Improved suture
A technology of sutures and medical devices, applied in medical science, surgery, prosthesis, etc., can solve problems such as adverse neovascularization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0066] Finite Element Analysis of the Suture / Tissue Interface for Sutured Abdominal Wall Closure
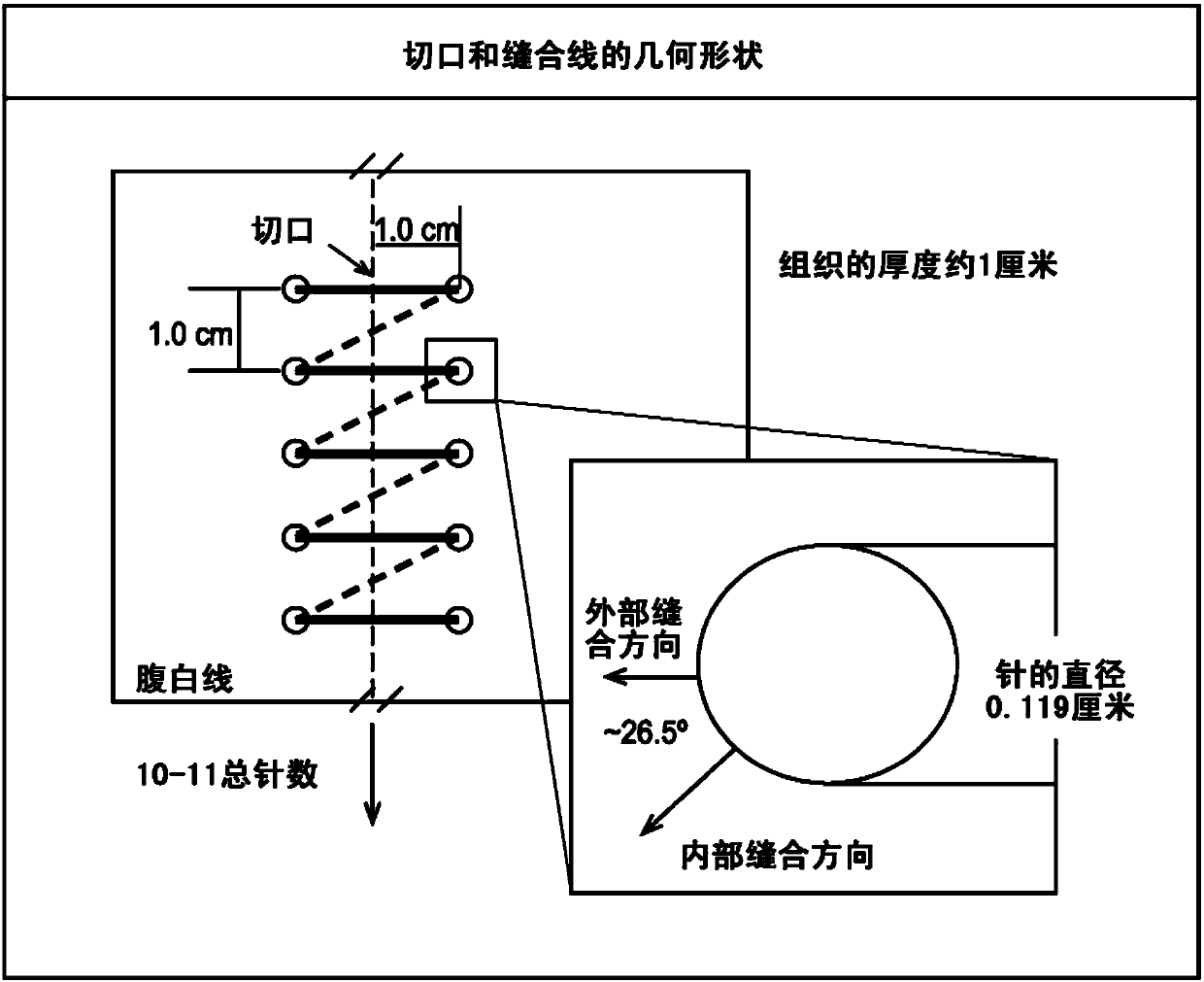
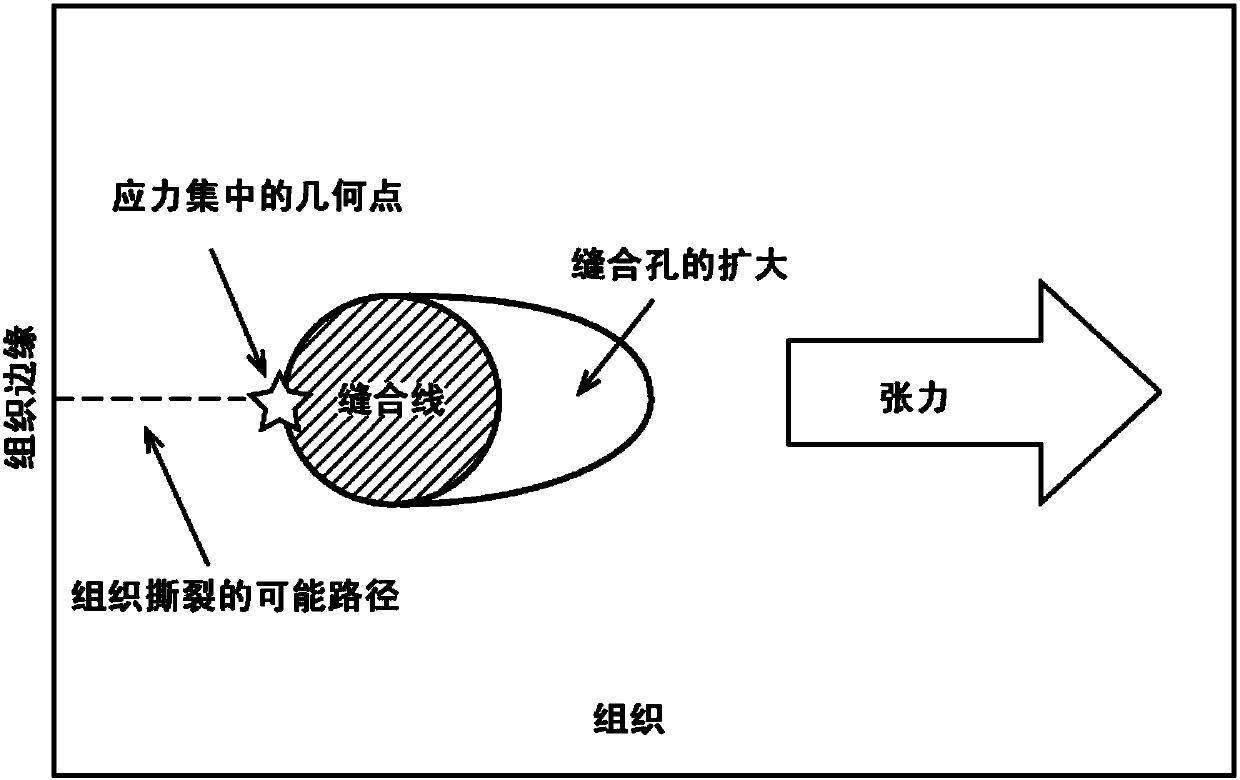
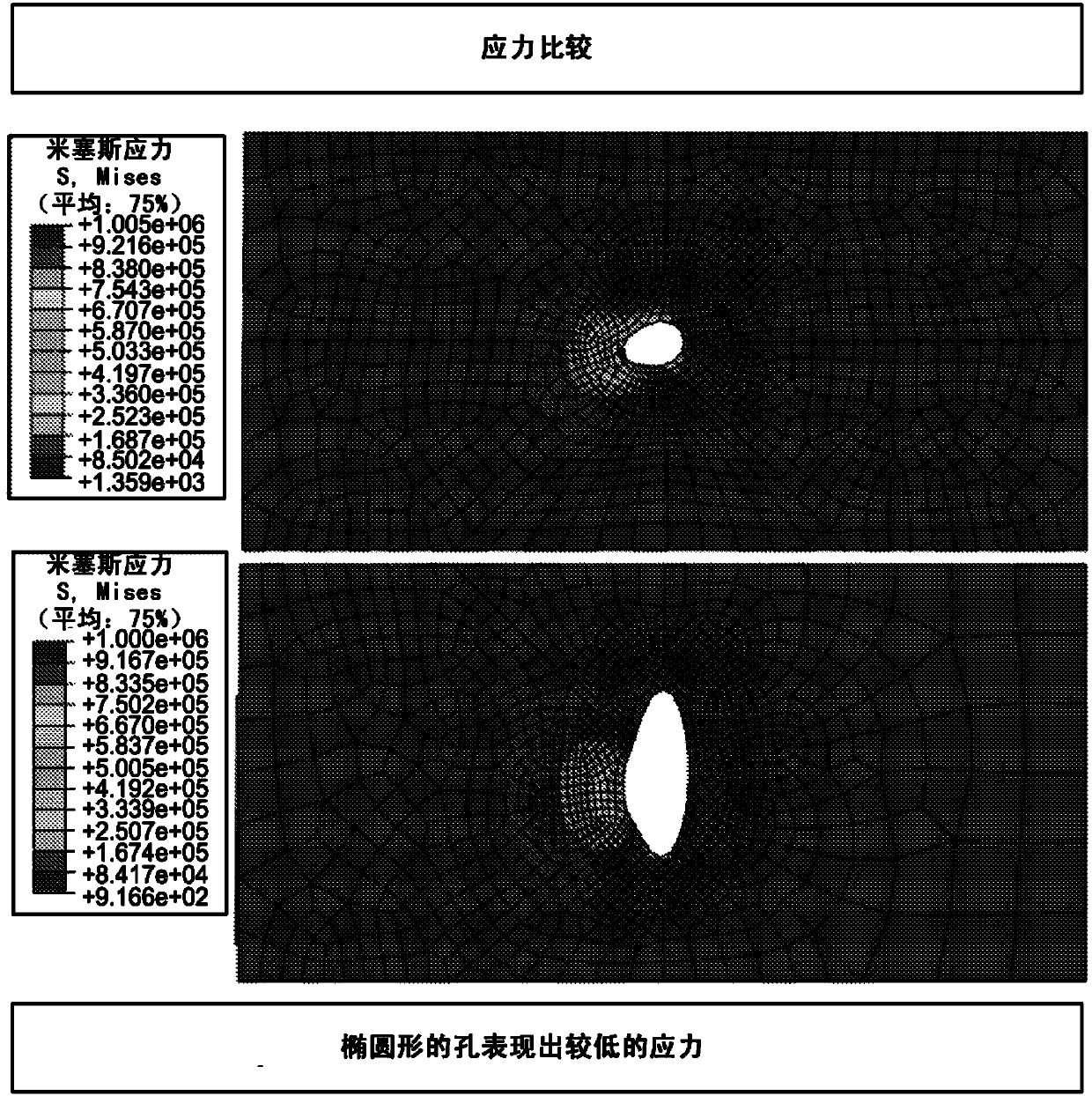
[0067] Experiments were performed during the development of embodiments of the present disclosure to perform finite element analysis of the suture / tissue interface for sutured abdominal wall closure. As a first step in the design of this series of inquiries, create a theoretical basis for intuitive concepts and clinical observations (see figure 1 , figure 2 ). A finite element analysis of the suture / tissue interface was performed ( image 3 ). Experiments have shown that increasing suture size (i.e., diameter) reduces the force at the suture / tissue interface as hypothesized ( Figure 4 ). also demonstrated that the shape of the suture affects the local force exerted by the suture on the tissue ( Figure 5 ).
example 2
[0069] An "equivalence" is created between conventional sutures and the macroporous sutures of the present disclosure.
[0070] O-shaped polypropylene suture is commonly used in hernia repair because of its handling and high strength characteristics. Experiments were performed to determine a relatively equivalent cross-sectional profiled suture to such sutures. A 2D suture is compared to this commonly used standard suture in terms of yield load, maximum load, and Young's modulus. An Instron 5964 was used for mechanical testing. Experiments have shown the relative equivalence between O-type polypropylene and 2D ribbon sutures with a width of 5 mm ( Figure 6 and Figure 7 ). A 5-0 polypropylene suture (used in experimental murine hernia repair) was equivalent to a 2 mm wide sample of the macroporous suture of the present disclosure.
example 3
[0072] Create and validate deep suture pullthrough models using biological tissue and tension measurements
[0073] The alba linea was purchased from a local abattoir to provide a practical trial of very deep suture pullthroughs. Standard sutures and macroporous sutures of the present disclosure were passed through porcine tissue equally. To reduce biological variability, adjacent sheets of fascia were randomized to either standard sutures or two-dimensional sutures, with suture perforations of width mimicking the clinical situation (1 cm from the edge). Tension measurements were performed using an Instron 5964, testing slow and fast suture pulls to simulate baseline suture tension and occasional high tension (eg, coughing, going up stairs, etc.). An appropriate number of trials were performed on both standard sutures and the macroporous sutures of the present disclosure, taking into account biological variability and readily available biomaterials.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com