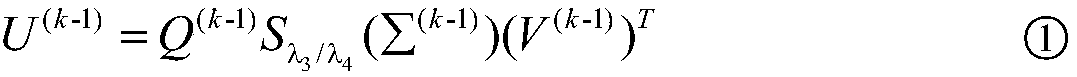De-noising method integrated with gradient histogram and low rank constraint
A gradient histogram, low-rank constraint technology, applied in image enhancement, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of poor denoising effect of denoising methods, and achieve the effect of enhancing denoising performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The technical solutions of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings in specific embodiments of the present invention.
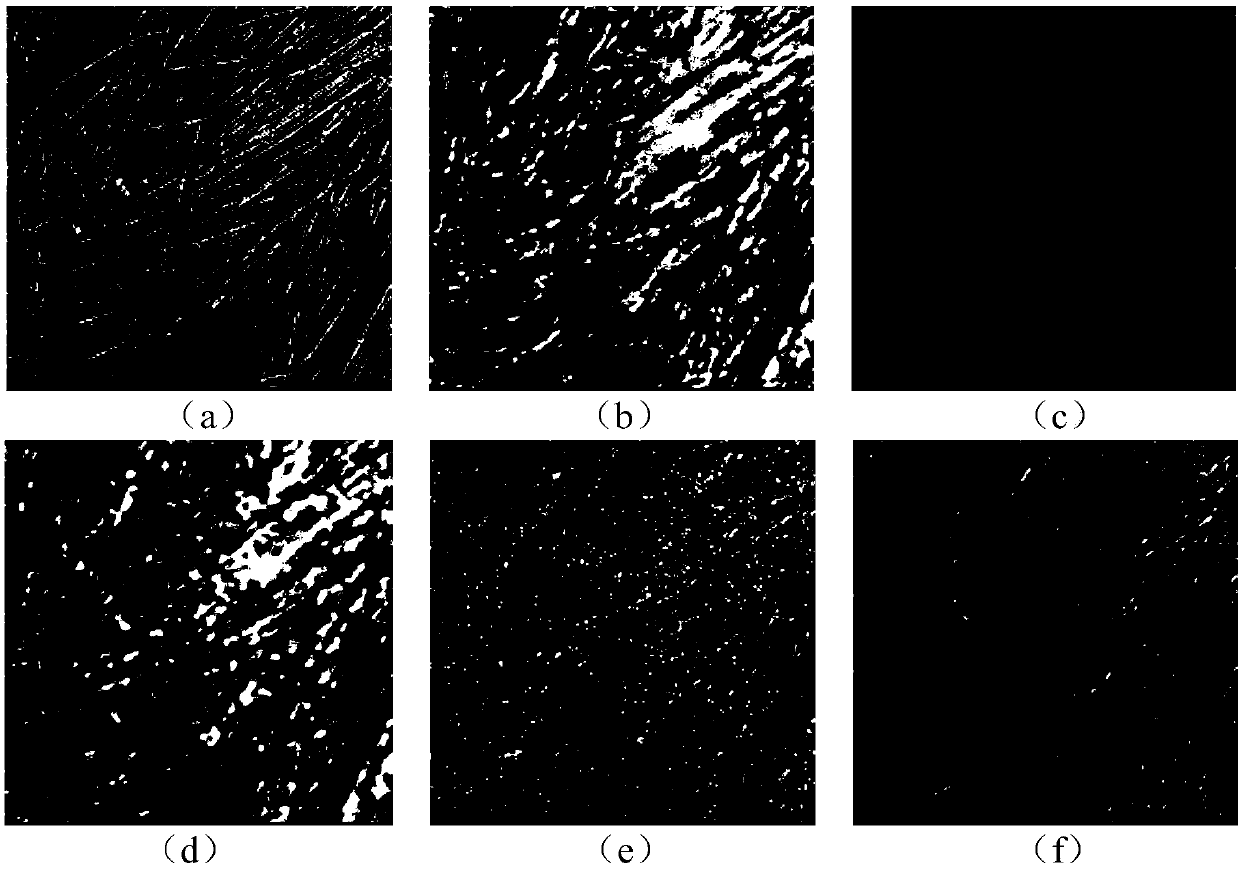
[0044] A denoising method that combines gradient histograms with low-rank constraints, such as figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0045] Step 1, read the noisy image, and obtain the matrix expression y of the image;
[0046] Step 2, logarithmically transform the noisy image to obtain the noisy image f in the logarithmic domain, and initialize the number of iterations k=1, z (0) =f, where z (0) is the image to be restored in the logarithmic domain, is the gradient of z;
[0047] Step 3, use the sliding window technique to convert the noisy image z (k-1) Divide into small blocks of 7×7, and use K-means to cluster these small image blocks into 70 categories;
[0048] Step 4, use the principal component analysis method to calculate the sub-dictionary in ea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com