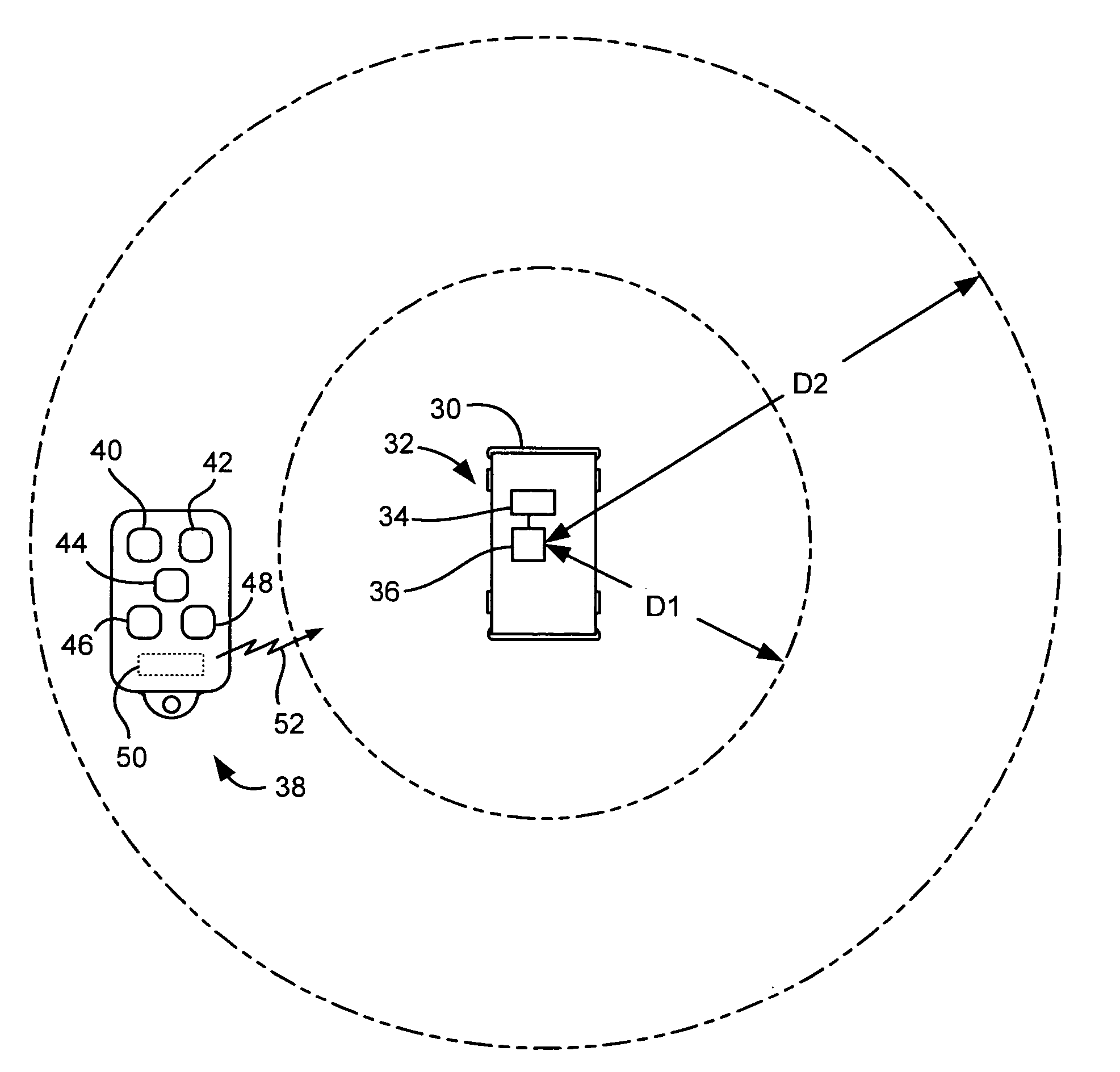
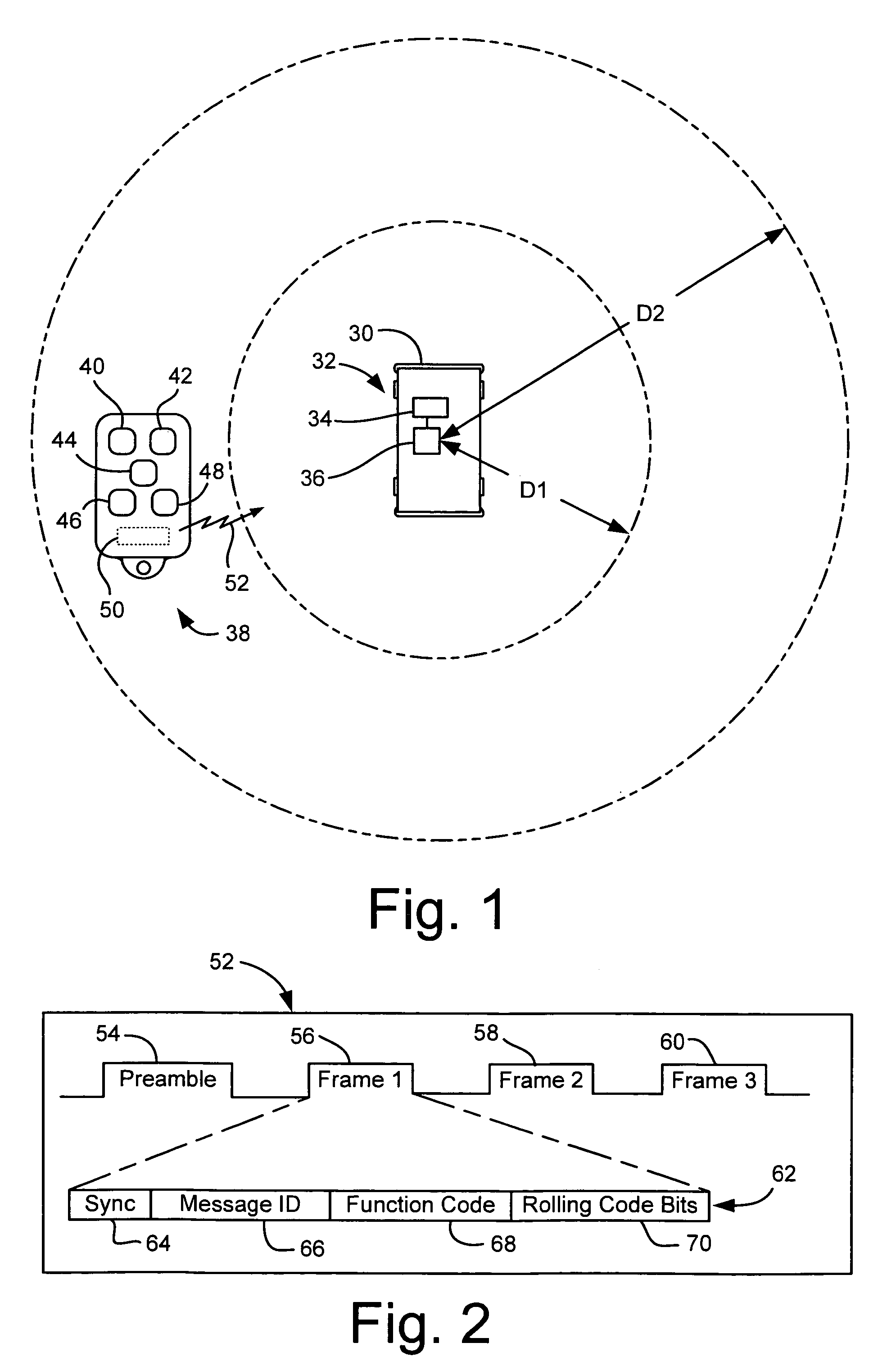
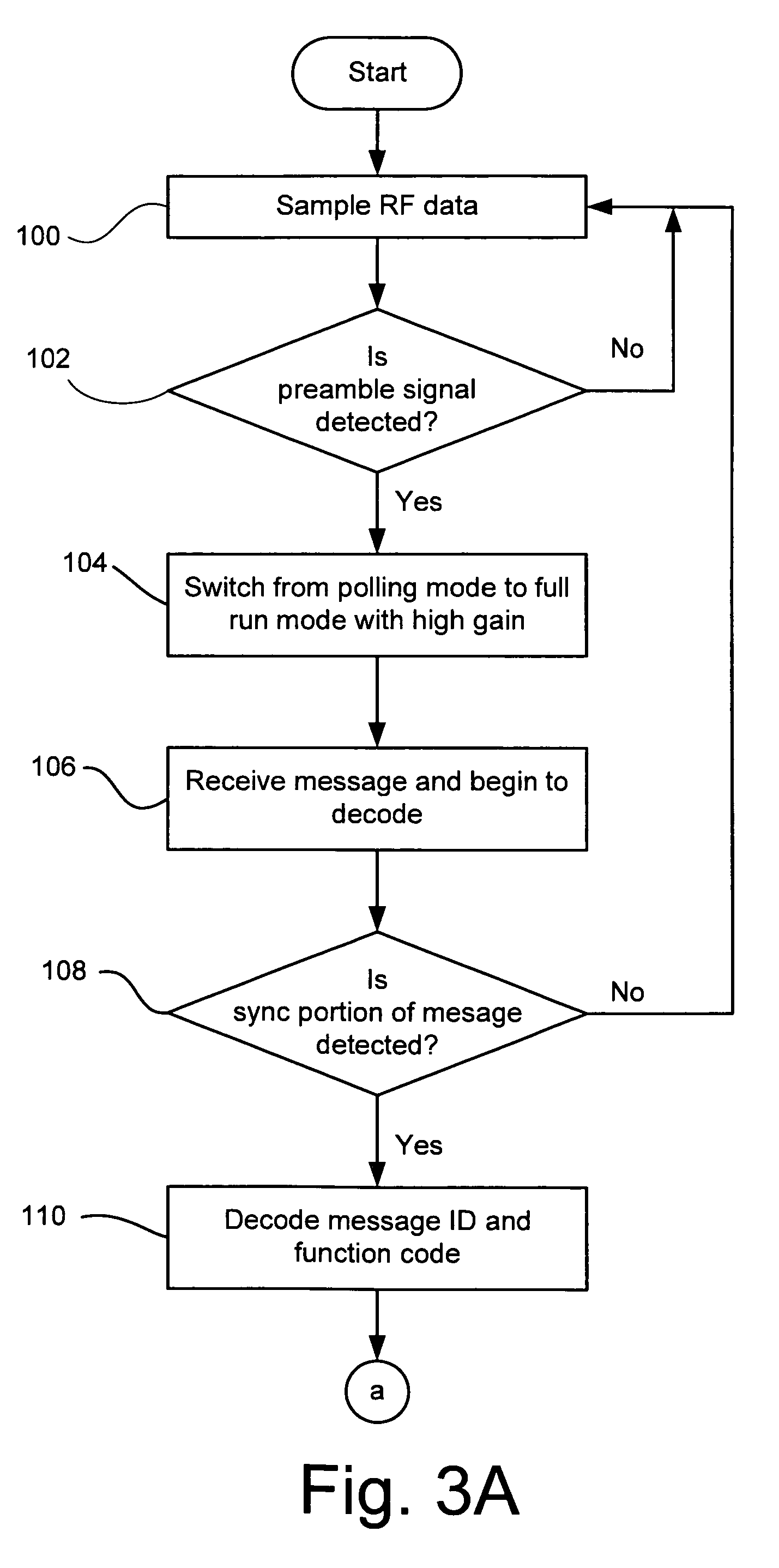
InactiveUS7397344B2Avoid accidental activationProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsShortest distanceRadio frequency signal
Owner:LEAR CORP
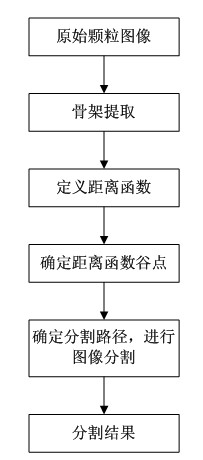
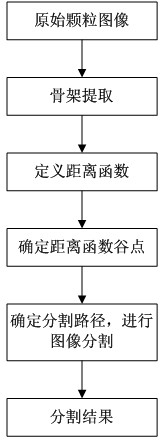
Segmentation method for adhering grain binary image
InactiveCN102663700AImprove Segmentation AccuracyReasonable divisionImage enhancementImage segmentationComputer vision
The invention relates to the technical field of complex grain image segmentation, in particular to a segmentation method for an adhering grain binary image. The segmentation method comprises the following steps: 1, extracting a skeleton of a target object for a binary area target; step 2, defining a boundary distance function of the skeleton in an Euclidean space; step 3, figuring out a minimum point, namely valley point, of the boundary distance function of the skeleton; and 4, taking the valley point as a center to segment the target object according to the minimum difference quotient of the area boundary distance function. The method provided by the invention facilitates segmentation of an adhering target area object in a binary image and has good antijamming capability.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method to reconstruct a surface from partially oriented 3-d points
InactiveUS20190259202A1Easy to implementQuality improvementImage generation3D modellingDiscretizationSmoothing approximation
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
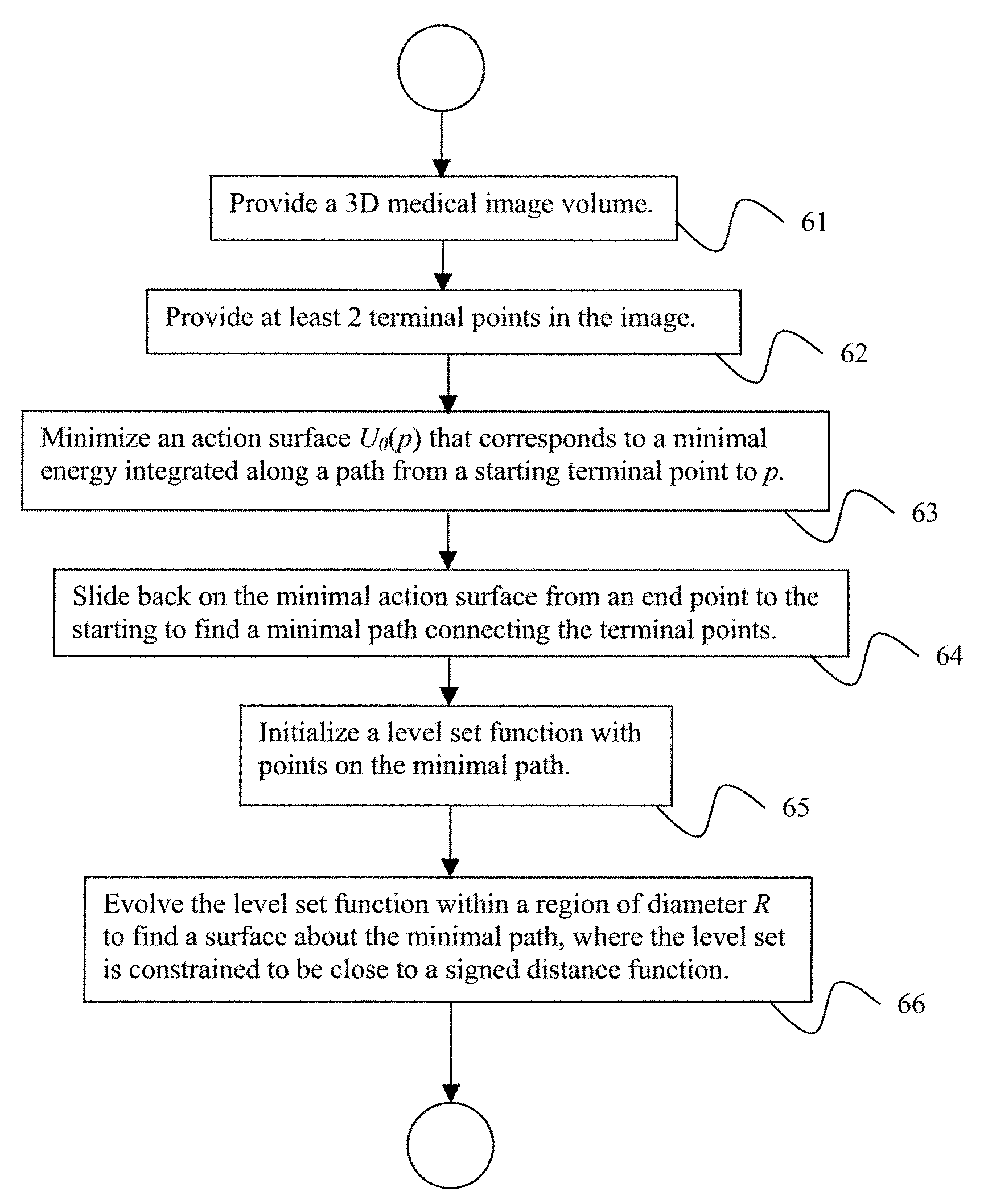
System and Method for Robust Segmentation of Tubular Structures in 2D and 3D Images
InactiveUS20090041315A1Fast computerUser input is slowImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageDigital image
A method for segmenting tubular structures in medical images includes providing at least a start point and an end point in a digital image volume, minimizing an action surface U0(p) which, at each image point p, corresponds to a minimal energy integrated along a path that starts at start point p0 and ends at p, sliding back on the minimal action surface from an end point to the start point to find a minimal path connecting the terminal points, initializing a level set function with points on the minimal path, and evolving the level set function to find a surface of a structure about the minimal path, wherein the level set function is constrained to be close to a signed distance function and wherein the level set function is prevented from growing wider than a predetermined diameter R, wherein the surface about the minimal path defines a tubular structure.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
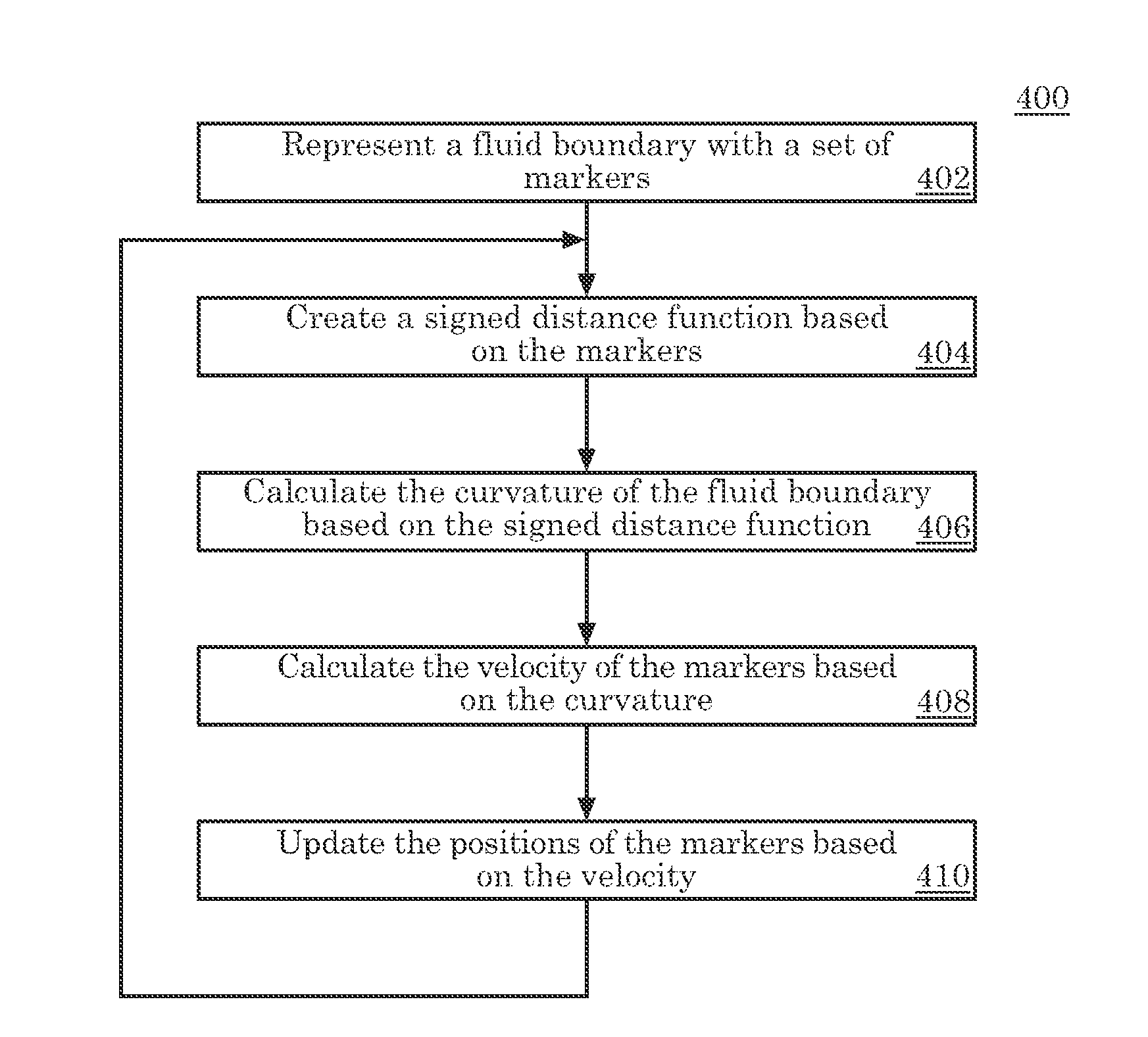
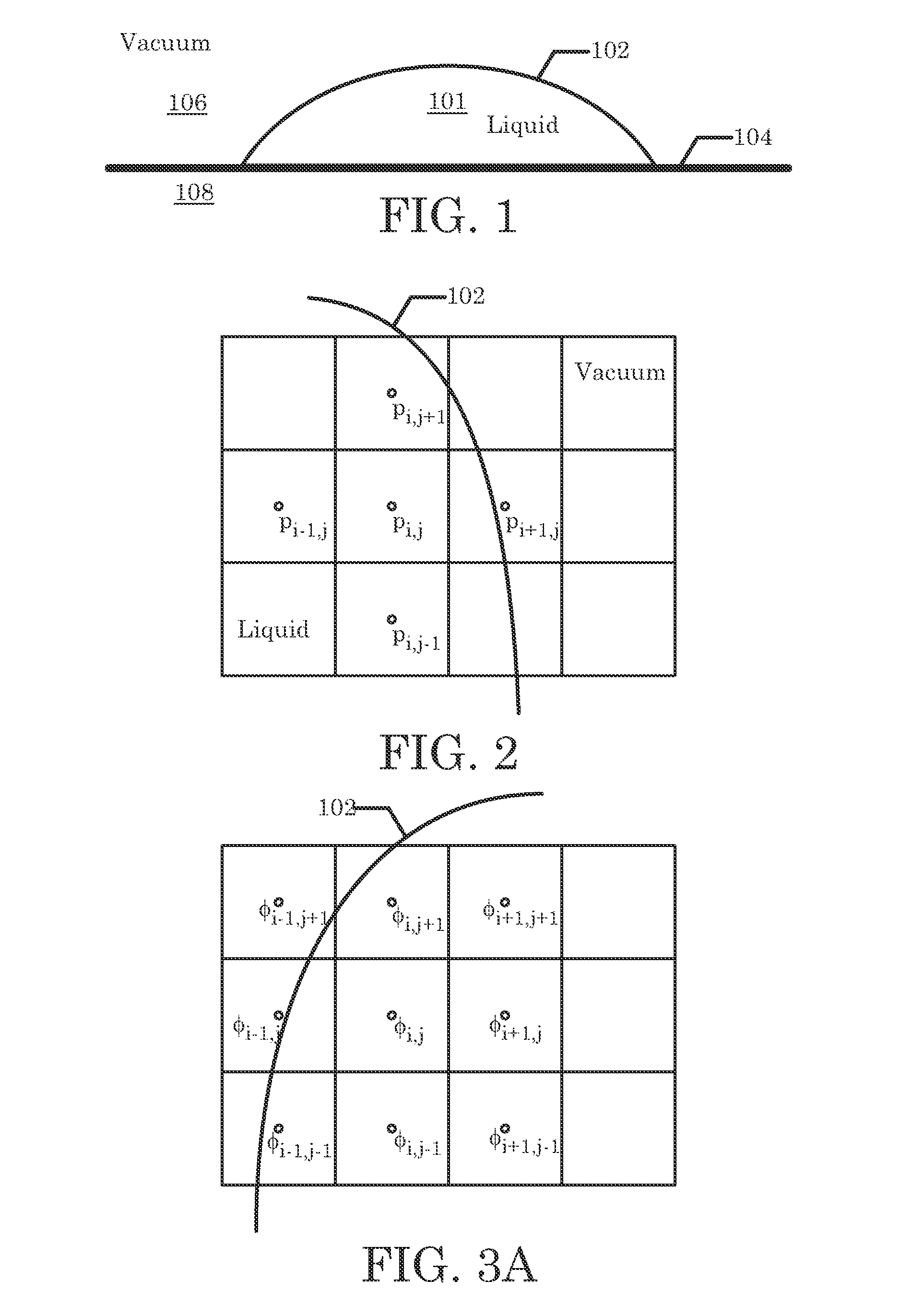
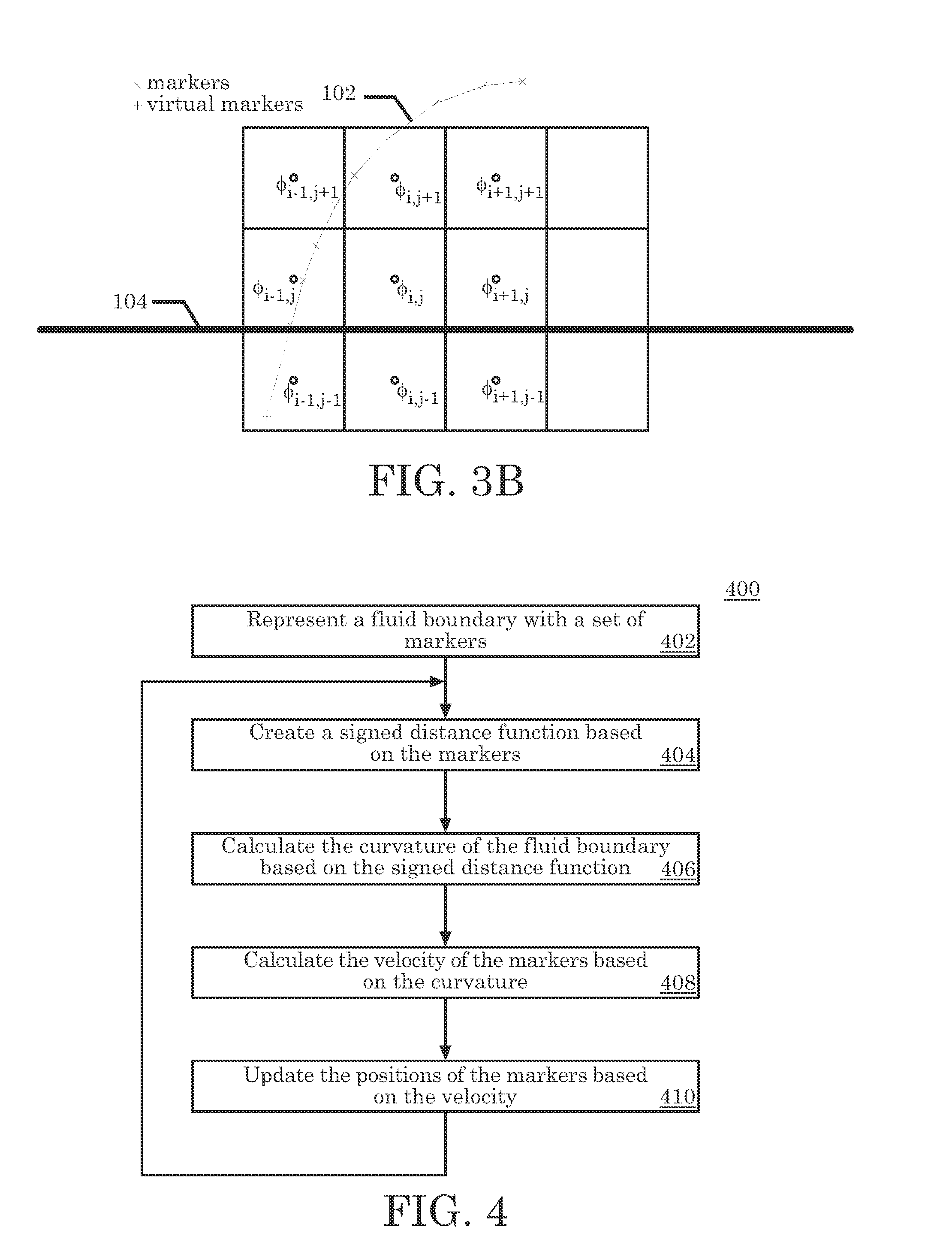
Hybrid method for enforcing curvature related boundary conditions in solving one-phase fluid flow over a deformable domain
InactiveUS7813907B2Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHybrid approachSingle phase
An embodiment of the present invention may be a system or method for simulating the flow of a single-phase fluid flow. Markers represent a moving fluid boundary of the single-phase fluid at a first point in time. The moving fluid boundary separates a simulation space into a fluid space and a non-fluid space. The single-phase fluid inhabits the fluid space. A signed distance function is evaluated at points surrounding the moving fluid boundary based upon markers. The curvature of the moving fluid boundary based on the signed distance function is evaluated near the markers in the non-fluid space. The curvature is not evaluated at the moving fluid boundary. The velocity of the fluid is calculated based upon the curvature of the level set in the non-fluid space. Update the position of the moving fluid boundary at a second point in time based on the velocity of the fluid.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
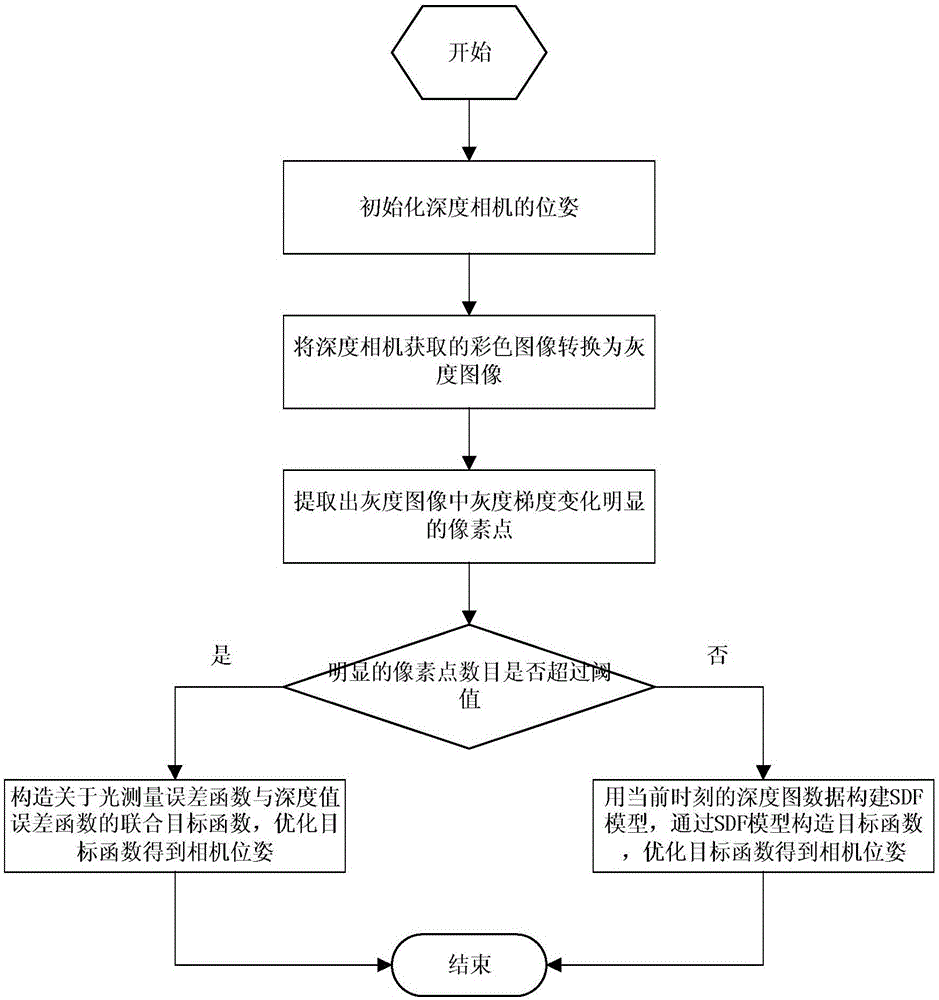
Camera tracking method for depth cameras
The invention discloses a camera tracking method for depth cameras. A camera tracking mode based on visual information or a camera tracking mode based on depth information is chosen according to whether the feature points of a gray image are obvious. A joint objective function about optical measurement error and depth value error is constructed in the camera tracking mode based on visual information. An objective function about a signed distance function model is constructed in the camera tracking mode based on depth information. Through dual-mode switching, the applicability of the system is enhanced, and the stability of the system is improved.
Owner:合肥朱曦科技有限公司
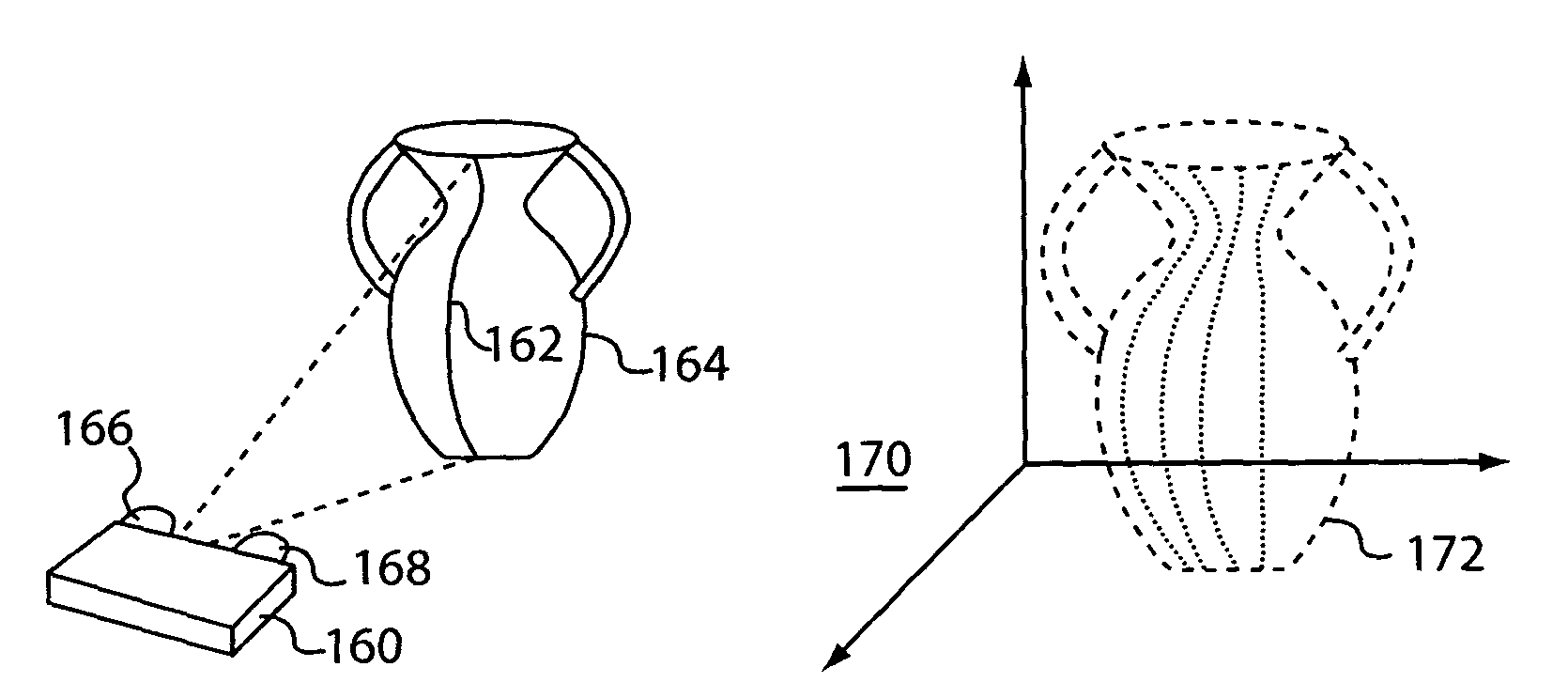
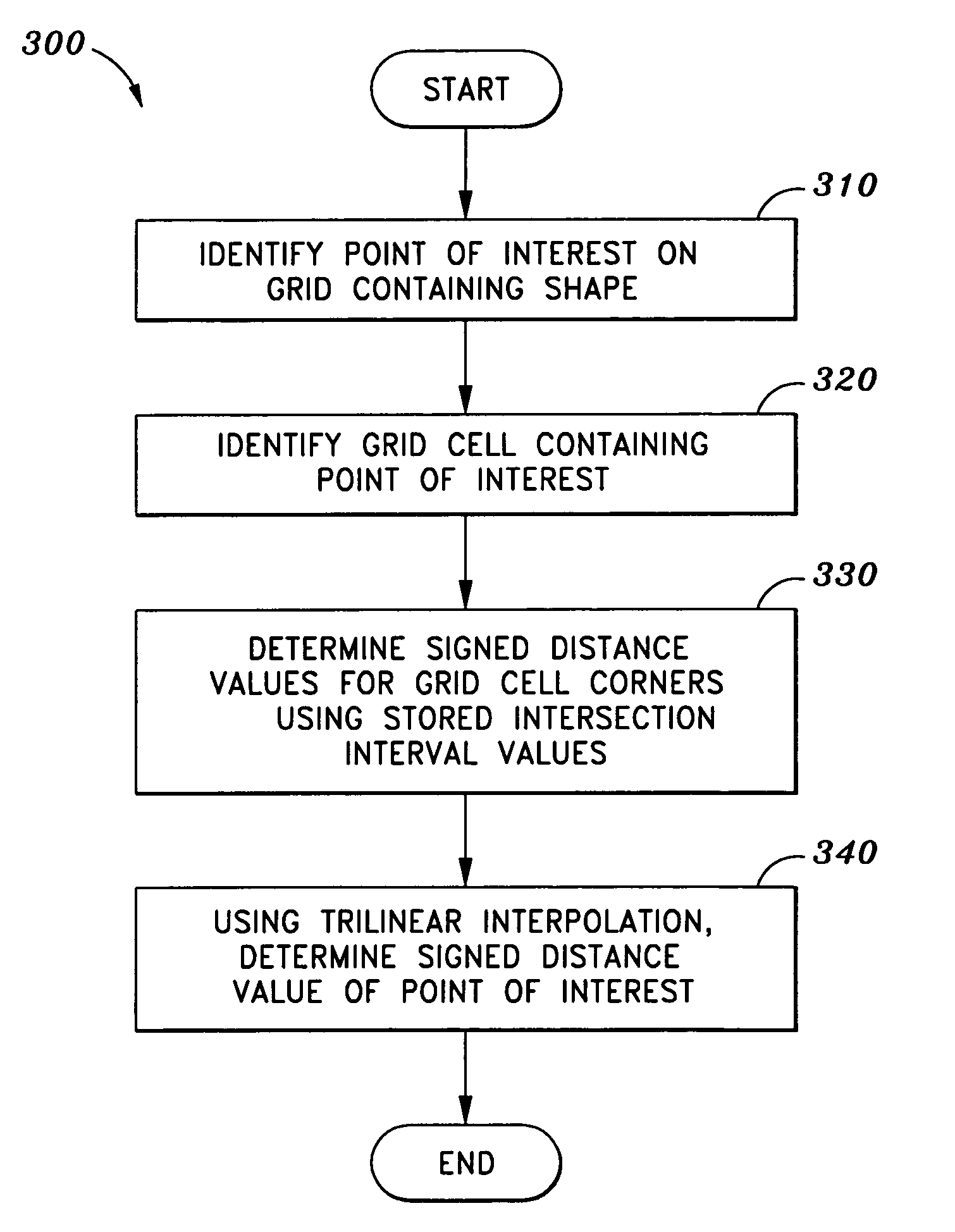
Systems and methods for representing signed distance functions
A system and method for implicitly computing signed distance values in a graphics application. In one embodiment, rather than storing numerous distance values along a given raster scan line, only two values are stored for each interval defining the intersection of the raster scan line with the shape. These two values represent the interior of the object to be rendered along a given grid line. In another embodiment each grid line may be parameterized (e.g., from 0 to 1). Each intersection interval may then be represented by the parameter value at an entry point of the surface and an exit point of the surface, along the given grid line.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
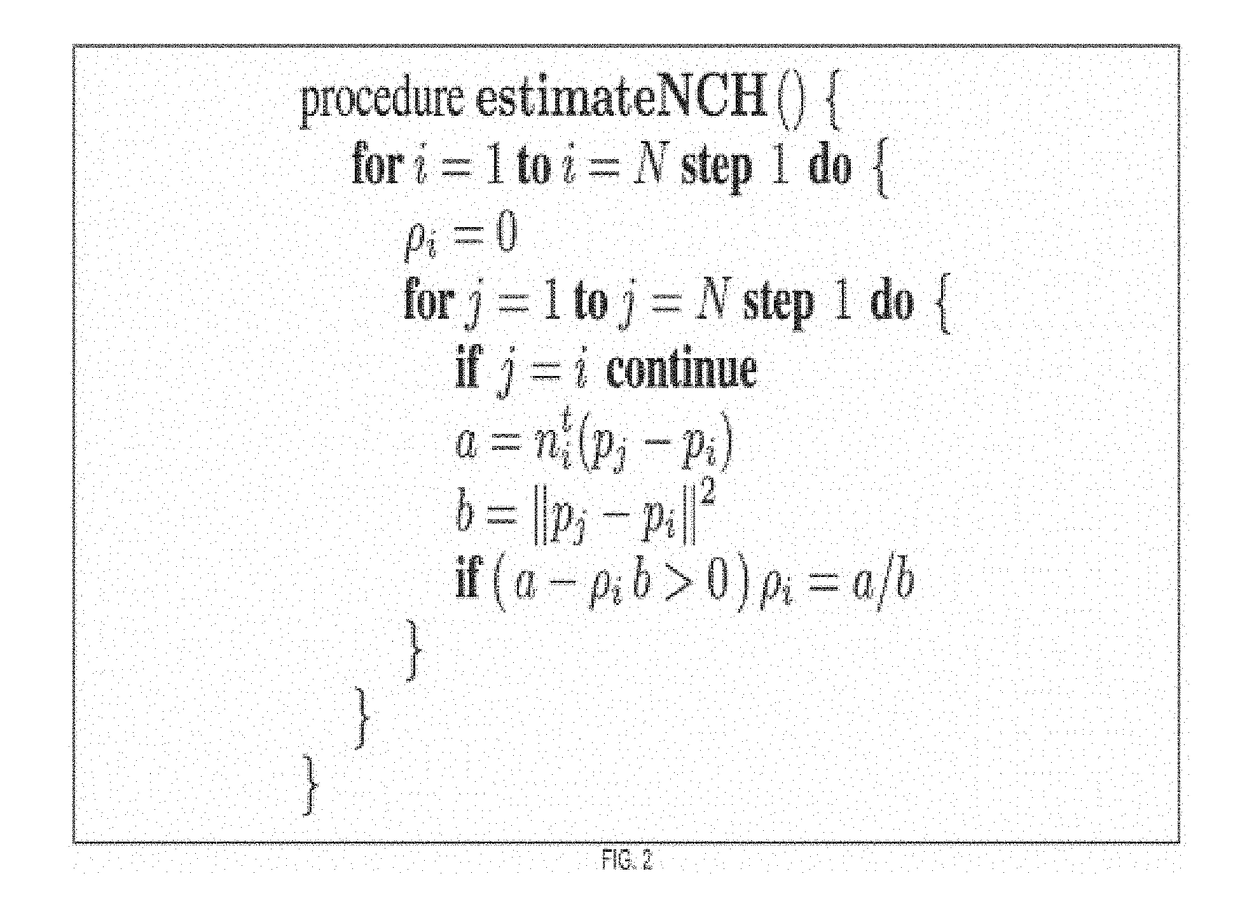
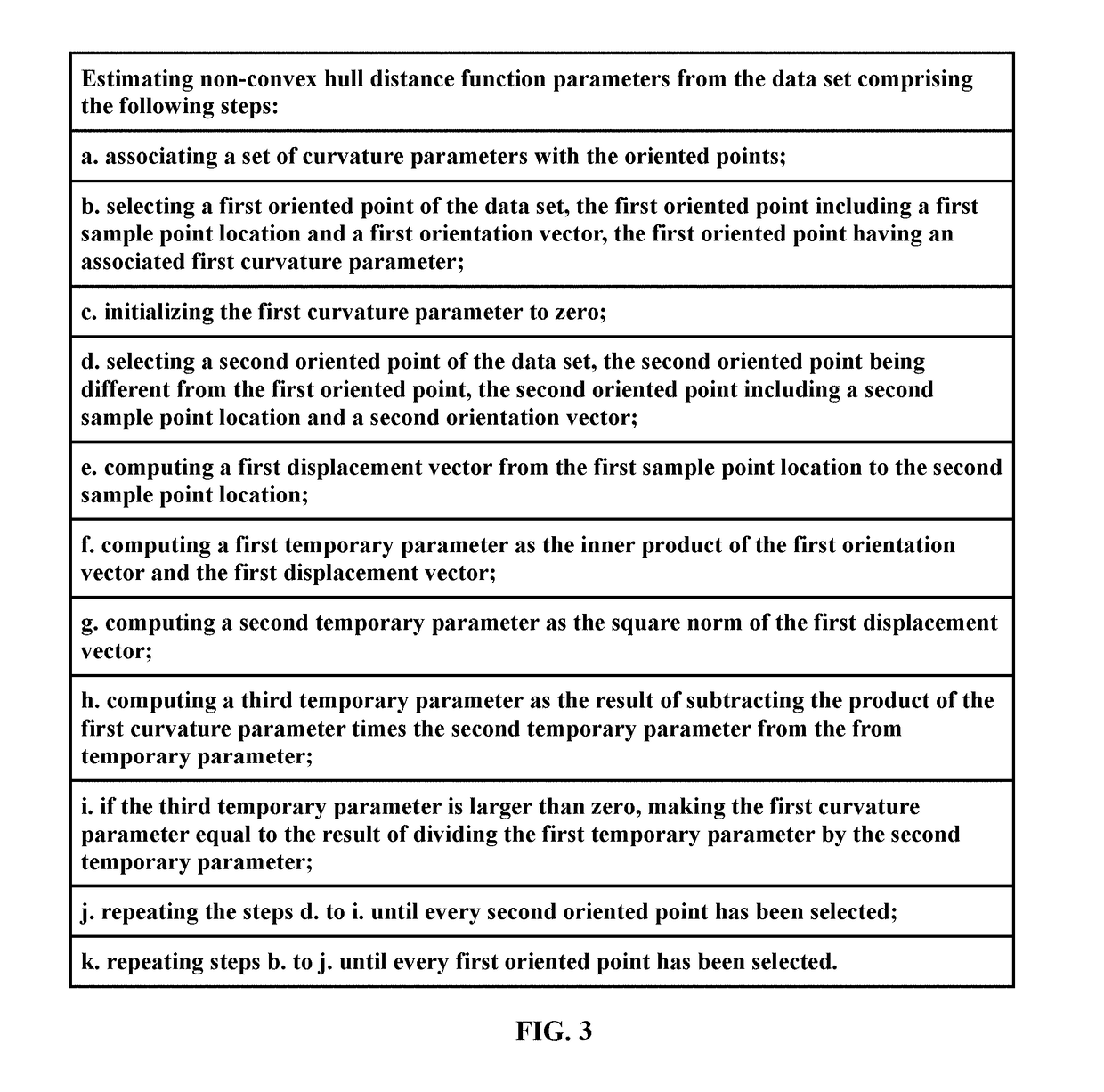
Non-convex hull surfaces
ActiveUS20150120260A1Computation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsData setPolygon mesh
The invention is a computer implemented method, device, system, or article for reconstructing a surface of an object. In particular, the invention comprises estimating a non-convex hull signed distance function parameters from a data set of an object and evaluating the non-convex hull signed distance function on vertices of a volumetric mesh. The invention further comprises approximating the zero level set of the non-convex hull signed distance function by a polygonal mesh using an isosurface algorithm to provide surface reconstruction of an object.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Hierarchical fuzzy C-means based image segmenting method
The invention discloses a hierarchical fuzzy C-means based image segmenting method. The hierarchical fuzzy C-means based image segmenting method includes simultaneously applying mean templates to the membership degree and the distance function so as to acquire better image segmenting results, effectively utilizing spatial context messages in images and acquiring better image segmenting quality. Meanwhile, operation time and calculation amount of the algorithm are lower, and the distance function is a hierarchical fuzzy C model, that is, the distance function is considered as a sub-fuzzy C-mean model, so that the distance function has better noise immunity than the conventional Euclidean distance function. The algorithm of the hierarchical fuzzy C-means based image segmenting method has better robustness.
Owner:广州市元博信息科技有限公司
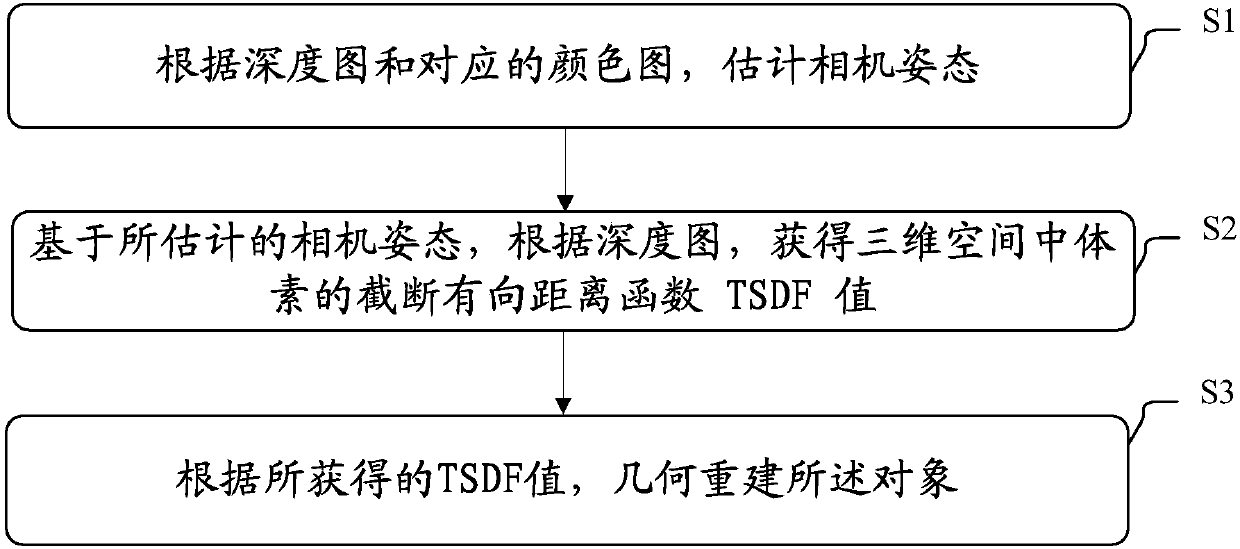
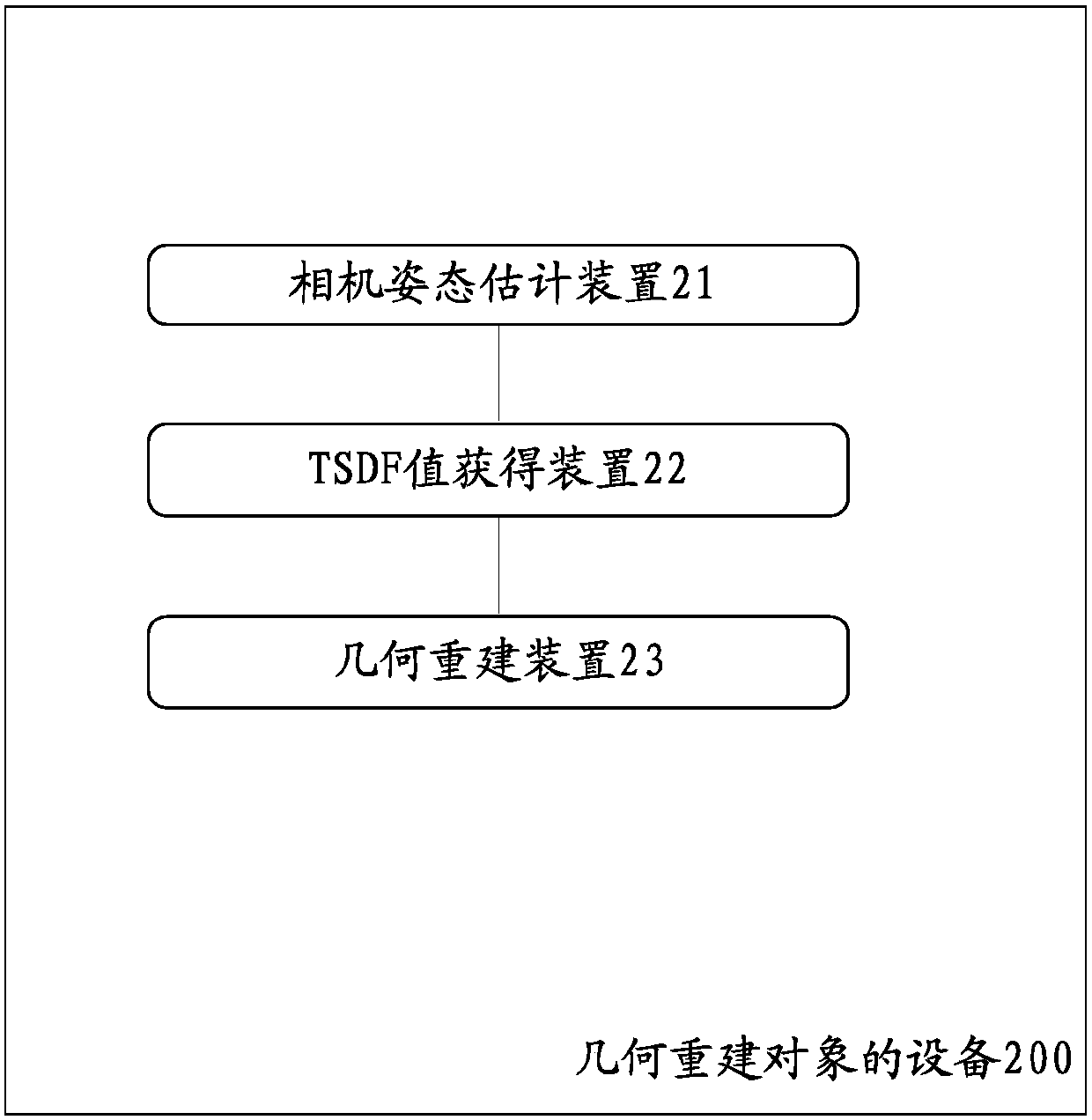
Method and device for geometrical reconstruction of object
The present invention discloses a method and a device for geometrical reconstruction of an object. The method comprises the steps that: estimating a camera attitude according to a depth map and a corresponding color map; obtaining TSDF (Truncated Signed Distance Function) values of voxels in a three-dimensional space according to the depth map based on the camera attitude; and performing geometrical reconstruction of an object according to the TSDF values, wherein an optimization problem is solved to estimate the camera attitude according to the depth map and the corresponding color map, and acost function is related to the following factors: a quadratic sum of distances of three-dimensional points of a current frame regulated through the camera attitude to be estimated in a camera coordinate space and corresponding three-dimensional points of all the previous frames in a global coordinate space, a quadratic sum of distance measures of colors, on a corresponding color map of the current frame, of the three-dimensional points of all the previous frames, regulated through the camera attitude to be estimated, in the global coordinate space and corresponding colors of all the previousframes in the global coordinate space, and non-rigid transformation of pixel positions of the three-dimensional points in the depth map or the color map.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
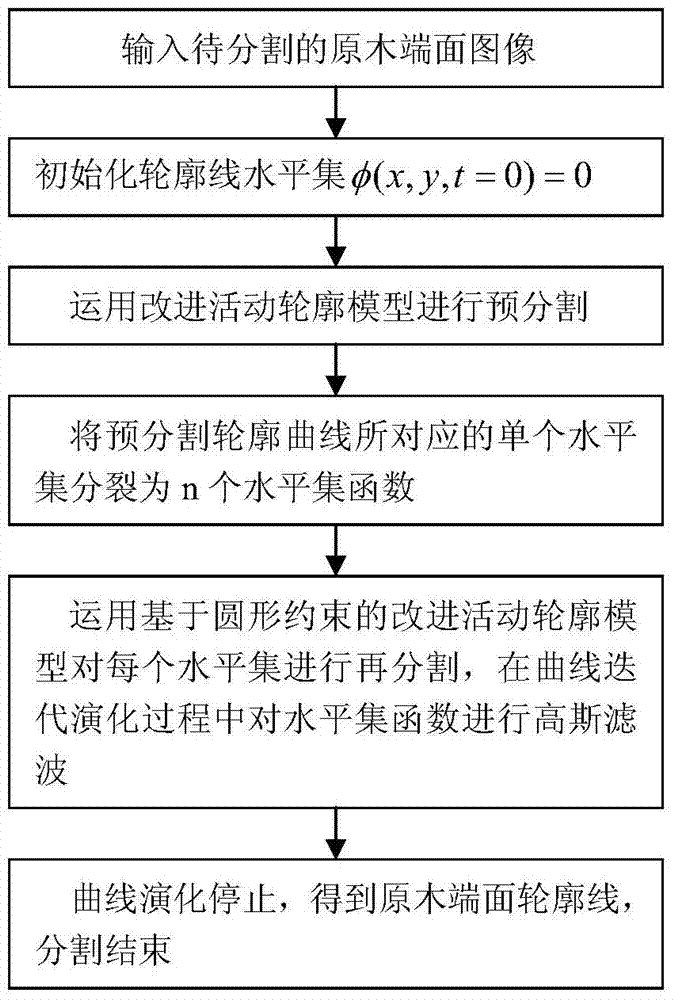
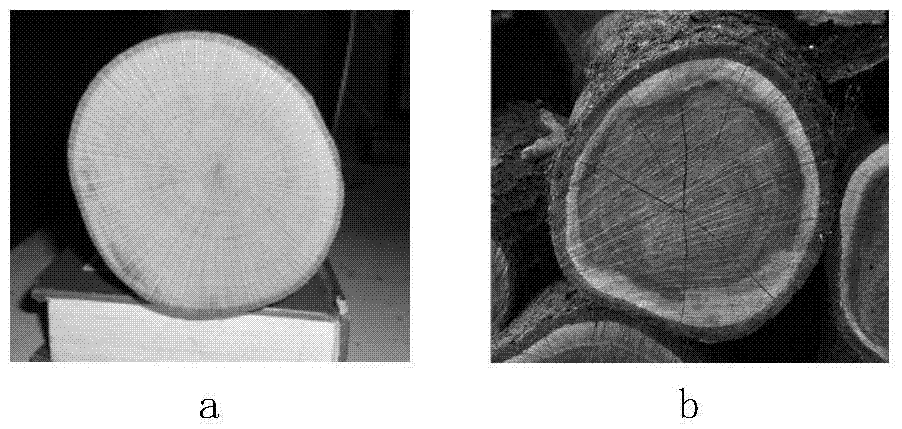
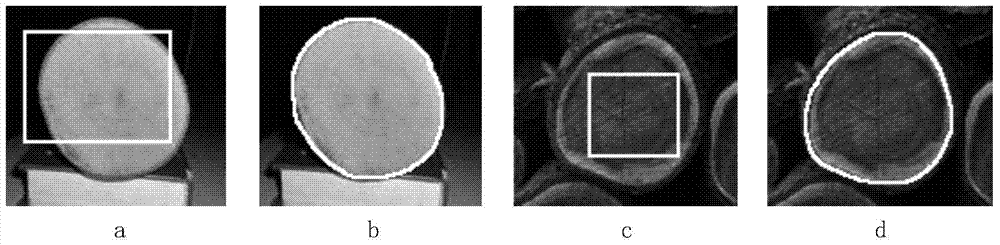
Log end surface image partitioning algorithm for improving active contour model based on circle constraint
InactiveCN103700095AGood segmentation effectAvoid interferenceImage analysisPattern recognitionImage segmentation algorithm
A log end surface image partitioning algorithm for improving an active contour model based on circle constraint comprises the following steps: initializing a contour line level set phi (x, y, t=0)=0, using an improved active contour model to control an evolution level set function, so as to complete precutting to log end surface images, then craking a single level set phi corresponding to the a pre-cut profile curve into n level set functions <phi>i (i=1,..., n, and n refers to a to-be-cut target number), using the <phi>i as an initial contour line, initializing into a signed distance function again, setting a proper circle constraint factor Tau, then using the improved active contour model based on circle constraint to divide the level set again so as to obtain a final log end surface contour line, and finishing cutting. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of an improved CV model and an LIF model at the same time, can effectively avoid image non-goal region and noise interferences through the combination of image overall and local information, the calculating is simple, the speed is fast, and the cutting effect on the log end surface is good. Great significance to accurate measuring and processing of the log end surface is achieved.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
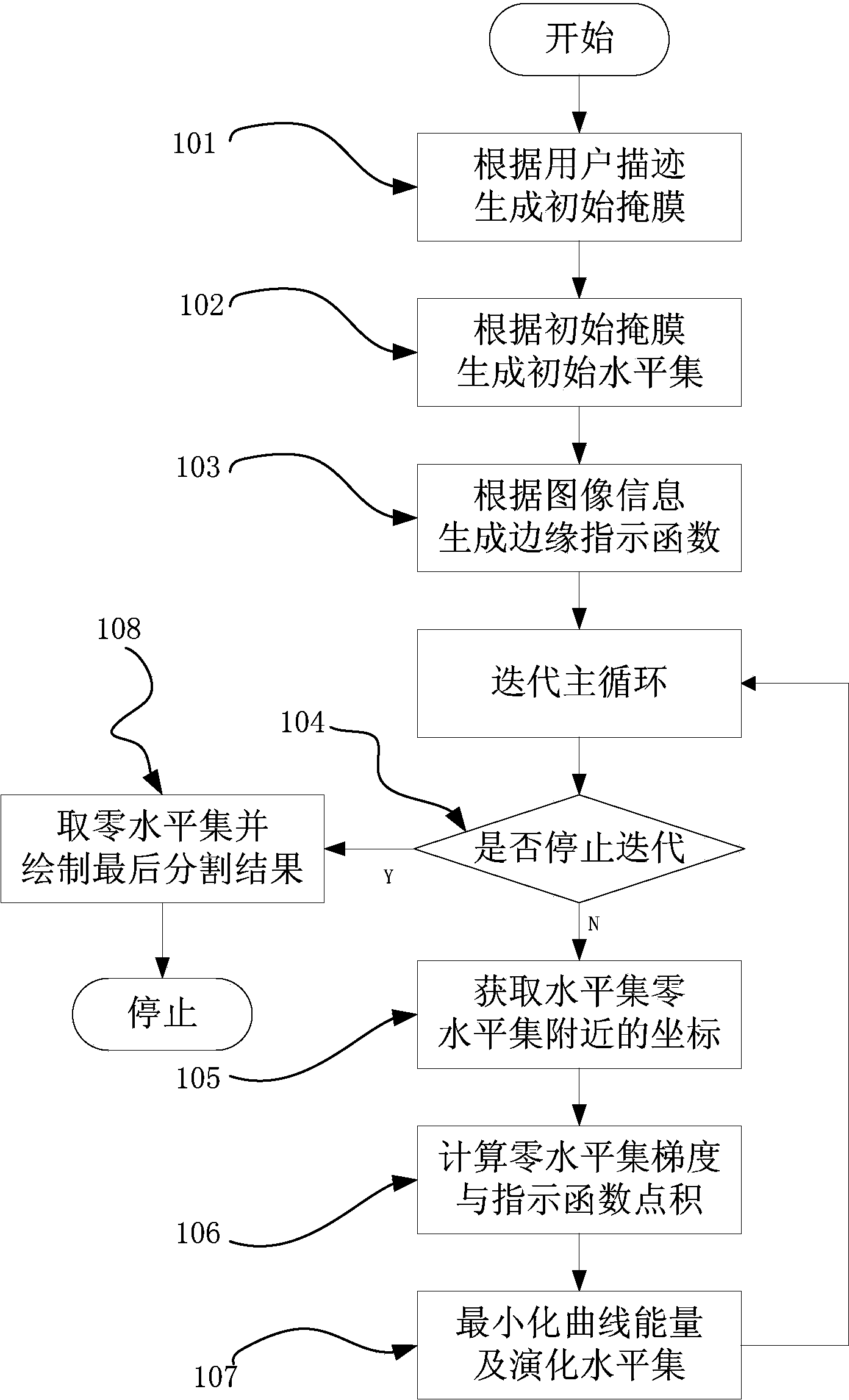
Ultrasonic endocardium tracing method
The invention is applicable to the fields of medical treatment and image processing and provides an ultrasonic endocardium tracing method. The ultrasonic endocardium tracing method comprises the steps of receiving a general endocardium boundary manually drawn by a tracer in a heart B ultrasonic image, wherein the endocardium boundary is an initial closed curve; selecting a first pixel at an upper left corner of the B ultrasonic image as a seed point and obtaining an initial mask after seed point departs to enter the Flood Fill depth-first search process; adopting a distance conversion method to obtain a signed distance function of the initial mask, using the signed distance function as a level set and enabling a zero level set to correspond to the initial closed curve; generating an edge indicator function; performing evolution iteration on the level set to obtain an iterated level set and obtaining a zero level set in the iterated level set, wherein the iterated zero level set is an ultrasonic endocardium. The ultrasonic endocardium tracing method has the advantages of improving boundary positioning accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN EMPEROR ELECTRONICS TECH
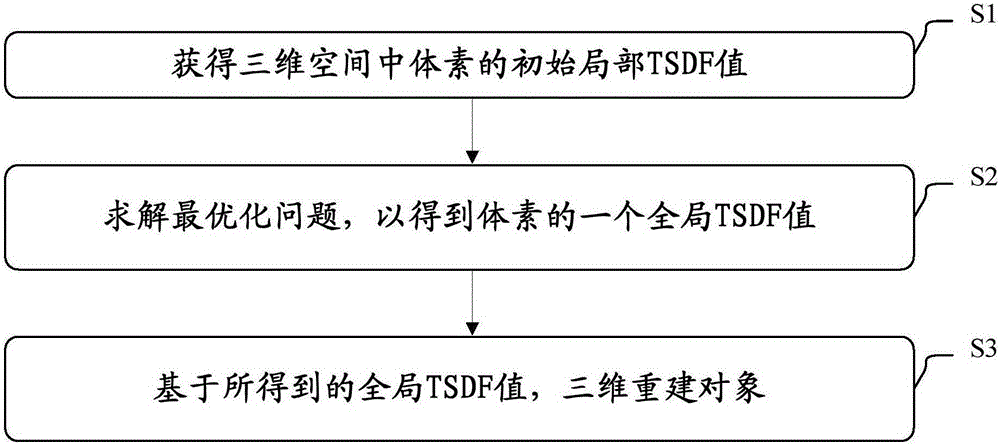
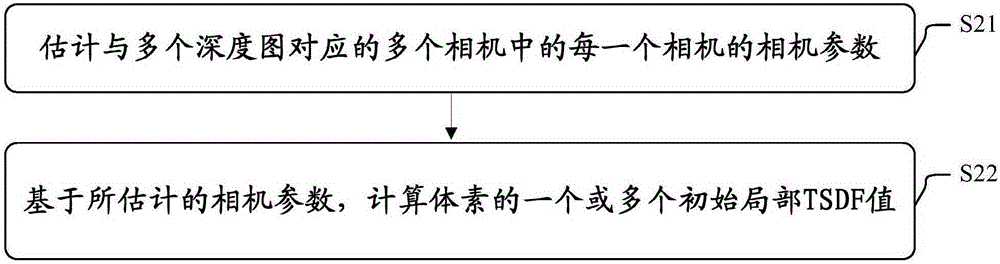
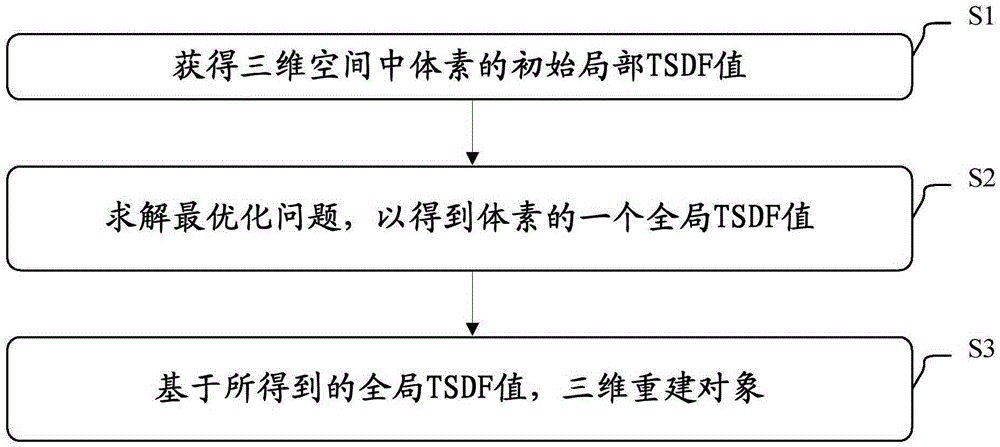
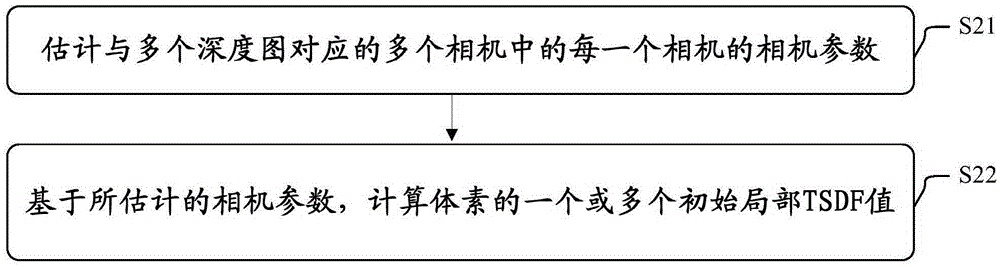
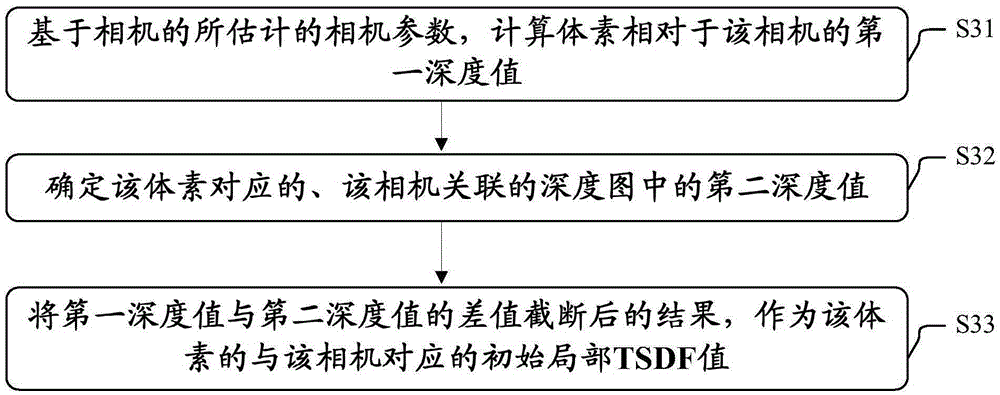
Object three-dimensional reconstruction method and apparatus
The present invention discloses an object three-dimensional reconstruction method and apparatus. The object three-dimensional reconstruction method includes the following steps that: the initial local truncated signed distance function (TSDF ) value of a voxel in a three-dimensional space is obtained; an optimization problem is solved, the global TSDF value of the voxel is obtained; and an object is reconstructed in a three-dimensional manner based on the global TSDF value. According to the optimization problem, the global TSDF value of the voxel is obtained based on the final local TSDF values of the voxel; the final local TSDF value of the voxel is equal to the initial TSDF value of a voxel which is corresponding to the voxel which has been subjected to rigid transformation; variables are the global TSDF value of the voxel and the parameter of the rigid transformation; and a cost function is related to the sum of squares of the difference of the global TSDF value of the voxel and the initial local TSDF value of the voxel corresponding to the voxel which has been subjected to the rigid transformation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Human body vein image feature extraction method
InactiveCN104091146AReduce computational complexityReduce the amount of calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionVeinHuman body
The invention discloses a human body vein image feature extraction method which comprises the steps of acquiring a human body vein image and establishing the image in a coordinate system, and then extracting the vein direction features through a directional filter. The method is characterized in that vein direction feature extraction through the directional filter is realized by performing convolution operation on the image established in the coordinate system by use of Radon transform to extract the features of the vein image. The whole feature extraction process comprises the following steps: (1) setting a distance function, which is shown in the description; (2) setting a neighborhood consistent with the distance function and dividing the neighborhood into k directions: Lk={(i, j):j=k(i-i0)+j0, i belongs to Zp}, wherein (i, j) belongs to local(i0, j0); and (3) calculating the energy response of the k directions according to a formula in the description. By adopting the human body vein image feature extraction method of the invention, excessive redundant information is removed, the complexity of calculation and the amount of calculation are reduced, more effective information can be contained, and the effective range of the filter neighborhood is determined through construction of the distance function so as to get a better identification effect.
Owner:GUANGDONG WICROWN INFORMATION TECH
Improved CLSVOF method for quickly building signed distance function by VOF function
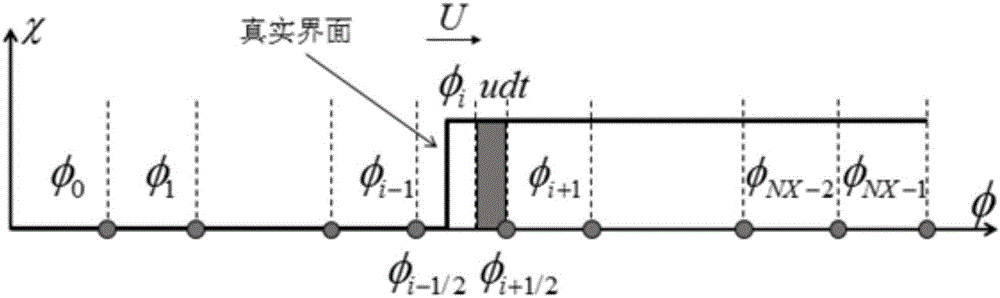
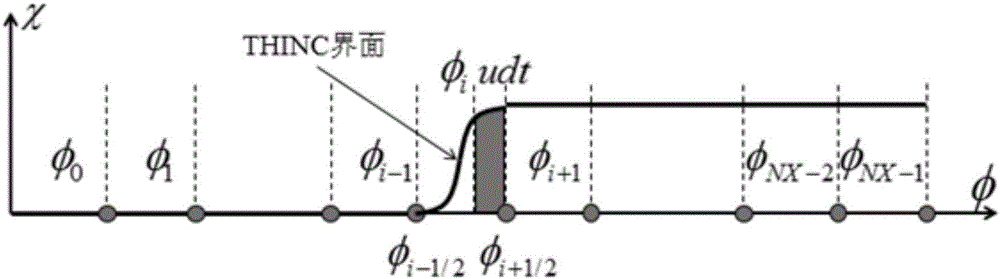
InactiveCN106445882ASimple logicEasy programmingComplex mathematical operationsUpwind schemeComputer science
For the problems of a complex signed distance function building process, difficult expansion to three dimensions, low building efficiency and the like in an existing CLSVOF method, the invention provides an improved CLSVOF method for quickly building a signed distance function by a VOF function. The method comprises the steps of firstly finding out an interface grid by utilizing a sub-grid technology; secondly converting a VOF function in the interface grid into a signed distance function through a Newton iteration method, and based on this, building a signed distance function of a whole calculation region by adopting a fast scanning method; thirdly performing calculation through a WENO format and an upwind scheme to obtain an accurate interface normal vector value; and finally solving a VOF equation by adopting a corrected THINC algorithm pair.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
System and method for robust segmentation of tubular structures in 2D and 3D images
InactiveUS7912266B2Fast computerUser input is slowImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageDigital image
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
3D object reconstruction method and device
The invention discloses a 3D object reconstruction method and device. The method comprises that an initial local TSDF (Truncated Signed Distance Function) value of a voxel in a 3D space is obtained; an optimization problem is solved to obtain a global TSDF value of the voxel; and 3D reconstruction of an object is realized on the basis of the obtained global TSDF value. In the optimization problem, the global TSDF value of the voxel is obtained on the basis of a final local TSDF value of the voxel, the final local TSDF value of the voxel equals an initial local TSDF value of a corresponding voxel which is obtained by carrying out non-rigid transformation on the original voxel, variables refer to parameters of the global TSDF value and non-rigid transformation of the voxel, and a cost function is related to factors including a quadratic sum of differences between the global TSDF values of specific voxels and initial local TSDF values of voxels obtained by carrying out non-rigid transformation on the specific voxels as well as a sum of offset amounts, caused by the non-rigid transformation, of the specific voxels.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
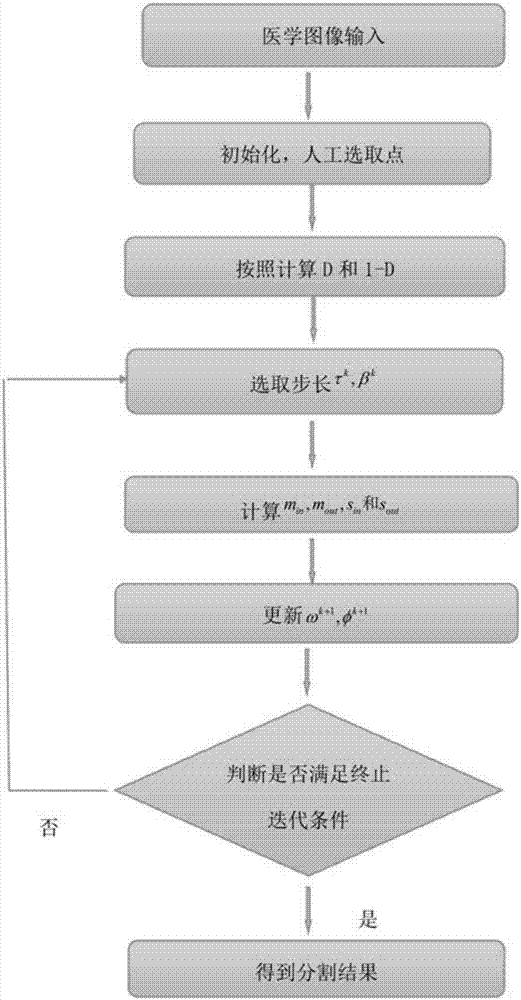
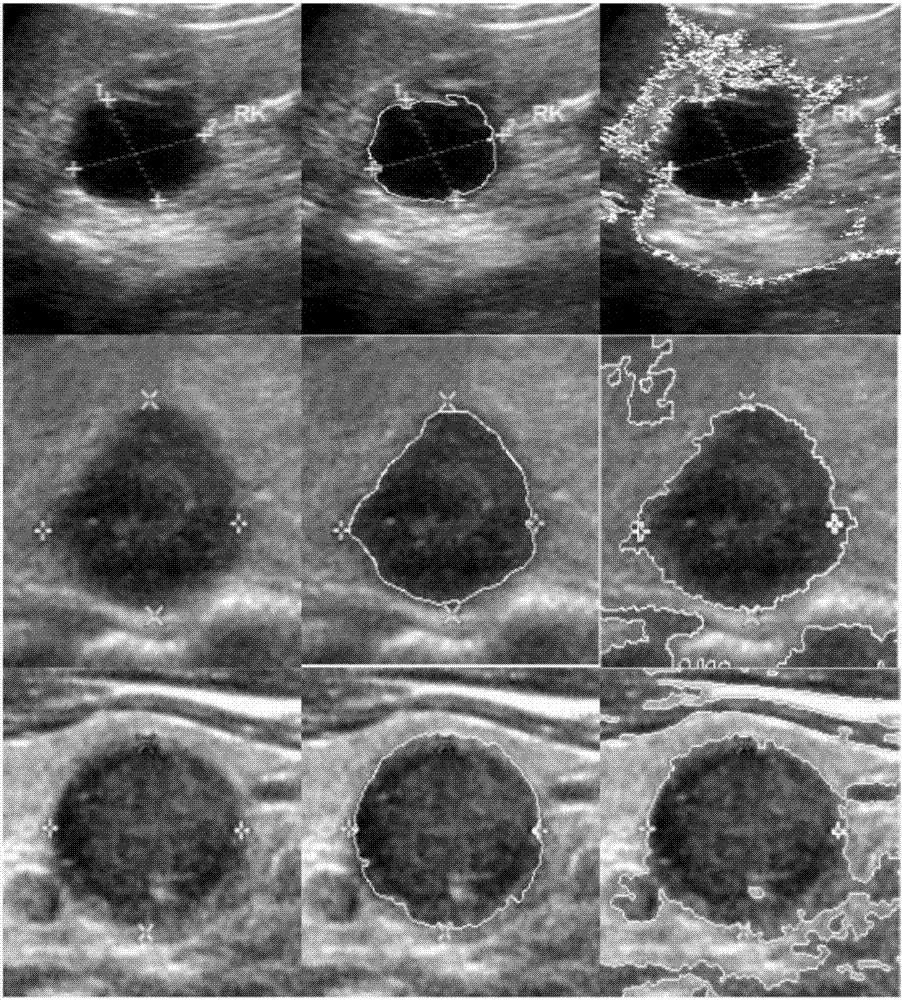
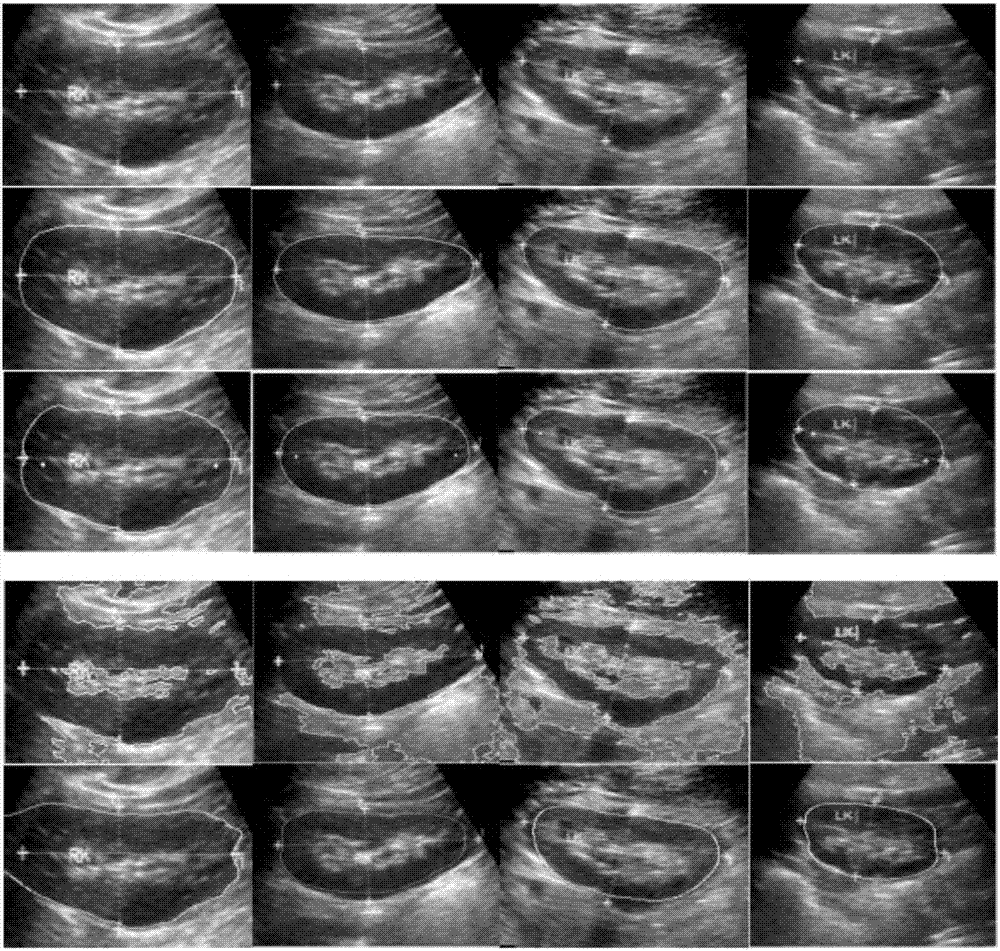
Semi-automatic medical image segmentation method based on shape constraint of point distance function
The invention discloses a semi-automatic medical image segmentation method based on the shape constraint of a point distance function. The method comprises the following steps of selecting to-be-processed medical image, and defining an n-point distance function in the plane of the image; merging the shape constraint of the point distance function into a variation frame to obtain an activity contour model based on the shape constraint of the point distance function; solving the activity contour model; and solving a gradient flow equation to realize the segmentation of the image. According to the invention, the shapes of a circle, a quasi-circle, an ellipse, a superellipse, a curved-edge triangle, a curved-edge quadrilateral, a heart-shaped shape and the like can be flexibly described. Meanwhile, a medical image with a missed boundary can be effectively segmented. Moreover, the establishment of target shape databases or optimized shape parameters is not required.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Non-convex hull surfaces
The invention is a computer implemented method, device, system, or article for reconstructing a surface of an object. In particular, the invention comprises estimating a non-convex hull signed distance function parameters from a data set of an object and evaluating the non-convex hull signed distance function on vertices of a volumetric mesh. The invention further comprises approximating the zero level set of the non-convex hull signed distance function by a polygonal mesh using an isosurface algorithm to provide surface reconstruction of an object.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Gait contour extraction method
InactiveCN105631452AGood localization effectImprove clarityCharacter and pattern recognitionSymbol of a differential operatorGait
Provided is a gait contour extraction method. A level set function is expressed in a spatial-temporal discrete grid. First, an SDF (Sign Distance Function) is constructed, and initialization for zeroing is carried out; then, the numerical solution of a partial differential equation is solved; and finally, re-initialization is carried out through a curvilinear sign distance function, whether the numerical value is stable or not is judged, iteration is stopped if the numerical value is stable, or the process is repeated. The gait contour extraction method has a good localization effect for image boundaries. The image edge and regional information are combined, and the definition and distinctiveness of the gait contour are improved.
Owner:安徽勤勉知识产权代理有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com