Structured LDPC coding and decoding method and device
An LDPC code and coding method technology, applied in the decoding method and device, the coding field of structured low-density parity check codes, can solve the problems of inability to support incremental redundancy HARQ and flexibility, insufficiency, etc., to achieve coding and decoding performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
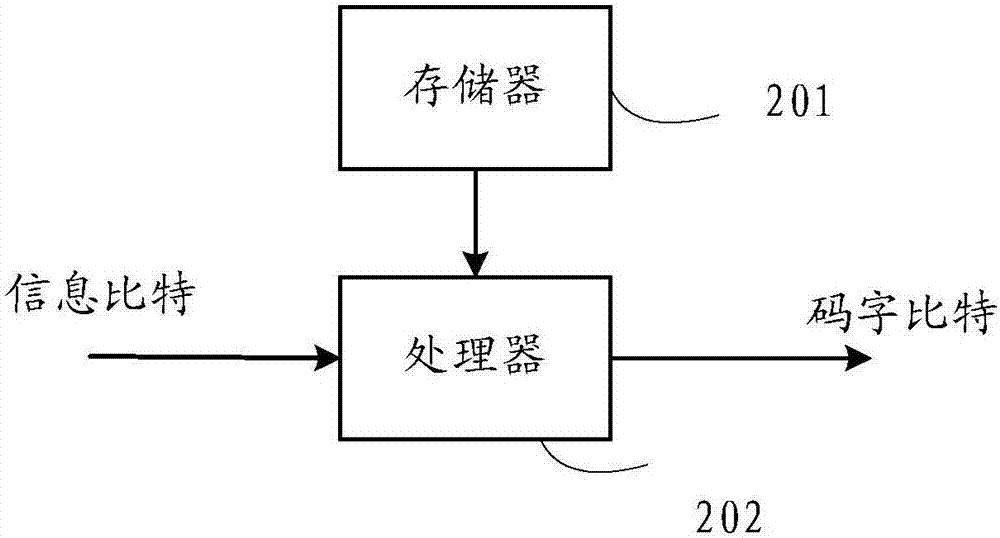
[0112] An embodiment of the present invention provides a coding device for structured low-density parity-check code LDPC in digital communication, the structure of which is as follows figure 2 As shown, at least a processor 202 and a memory 201 are included.
[0113] The memory 201 is configured to at least store a fundamental matrix used in encoding.
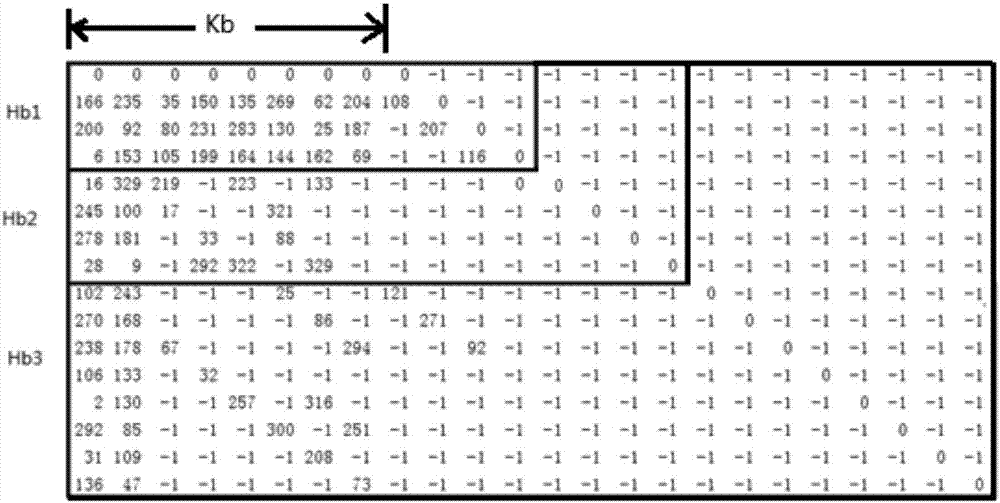
[0114] The basic matrix includes a block A of Mb×Kb corresponding to systematic bits and a block B of Mb×Mb corresponding to parity bits, that is, Hb=[A,B], where hb ij Represent the elements of the ith row and j column of the basic matrix, i is the row index of the basic matrix, j is the column index of the basic matrix, Kb=Nb-Mb, Nb is an integer, and Kb is greater than or equal to 4 an integer of . i=1,...,Mb, j=1,...,Nb.
[0115] Described basic matrix Hb comprises one or more sub-matrixes, and described sub-matrix comprises: sub-matrix Hb1 of upper left corner and sub-matrix Hb2 of upper left corner, wherein, the numbe...
Embodiment 2
[0150] An embodiment of the present invention provides a decoding device for a structured low-density parity-check code LDPC in digital communication, the structure of which is as follows Figure 4 As shown, at least a processor 402 and a memory 401 are included.
[0151] The memory 401 is configured to at least store a fundamental matrix used in encoding. The basic parity check matrix includes the following features:
[0152] The basic matrix includes a block A of Mb×Kb corresponding to systematic bits and a block B of Mb×Mb corresponding to parity bits, that is, Hb=[A,B], where hb ij Represent the elements of the ith row and j column of the basic matrix, i is the row index of the basic matrix, j is the column index of the basic matrix, Kb=Nb-Mb, Kb is an integer greater than or equal to 4, Nb is an integer. i=1,...,Mb, j=1,...,Nb.
[0153] Described basic matrix Hb comprises one or more sub-matrixes, and described sub-matrix comprises: sub-matrix Hb1 of upper left corner...
Embodiment 3
[0184] The embodiment of the present invention provides a coding method of a structured LDPC code, and the process of using this method to complete LDPC coding is as follows: Figure 5 shown, including:
[0185] Step 501, determine the basic matrix Hb used for encoding;
[0186] Optionally, the basic parity check matrix includes the following features:
[0187] The basic matrix includes a block A of Mb×Kb corresponding to systematic bits and a block B of Mb×Mb corresponding to parity bits, that is, Hb=[A,B], where hb ij Represent the elements of the ith row and j column of the basic matrix, i is the row index of the basic matrix, j is the column index of the basic matrix, Kb=Nb-Mb, Kb is an integer greater than or equal to 4, Nb is an integer. i=1,...,Mb, j=1,...,Nb.
[0188] Optionally, the basic matrix Hb at least further includes the following features: the basic matrix Hb includes one or more sub-matrices, and the sub-matrices include: the upper left sub-matrix Hb1 and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com